Sameena Shah
Where is this coming from? Making groundedness count in the evaluation of Document VQA models
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Document Visual Question Answering (VQA) models have evolved at an impressive rate over the past few years, coming close to or matching human performance on some benchmarks. We argue that common evaluation metrics used by popular benchmarks do not account for the semantic and multimodal groundedness of a model's outputs. As a result, hallucinations and major semantic errors are treated the same way as well-grounded outputs, and the evaluation scores do not reflect the reasoning capabilities of the model. In response, we propose a new evaluation methodology that accounts for the groundedness of predictions with regard to the semantic characteristics of the output as well as the multimodal placement of the output within the input document. Our proposed methodology is parameterized in such a way that users can configure the score according to their preferences. We validate our scoring methodology using human judgment and show its potential impact on existing popular leaderboards. Through extensive analyses, we demonstrate that our proposed method produces scores that are a better indicator of a model's robustness and tends to give higher rewards to better-calibrated answers.
BuDDIE: A Business Document Dataset for Multi-task Information Extraction
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:The field of visually rich document understanding (VRDU) aims to solve a multitude of well-researched NLP tasks in a multi-modal domain. Several datasets exist for research on specific tasks of VRDU such as document classification (DC), key entity extraction (KEE), entity linking, visual question answering (VQA), inter alia. These datasets cover documents like invoices and receipts with sparse annotations such that they support one or two co-related tasks (e.g., entity extraction and entity linking). Unfortunately, only focusing on a single specific of documents or task is not representative of how documents often need to be processed in the wild - where variety in style and requirements is expected. In this paper, we introduce BuDDIE (Business Document Dataset for Information Extraction), the first multi-task dataset of 1,665 real-world business documents that contains rich and dense annotations for DC, KEE, and VQA. Our dataset consists of publicly available business entity documents from US state government websites. The documents are structured and vary in their style and layout across states and types (e.g., forms, certificates, reports, etc.). We provide data variety and quality metrics for BuDDIE as well as a series of baselines for each task. Our baselines cover traditional textual, multi-modal, and large language model approaches to VRDU.
Large Language Models as Financial Data Annotators: A Study on Effectiveness and Efficiency
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Collecting labeled datasets in finance is challenging due to scarcity of domain experts and higher cost of employing them. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in data annotation tasks on general domain datasets, their effectiveness on domain specific datasets remains underexplored. To address this gap, we investigate the potential of LLMs as efficient data annotators for extracting relations in financial documents. We compare the annotations produced by three LLMs (GPT-4, PaLM 2, and MPT Instruct) against expert annotators and crowdworkers. We demonstrate that the current state-of-the-art LLMs can be sufficient alternatives to non-expert crowdworkers. We analyze models using various prompts and parameter settings and find that customizing the prompts for each relation group by providing specific examples belonging to those groups is paramount. Furthermore, we introduce a reliability index (LLM-RelIndex) used to identify outputs that may require expert attention. Finally, we perform an extensive time, cost and error analysis and provide recommendations for the collection and usage of automated annotations in domain-specific settings.
Log Summarisation for Defect Evolution Analysis
Mar 13, 2024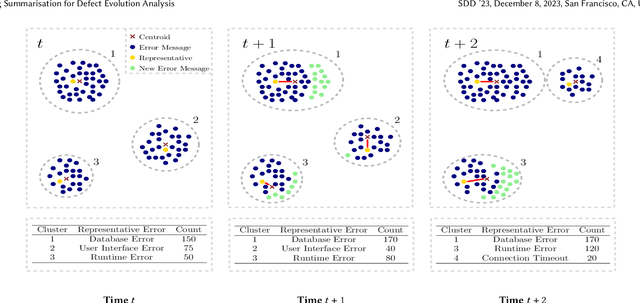
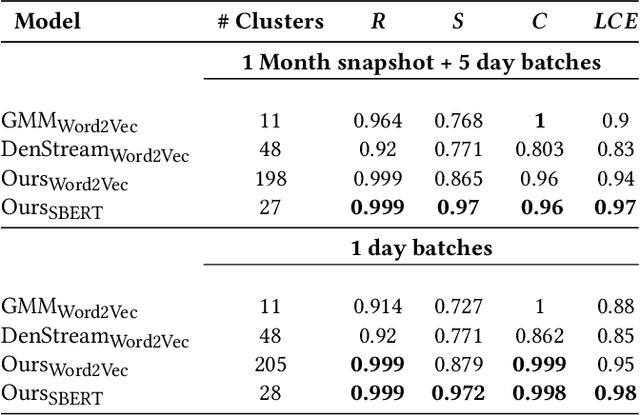
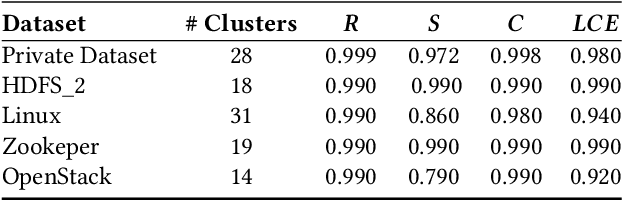
Abstract:Log analysis and monitoring are essential aspects in software maintenance and identifying defects. In particular, the temporal nature and vast size of log data leads to an interesting and important research question: How can logs be summarised and monitored over time? While this has been a fundamental topic of research in the software engineering community, work has typically focused on heuristic-, syntax-, or static-based methods. In this work, we suggest an online semantic-based clustering approach to error logs that dynamically updates the log clusters to enable monitoring code error life-cycles. We also introduce a novel metric to evaluate the performance of temporal log clusters. We test our system and evaluation metric with an industrial dataset and find that our solution outperforms similar systems. We hope that our work encourages further temporal exploration in defect datasets.
TreeForm: End-to-end Annotation and Evaluation for Form Document Parsing
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:Visually Rich Form Understanding (VRFU) poses a complex research problem due to the documents' highly structured nature and yet highly variable style and content. Current annotation schemes decompose form understanding and omit key hierarchical structure, making development and evaluation of end-to-end models difficult. In this paper, we propose a novel F1 metric to evaluate form parsers and describe a new content-agnostic, tree-based annotation scheme for VRFU: TreeForm. We provide methods to convert previous annotation schemes into TreeForm structures and evaluate TreeForm predictions using a modified version of the normalized tree-edit distance. We present initial baselines for our end-to-end performance metric and the TreeForm edit distance, averaged over the FUNSD and XFUND datasets, of 61.5 and 26.4 respectively. We hope that TreeForm encourages deeper research in annotating, modeling, and evaluating the complexities of form-like documents.
DocGraphLM: Documental Graph Language Model for Information Extraction
Jan 05, 2024



Abstract:Advances in Visually Rich Document Understanding (VrDU) have enabled information extraction and question answering over documents with complex layouts. Two tropes of architectures have emerged -- transformer-based models inspired by LLMs, and Graph Neural Networks. In this paper, we introduce DocGraphLM, a novel framework that combines pre-trained language models with graph semantics. To achieve this, we propose 1) a joint encoder architecture to represent documents, and 2) a novel link prediction approach to reconstruct document graphs. DocGraphLM predicts both directions and distances between nodes using a convergent joint loss function that prioritizes neighborhood restoration and downweighs distant node detection. Our experiments on three SotA datasets show consistent improvement on IE and QA tasks with the adoption of graph features. Moreover, we report that adopting the graph features accelerates convergence in the learning process during training, despite being solely constructed through link prediction.
Can GPT models be Financial Analysts? An Evaluation of ChatGPT and GPT-4 on mock CFA Exams
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a wide range of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, often matching or even beating state-of-the-art task-specific models. This study aims at assessing the financial reasoning capabilities of LLMs. We leverage mock exam questions of the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) Program to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of ChatGPT and GPT-4 in financial analysis, considering Zero-Shot (ZS), Chain-of-Thought (CoT), and Few-Shot (FS) scenarios. We present an in-depth analysis of the models' performance and limitations, and estimate whether they would have a chance at passing the CFA exams. Finally, we outline insights into potential strategies and improvements to enhance the applicability of LLMs in finance. In this perspective, we hope this work paves the way for future studies to continue enhancing LLMs for financial reasoning through rigorous evaluation.
Synthetic Text Generation using Hypergraph Representations
Sep 06, 2023Abstract:Generating synthetic variants of a document is often posed as text-to-text transformation. We propose an alternate LLM based method that first decomposes a document into semantic frames and then generates text using this interim sparse format. The frames are modeled using a hypergraph, which allows perturbing the frame contents in a principled manner. Specifically, new hyperedges are mined through topological analysis and complex polyadic relationships including hierarchy and temporal dynamics are accommodated. We show that our solution generates documents that are diverse, coherent and vary in style, sentiment, format, composition and facts.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation using Lexical Transformations and Label Injection for Twitter Data
Jul 14, 2023



Abstract:Domain adaptation is an important and widely studied problem in natural language processing. A large body of literature tries to solve this problem by adapting models trained on the source domain to the target domain. In this paper, we instead solve this problem from a dataset perspective. We modify the source domain dataset with simple lexical transformations to reduce the domain shift between the source dataset distribution and the target dataset distribution. We find that models trained on the transformed source domain dataset performs significantly better than zero-shot models. Using our proposed transformations to convert standard English to tweets, we reach an unsupervised part-of-speech (POS) tagging accuracy of 92.14% (from 81.54% zero shot accuracy), which is only slightly below the supervised performance of 94.45%. We also use our proposed transformations to synthetically generate tweets and augment the Twitter dataset to achieve state-of-the-art performance for POS tagging.
How Effective Are Neural Networks for Fixing Security Vulnerabilities
May 29, 2023Abstract:Security vulnerability repair is a difficult task that is in dire need of automation. Two groups of techniques have shown promise: (1) large code language models (LLMs) that have been pre-trained on source code for tasks such as code completion, and (2) automated program repair (APR) techniques that use deep learning (DL) models to automatically fix software bugs. This paper is the first to study and compare Java vulnerability repair capabilities of LLMs and DL-based APR models. The contributions include that we (1) apply and evaluate five LLMs (Codex, CodeGen, CodeT5, PLBART and InCoder), four fine-tuned LLMs, and four DL-based APR techniques on two real-world Java vulnerability benchmarks (Vul4J and VJBench), (2) design code transformations to address the training and test data overlapping threat to Codex, (3) create a new Java vulnerability repair benchmark VJBench, and its transformed version VJBench-trans and (4) evaluate LLMs and APR techniques on the transformed vulnerabilities in VJBench-trans. Our findings include that (1) existing LLMs and APR models fix very few Java vulnerabilities. Codex fixes 10.2 (20.4%), the most number of vulnerabilities. (2) Fine-tuning with general APR data improves LLMs' vulnerability-fixing capabilities. (3) Our new VJBench reveals that LLMs and APR models fail to fix many Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) types, such as CWE-325 Missing cryptographic step and CWE-444 HTTP request smuggling. (4) Codex still fixes 8.3 transformed vulnerabilities, outperforming all the other LLMs and APR models on transformed vulnerabilities. The results call for innovations to enhance automated Java vulnerability repair such as creating larger vulnerability repair training data, tuning LLMs with such data, and applying code simplification transformation to facilitate vulnerability repair.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge