Carolyn Rose
MetaLint: Generalizable Idiomatic Code Quality Analysis through Instruction-Following and Easy-to-Hard Generalization
Jul 15, 2025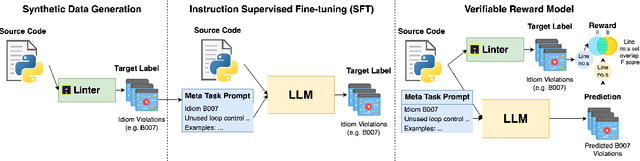
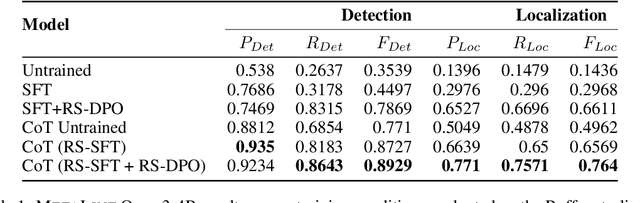
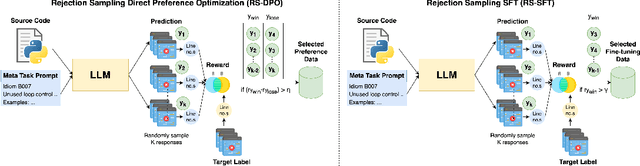

Abstract:Large Language Models, though successful in code generation, struggle with code quality analysis because they are limited by static training data and can't easily adapt to evolving best practices. We introduce MetaLint, a new instruction-following framework that formulates code quality analysis as the task of detecting and fixing problematic semantic code fragments or code idioms based on high-level specifications. Unlike conventional approaches that train models on static, rule-based data, MetaLint employs instruction tuning on synthetic linter-generated data to support easy-to-hard generalization, enabling models to adapt to novel or complex code patterns without retraining. To evaluate this, we construct a benchmark of challenging idioms inspired by real-world coding standards such as Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs) and assess whether MetaLint-trained models reason adaptively or simply memorize. Our results show that MetaLint improves generalization to unseen PEP idioms, achieving a 70.37% F-score on idiom detection with the highest recall (70.43%) among all evaluated models. It also achieves 26.73% on localization, competitive for its 4B parameter size and comparable to larger state-of-the-art models like o3-mini, highlighting its potential for future-proof code quality analysis.
PBEBench: A Multi-Step Programming by Examples Reasoning Benchmark inspired by Historical Linguistics
May 29, 2025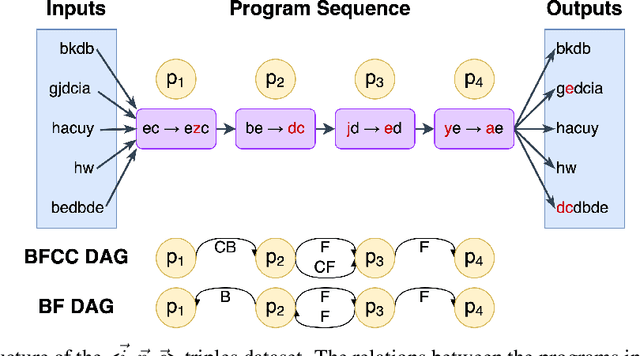
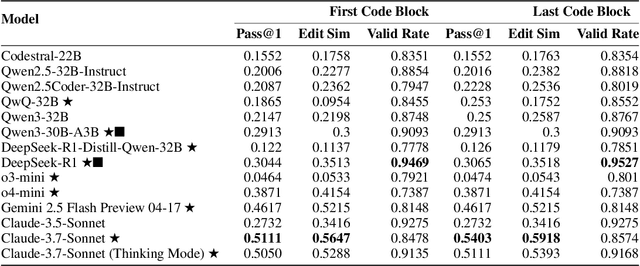
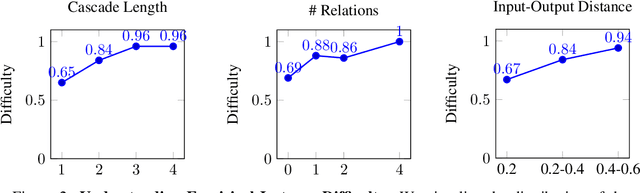
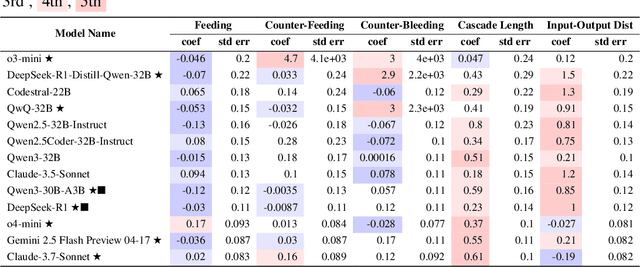
Abstract:Recently, long chain of thought (LCoT), Large Language Models (LLMs), have taken the machine learning world by storm with their breathtaking reasoning capabilities. However, are the abstract reasoning abilities of these models general enough for problems of practical importance? Unlike past work, which has focused mainly on math, coding, and data wrangling, we focus on a historical linguistics-inspired inductive reasoning problem, formulated as Programming by Examples. We develop a fully automated pipeline for dynamically generating a benchmark for this task with controllable difficulty in order to tackle scalability and contamination issues to which many reasoning benchmarks are subject. Using our pipeline, we generate a test set with nearly 1k instances that is challenging for all state-of-the-art reasoning LLMs, with the best model (Claude-3.7-Sonnet) achieving a mere 54% pass rate, demonstrating that LCoT LLMs still struggle with a class or reasoning that is ubiquitous in historical linguistics as well as many other domains.
An Empirical Study on Strong-Weak Model Collaboration for Repo-level Code Generation
May 26, 2025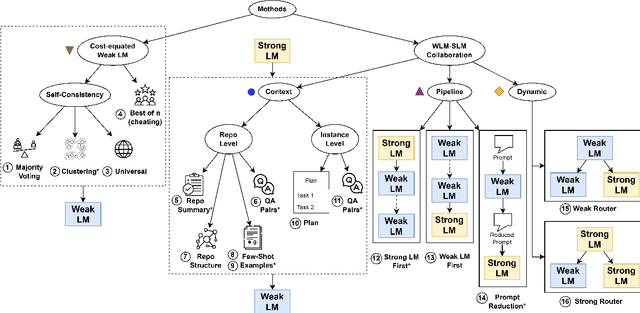
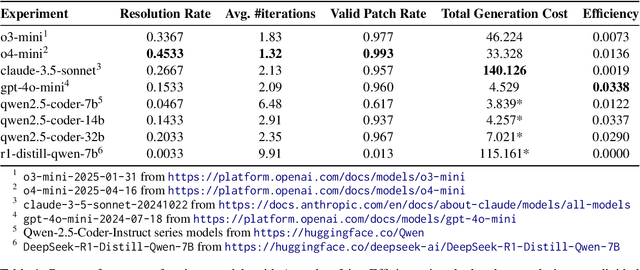
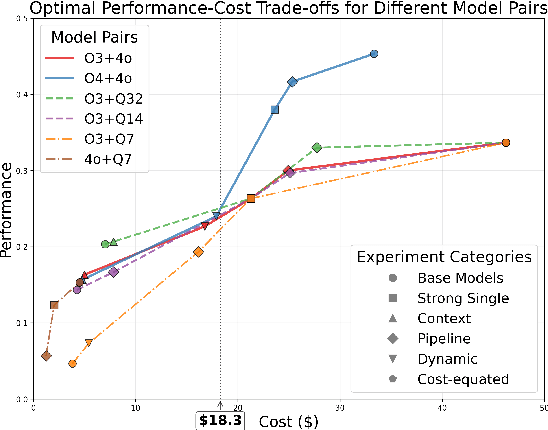
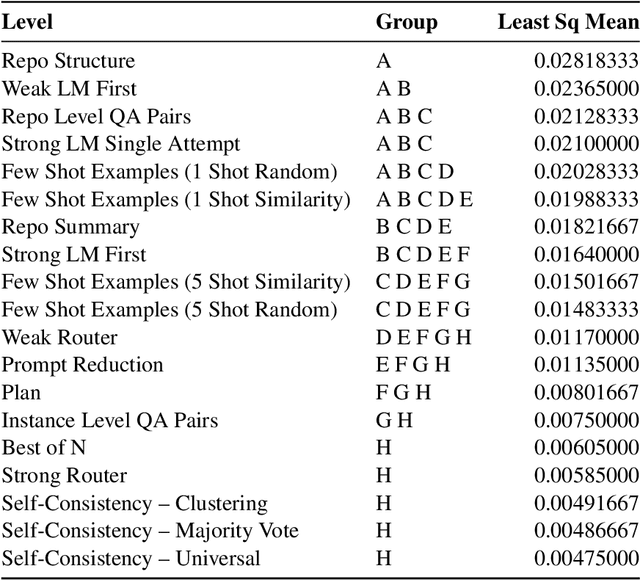
Abstract:We study cost-efficient collaboration between strong and weak language models for repository-level code generation, where the weak model handles simpler tasks at lower cost, and the most challenging tasks are delegated to the strong model. While many works propose architectures for this task, few analyze performance relative to cost. We evaluate a broad spectrum of collaboration strategies: context-based, pipeline-based, and dynamic, on GitHub issue resolution. Our most effective collaborative strategy achieves equivalent performance to the strong model while reducing the cost by 40%. Based on our findings, we offer actionable guidelines for choosing collaboration strategies under varying budget and performance constraints. Our results show that strong-weak collaboration substantially boosts the weak model's performance at a fraction of the cost, pipeline and context-based methods being most efficient. We release the code for our work at https://github.com/shubhamrgandhi/codegen-strong-weak-collab.
Where is this coming from? Making groundedness count in the evaluation of Document VQA models
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Document Visual Question Answering (VQA) models have evolved at an impressive rate over the past few years, coming close to or matching human performance on some benchmarks. We argue that common evaluation metrics used by popular benchmarks do not account for the semantic and multimodal groundedness of a model's outputs. As a result, hallucinations and major semantic errors are treated the same way as well-grounded outputs, and the evaluation scores do not reflect the reasoning capabilities of the model. In response, we propose a new evaluation methodology that accounts for the groundedness of predictions with regard to the semantic characteristics of the output as well as the multimodal placement of the output within the input document. Our proposed methodology is parameterized in such a way that users can configure the score according to their preferences. We validate our scoring methodology using human judgment and show its potential impact on existing popular leaderboards. Through extensive analyses, we demonstrate that our proposed method produces scores that are a better indicator of a model's robustness and tends to give higher rewards to better-calibrated answers.
RepoST: Scalable Repository-Level Coding Environment Construction with Sandbox Testing
Mar 10, 2025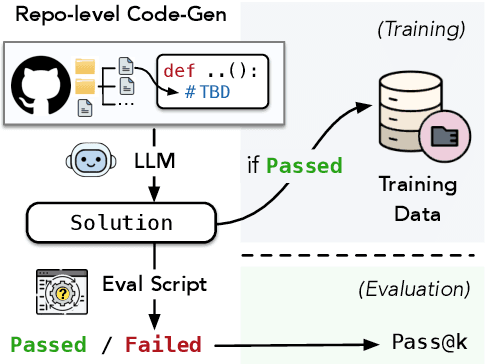
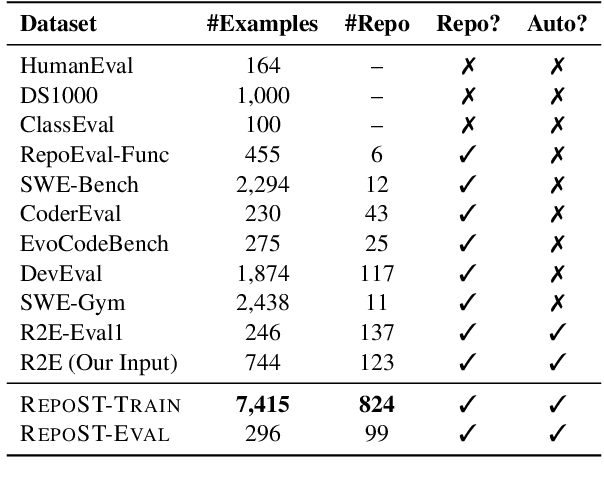
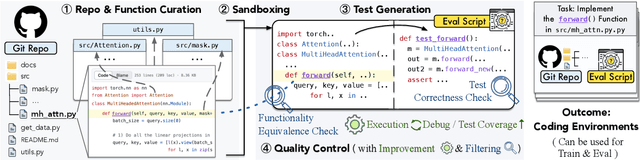
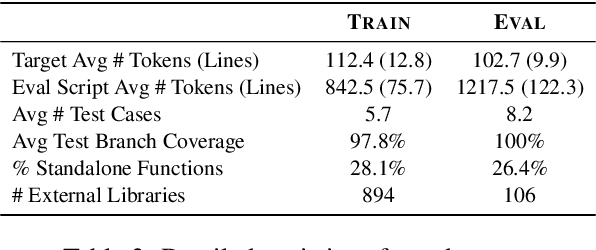
Abstract:We present RepoST, a scalable method to construct environments that provide execution feedback for repository-level code generation for both training and evaluation. Unlike existing works that aim to build entire repositories for execution, which is challenging for both human and LLMs, we provide execution feedback with sandbox testing, which isolates a given target function and its dependencies to a separate script for testing. Sandbox testing reduces the complexity of external dependencies and enables constructing environments at a large scale. We use our method to construct RepoST-Train, a large-scale train set with 7,415 functions from 832 repositories. Training with the execution feedback provided by RepoST-Train leads to a performance gain of 5.5% Pass@1 on HumanEval and 3.5% Pass@1 on RepoEval. We also build an evaluation dataset, RepoST-Eval, and benchmark 12 code generation models.
Programming by Examples Meets Historical Linguistics: A Large Language Model Based Approach to Sound Law Induction
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Historical linguists have long written "programs" that convert reconstructed words in an ancestor language into their attested descendants via ordered string rewrite functions (called sound laws) However, writing these programs is time-consuming, motivating the development of automated Sound Law Induction (SLI) which we formulate as Programming by Examples (PBE) with Large Language Models (LLMs) in this paper. While LLMs have been effective for code generation, recent work has shown that PBE is challenging but improvable by fine-tuning, especially with training data drawn from the same distribution as evaluation data. In this paper, we create a conceptual framework of what constitutes a "similar distribution" for SLI and propose four kinds of synthetic data generation methods with varying amounts of inductive bias to investigate what leads to the best performance. Based on the results we create a SOTA open-source model for SLI as PBE (+6% pass rate with a third of the parameters of the second-best LLM) and also highlight exciting future directions for PBE research.
Improving Model Factuality with Fine-grained Critique-based Evaluator
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Factuality evaluation aims to detect factual errors produced by language models (LMs) and hence guide the development of more factual models. Towards this goal, we train a factuality evaluator, FenCE, that provides LM generators with claim-level factuality feedback. We conduct data augmentation on a combination of public judgment datasets to train FenCE to (1) generate textual critiques along with scores and (2) make claim-level judgment based on diverse source documents obtained by various tools. We then present a framework that leverages FenCE to improve the factuality of LM generators by constructing training data. Specifically, we generate a set of candidate responses, leverage FenCE to revise and score each response without introducing lesser-known facts, and train the generator by preferring highly scored revised responses. Experiments show that our data augmentation methods improve the evaluator's accuracy by 2.9% on LLM-AggreFact. With FenCE, we improve Llama3-8B-chat's factuality rate by 14.45% on FActScore, outperforming state-of-the-art factuality finetuning methods by 6.96%.
CRScore: Grounding Automated Evaluation of Code Review Comments in Code Claims and Smells
Sep 29, 2024
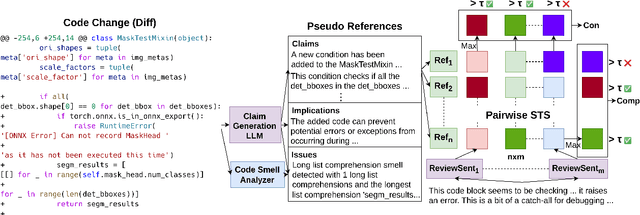
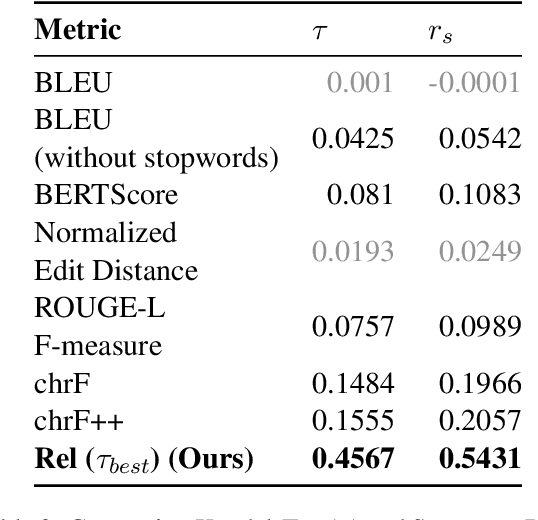
Abstract:The task of automated code review has recently gained a lot of attention from the machine learning community. However, current review comment evaluation metrics rely on comparisons with a human-written reference for a given code change (also called a diff), even though code review is a one-to-many problem like generation and summarization with many "valid reviews" for a diff. To tackle these issues we develop a CRScore - a reference-free metric to measure dimensions of review quality like conciseness, comprehensiveness, and relevance. We design CRScore to evaluate reviews in a way that is grounded in claims and potential issues detected in the code by LLMs and static analyzers. We demonstrate that CRScore can produce valid, fine-grained scores of review quality that have the greatest alignment with human judgment (0.54 Spearman correlation) and are more sensitive than reference-based metrics. We also release a corpus of 2.6k human-annotated review quality scores for machine-generated and GitHub review comments to support the development of automated metrics.
CodeBenchGen: Creating Scalable Execution-based Code Generation Benchmarks
Mar 31, 2024



Abstract:To facilitate evaluation of code generation systems across diverse scenarios, we present CodeBenchGen, a framework to create scalable execution-based benchmarks that only requires light guidance from humans. Specifically, we leverage a large language model (LLM) to convert an arbitrary piece of code into an evaluation example, including test cases for execution-based evaluation. We illustrate the usefulness of our framework by creating a dataset, Exec-CSN, which includes 1,931 examples involving 293 libraries revised from code in 367 GitHub repositories taken from the CodeSearchNet dataset. To demonstrate the complexity and solvability of examples in Exec-CSN, we present a human study demonstrating that 81.3% of the examples can be solved by humans and 61% are rated as ``requires effort to solve''. We conduct code generation experiments on open-source and proprietary models and analyze the performance of both humans and models. We will release the code of both the framework and the dataset upon acceptance.
Data Augmentation for Code Translation with Comparable Corpora and Multiple References
Nov 01, 2023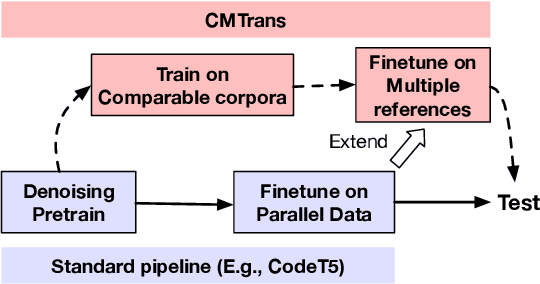


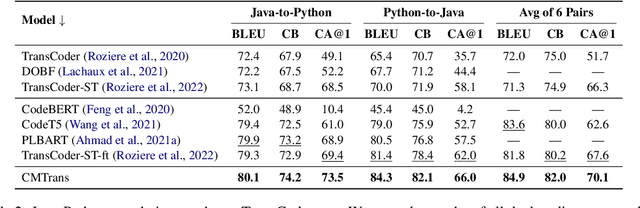
Abstract:One major challenge of translating code between programming languages is that parallel training data is often limited. To overcome this challenge, we present two data augmentation techniques, one that builds comparable corpora (i.e., code pairs with similar functionality), and another that augments existing parallel data with multiple reference translations. Specifically, we build and analyze multiple types of comparable corpora, including programs generated from natural language documentation using a code generation model. Furthermore, to reduce overfitting to a single reference translation, we automatically generate additional translation references for available parallel data and filter the translations by unit tests, which increases variation in target translations. Experiments show that our data augmentation techniques significantly improve CodeT5 for translation between Java, Python, and C++ by an average of 7.5% Computational Accuracy (CA@1), which verifies the correctness of translations by execution. The code is available at https://github.com/Veronicium/CMTrans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge