Peiran Li
Rethinking the Reranker: Boundary-Aware Evidence Selection for Robust Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems remain brittle under realistic retrieval noise, even when the required evidence appears in the top-K results. A key reason is that retrievers and rerankers optimize solely for relevance, often selecting either trivial, answer-revealing passages or evidence that lacks the critical information required to answer the question, without considering whether the evidence is suitable for the generator. We propose BAR-RAG, which reframes the reranker as a boundary-aware evidence selector that targets the generator's Goldilocks Zone -- evidence that is neither trivially easy nor fundamentally unanswerable for the generator, but is challenging yet sufficient for inference and thus provides the strongest learning signal. BAR-RAG trains the selector with reinforcement learning using generator feedback, and adopts a two-stage pipeline that fine-tunes the generator under the induced evidence distribution to mitigate the distribution mismatch between training and inference. Experiments on knowledge-intensive question answering benchmarks show that BAR-RAG consistently improves end-to-end performance under noisy retrieval, achieving an average gain of 10.3 percent over strong RAG and reranking baselines while substantially improving robustness. Code is publicly avaliable at https://github.com/GasolSun36/BAR-RAG.
Position: Human-Centric AI Requires a Minimum Viable Level of Human Understanding
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:AI systems increasingly produce fluent, correct, end-to-end outcomes. Over time, this erodes users' ability to explain, verify, or intervene. We define this divergence as the Capability-Comprehension Gap: a decoupling where assisted performance improves while users' internal models deteriorate. This paper argues that prevailing approaches to transparency, user control, literacy, and governance do not define the foundational understanding humans must retain for oversight under sustained AI delegation. To formalize this, we define the Cognitive Integrity Threshold (CIT) as the minimum comprehension required to preserve oversight, autonomy, and accountable participation under AI assistance. CIT does not require full reasoning reconstruction, nor does it constrain automation. It identifies the threshold beyond which oversight becomes procedural and contestability fails. We operatinalize CIT through three functional dimensions: (i) verification capacity, (ii) comprehension-preserving interaction, and (iii) institutional scaffolds for governance. This motivates a design and governance agenda that aligns human-AI interaction with cognitive sustainability in responsibility-critical settings.
BibAgent: An Agentic Framework for Traceable Miscitation Detection in Scientific Literature
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Citations are the bedrock of scientific authority, yet their integrity is compromised by widespread miscitations: ranging from nuanced distortions to fabricated references. Systematic citation verification is currently unfeasible; manual review cannot scale to modern publishing volumes, while existing automated tools are restricted by abstract-only analysis or small-scale, domain-specific datasets in part due to the "paywall barrier" of full-text access. We introduce BibAgent, a scalable, end-to-end agentic framework for automated citation verification. BibAgent integrates retrieval, reasoning, and adaptive evidence aggregation, applying distinct strategies for accessible and paywalled sources. For paywalled references, it leverages a novel Evidence Committee mechanism that infers citation validity via downstream citation consensus. To support systematic evaluation, we contribute a 5-category Miscitation Taxonomy and MisciteBench, a massive cross-disciplinary benchmark comprising 6,350 miscitation samples spanning 254 fields. Our results demonstrate that BibAgent outperforms state-of-the-art Large Language Model (LLM) baselines in citation verification accuracy and interpretability, providing scalable, transparent detection of citation misalignments across the scientific literature.
ToxiGAN: Toxic Data Augmentation via LLM-Guided Directional Adversarial Generation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Augmenting toxic language data in a controllable and class-specific manner is crucial for improving robustness in toxicity classification, yet remains challenging due to limited supervision and distributional skew. We propose ToxiGAN, a class-aware text augmentation framework that combines adversarial generation with semantic guidance from large language models (LLMs). To address common issues in GAN-based augmentation such as mode collapse and semantic drift, ToxiGAN introduces a two-step directional training strategy and leverages LLM-generated neutral texts as semantic ballast. Unlike prior work that treats LLMs as static generators, our approach dynamically selects neutral exemplars to provide balanced guidance. Toxic samples are explicitly optimized to diverge from these exemplars, reinforcing class-specific contrastive signals. Experiments on four hate speech benchmarks show that ToxiGAN achieves the strongest average performance in both macro-F1 and hate-F1, consistently outperforming traditional and LLM-based augmentation methods. Ablation and sensitivity analyses further confirm the benefits of semantic ballast and directional training in enhancing classifier robustness.
GRACE: Generative Representation Learning via Contrastive Policy Optimization
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Prevailing methods for training Large Language Models (LLMs) as text encoders rely on contrastive losses that treat the model as a black box function, discarding its generative and reasoning capabilities in favor of static embeddings. We introduce GRACE (Generative Representation Learning via Contrastive Policy Optimization), a novel framework that reimagines contrastive signals not as losses to be minimized, but as rewards that guide a generative policy. In GRACE, the LLM acts as a policy that produces explicit, human-interpretable rationales--structured natural language explanations of its semantic understanding. These rationales are then encoded into high-quality embeddings via mean pooling. Using policy gradient optimization, we train the model with a multi-component reward function that maximizes similarity between query positive pairs and minimizes similarity with negatives. This transforms the LLM from an opaque encoder into an interpretable agent whose reasoning process is transparent and inspectable. On MTEB benchmark, GRACE yields broad cross category gains: averaged over four backbones, the supervised setting improves overall score by 11.5% over base models, and the unsupervised variant adds 6.9%, while preserving general capabilities. This work treats contrastive objectives as rewards over rationales, unifying representation learning with generation to produce stronger embeddings and transparent rationales. The model, data and code are available at https://github.com/GasolSun36/GRACE.
Demystifying the Visual Quality Paradox in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel on benchmark vision-language tasks, yet little is known about how input visual quality shapes their responses. Does higher perceptual quality of images already translate to better MLLM understanding? We conduct the first systematic study spanning leading MLLMs and a suite of vision-language benchmarks, applying controlled degradations and stylistic shifts to each image. Surprisingly, we uncover a visual-quality paradox: model, task, and even individual-instance performance can improve when images deviate from human-perceived fidelity. Off-the-shelf restoration pipelines fail to reconcile these idiosyncratic preferences. To close the gap, we introduce Visual-Quality Test-Time Tuning (VQ-TTT)-a lightweight adaptation module that: (1) inserts a learnable, low-rank kernel before the frozen vision encoder to modulate frequency content; and (2) fine-tunes only shallow vision-encoder layers via LoRA. VQ-TTT dynamically adjusts each input image in a single forward pass, aligning it with task-specific model preferences. Across the evaluated MLLMs and all datasets, VQ-TTT lifts significant average accuracy, with no external models, cached features, or extra training data. These findings redefine ``better'' visual inputs for MLLMs and highlight the need for adaptive, rather than universally ``clean'', imagery, in the new era of AI being the main data customer.
SAFEFLOW: A Principled Protocol for Trustworthy and Transactional Autonomous Agent Systems
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) have enabled powerful autonomous agents capable of complex reasoning and multi-modal tool use. Despite their growing capabilities, today's agent frameworks remain fragile, lacking principled mechanisms for secure information flow, reliability, and multi-agent coordination. In this work, we introduce SAFEFLOW, a new protocol-level framework for building trustworthy LLM/VLM-based agents. SAFEFLOW enforces fine-grained information flow control (IFC), precisely tracking provenance, integrity, and confidentiality of all the data exchanged between agents, tools, users, and environments. By constraining LLM reasoning to respect these security labels, SAFEFLOW prevents untrusted or adversarial inputs from contaminating high-integrity decisions. To ensure robustness in concurrent multi-agent settings, SAFEFLOW introduces transactional execution, conflict resolution, and secure scheduling over shared state, preserving global consistency across agents. We further introduce mechanisms, including write-ahead logging, rollback, and secure caches, that further enhance resilience against runtime errors and policy violations. To validate the performances, we built SAFEFLOWBENCH, a comprehensive benchmark suite designed to evaluate agent reliability under adversarial, noisy, and concurrent operational conditions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that agents built with SAFEFLOW maintain impressive task performance and security guarantees even in hostile environments, substantially outperforming state-of-the-art. Together, SAFEFLOW and SAFEFLOWBENCH lay the groundwork for principled, robust, and secure agent ecosystems, advancing the frontier of reliable autonomy.
Generative AI for Autonomous Driving: Frontiers and Opportunities
May 13, 2025Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) constitutes a transformative technological wave that reconfigures industries through its unparalleled capabilities for content creation, reasoning, planning, and multimodal understanding. This revolutionary force offers the most promising path yet toward solving one of engineering's grandest challenges: achieving reliable, fully autonomous driving, particularly the pursuit of Level 5 autonomy. This survey delivers a comprehensive and critical synthesis of the emerging role of GenAI across the autonomous driving stack. We begin by distilling the principles and trade-offs of modern generative modeling, encompassing VAEs, GANs, Diffusion Models, and Large Language Models (LLMs). We then map their frontier applications in image, LiDAR, trajectory, occupancy, video generation as well as LLM-guided reasoning and decision making. We categorize practical applications, such as synthetic data workflows, end-to-end driving strategies, high-fidelity digital twin systems, smart transportation networks, and cross-domain transfer to embodied AI. We identify key obstacles and possibilities such as comprehensive generalization across rare cases, evaluation and safety checks, budget-limited implementation, regulatory compliance, ethical concerns, and environmental effects, while proposing research plans across theoretical assurances, trust metrics, transport integration, and socio-technical influence. By unifying these threads, the survey provides a forward-looking reference for researchers, engineers, and policymakers navigating the convergence of generative AI and advanced autonomous mobility. An actively maintained repository of cited works is available at https://github.com/taco-group/GenAI4AD.
Multi-label classification for multi-temporal, multi-spatial coral reef condition monitoring using vision foundation model with adapter learning
Mar 29, 2025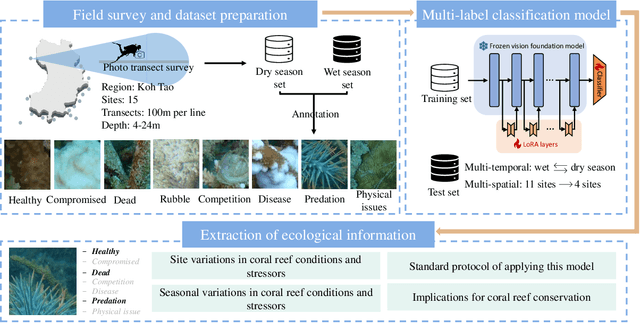
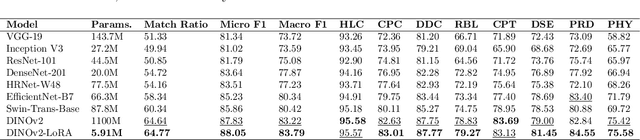
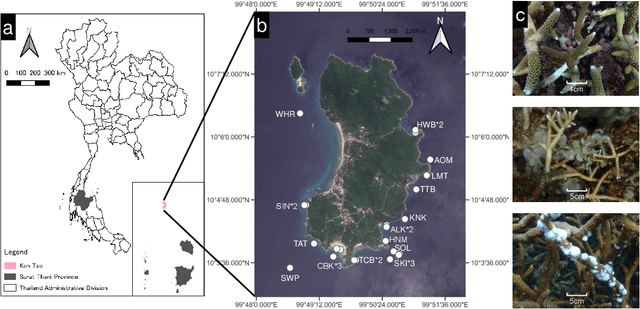
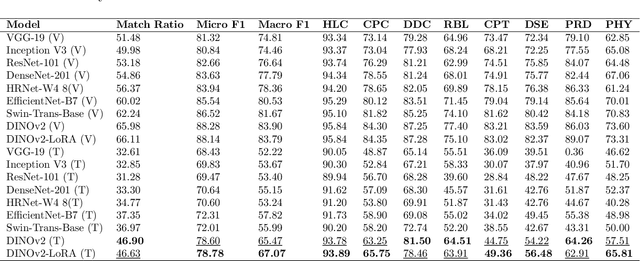
Abstract:Coral reef ecosystems provide essential ecosystem services, but face significant threats from climate change and human activities. Although advances in deep learning have enabled automatic classification of coral reef conditions, conventional deep models struggle to achieve high performance when processing complex underwater ecological images. Vision foundation models, known for their high accuracy and cross-domain generalizability, offer promising solutions. However, fine-tuning these models requires substantial computational resources and results in high carbon emissions. To address these challenges, adapter learning methods such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) have emerged as a solution. This study introduces an approach integrating the DINOv2 vision foundation model with the LoRA fine-tuning method. The approach leverages multi-temporal field images collected through underwater surveys at 15 dive sites at Koh Tao, Thailand, with all images labeled according to universal standards used in citizen science-based conservation programs. The experimental results demonstrate that the DINOv2-LoRA model achieved superior accuracy, with a match ratio of 64.77%, compared to 60.34% achieved by the best conventional model. Furthermore, incorporating LoRA reduced the trainable parameters from 1,100M to 5.91M. Transfer learning experiments conducted under different temporal and spatial settings highlight the exceptional generalizability of DINOv2-LoRA across different seasons and sites. This study is the first to explore the efficient adaptation of foundation models for multi-label classification of coral reef conditions under multi-temporal and multi-spatial settings. The proposed method advances the classification of coral reef conditions and provides a tool for monitoring, conserving, and managing coral reef ecosystems.
Re-Align: Aligning Vision Language Models via Retrieval-Augmented Direct Preference Optimization
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:The emergence of large Vision Language Models (VLMs) has broadened the scope and capabilities of single-modal Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating visual modalities, thereby unlocking transformative cross-modal applications in a variety of real-world scenarios. Despite their impressive performance, VLMs are prone to significant hallucinations, particularly in the form of cross-modal inconsistencies. Building on the success of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) in aligning LLMs, recent advancements have focused on applying direct preference optimization (DPO) on carefully curated datasets to mitigate these issues. Yet, such approaches typically introduce preference signals in a brute-force manner, neglecting the crucial role of visual information in the alignment process. In this paper, we introduce Re-Align, a novel alignment framework that leverages image retrieval to construct a dual-preference dataset, effectively incorporating both textual and visual preference signals. We further introduce rDPO, an extension of the standard direct preference optimization that incorporates an additional visual preference objective during fine-tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that Re-Align not only mitigates hallucinations more effectively than previous methods but also yields significant performance gains in general visual question-answering (VQA) tasks. Moreover, we show that Re-Align maintains robustness and scalability across a wide range of VLM sizes and architectures. This work represents a significant step forward in aligning multimodal LLMs, paving the way for more reliable and effective cross-modal applications. We release all the code in https://github.com/taco-group/Re-Align.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge