Sanghoon Kim
Solar Open Technical Report
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Solar Open, a 102B-parameter bilingual Mixture-of-Experts language model for underserved languages. Solar Open demonstrates a systematic methodology for building competitive LLMs by addressing three interconnected challenges. First, to train effectively despite data scarcity for underserved languages, we synthesize 4.5T tokens of high-quality, domain-specific, and RL-oriented data. Second, we coordinate this data through a progressive curriculum jointly optimizing composition, quality thresholds, and domain coverage across 20 trillion tokens. Third, to enable reasoning capabilities through scalable RL, we apply our proposed framework SnapPO for efficient optimization. Across benchmarks in English and Korean, Solar Open achieves competitive performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of this methodology for underserved language AI development.
BemaGANv2: A Tutorial and Comparative Survey of GAN-based Vocoders for Long-Term Audio Generation
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a tutorial-style survey and implementation guide of BemaGANv2, an advanced GAN-based vocoder designed for high-fidelity and long-term audio generation. Built upon the original BemaGAN architecture, BemaGANv2 incorporates major architectural innovations by replacing traditional ResBlocks in the generator with the Anti-aliased Multi-Periodicity composition (AMP) module, which internally applies the Snake activation function to better model periodic structures. In the discriminator framework, we integrate the Multi-Envelope Discriminator (MED), a novel architecture we originally proposed, to extract rich temporal envelope features crucial for periodicity detection. Coupled with the Multi-Resolution Discriminator (MRD), this combination enables more accurate modeling of long-range dependencies in audio. We systematically evaluate various discriminator configurations, including MSD + MED, MSD + MRD, and MPD + MED + MRD, using objective metrics (FAD, SSIM, PLCC, MCD) and subjective evaluations (MOS, SMOS). This paper also provides a comprehensive tutorial on the model architecture, training methodology, and implementation to promote reproducibility. The code and pre-trained models are available at: https://github.com/dinhoitt/BemaGANv2.
Open Ko-LLM Leaderboard: Evaluating Large Language Models in Korean with Ko-H5 Benchmark
May 31, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces the Open Ko-LLM Leaderboard and the Ko-H5 Benchmark as vital tools for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) in Korean. Incorporating private test sets while mirroring the English Open LLM Leaderboard, we establish a robust evaluation framework that has been well integrated in the Korean LLM community. We perform data leakage analysis that shows the benefit of private test sets along with a correlation study within the Ko-H5 benchmark and temporal analyses of the Ko-H5 score. Moreover, we present empirical support for the need to expand beyond set benchmarks. We hope the Open Ko-LLM Leaderboard sets precedent for expanding LLM evaluation to foster more linguistic diversity.
sDPO: Don't Use Your Data All at Once
Mar 28, 2024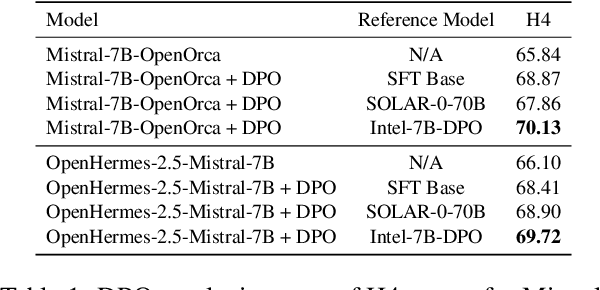
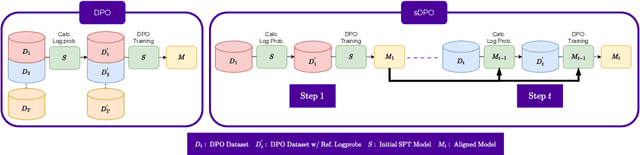
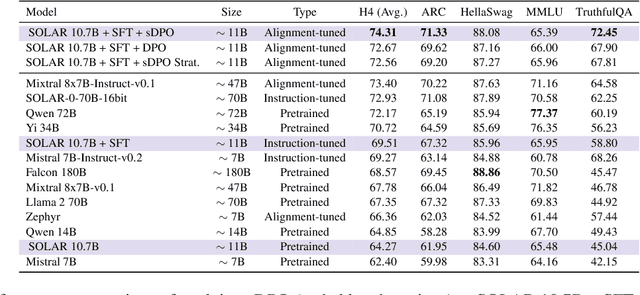
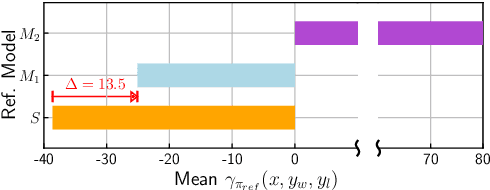
Abstract:As development of large language models (LLM) progresses, aligning them with human preferences has become increasingly important. We propose stepwise DPO (sDPO), an extension of the recently popularized direct preference optimization (DPO) for alignment tuning. This approach involves dividing the available preference datasets and utilizing them in a stepwise manner, rather than employing it all at once. We demonstrate that this method facilitates the use of more precisely aligned reference models within the DPO training framework. Furthermore, sDPO trains the final model to be more performant, even outperforming other popular LLMs with more parameters.
SOLAR 10.7B: Scaling Large Language Models with Simple yet Effective Depth Up-Scaling
Dec 29, 2023



Abstract:We introduce SOLAR 10.7B, a large language model (LLM) with 10.7 billion parameters, demonstrating superior performance in various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Inspired by recent efforts to efficiently up-scale LLMs, we present a method for scaling LLMs called depth up-scaling (DUS), which encompasses depthwise scaling and continued pretraining. In contrast to other LLM up-scaling methods that use mixture-of-experts, DUS does not require complex changes to train and inference efficiently. We show experimentally that DUS is simple yet effective in scaling up high-performance LLMs from small ones. Building on the DUS model, we additionally present SOLAR 10.7B-Instruct, a variant fine-tuned for instruction-following capabilities, surpassing Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct. SOLAR 10.7B is publicly available under the Apache 2.0 license, promoting broad access and application in the LLM field.
Interactive Multi-Class Tiny-Object Detection
Mar 29, 2022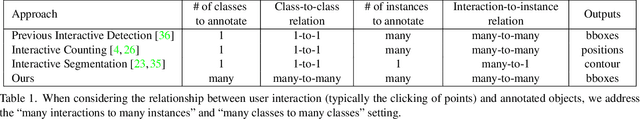

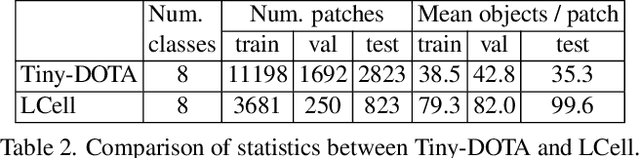
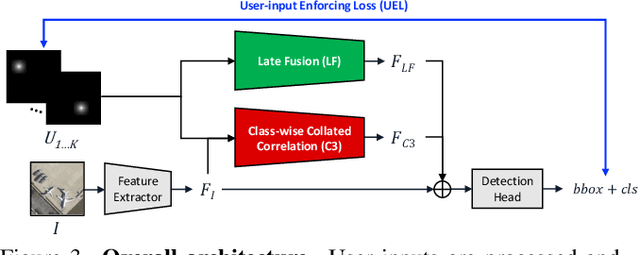
Abstract:Annotating tens or hundreds of tiny objects in a given image is laborious yet crucial for a multitude of Computer Vision tasks. Such imagery typically contains objects from various categories, yet the multi-class interactive annotation setting for the detection task has thus far been unexplored. To address these needs, we propose a novel interactive annotation method for multiple instances of tiny objects from multiple classes, based on a few point-based user inputs. Our approach, C3Det, relates the full image context with annotator inputs in a local and global manner via late-fusion and feature-correlation, respectively. We perform experiments on the Tiny-DOTA and LCell datasets using both two-stage and one-stage object detection architectures to verify the efficacy of our approach. Our approach outperforms existing approaches in interactive annotation, achieving higher mAP with fewer clicks. Furthermore, we validate the annotation efficiency of our approach in a user study where it is shown to be 2.85x faster and yield only 0.36x task load (NASA-TLX, lower is better) compared to manual annotation. The code is available at https://github.com/ChungYi347/Interactive-Multi-Class-Tiny-Object-Detection.
A community-powered search of machine learning strategy space to find NMR property prediction models
Aug 13, 2020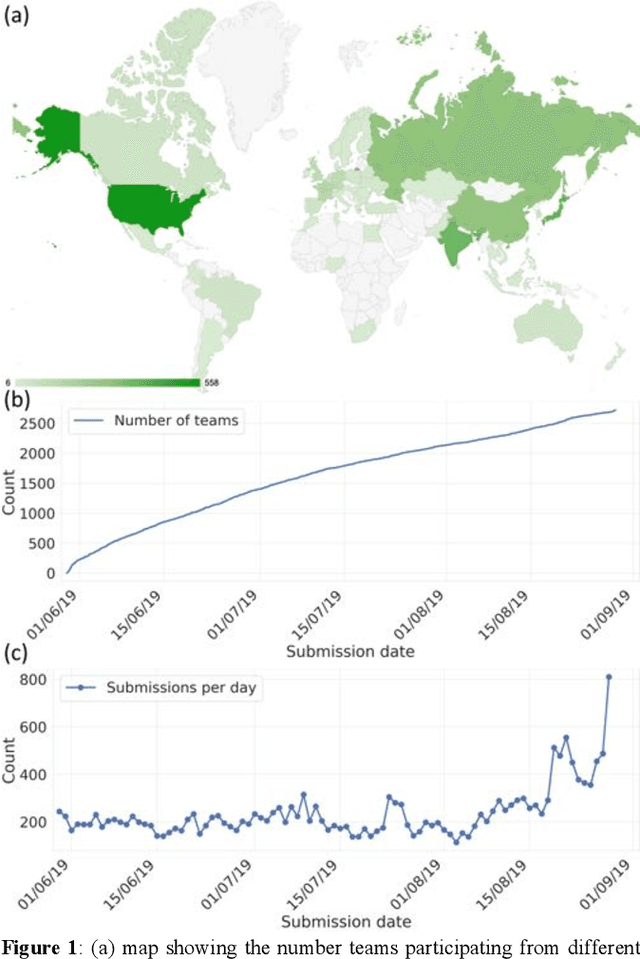
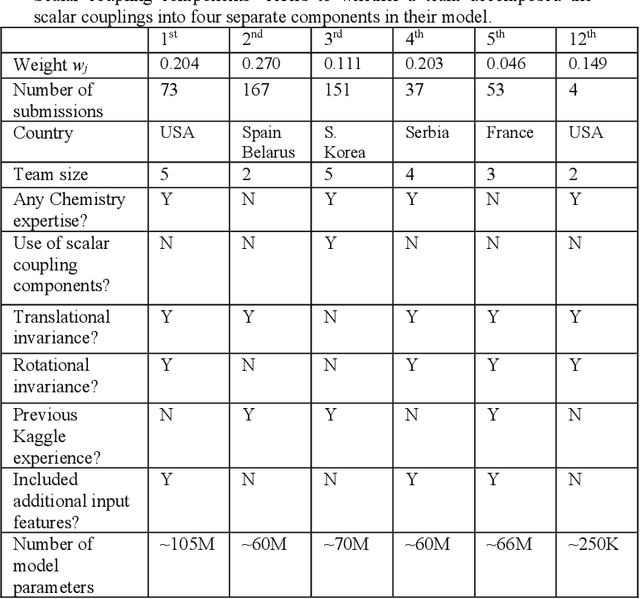
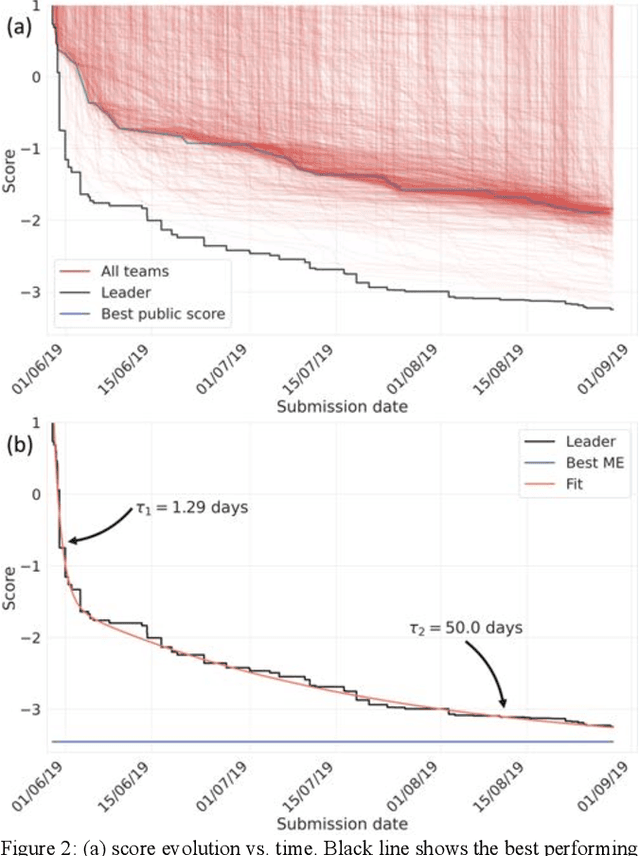
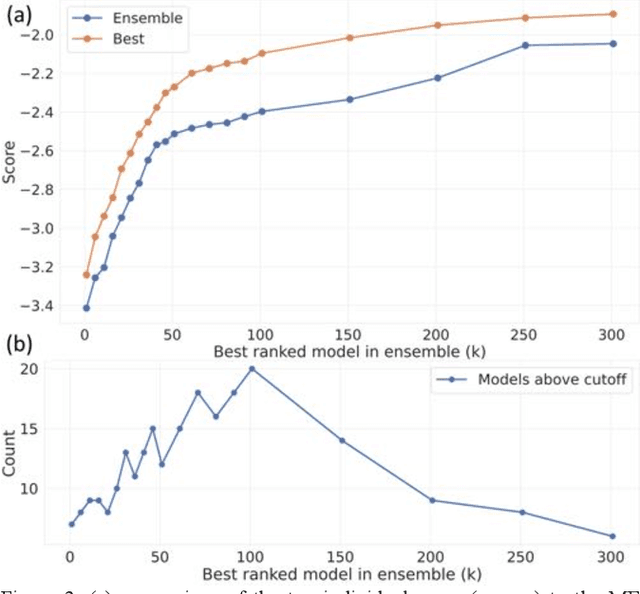
Abstract:The rise of machine learning (ML) has created an explosion in the potential strategies for using data to make scientific predictions. For physical scientists wishing to apply ML strategies to a particular domain, it can be difficult to assess in advance what strategy to adopt within a vast space of possibilities. Here we outline the results of an online community-powered effort to swarm search the space of ML strategies and develop algorithms for predicting atomic-pairwise nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) properties in molecules. Using an open-source dataset, we worked with Kaggle to design and host a 3-month competition which received 47,800 ML model predictions from 2,700 teams in 84 countries. Within 3 weeks, the Kaggle community produced models with comparable accuracy to our best previously published "in-house" efforts. A meta-ensemble model constructed as a linear combination of the top predictions has a prediction accuracy which exceeds that of any individual model, 7-19x better than our previous state-of-the-art. The results highlight the potential of transformer architectures for predicting quantum mechanical (QM) molecular properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge