Oleg Serikov
SemSketches-2021: experimenting with the machine processing of the pilot semantic sketches corpus
May 23, 2025Abstract:The paper deals with elaborating different approaches to the machine processing of semantic sketches. It presents the pilot open corpus of semantic sketches. Different aspects of creating the sketches are discussed, as well as the tasks that the sketches can help to solve. Special attention is paid to the creation of the machine processing tools for the corpus. For this purpose, the SemSketches-2021 Shared Task was organized. The participants were given the anonymous sketches and a set of contexts containing the necessary predicates. During the Task, one had to assign the proper contexts to the corresponding sketches.
How to Correctly do Semantic Backpropagation on Language-based Agentic Systems
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:Language-based agentic systems have shown great promise in recent years, transitioning from solving small-scale research problems to being deployed in challenging real-world tasks. However, optimizing these systems often requires substantial manual labor. Recent studies have demonstrated that these systems can be represented as computational graphs, enabling automatic optimization. Despite these advancements, most current efforts in Graph-based Agentic System Optimization (GASO) fail to properly assign feedback to the system's components given feedback on the system's output. To address this challenge, we formalize the concept of semantic backpropagation with semantic gradients -- a generalization that aligns several key optimization techniques, including reverse-mode automatic differentiation and the more recent TextGrad by exploiting the relationship among nodes with a common successor. This serves as a method for computing directional information about how changes to each component of an agentic system might improve the system's output. To use these gradients, we propose a method called semantic gradient descent which enables us to solve GASO effectively. Our results on both BIG-Bench Hard and GSM8K show that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods for solving GASO problems. A detailed ablation study on the LIAR dataset demonstrates the parsimonious nature of our method. A full copy of our implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/HishamAlyahya/semantic_backprop
The Languini Kitchen: Enabling Language Modelling Research at Different Scales of Compute
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:The Languini Kitchen serves as both a research collective and codebase designed to empower researchers with limited computational resources to contribute meaningfully to the field of language modelling. We introduce an experimental protocol that enables model comparisons based on equivalent compute, measured in accelerator hours. The number of tokens on which a model is trained is defined by the model's throughput and the chosen compute class. Notably, this approach avoids constraints on critical hyperparameters which affect total parameters or floating-point operations. For evaluation, we pre-process an existing large, diverse, and high-quality dataset of books that surpasses existing academic benchmarks in quality, diversity, and document length. On it, we compare methods based on their empirical scaling trends which are estimated through experiments at various levels of compute. This work also provides two baseline models: a feed-forward model derived from the GPT-2 architecture and a recurrent model in the form of a novel LSTM with ten-fold throughput. While the GPT baseline achieves better perplexity throughout all our levels of compute, our LSTM baseline exhibits a predictable and more favourable scaling law. This is due to the improved throughput and the need for fewer training tokens to achieve the same decrease in test perplexity. Extrapolating the scaling laws leads of both models results in an intersection at roughly 50,000 accelerator hours. We hope this work can serve as the foundation for meaningful and reproducible language modelling research.
BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be able to perform new tasks based on a few demonstrations or natural language instructions. While these capabilities have led to widespread adoption, most LLMs are developed by resource-rich organizations and are frequently kept from the public. As a step towards democratizing this powerful technology, we present BLOOM, a 176B-parameter open-access language model designed and built thanks to a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. BLOOM is a decoder-only Transformer language model that was trained on the ROOTS corpus, a dataset comprising hundreds of sources in 46 natural and 13 programming languages (59 in total). We find that BLOOM achieves competitive performance on a wide variety of benchmarks, with stronger results after undergoing multitask prompted finetuning. To facilitate future research and applications using LLMs, we publicly release our models and code under the Responsible AI License.
Universal and Independent: Multilingual Probing Framework for Exhaustive Model Interpretation and Evaluation
Oct 24, 2022



Abstract:Linguistic analysis of language models is one of the ways to explain and describe their reasoning, weaknesses, and limitations. In the probing part of the model interpretability research, studies concern individual languages as well as individual linguistic structures. The question arises: are the detected regularities linguistically coherent, or on the contrary, do they dissonate at the typological scale? Moreover, the majority of studies address the inherent set of languages and linguistic structures, leaving the actual typological diversity knowledge out of scope. In this paper, we present and apply the GUI-assisted framework allowing us to easily probe a massive number of languages for all the morphosyntactic features present in the Universal Dependencies data. We show that reflecting the anglo-centric trend in NLP over the past years, most of the regularities revealed in the mBERT model are typical for the western-European languages. Our framework can be integrated with the existing probing toolboxes, model cards, and leaderboards, allowing practitioners to use and share their standard probing methods to interpret multilingual models. Thus we propose a toolkit to systematize the multilingual flaws in multilingual models, providing a reproducible experimental setup for 104 languages and 80 morphosyntactic features. https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/Probing_framework
Is neural language acquisition similar to natural? A chronological probing study
Jul 01, 2022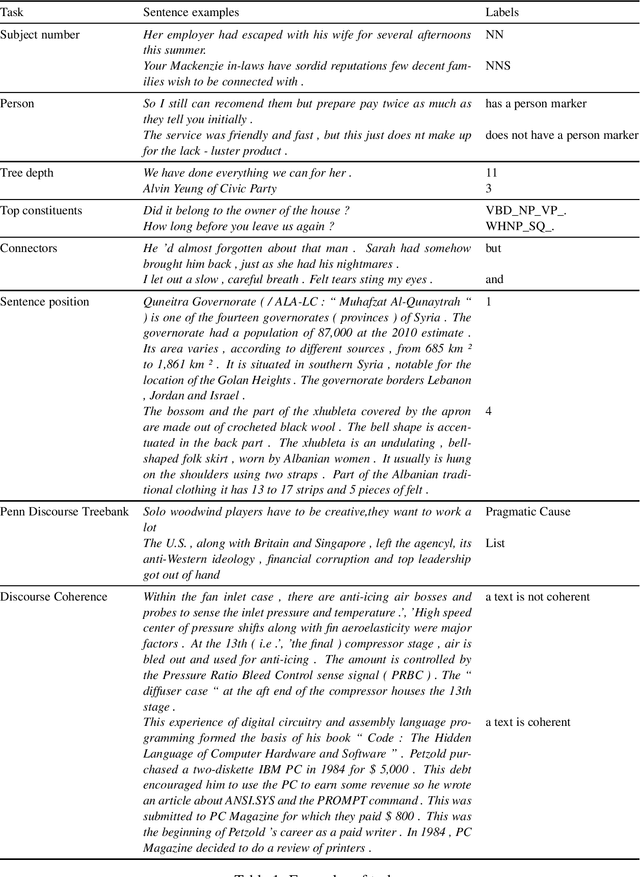
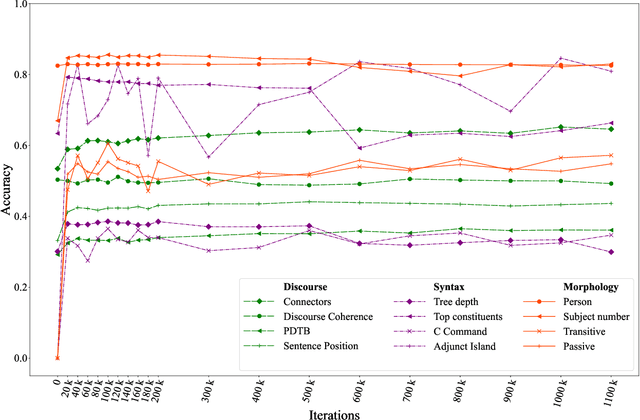

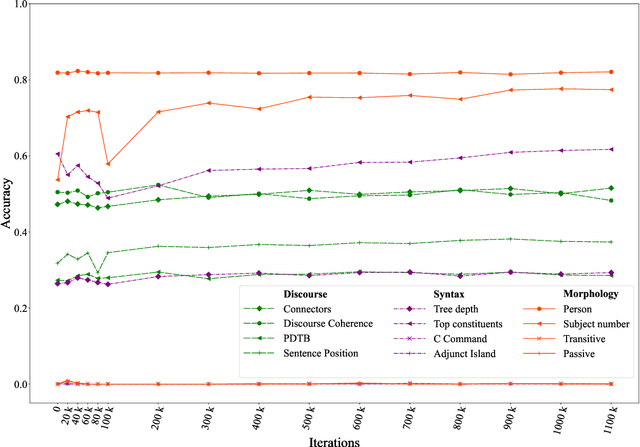
Abstract:The probing methodology allows one to obtain a partial representation of linguistic phenomena stored in the inner layers of the neural network, using external classifiers and statistical analysis. Pre-trained transformer-based language models are widely used both for natural language understanding (NLU) and natural language generation (NLG) tasks making them most commonly used for downstream applications. However, little analysis was carried out, whether the models were pre-trained enough or contained knowledge correlated with linguistic theory. We are presenting the chronological probing study of transformer English models such as MultiBERT and T5. We sequentially compare the information about the language learned by the models in the process of training on corpora. The results show that 1) linguistic information is acquired in the early stages of training 2) both language models demonstrate capabilities to capture various features from various levels of language, including morphology, syntax, and even discourse, while they also can inconsistently fail on tasks that are perceived as easy. We also introduce the open-source framework for chronological probing research, compatible with other transformer-based models. https://github.com/EkaterinaVoloshina/chronological_probing
Razmecheno: Named Entity Recognition from Digital Archive of Diaries "Prozhito"
Jan 24, 2022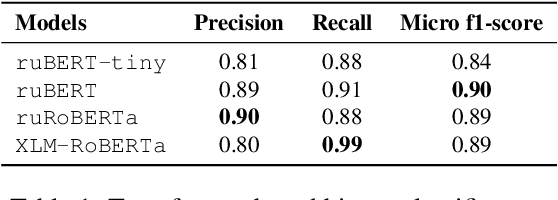

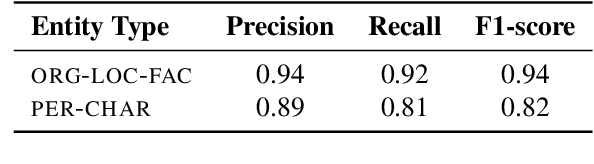
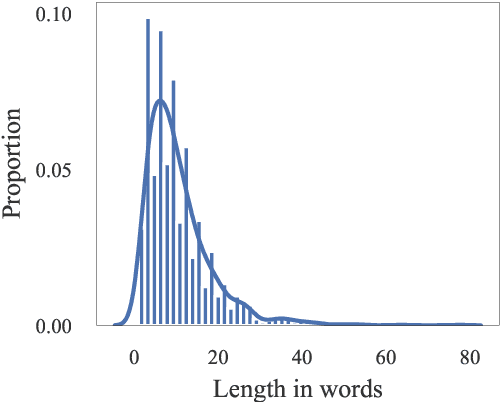
Abstract:The vast majority of existing datasets for Named Entity Recognition (NER) are built primarily on news, research papers and Wikipedia with a few exceptions, created from historical and literary texts. What is more, English is the main source for data for further labelling. This paper aims to fill in multiple gaps by creating a novel dataset "Razmecheno", gathered from the diary texts of the project "Prozhito" in Russian. Our dataset is of interest for multiple research lines: literary studies of diary texts, transfer learning from other domains, low-resource or cross-lingual named entity recognition. Razmecheno comprises 1331 sentences and 14119 tokens, sampled from diaries, written during the Perestroika. The annotation schema consists of five commonly used entity tags: person, characteristics, location, organisation, and facility. The labelling is carried out on the crowdsourcing platfrom Yandex.Toloka in two stages. First, workers selected sentences, which contain an entity of particular type. Second, they marked up entity spans. As a result 1113 entities were obtained. Empirical evaluation of Razmecheno is carried out with off-the-shelf NER tools and by fine-tuning pre-trained contextualized encoders. We release the annotated dataset for open access.
SIGTYP 2021 Shared Task: Robust Spoken Language Identification
Jun 07, 2021



Abstract:While language identification is a fundamental speech and language processing task, for many languages and language families it remains a challenging task. For many low-resource and endangered languages this is in part due to resource availability: where larger datasets exist, they may be single-speaker or have different domains than desired application scenarios, demanding a need for domain and speaker-invariant language identification systems. This year's shared task on robust spoken language identification sought to investigate just this scenario: systems were to be trained on largely single-speaker speech from one domain, but evaluated on data in other domains recorded from speakers under different recording circumstances, mimicking realistic low-resource scenarios. We see that domain and speaker mismatch proves very challenging for current methods which can perform above 95% accuracy in-domain, which domain adaptation can address to some degree, but that these conditions merit further investigation to make spoken language identification accessible in many scenarios.
Teaching a Massive Open Online Course on Natural Language Processing
May 04, 2021

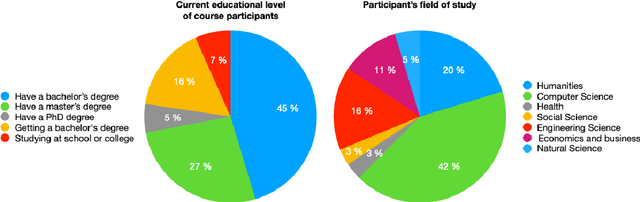
Abstract:This paper presents a new Massive Open Online Course on Natural Language Processing, targeted at non-English speaking students. The course lasts 12 weeks; every week consists of lectures, practical sessions, and quiz assignments. Three weeks out of 12 are followed by Kaggle-style coding assignments. Our course intends to serve multiple purposes: (i) familiarize students with the core concepts and methods in NLP, such as language modeling or word or sentence representations, (ii) show that recent advances, including pre-trained Transformer-based models, are built upon these concepts; (iii) introduce architectures for most demanded real-life applications, (iv) develop practical skills to process texts in multiple languages. The course was prepared and recorded during 2020, launched by the end of the year, and in early 2021 has received positive feedback.
Morph Call: Probing Morphosyntactic Content of Multilingual Transformers
May 04, 2021



Abstract:The outstanding performance of transformer-based language models on a great variety of NLP and NLU tasks has stimulated interest in exploring their inner workings. Recent research has focused primarily on higher-level and complex linguistic phenomena such as syntax, semantics, world knowledge, and common sense. The majority of the studies are anglocentric, and little remains known regarding other languages, precisely their morphosyntactic properties. To this end, our work presents Morph Call, a suite of 46 probing tasks for four Indo-European languages of different morphology: English, French, German and Russian. We propose a new type of probing task based on the detection of guided sentence perturbations. We use a combination of neuron-, layer- and representation-level introspection techniques to analyze the morphosyntactic content of four multilingual transformers, including their less explored distilled versions. Besides, we examine how fine-tuning for POS-tagging affects the model knowledge. The results show that fine-tuning can improve and decrease the probing performance and change how morphosyntactic knowledge is distributed across the model. The code and data are publicly available, and we hope to fill the gaps in the less studied aspect of transformers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge