Seonwook Park
Instant Expressive Gaussian Head Avatar via 3D-Aware Expression Distillation
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Portrait animation has witnessed tremendous quality improvements thanks to recent advances in video diffusion models. However, these 2D methods often compromise 3D consistency and speed, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios, such as digital twins or telepresence. In contrast, 3D-aware facial animation feedforward methods -- built upon explicit 3D representations, such as neural radiance fields or Gaussian splatting -- ensure 3D consistency and achieve faster inference speed, but come with inferior expression details. In this paper, we aim to combine their strengths by distilling knowledge from a 2D diffusion-based method into a feed-forward encoder, which instantly converts an in-the-wild single image into a 3D-consistent, fast yet expressive animatable representation. Our animation representation is decoupled from the face's 3D representation and learns motion implicitly from data, eliminating the dependency on pre-defined parametric models that often constrain animation capabilities. Unlike previous computationally intensive global fusion mechanisms (e.g., multiple attention layers) for fusing 3D structural and animation information, our design employs an efficient lightweight local fusion strategy to achieve high animation expressivity. As a result, our method runs at 107.31 FPS for animation and pose control while achieving comparable animation quality to the state-of-the-art, surpassing alternative designs that trade speed for quality or vice versa. Project website is https://research.nvidia.com/labs/amri/projects/instant4d
Generalizing AI-driven Assessment of Immunohistochemistry across Immunostains and Cancer Types: A Universal Immunohistochemistry Analyzer
Jul 30, 2024Abstract:Despite advancements in methodologies, immunohistochemistry (IHC) remains the most utilized ancillary test for histopathologic and companion diagnostics in targeted therapies. However, objective IHC assessment poses challenges. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a potential solution, yet its development requires extensive training for each cancer and IHC type, limiting versatility. We developed a Universal IHC (UIHC) analyzer, an AI model for interpreting IHC images regardless of tumor or IHC types, using training datasets from various cancers stained for PD-L1 and/or HER2. This multi-cohort trained model outperforms conventional single-cohort models in interpreting unseen IHCs (Kappa score 0.578 vs. up to 0.509) and consistently shows superior performance across different positive staining cutoff values. Qualitative analysis reveals that UIHC effectively clusters patches based on expression levels. The UIHC model also quantitatively assesses c-MET expression with MET mutations, representing a significant advancement in AI application in the era of personalized medicine and accumulating novel biomarkers.
EFE: End-to-end Frame-to-Gaze Estimation
May 09, 2023
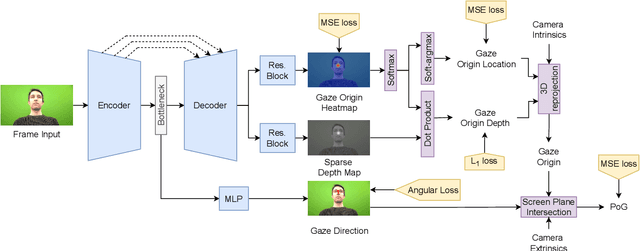
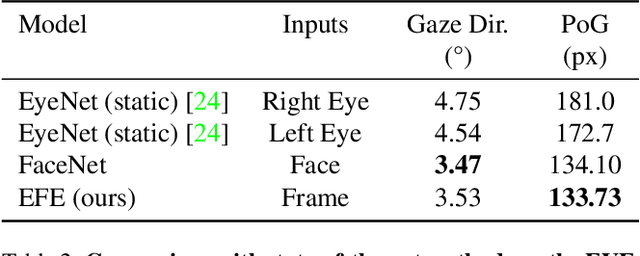
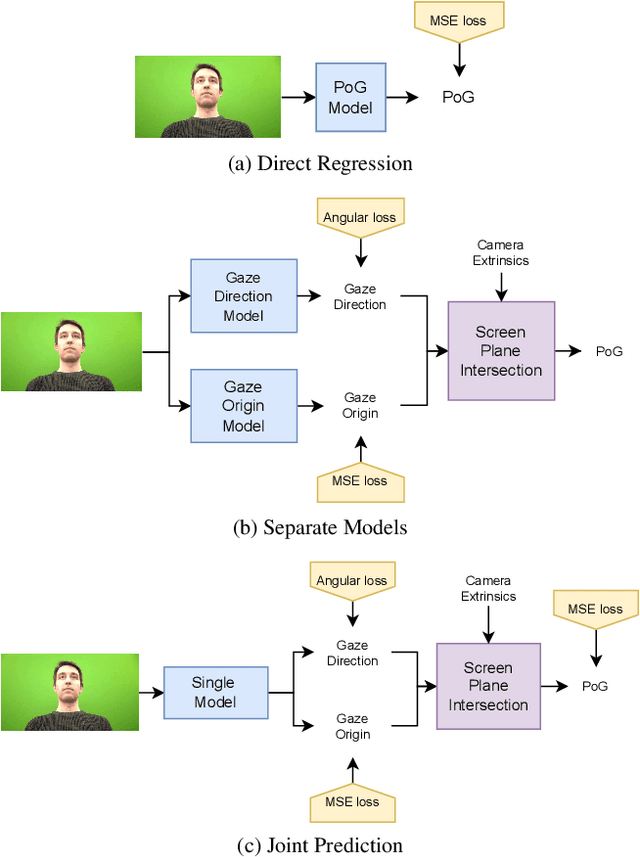
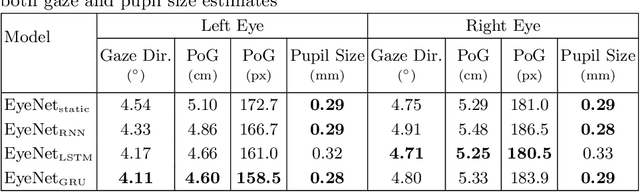
Abstract:Despite the recent development of learning-based gaze estimation methods, most methods require one or more eye or face region crops as inputs and produce a gaze direction vector as output. Cropping results in a higher resolution in the eye regions and having fewer confounding factors (such as clothing and hair) is believed to benefit the final model performance. However, this eye/face patch cropping process is expensive, erroneous, and implementation-specific for different methods. In this paper, we propose a frame-to-gaze network that directly predicts both 3D gaze origin and 3D gaze direction from the raw frame out of the camera without any face or eye cropping. Our method demonstrates that direct gaze regression from the raw downscaled frame, from FHD/HD to VGA/HVGA resolution, is possible despite the challenges of having very few pixels in the eye region. The proposed method achieves comparable results to state-of-the-art methods in Point-of-Gaze (PoG) estimation on three public gaze datasets: GazeCapture, MPIIFaceGaze, and EVE, and generalizes well to extreme camera view changes.
OCELOT: Overlapped Cell on Tissue Dataset for Histopathology
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:Cell detection is a fundamental task in computational pathology that can be used for extracting high-level medical information from whole-slide images. For accurate cell detection, pathologists often zoom out to understand the tissue-level structures and zoom in to classify cells based on their morphology and the surrounding context. However, there is a lack of efforts to reflect such behaviors by pathologists in the cell detection models, mainly due to the lack of datasets containing both cell and tissue annotations with overlapping regions. To overcome this limitation, we propose and publicly release OCELOT, a dataset purposely dedicated to the study of cell-tissue relationships for cell detection in histopathology. OCELOT provides overlapping cell and tissue annotations on images acquired from multiple organs. Within this setting, we also propose multi-task learning approaches that benefit from learning both cell and tissue tasks simultaneously. When compared against a model trained only for the cell detection task, our proposed approaches improve cell detection performance on 3 datasets: proposed OCELOT, public TIGER, and internal CARP datasets. On the OCELOT test set in particular, we show up to 6.79 improvement in F1-score. We believe the contributions of this paper, including the release of the OCELOT dataset at https://lunit-io.github.io/research/publications/ocelot are a crucial starting point toward the important research direction of incorporating cell-tissue relationships in computation pathology.
Benchmarking Self-Supervised Learning on Diverse Pathology Datasets
Dec 09, 2022

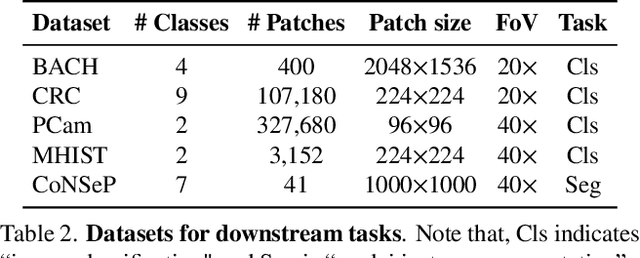

Abstract:Computational pathology can lead to saving human lives, but models are annotation hungry and pathology images are notoriously expensive to annotate. Self-supervised learning has shown to be an effective method for utilizing unlabeled data, and its application to pathology could greatly benefit its downstream tasks. Yet, there are no principled studies that compare SSL methods and discuss how to adapt them for pathology. To address this need, we execute the largest-scale study of SSL pre-training on pathology image data, to date. Our study is conducted using 4 representative SSL methods on diverse downstream tasks. We establish that large-scale domain-aligned pre-training in pathology consistently out-performs ImageNet pre-training in standard SSL settings such as linear and fine-tuning evaluations, as well as in low-label regimes. Moreover, we propose a set of domain-specific techniques that we experimentally show leads to a performance boost. Lastly, for the first time, we apply SSL to the challenging task of nuclei instance segmentation and show large and consistent performance improvements under diverse settings.
Interactive Multi-Class Tiny-Object Detection
Mar 29, 2022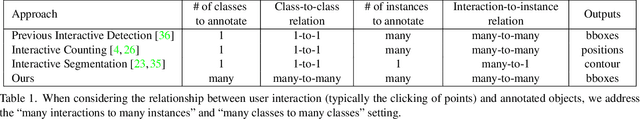

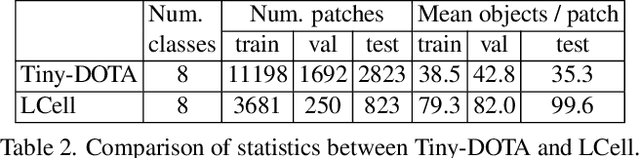
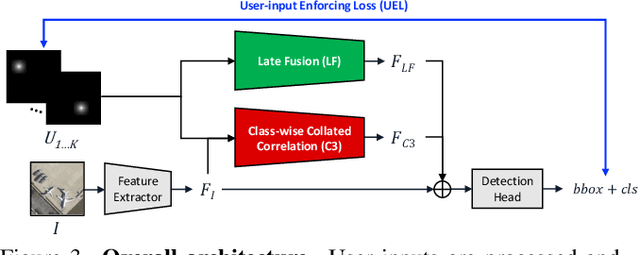
Abstract:Annotating tens or hundreds of tiny objects in a given image is laborious yet crucial for a multitude of Computer Vision tasks. Such imagery typically contains objects from various categories, yet the multi-class interactive annotation setting for the detection task has thus far been unexplored. To address these needs, we propose a novel interactive annotation method for multiple instances of tiny objects from multiple classes, based on a few point-based user inputs. Our approach, C3Det, relates the full image context with annotator inputs in a local and global manner via late-fusion and feature-correlation, respectively. We perform experiments on the Tiny-DOTA and LCell datasets using both two-stage and one-stage object detection architectures to verify the efficacy of our approach. Our approach outperforms existing approaches in interactive annotation, achieving higher mAP with fewer clicks. Furthermore, we validate the annotation efficiency of our approach in a user study where it is shown to be 2.85x faster and yield only 0.36x task load (NASA-TLX, lower is better) compared to manual annotation. The code is available at https://github.com/ChungYi347/Interactive-Multi-Class-Tiny-Object-Detection.
Weakly-Supervised Physically Unconstrained Gaze Estimation
May 20, 2021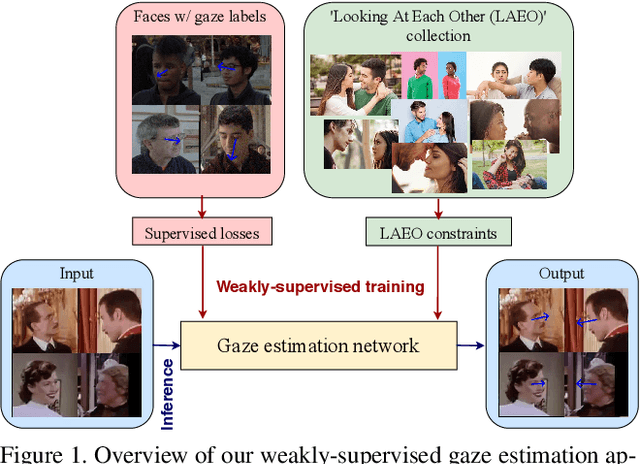
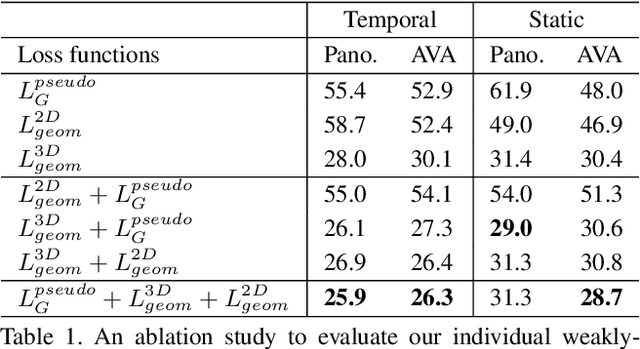
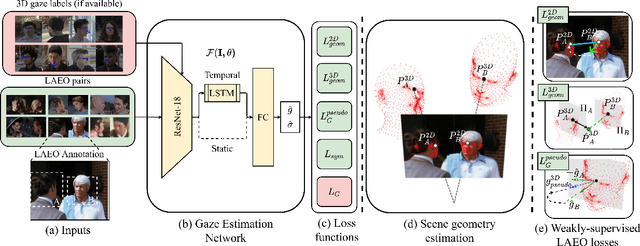
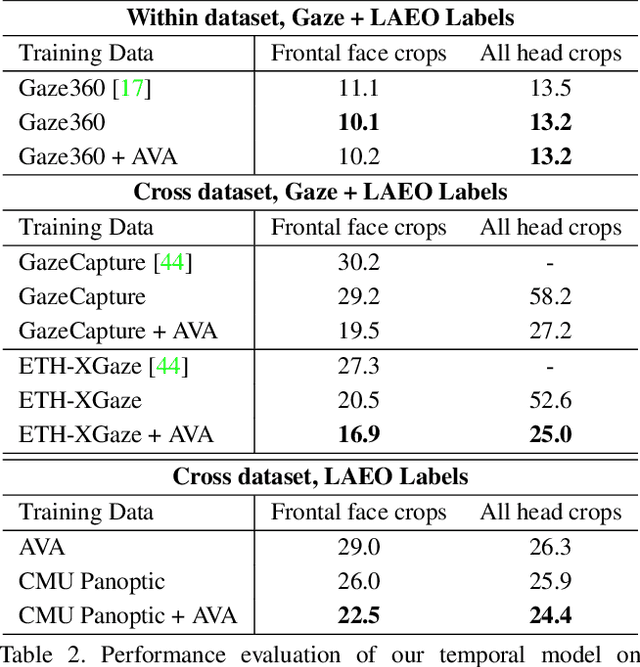
Abstract:A major challenge for physically unconstrained gaze estimation is acquiring training data with 3D gaze annotations for in-the-wild and outdoor scenarios. In contrast, videos of human interactions in unconstrained environments are abundantly available and can be much more easily annotated with frame-level activity labels. In this work, we tackle the previously unexplored problem of weakly-supervised gaze estimation from videos of human interactions. We leverage the insight that strong gaze-related geometric constraints exist when people perform the activity of "looking at each other" (LAEO). To acquire viable 3D gaze supervision from LAEO labels, we propose a training algorithm along with several novel loss functions especially designed for the task. With weak supervision from two large scale CMU-Panoptic and AVA-LAEO activity datasets, we show significant improvements in (a) the accuracy of semi-supervised gaze estimation and (b) cross-domain generalization on the state-of-the-art physically unconstrained in-the-wild Gaze360 gaze estimation benchmark. We open source our code at https://github.com/NVlabs/weakly-supervised-gaze.
Self-Learning Transformations for Improving Gaze and Head Redirection
Oct 23, 2020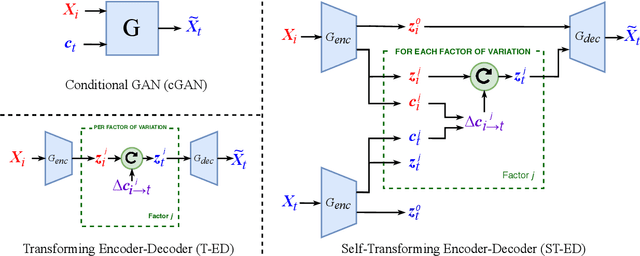
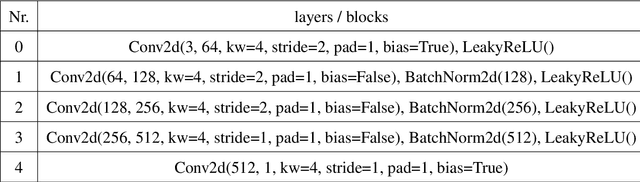
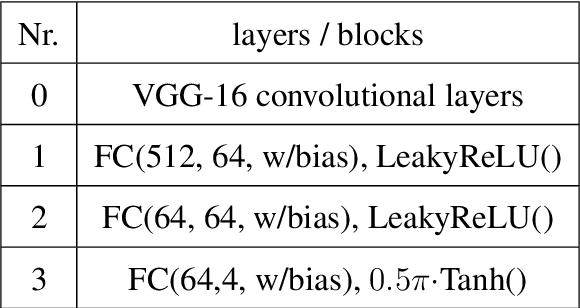
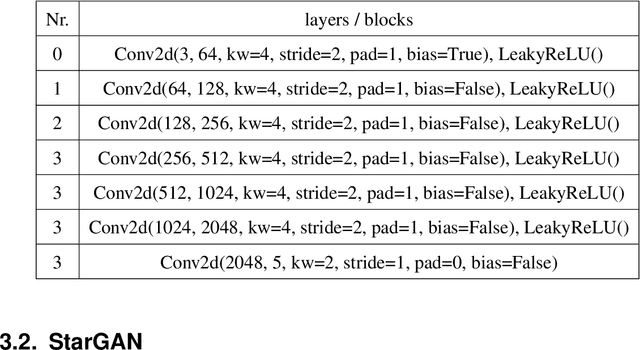
Abstract:Many computer vision tasks rely on labeled data. Rapid progress in generative modeling has led to the ability to synthesize photorealistic images. However, controlling specific aspects of the generation process such that the data can be used for supervision of downstream tasks remains challenging. In this paper we propose a novel generative model for images of faces, that is capable of producing high-quality images under fine-grained control over eye gaze and head orientation angles. This requires the disentangling of many appearance related factors including gaze and head orientation but also lighting, hue etc. We propose a novel architecture which learns to discover, disentangle and encode these extraneous variations in a self-learned manner. We further show that explicitly disentangling task-irrelevant factors results in more accurate modelling of gaze and head orientation. A novel evaluation scheme shows that our method improves upon the state-of-the-art in redirection accuracy and disentanglement between gaze direction and head orientation changes. Furthermore, we show that in the presence of limited amounts of real-world training data, our method allows for improvements in the downstream task of semi-supervised cross-dataset gaze estimation. Please check our project page at: https://ait.ethz.ch/projects/2020/STED-gaze/
ETH-XGaze: A Large Scale Dataset for Gaze Estimation under Extreme Head Pose and Gaze Variation
Jul 31, 2020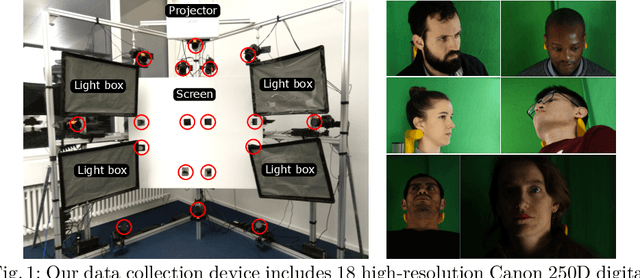
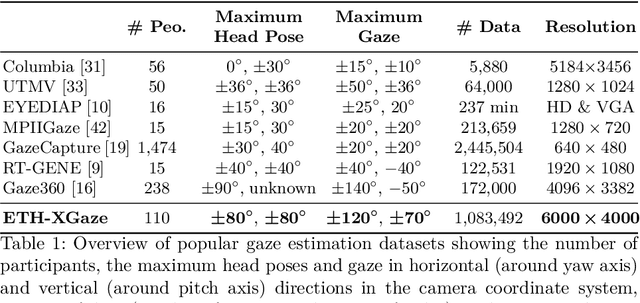
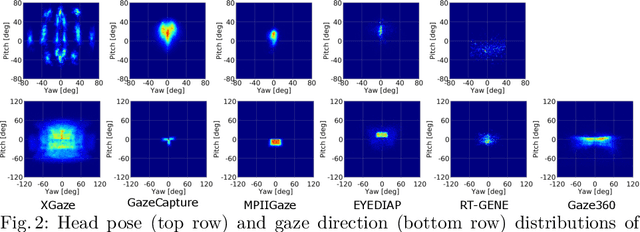
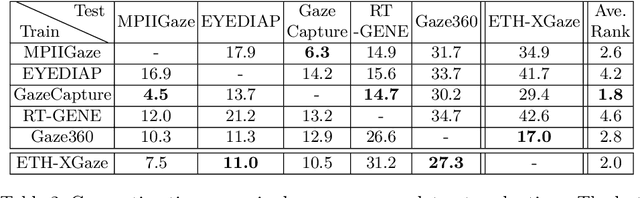
Abstract:Gaze estimation is a fundamental task in many applications of computer vision, human computer interaction and robotics. Many state-of-the-art methods are trained and tested on custom datasets, making comparison across methods challenging. Furthermore, existing gaze estimation datasets have limited head pose and gaze variations, and the evaluations are conducted using different protocols and metrics. In this paper, we propose a new gaze estimation dataset called ETH-XGaze, consisting of over one million high-resolution images of varying gaze under extreme head poses. We collect this dataset from 110 participants with a custom hardware setup including 18 digital SLR cameras and adjustable illumination conditions, and a calibrated system to record ground truth gaze targets. We show that our dataset can significantly improve the robustness of gaze estimation methods across different head poses and gaze angles. Additionally, we define a standardized experimental protocol and evaluation metric on ETH-XGaze, to better unify gaze estimation research going forward. The dataset and benchmark website are available at https://ait.ethz.ch/projects/2020/ETH-XGaze
Towards End-to-end Video-based Eye-Tracking
Jul 26, 2020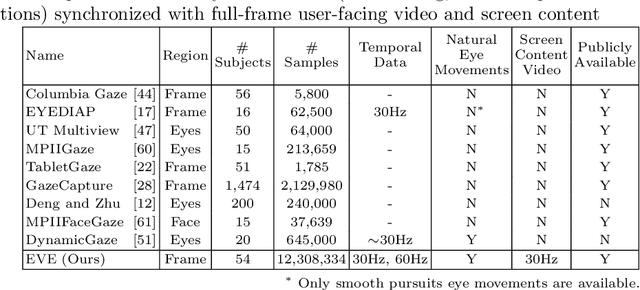

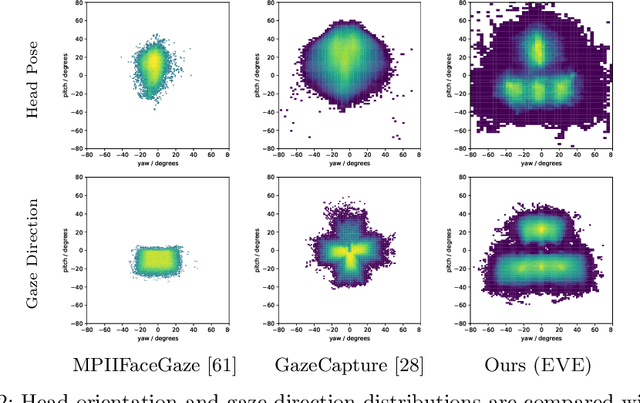
Abstract:Estimating eye-gaze from images alone is a challenging task, in large parts due to un-observable person-specific factors. Achieving high accuracy typically requires labeled data from test users which may not be attainable in real applications. We observe that there exists a strong relationship between what users are looking at and the appearance of the user's eyes. In response to this understanding, we propose a novel dataset and accompanying method which aims to explicitly learn these semantic and temporal relationships. Our video dataset consists of time-synchronized screen recordings, user-facing camera views, and eye gaze data, which allows for new benchmarks in temporal gaze tracking as well as label-free refinement of gaze. Importantly, we demonstrate that the fusion of information from visual stimuli as well as eye images can lead towards achieving performance similar to literature-reported figures acquired through supervised personalization. Our final method yields significant performance improvements on our proposed EVE dataset, with up to a 28 percent improvement in Point-of-Gaze estimates (resulting in 2.49 degrees in angular error), paving the path towards high-accuracy screen-based eye tracking purely from webcam sensors. The dataset and reference source code are available at https://ait.ethz.ch/projects/2020/EVE
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge