Sahana Ramnath
ELI-Why: Evaluating the Pedagogical Utility of Language Model Explanations
Jun 17, 2025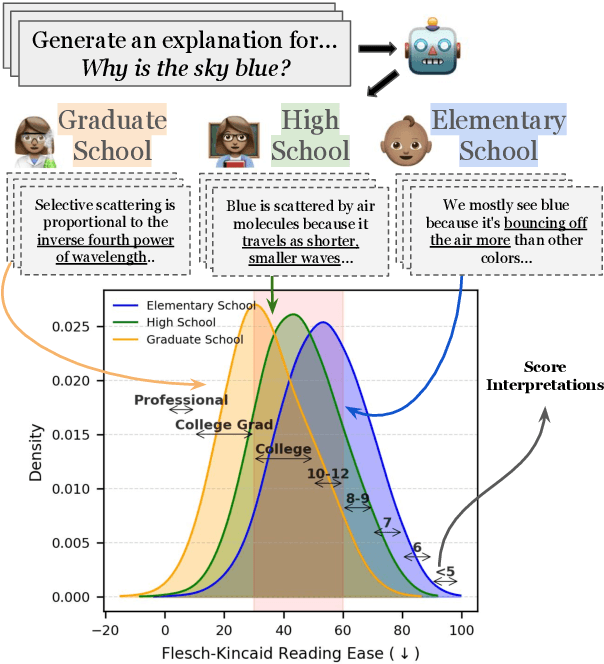
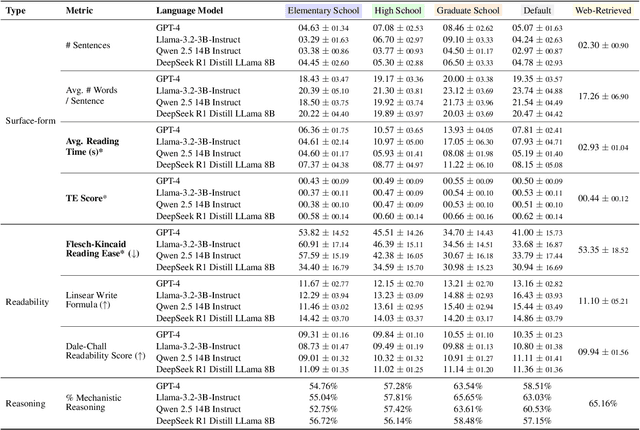
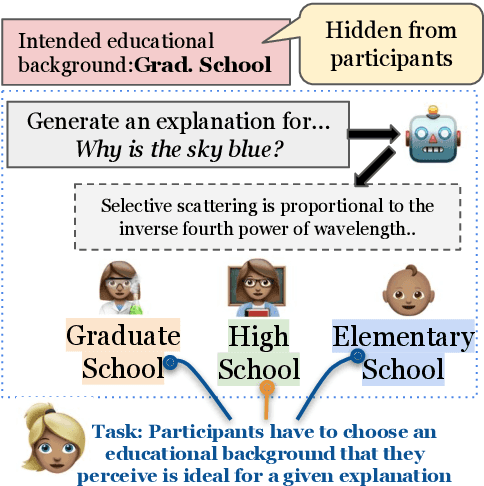

Abstract:Language models today are widely used in education, yet their ability to tailor responses for learners with varied informational needs and knowledge backgrounds remains under-explored. To this end, we introduce ELI-Why, a benchmark of 13.4K "Why" questions to evaluate the pedagogical capabilities of language models. We then conduct two extensive human studies to assess the utility of language model-generated explanatory answers (explanations) on our benchmark, tailored to three distinct educational grades: elementary, high-school and graduate school. In our first study, human raters assume the role of an "educator" to assess model explanations' fit to different educational grades. We find that GPT-4-generated explanations match their intended educational background only 50% of the time, compared to 79% for lay human-curated explanations. In our second study, human raters assume the role of a learner to assess if an explanation fits their own informational needs. Across all educational backgrounds, users deemed GPT-4-generated explanations 20% less suited on average to their informational needs, when compared to explanations curated by lay people. Additionally, automated evaluation metrics reveal that explanations generated across different language model families for different informational needs remain indistinguishable in their grade-level, limiting their pedagogical effectiveness.
Amulet: Putting Complex Multi-Turn Conversations on the Stand with LLM Juries
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Today, large language models are widely used as judges to evaluate responses from other language models. Hence, it is imperative to benchmark and improve these LLM-judges on real-world language model usage: a typical human-assistant conversation is lengthy, and shows significant diversity in topics, intents, and requirements across turns, e.g. social interactions, task requests, feedback. We present Amulet, a framework that leverages pertinent linguistic concepts of dialog-acts and maxims to improve the accuracy of LLM-judges on preference data with complex, multi-turn conversational context. Amulet presents valuable insights about (a) the communicative structures and intents present in the conversation (dialog acts), and (b) the satisfaction of conversational principles (maxims) by the preference responses, and uses them to make judgments. On four challenging datasets, Amulet shows that (a) humans frequently (60 to 70 percent of the time) change their intents from one turn of the conversation to the next, and (b) in 75 percent of instances, the preference responses can be differentiated via dialog acts and/or maxims, reiterating the latter's significance in judging such data. Amulet can be used either as a judge by applying the framework to a single LLM, or integrated into a jury with different LLM judges; our judges and juries show strong improvements on relevant baselines for all four datasets.
CAVE: Controllable Authorship Verification Explanations
Jun 24, 2024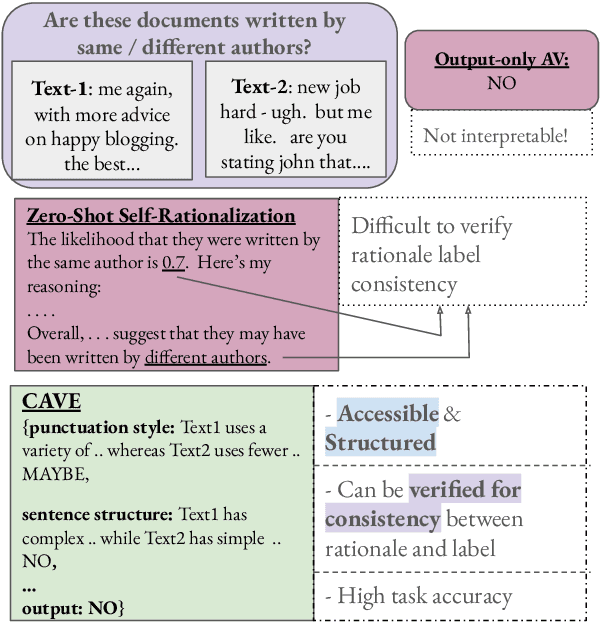
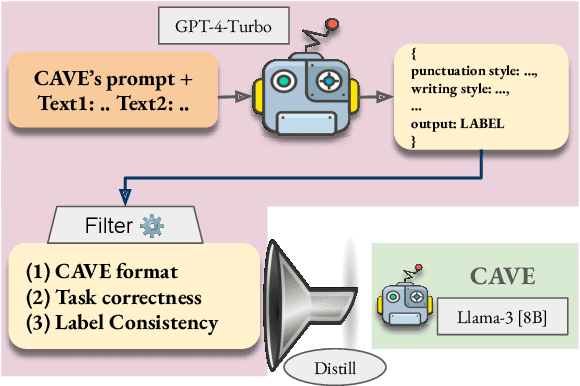
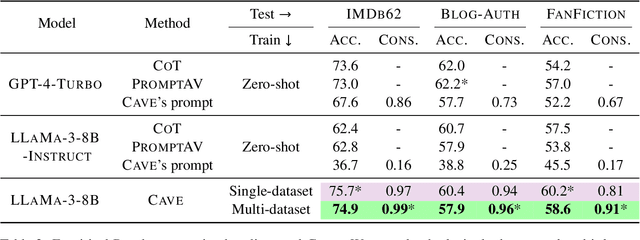
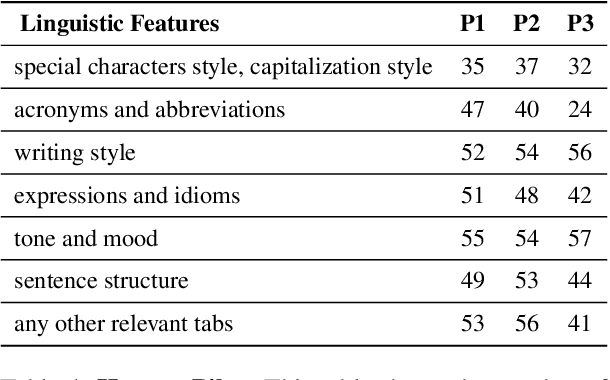
Abstract:Authorship Verification (AV) (do two documents have the same author?) is essential for many sensitive real-life applications. AV is often used in proprietary domains that require a private, offline model, making SOTA online models like ChatGPT undesirable. Other SOTA systems use methods, e.g. Siamese Networks, that are uninterpretable, and hence cannot be trusted in high-stakes applications. In this work, we take the first step to address the above challenges with our model CAVE (Controllable Authorship Verification Explanations): CAVE generates free-text AV explanations that are controlled to be 1) structured (can be decomposed into sub-explanations with respect to relevant linguistic features), and 2) easily verified for explanation-label consistency (via intermediate labels in sub-explanations). In this work, we train a Llama-3-8B as CAVE; since there are no human-written corpora for AV explanations, we sample silver-standard explanations from GPT-4-TURBO and distill them into a pretrained Llama-3-8B. Results on three difficult AV datasets IMdB2, Blog-Auth, and FanFiction show that CAVE generates high quality explanations (as measured by automatic and human evaluation) as well as competitive task accuracies.
Tailoring Self-Rationalizers with Multi-Reward Distillation
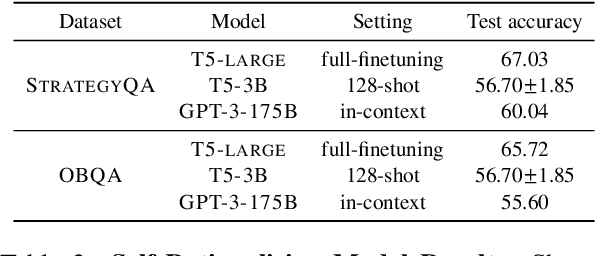
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LMs) are capable of generating free-text rationales to aid question answering. However, prior work 1) suggests that useful self-rationalization is emergent only at significant scales (e.g., 175B parameter GPT-3); and 2) focuses largely on downstream performance, ignoring the semantics of the rationales themselves, e.g., are they faithful, true, and helpful for humans? In this work, we enable small-scale LMs (approx. 200x smaller than GPT-3) to generate rationales that not only improve downstream task performance, but are also more plausible, consistent, and diverse, assessed both by automatic and human evaluation. Our method, MaRio (Multi-rewArd RatIOnalization), is a multi-reward conditioned self-rationalization algorithm that optimizes multiple distinct properties like plausibility, diversity and consistency. Results on five difficult question-answering datasets StrategyQA, QuaRel, OpenBookQA, NumerSense and QASC show that not only does MaRio improve task accuracy, but it also improves the self-rationalization quality of small LMs across the aforementioned axes better than a supervised fine-tuning (SFT) baseline. Extensive human evaluations confirm that MaRio rationales are preferred vs. SFT rationales, as well as qualitative improvements in plausibility and consistency.
Inference-Time Policy Adapters (IPA): Tailoring Extreme-Scale LMs without Fine-tuning
May 24, 2023Abstract:Large language models excel at a variety of language tasks when prompted with examples or instructions. Yet controlling these models through prompting alone is limited. Tailoring language models through fine-tuning (e.g., via reinforcement learning) can be effective, but it is expensive and requires model access. We propose Inference-time Policy Adapters (IPA), which efficiently tailors a language model such as GPT-3 without fine-tuning it. IPA guides a large base model during decoding time through a lightweight policy adaptor trained to optimize an arbitrary user objective with reinforcement learning. On five challenging text generation tasks, such as toxicity reduction and open-domain generation, IPA consistently brings significant improvements over off-the-shelf language models. It outperforms competitive baseline methods, sometimes even including expensive fine-tuning. In particular, tailoring GPT-2 with IPA can outperform GPT-3, while tailoring GPT- 3 with IPA brings a major performance boost over GPT-3 (and sometimes even over GPT-4). Our promising results highlight the potential of IPA as a lightweight alternative to tailoring extreme-scale language models.
Are Machine Rationales (Not) Useful to Humans? Measuring and Improving Human Utility of Free-Text Rationales
May 11, 2023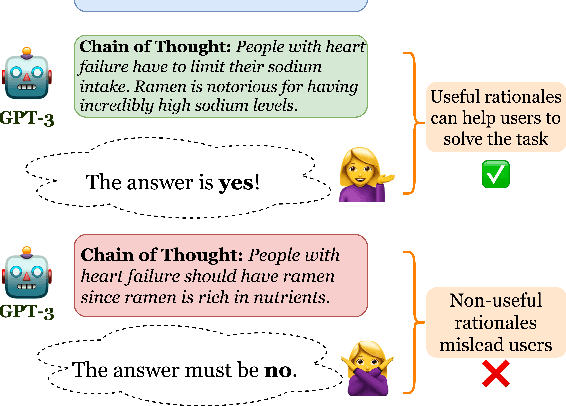

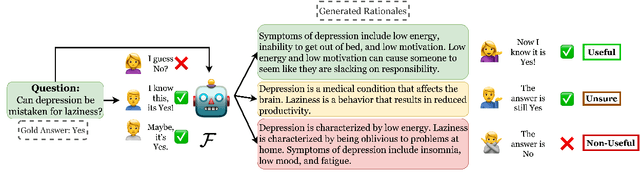
Abstract:Among the remarkable emergent capabilities of large language models (LMs) is free-text rationalization; beyond a certain scale, large LMs are capable of generating seemingly useful rationalizations, which in turn, can dramatically enhance their performances on leaderboards. This phenomenon raises a question: can machine generated rationales also be useful for humans, especially when lay humans try to answer questions based on those machine rationales? We observe that human utility of existing rationales is far from satisfactory, and expensive to estimate with human studies. Existing metrics like task performance of the LM generating the rationales, or similarity between generated and gold rationales are not good indicators of their human utility. While we observe that certain properties of rationales like conciseness and novelty are correlated with their human utility, estimating them without human involvement is challenging. We show that, by estimating a rationale's helpfulness in answering similar unseen instances, we can measure its human utility to a better extent. We also translate this finding into an automated score, GEN-U, that we propose, which can help improve LMs' ability to generate rationales with better human utility, while maintaining most of its task performance. Lastly, we release all code and collected data with this project.
A Framework for Rationale Extraction for Deep QA models
Oct 09, 2021
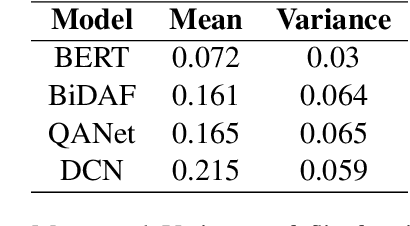

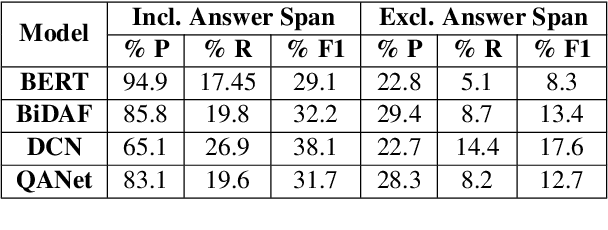
Abstract:As neural-network-based QA models become deeper and more complex, there is a demand for robust frameworks which can access a model's rationale for its prediction. Current techniques that provide insights on a model's working are either dependent on adversarial datasets or are proposing models with explicit explanation generation components. These techniques are time-consuming and challenging to extend to existing models and new datasets. In this work, we use `Integrated Gradients' to extract rationale for existing state-of-the-art models in the task of Reading Comprehension based Question Answering (RCQA). On detailed analysis and comparison with collected human rationales, we find that though ~40-80% words of extracted rationale coincide with the human rationale (precision), only 6-19% of human rationale is present in the extracted rationale (recall).
HintedBT: Augmenting Back-Translation with Quality and Transliteration Hints
Sep 09, 2021

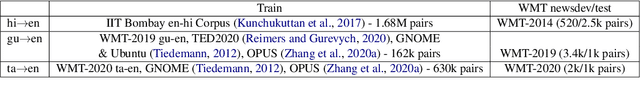

Abstract:Back-translation (BT) of target monolingual corpora is a widely used data augmentation strategy for neural machine translation (NMT), especially for low-resource language pairs. To improve effectiveness of the available BT data, we introduce HintedBT -- a family of techniques which provides hints (through tags) to the encoder and decoder. First, we propose a novel method of using both high and low quality BT data by providing hints (as source tags on the encoder) to the model about the quality of each source-target pair. We don't filter out low quality data but instead show that these hints enable the model to learn effectively from noisy data. Second, we address the problem of predicting whether a source token needs to be translated or transliterated to the target language, which is common in cross-script translation tasks (i.e., where source and target do not share the written script). For such cases, we propose training the model with additional hints (as target tags on the decoder) that provide information about the operation required on the source (translation or both translation and transliteration). We conduct experiments and detailed analyses on standard WMT benchmarks for three cross-script low/medium-resource language pairs: {Hindi,Gujarati,Tamil}-to-English. Our methods compare favorably with five strong and well established baselines. We show that using these hints, both separately and together, significantly improves translation quality and leads to state-of-the-art performance in all three language pairs in corresponding bilingual settings.
Towards Interpreting BERT for Reading Comprehension Based QA
Oct 18, 2020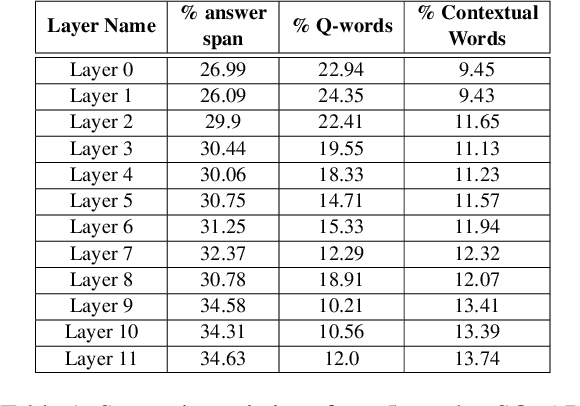
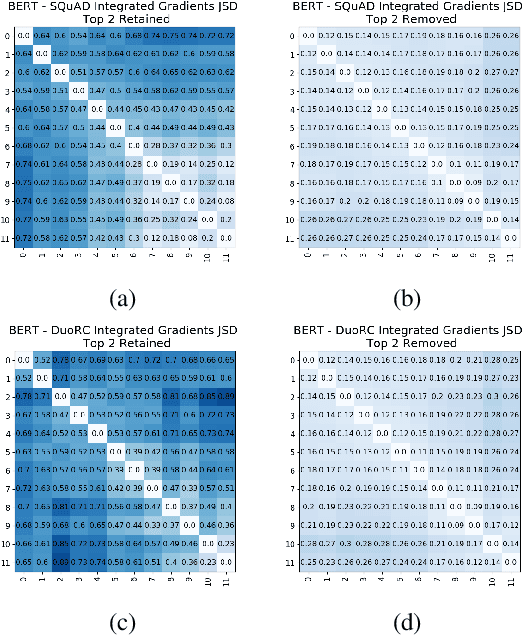
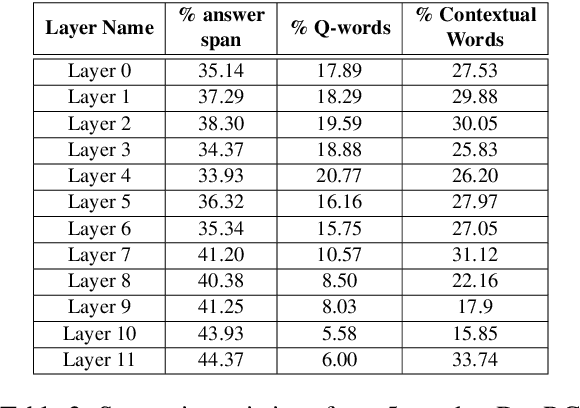
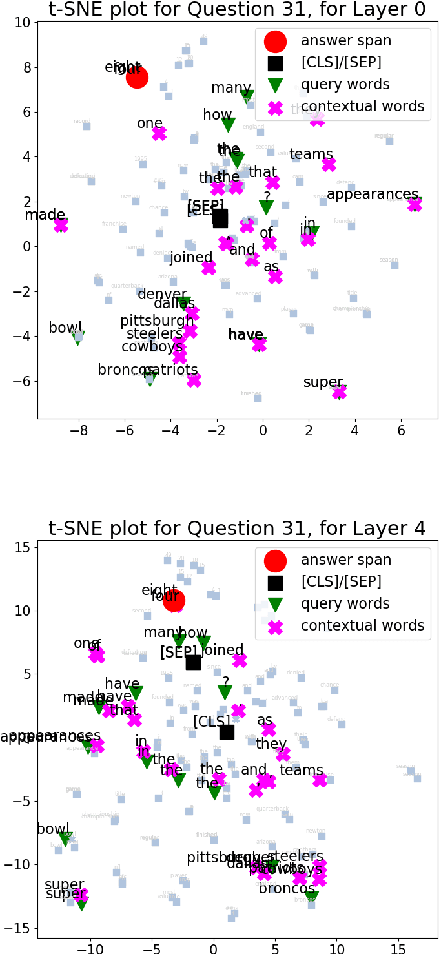
Abstract:BERT and its variants have achieved state-of-the-art performance in various NLP tasks. Since then, various works have been proposed to analyze the linguistic information being captured in BERT. However, the current works do not provide an insight into how BERT is able to achieve near human-level performance on the task of Reading Comprehension based Question Answering. In this work, we attempt to interpret BERT for RCQA. Since BERT layers do not have predefined roles, we define a layer's role or functionality using Integrated Gradients. Based on the defined roles, we perform a preliminary analysis across all layers. We observed that the initial layers focus on query-passage interaction, whereas later layers focus more on contextual understanding and enhancing the answer prediction. Specifically for quantifier questions (how much/how many), we notice that BERT focuses on confusing words (i.e., on other numerical quantities in the passage) in the later layers, but still manages to predict the answer correctly. The fine-tuning and analysis scripts will be publicly available at https://github.com/iitmnlp/BERT-Analysis-RCQA .
Scene Graph based Image Retrieval -- A case study on the CLEVR Dataset
Nov 03, 2019Abstract:With the prolification of multimodal interaction in various domains, recently there has been much interest in text based image retrieval in the computer vision community. However most of the state of the art techniques model this problem in a purely neural way, which makes it difficult to incorporate pragmatic strategies in searching a large scale catalog especially when the search requirements are insufficient and the model needs to resort to an interactive retrieval process through multiple iterations of question-answering. Motivated by this, we propose a neural-symbolic approach for a one-shot retrieval of images from a large scale catalog, given the caption description. To facilitate this, we represent the catalog and caption as scene-graphs and model the retrieval task as a learnable graph matching problem, trained end-to-end with a REINFORCE algorithm. Further, we briefly describe an extension of this pipeline to an iterative retrieval framework, based on interactive questioning and answering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge