Qiantong Xu
SambaLingo: Teaching Large Language Models New Languages
Apr 08, 2024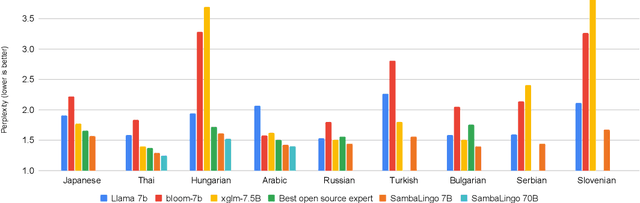
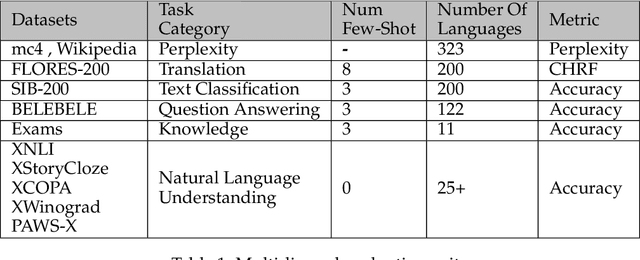
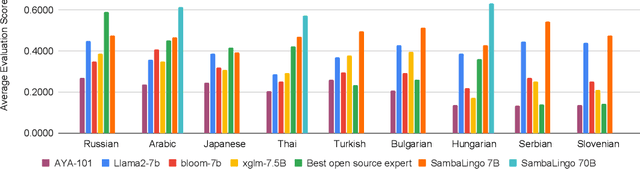
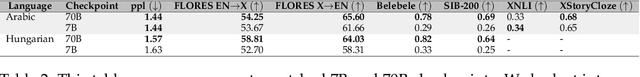
Abstract:Despite the widespread availability of LLMs, there remains a substantial gap in their capabilities and availability across diverse languages. One approach to address these issues has been to take an existing pre-trained LLM and continue to train it on new languages. While prior works have experimented with language adaptation, many questions around best practices and methodology have not been covered. In this paper, we present a comprehensive investigation into the adaptation of LLMs to new languages. Our study covers the key components in this process, including vocabulary extension, direct preference optimization and the data scarcity problem for human alignment in low-resource languages. We scale these experiments across 9 languages and 2 parameter scales (7B and 70B). We compare our models against Llama 2, Aya-101, XGLM, BLOOM and existing language experts, outperforming all prior published baselines. Additionally, all evaluation code and checkpoints are made public to facilitate future research.
Efficiently Adapting Pretrained Language Models To New Languages
Nov 09, 2023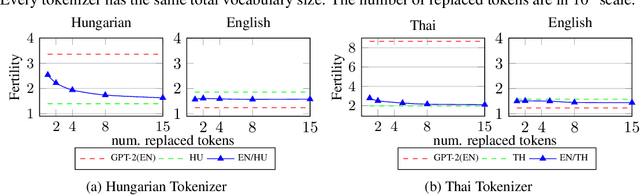
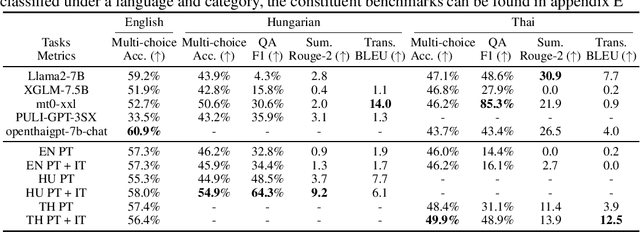
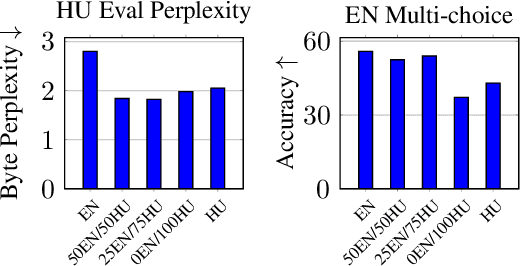
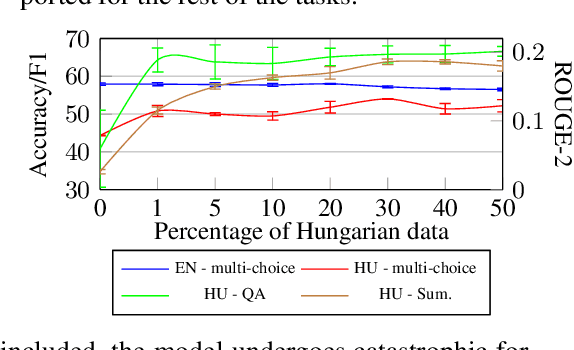
Abstract:Recent large language models (LLM) exhibit sub-optimal performance on low-resource languages, as the training data of these models is usually dominated by English and other high-resource languages. Furthermore, it is challenging to train models for low-resource languages, especially from scratch, due to a lack of high quality training data. Adapting pretrained LLMs reduces the need for data in the new language while also providing cross lingual transfer capabilities. However, naively adapting to new languages leads to catastrophic forgetting and poor tokenizer efficiency. In this work, we study how to efficiently adapt any existing pretrained LLM to a new language without running into these issues. In particular, we improve the encoding efficiency of the tokenizer by adding new tokens from the target language and study the data mixing recipe to mitigate forgetting. Our experiments on adapting an English LLM to Hungarian and Thai show that our recipe can reach better performance than open source models on the target language, with minimal regressions on English.
On the Tool Manipulation Capability of Open-source Large Language Models
May 25, 2023Abstract:Recent studies on software tool manipulation with large language models (LLMs) mostly rely on closed model APIs. The industrial adoption of these models is substantially constrained due to the security and robustness risks in exposing information to closed LLM API services. In this paper, we ask can we enhance open-source LLMs to be competitive to leading closed LLM APIs in tool manipulation, with practical amount of human supervision. By analyzing common tool manipulation failures, we first demonstrate that open-source LLMs may require training with usage examples, in-context demonstration and generation style regulation to resolve failures. These insights motivate us to revisit classical methods in LLM literature, and demonstrate that we can adapt them as model alignment with programmatic data generation, system prompts and in-context demonstration retrievers to enhance open-source LLMs for tool manipulation. To evaluate these techniques, we create the ToolBench, a tool manipulation benchmark consisting of diverse software tools for real-world tasks. We demonstrate that our techniques can boost leading open-source LLMs by up to 90% success rate, showing capabilities competitive to OpenAI GPT-4 in 4 out of 8 ToolBench tasks. We show that such enhancement typically requires about one developer day to curate data for each tool, rendering a recipe with practical amount of human supervision.
data2vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language
Feb 07, 2022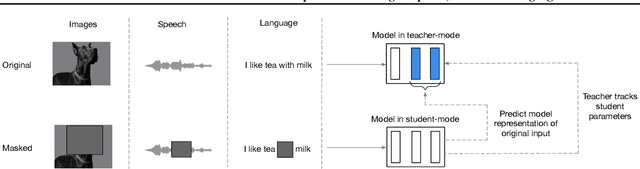
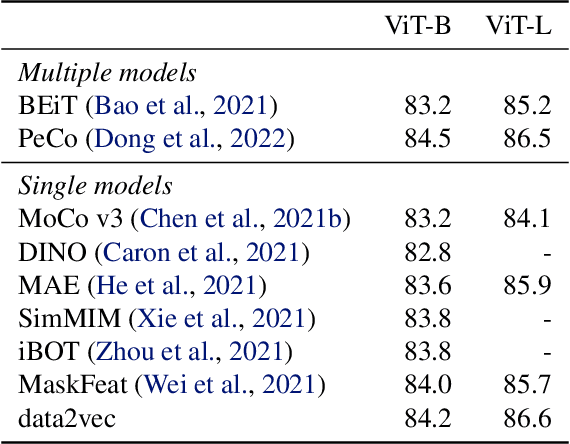
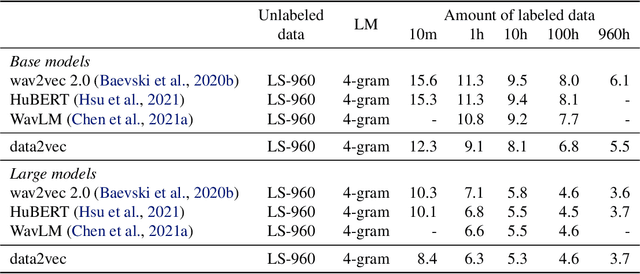
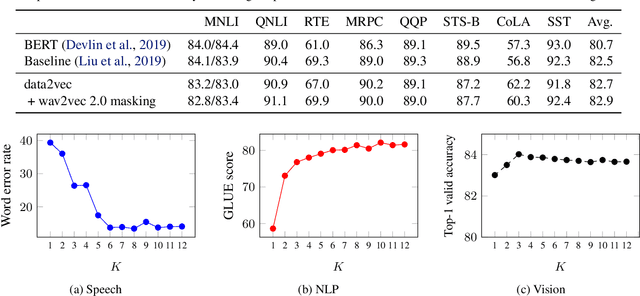
Abstract:While the general idea of self-supervised learning is identical across modalities, the actual algorithms and objectives differ widely because they were developed with a single modality in mind. To get us closer to general self-supervised learning, we present data2vec, a framework that uses the same learning method for either speech, NLP or computer vision. The core idea is to predict latent representations of the full input data based on a masked view of the input in a self-distillation setup using a standard Transformer architecture. Instead of predicting modality-specific targets such as words, visual tokens or units of human speech which are local in nature, data2vec predicts contextualized latent representations that contain information from the entire input. Experiments on the major benchmarks of speech recognition, image classification, and natural language understanding demonstrate a new state of the art or competitive performance to predominant approaches.
Flashlight: Enabling Innovation in Tools for Machine Learning
Jan 29, 2022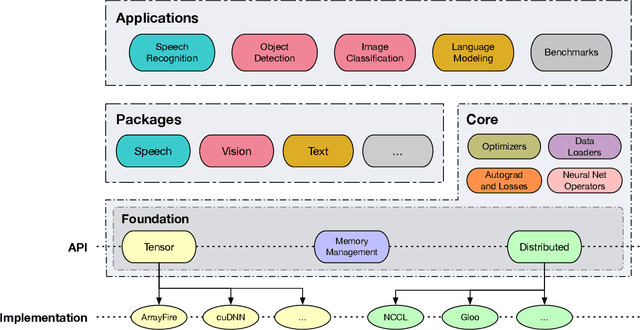
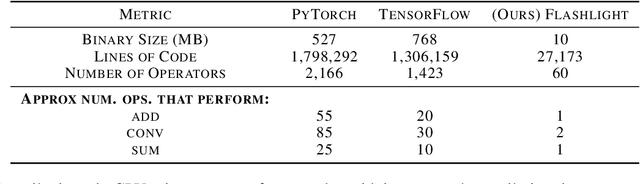
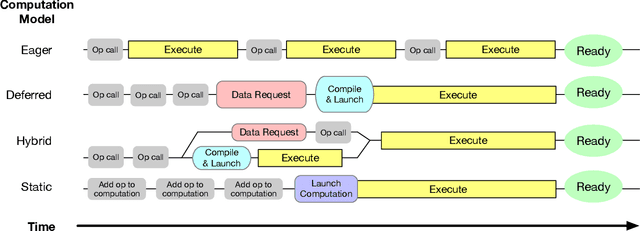
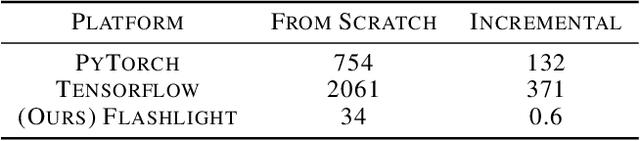
Abstract:As the computational requirements for machine learning systems and the size and complexity of machine learning frameworks increases, essential framework innovation has become challenging. While computational needs have driven recent compiler, networking, and hardware advancements, utilization of those advancements by machine learning tools is occurring at a slower pace. This is in part due to the difficulties involved in prototyping new computational paradigms with existing frameworks. Large frameworks prioritize machine learning researchers and practitioners as end users and pay comparatively little attention to systems researchers who can push frameworks forward -- we argue that both are equally important stakeholders. We introduce Flashlight, an open-source library built to spur innovation in machine learning tools and systems by prioritizing open, modular, customizable internals and state-of-the-art, research-ready models and training setups across a variety of domains. Flashlight allows systems researchers to rapidly prototype and experiment with novel ideas in machine learning computation and has low overhead, competing with and often outperforming other popular machine learning frameworks. We see Flashlight as a tool enabling research that can benefit widely used libraries downstream and bring machine learning and systems researchers closer together.
XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale
Nov 19, 2021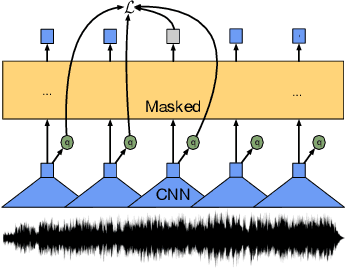
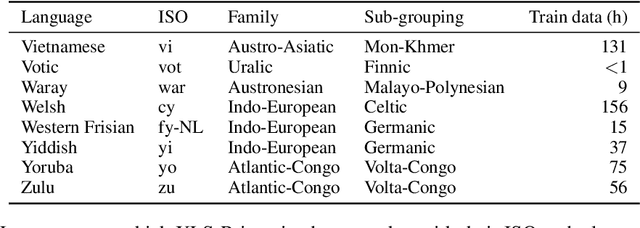

Abstract:This paper presents XLS-R, a large-scale model for cross-lingual speech representation learning based on wav2vec 2.0. We train models with up to 2B parameters on nearly half a million hours of publicly available speech audio in 128 languages, an order of magnitude more public data than the largest known prior work. Our evaluation covers a wide range of tasks, domains, data regimes and languages, both high and low-resource. On the CoVoST-2 speech translation benchmark, we improve the previous state of the art by an average of 7.4 BLEU over 21 translation directions into English. For speech recognition, XLS-R improves over the best known prior work on BABEL, MLS, CommonVoice as well as VoxPopuli, lowering error rates by 14-34% relative on average. XLS-R also sets a new state of the art on VoxLingua107 language identification. Moreover, we show that with sufficient model size, cross-lingual pretraining can outperform English-only pretraining when translating English speech into other languages, a setting which favors monolingual pretraining. We hope XLS-R can help to improve speech processing tasks for many more languages of the world.
Word Order Does Not Matter For Speech Recognition
Oct 18, 2021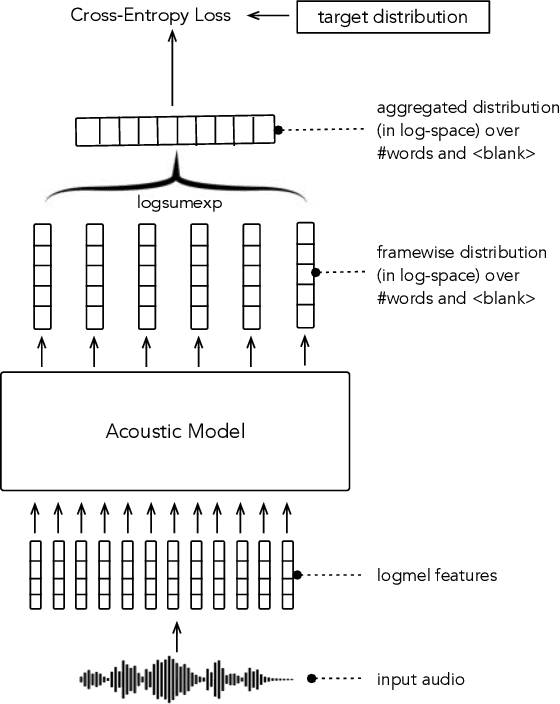
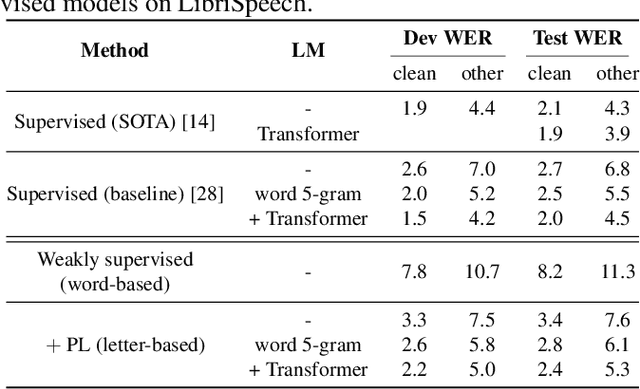
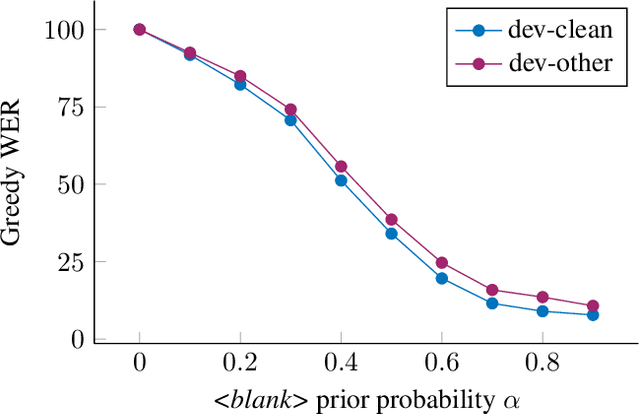
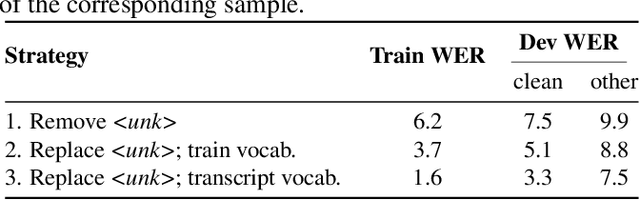
Abstract:In this paper, we study training of automatic speech recognition system in a weakly supervised setting where the order of words in transcript labels of the audio training data is not known. We train a word-level acoustic model which aggregates the distribution of all output frames using LogSumExp operation and uses a cross-entropy loss to match with the ground-truth words distribution. Using the pseudo-labels generated from this model on the training set, we then train a letter-based acoustic model using Connectionist Temporal Classification loss. Our system achieves 2.3%/4.6% on test-clean/test-other subsets of LibriSpeech, which closely matches with the supervised baseline's performance.
Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition
Sep 23, 2021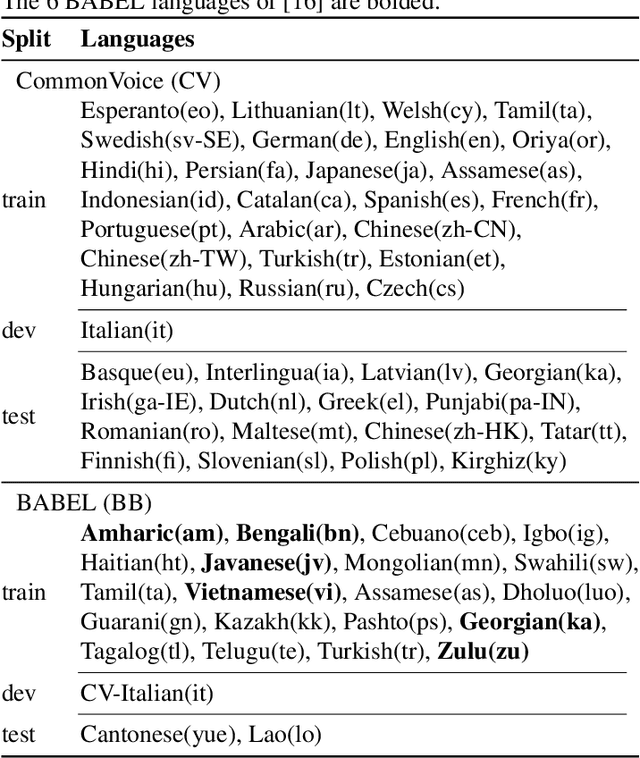
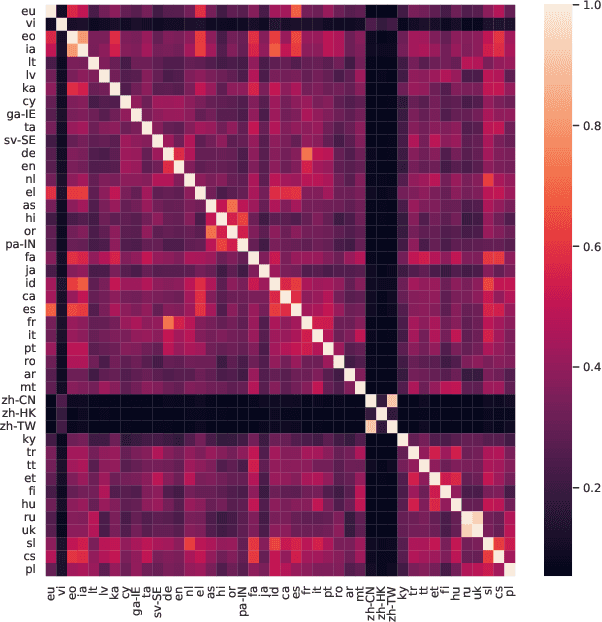
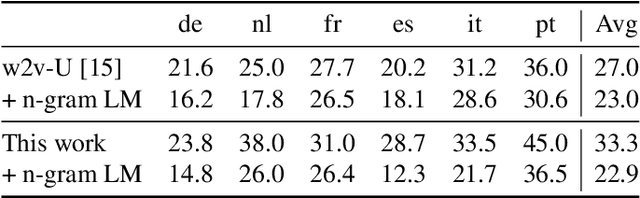
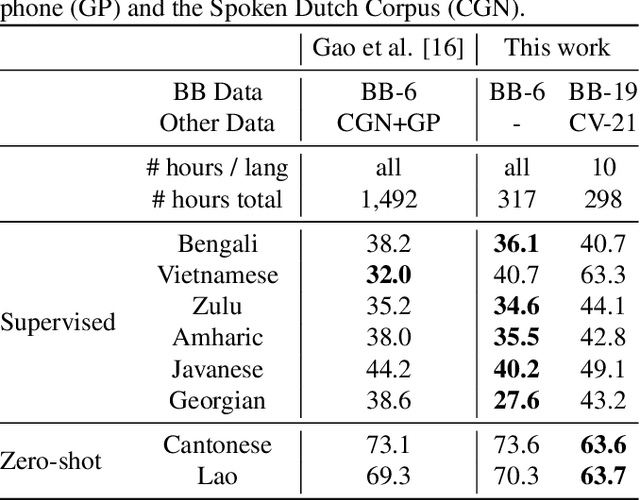
Abstract:Recent progress in self-training, self-supervised pretraining and unsupervised learning enabled well performing speech recognition systems without any labeled data. However, in many cases there is labeled data available for related languages which is not utilized by these methods. This paper extends previous work on zero-shot cross-lingual transfer learning by fine-tuning a multilingually pretrained wav2vec 2.0 model to transcribe unseen languages. This is done by mapping phonemes of the training languages to the target language using articulatory features. Experiments show that this simple method significantly outperforms prior work which introduced task-specific architectures and used only part of a monolingually pretrained model.
Kaizen: Continuously improving teacher using Exponential Moving Average for semi-supervised speech recognition
Jun 14, 2021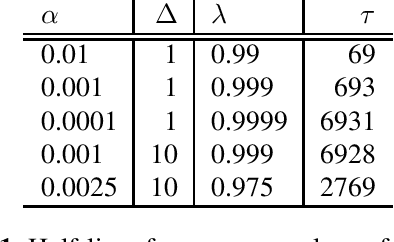
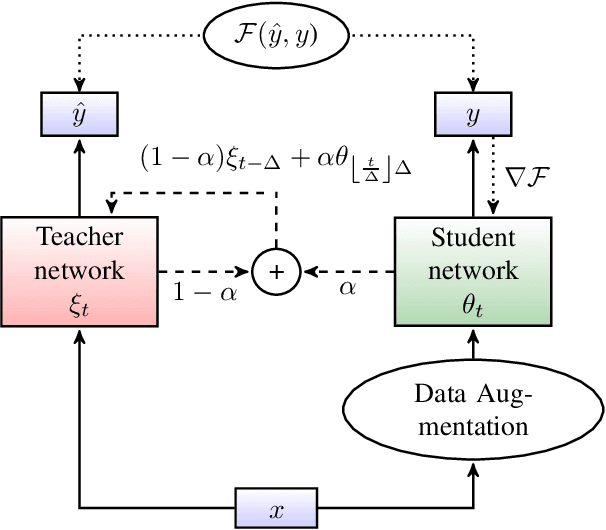
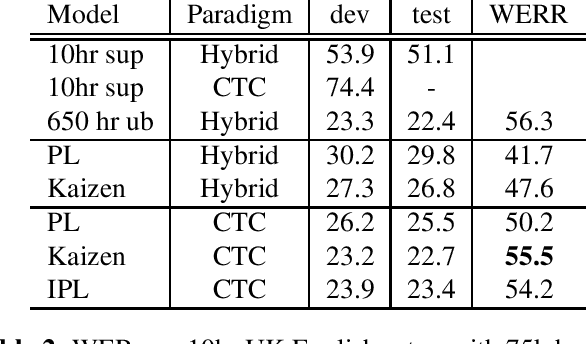
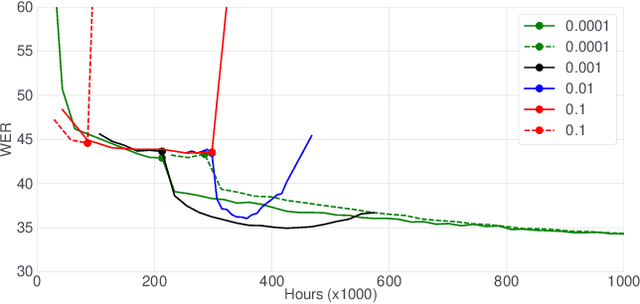
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Kaizen framework that uses a continuously improving teacher to generate pseudo-labels for semi-supervised training. The proposed approach uses a teacher model which is updated as the exponential moving average of the student model parameters. This can be seen as a continuous version of the iterative pseudo-labeling approach for semi-supervised training. It is applicable for different training criteria, and in this paper we demonstrate it for frame-level hybrid hidden Markov model - deep neural network (HMM-DNN) models and sequence-level connectionist temporal classification (CTC) based models. The proposed approach shows more than 10% word error rate (WER) reduction over standard teacher-student training and more than 50\% relative WER reduction over 10 hour supervised baseline when using large scale realistic unsupervised public videos in UK English and Italian languages.
CAPE: Encoding Relative Positions with Continuous Augmented Positional Embeddings
Jun 06, 2021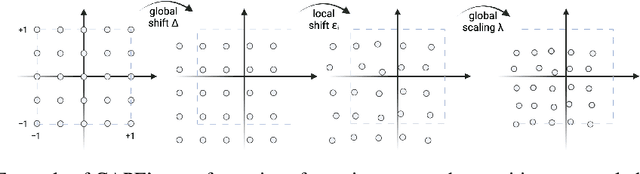
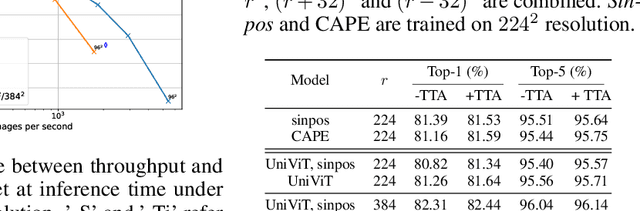
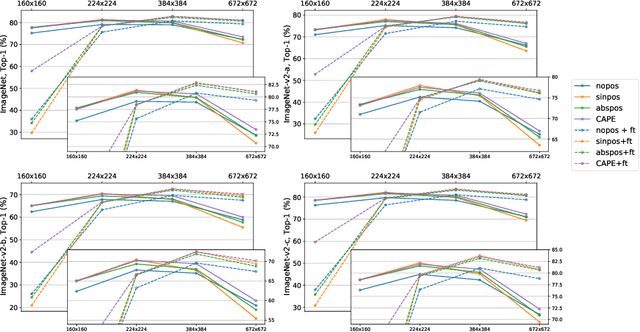
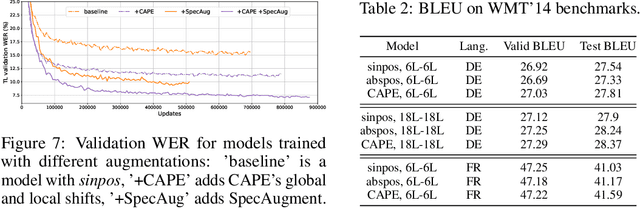
Abstract:Without positional information, attention-based transformer neural networks are permutation-invariant. Absolute or relative positional embeddings are the most popular ways to feed transformer models positional information. Absolute positional embeddings are simple to implement, but suffer from generalization issues when evaluating on sequences of different length than those seen at training time. Relative positions are more robust to length change, but are more complex to implement and yield inferior model throughput. In this paper, we propose an augmentation-based approach (CAPE) for absolute positional embeddings, which keeps the advantages of both absolute (simplicity and speed) and relative position embeddings (better generalization). In addition, our empirical evaluation on state-of-the-art models in machine translation, image and speech recognition demonstrates that CAPE leads to better generalization performance as well as increased stability with respect to training hyper-parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge