Geoffrey Zweig
Kaizen: Continuously improving teacher using Exponential Moving Average for semi-supervised speech recognition
Jun 14, 2021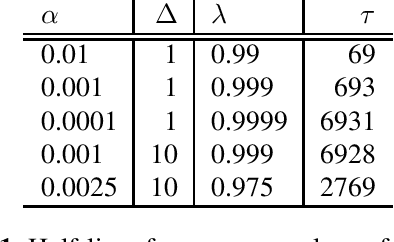
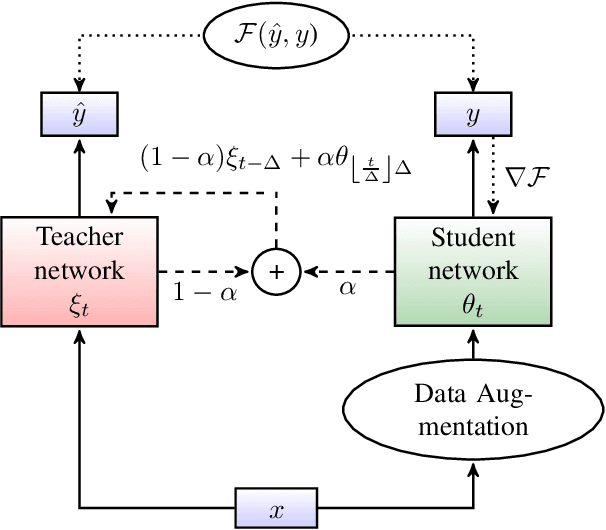
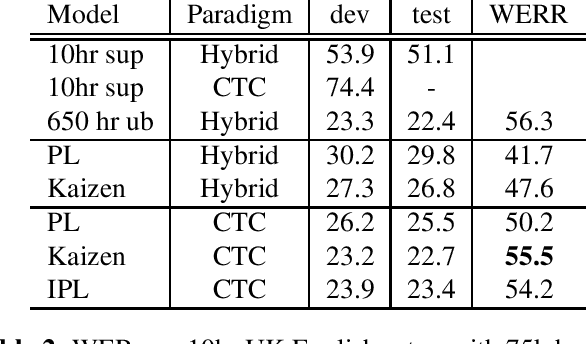
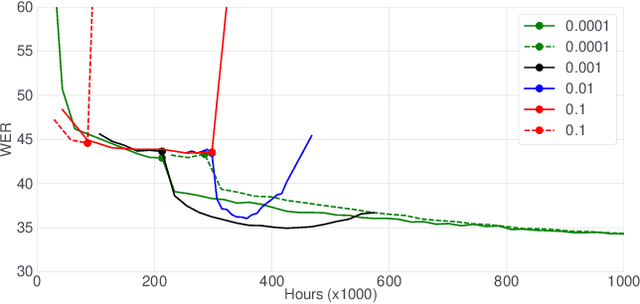
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Kaizen framework that uses a continuously improving teacher to generate pseudo-labels for semi-supervised training. The proposed approach uses a teacher model which is updated as the exponential moving average of the student model parameters. This can be seen as a continuous version of the iterative pseudo-labeling approach for semi-supervised training. It is applicable for different training criteria, and in this paper we demonstrate it for frame-level hybrid hidden Markov model - deep neural network (HMM-DNN) models and sequence-level connectionist temporal classification (CTC) based models. The proposed approach shows more than 10% word error rate (WER) reduction over standard teacher-student training and more than 50\% relative WER reduction over 10 hour supervised baseline when using large scale realistic unsupervised public videos in UK English and Italian languages.
Improving RNN Transducer Based ASR with Auxiliary Tasks
Nov 09, 2020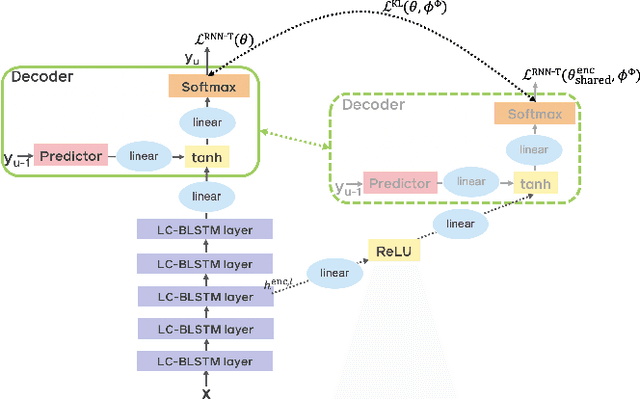
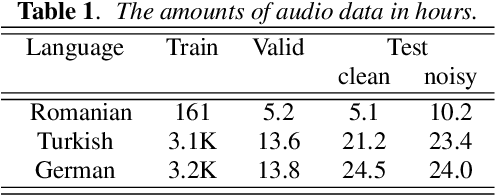
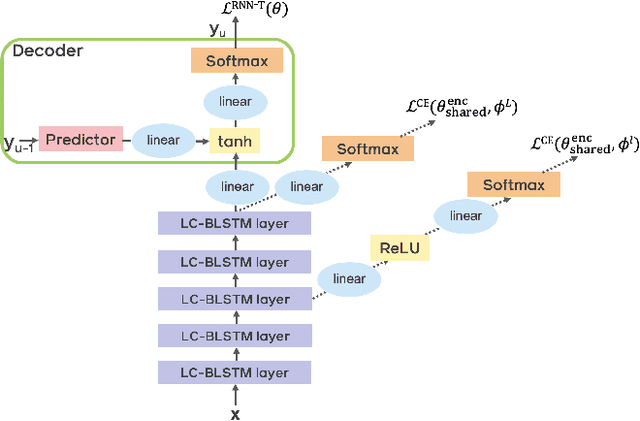
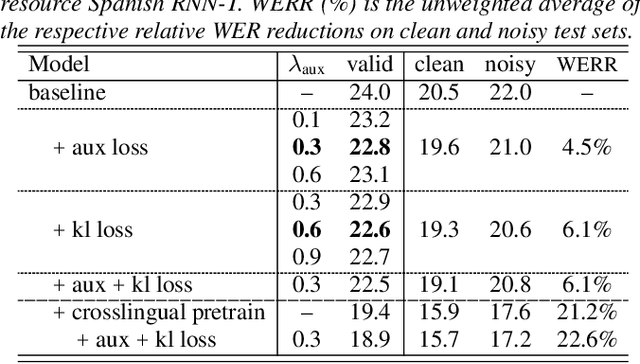
Abstract:End-to-end automatic speech recognition (ASR) models with a single neural network have recently demonstrated state-of-the-art results compared to conventional hybrid speech recognizers. Specifically, recurrent neural network transducer (RNN-T) has shown competitive ASR performance on various benchmarks. In this work, we examine ways in which RNN-T can achieve better ASR accuracy via performing auxiliary tasks. We propose (i) using the same auxiliary task as primary RNN-T ASR task, and (ii) performing context-dependent graphemic state prediction as in conventional hybrid modeling. In transcribing social media videos with varying training data size, we first evaluate the streaming ASR performance on three languages: Romanian, Turkish and German. We find that both proposed methods provide consistent improvements. Next, we observe that both auxiliary tasks demonstrate efficacy in learning deep transformer encoders for RNN-T criterion, thus achieving competitive results - 2.0%/4.2% WER on LibriSpeech test-clean/other - as compared to prior top performing models.
Fast, Simpler and More Accurate Hybrid ASR Systems Using Wordpieces
May 19, 2020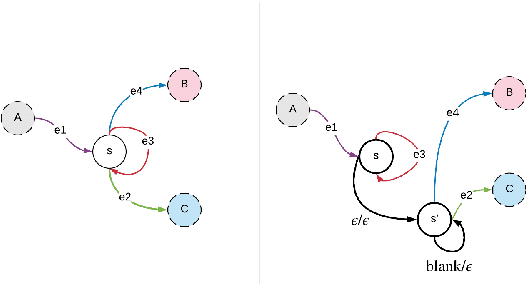
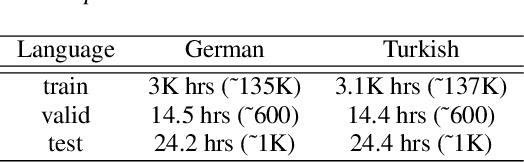
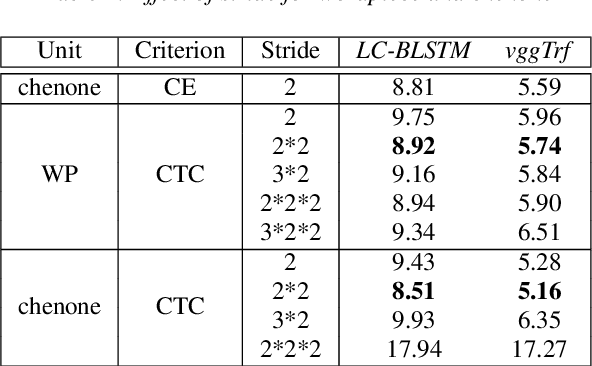
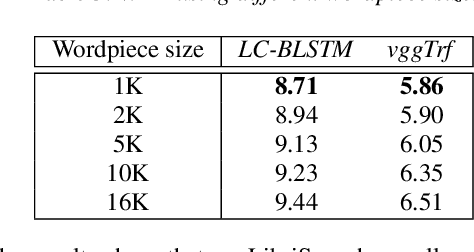
Abstract:In this work, we first show that on the widely used LibriSpeech benchmark, our transformer-based context-dependent connectionist temporal classification (CTC) system produces state-of-the-art results. We then show that using wordpieces as modeling units combined with CTC training, we can greatly simplify the engineering pipeline compared to conventional frame-based cross-entropy training by excluding all the GMM bootstrapping, decision tree building and force alignment steps, while still achieving very competitive word-error-rate. Additionally, using wordpieces as modeling units can significantly improve runtime efficiency since we can use larger stride without losing accuracy. We further confirm these findings on two internal \emph{VideoASR} datasets: German, which is similar to English as a fusional language, and Turkish, which is an agglutinative language.
Large scale weakly and semi-supervised learning for low-resource video ASR
May 16, 2020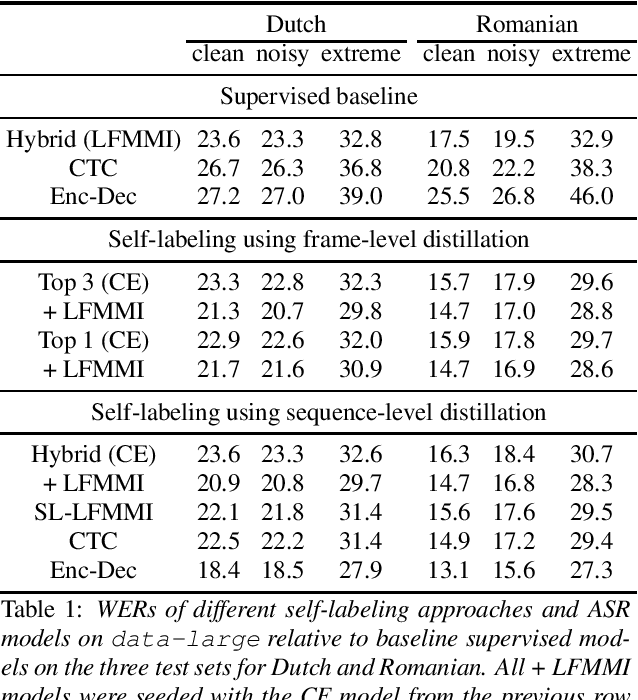
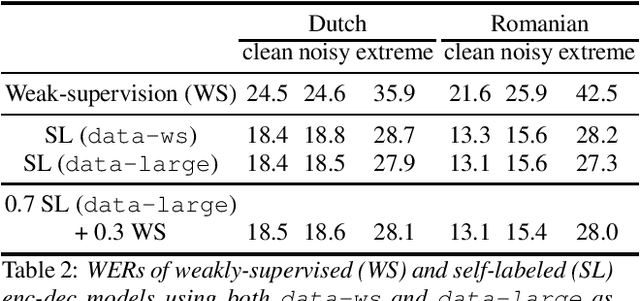
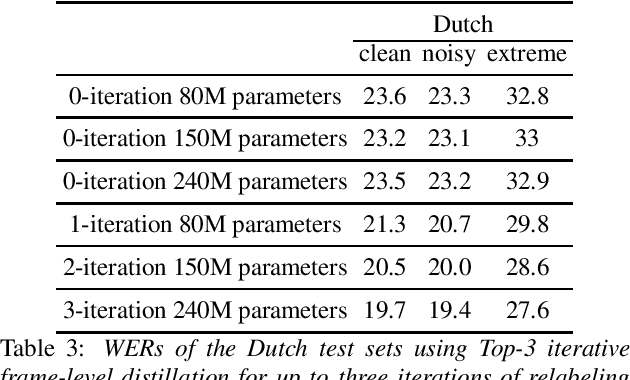
Abstract:Many semi- and weakly-supervised approaches have been investigated for overcoming the labeling cost of building high quality speech recognition systems. On the challenging task of transcribing social media videos in low-resource conditions, we conduct a large scale systematic comparison between two self-labeling methods on one hand, and weakly-supervised pretraining using contextual metadata on the other. We investigate distillation methods at the frame level and the sequence level for hybrid, encoder-only CTC-based, and encoder-decoder speech recognition systems on Dutch and Romanian languages using 27,000 and 58,000 hours of unlabeled audio respectively. Although all approaches improved upon their respective baseline WERs by more than 8%, sequence-level distillation for encoder-decoder models provided the largest relative WER reduction of 20% compared to the strongest data-augmented supervised baseline.
Contextualizing ASR Lattice Rescoring with Hybrid Pointer Network Language Model
May 15, 2020
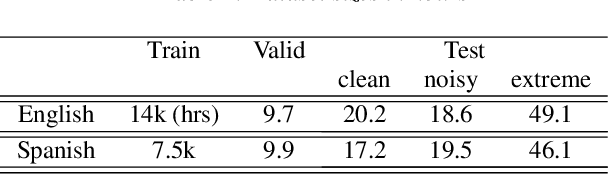
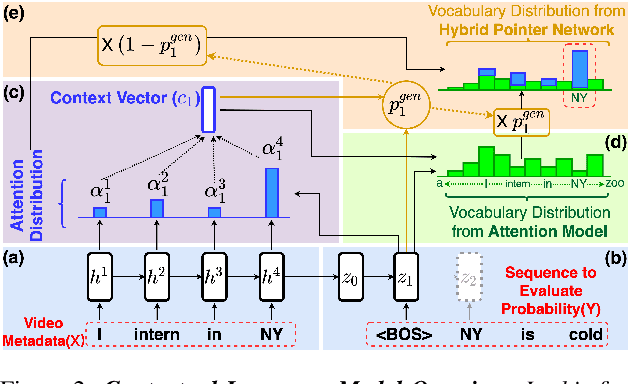
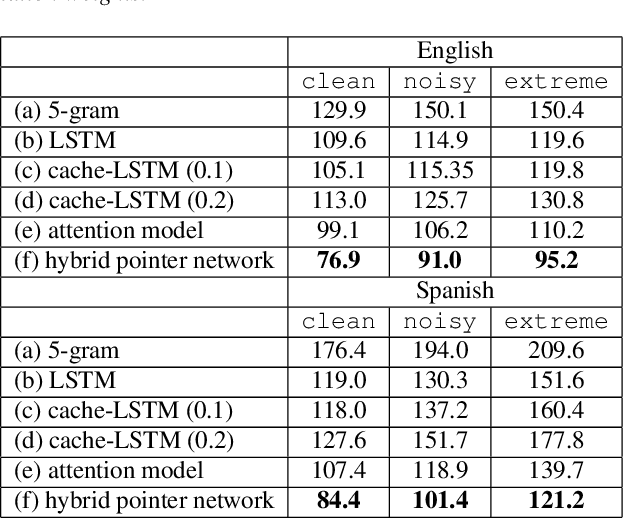
Abstract:Videos uploaded on social media are often accompanied with textual descriptions. In building automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems for videos, we can exploit the contextual information provided by such video metadata. In this paper, we explore ASR lattice rescoring by selectively attending to the video descriptions. We first use an attention based method to extract contextual vector representations of video metadata, and use these representations as part of the inputs to a neural language model during lattice rescoring. Secondly, we propose a hybrid pointer network approach to explicitly interpolate the word probabilities of the word occurrences in metadata. We perform experimental evaluations on both language modeling and ASR tasks, and demonstrate that both proposed methods provide performance improvements by selectively leveraging the video metadata.
Multi-modal Self-Supervision from Generalized Data Transformations
Mar 09, 2020



Abstract:Self-supervised learning has advanced rapidly, with several results beating supervised models for pre-training feature representations. While the focus of most of these works has been new loss functions or tasks, little attention has been given to the data transformations that build the foundation of learning representations with desirable invariances. In this work, we introduce a framework for multi-modal data transformations that preserve semantics and induce the learning of high-level representations across modalities. We do this by combining two steps: inter-modality slicing, and intra-modality augmentation. Using a contrastive loss as the training task, we show that choosing the right transformations is key and that our method yields state-of-the-art results on downstream video and audio classification tasks such as HMDB51, UCF101 and DCASE2014 with Kinetics-400 pretraining.
Training ASR models by Generation of Contextual Information
Oct 27, 2019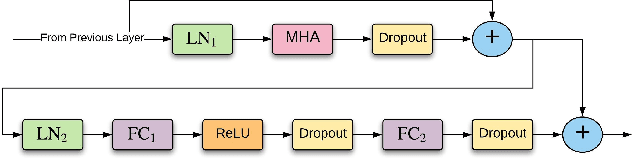
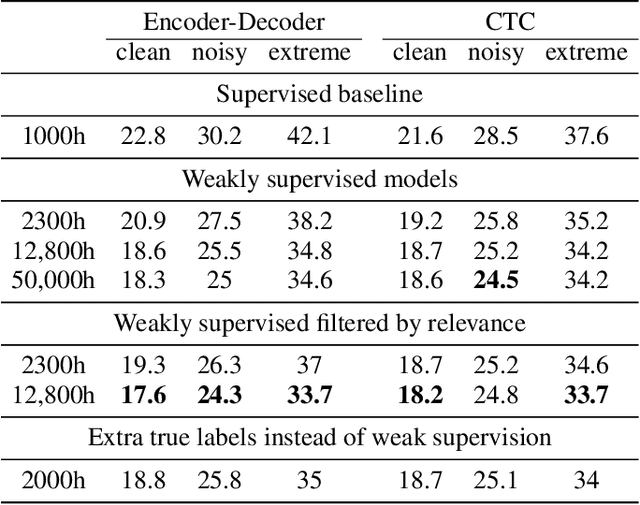
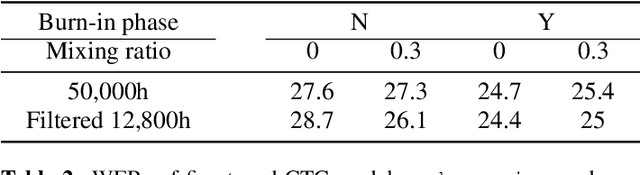
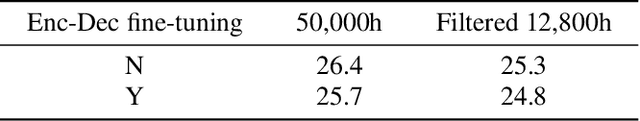
Abstract:Supervised ASR models have reached unprecedented levels of accuracy, thanks in part to ever-increasing amounts of labelled training data. However, in many applications and locales, only moderate amounts of data are available, which has led to a surge in semi- and weakly-supervised learning research. In this paper, we conduct a large-scale study evaluating the effectiveness of weakly-supervised learning for speech recognition by using loosely related contextual information as a surrogate for ground-truth labels. For weakly supervised training, we use 50k hours of public English social media videos along with their respective titles and post text to train an encoder-decoder transformer model. Our best encoder-decoder models achieve an average of 20.8% WER reduction over a 1000 hours supervised baseline, and an average of 13.4% WER reduction when using only the weakly supervised encoder for CTC fine-tuning. Our results show that our setup for weak supervision improved both the encoder acoustic representations as well as the decoder language generation abilities.
Deja-vu: Double Feature Presentation in Deep Transformer Networks
Oct 23, 2019



Abstract:Deep acoustic models typically receive features in the first layer of the network, and process increasingly abstract representations in the subsequent layers. Here, we propose to feed the input features at multiple depths in the acoustic model. As our motivation is to allow acoustic models to re-examine their input features in light of partial hypotheses we introduce intermediate model heads and loss function. We study this architecture in the context of deep Transformer networks, and we use an attention mechanism over both the previous layer activations and the input features. To train this model's intermediate output hypothesis, we apply the objective function at each layer right before feature re-use. We find that the use of such intermediate losses significantly improves performance by itself, as well as enabling input feature re-use. We present results on both Librispeech, and a large scale video dataset, with relative improvements of 10 - 20% for Librispeech and 3.2 - 13% for videos.
Transformer-based Acoustic Modeling for Hybrid Speech Recognition
Oct 22, 2019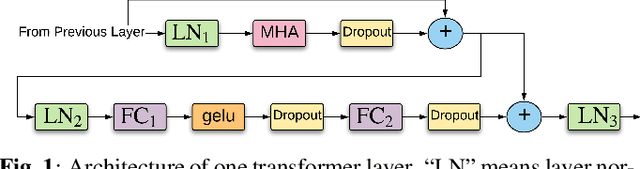
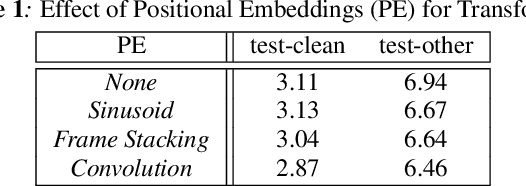
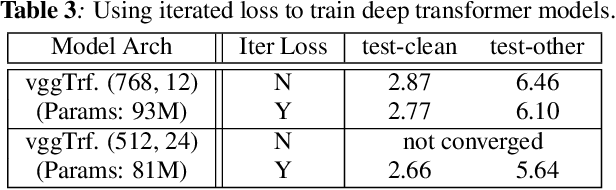
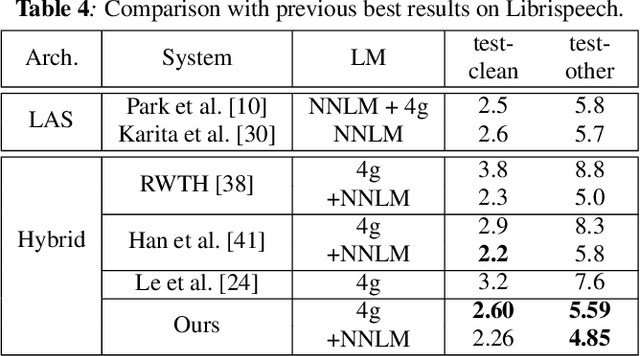
Abstract:We propose and evaluate transformer-based acoustic models (AMs) for hybrid speech recognition. Several modeling choices are discussed in this work, including various positional embedding methods and an iterated loss to enable training deep transformers. We also present a preliminary study of using limited right context in transformer models, which makes it possible for streaming applications. We demonstrate that on the widely used Librispeech benchmark, our transformer-based AM outperforms the best published hybrid result by 19% to 26% relative when the standard n-gram language model (LM) is used. Combined with neural network LM for rescoring, our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art results on Librispeech. Our findings are also confirmed on a much larger internal dataset.
From Senones to Chenones: Tied Context-Dependent Graphemes for Hybrid Speech Recognition
Oct 11, 2019



Abstract:There is an implicit assumption that traditional hybrid approaches for automatic speech recognition (ASR) cannot directly model graphemes and need to rely on phonetic lexicons to get competitive performance, especially on English which has poor grapheme-phoneme correspondence. In this work, we show for the first time that, on English, hybrid ASR systems can in fact model graphemes effectively by leveraging tied context-dependent graphemes, i.e., chenones. Our chenone-based systems significantly outperform equivalent senone baselines by 4.5% to 11.1% relative on three different English datasets. Our results on Librispeech are state-of-the-art compared to other hybrid approaches and competitive with previously published end-to-end numbers. Further analysis shows that chenones can better utilize powerful acoustic models and large training data, and require context- and position-dependent modeling to work well. Chenone-based systems also outperform senone baselines on proper noun and rare word recognition, an area where the latter is traditionally thought to have an advantage. Our work provides an alternative for end-to-end ASR and establishes that hybrid systems can be improved by dropping the reliance on phonetic knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge