Dylan Ashley
Agent-as-a-Judge: Evaluate Agents with Agents
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Contemporary evaluation techniques are inadequate for agentic systems. These approaches either focus exclusively on final outcomes -- ignoring the step-by-step nature of agentic systems, or require excessive manual labour. To address this, we introduce the Agent-as-a-Judge framework, wherein agentic systems are used to evaluate agentic systems. This is an organic extension of the LLM-as-a-Judge framework, incorporating agentic features that enable intermediate feedback for the entire task-solving process. We apply the Agent-as-a-Judge to the task of code generation. To overcome issues with existing benchmarks and provide a proof-of-concept testbed for Agent-as-a-Judge, we present DevAI, a new benchmark of 55 realistic automated AI development tasks. It includes rich manual annotations, like a total of 365 hierarchical user requirements. We benchmark three of the popular agentic systems using Agent-as-a-Judge and find it dramatically outperforms LLM-as-a-Judge and is as reliable as our human evaluation baseline. Altogether, we believe that Agent-as-a-Judge marks a concrete step forward for modern agentic systems -- by providing rich and reliable reward signals necessary for dynamic and scalable self-improvement.
The Languini Kitchen: Enabling Language Modelling Research at Different Scales of Compute
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:The Languini Kitchen serves as both a research collective and codebase designed to empower researchers with limited computational resources to contribute meaningfully to the field of language modelling. We introduce an experimental protocol that enables model comparisons based on equivalent compute, measured in accelerator hours. The number of tokens on which a model is trained is defined by the model's throughput and the chosen compute class. Notably, this approach avoids constraints on critical hyperparameters which affect total parameters or floating-point operations. For evaluation, we pre-process an existing large, diverse, and high-quality dataset of books that surpasses existing academic benchmarks in quality, diversity, and document length. On it, we compare methods based on their empirical scaling trends which are estimated through experiments at various levels of compute. This work also provides two baseline models: a feed-forward model derived from the GPT-2 architecture and a recurrent model in the form of a novel LSTM with ten-fold throughput. While the GPT baseline achieves better perplexity throughout all our levels of compute, our LSTM baseline exhibits a predictable and more favourable scaling law. This is due to the improved throughput and the need for fewer training tokens to achieve the same decrease in test perplexity. Extrapolating the scaling laws leads of both models results in an intersection at roughly 50,000 accelerator hours. We hope this work can serve as the foundation for meaningful and reproducible language modelling research.
Back to Square One: Superhuman Performance in Chutes and Ladders Through Deep Neural Networks and Tree Search
Apr 01, 2021
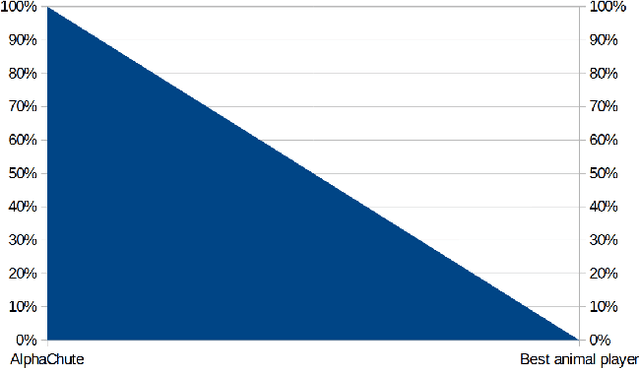
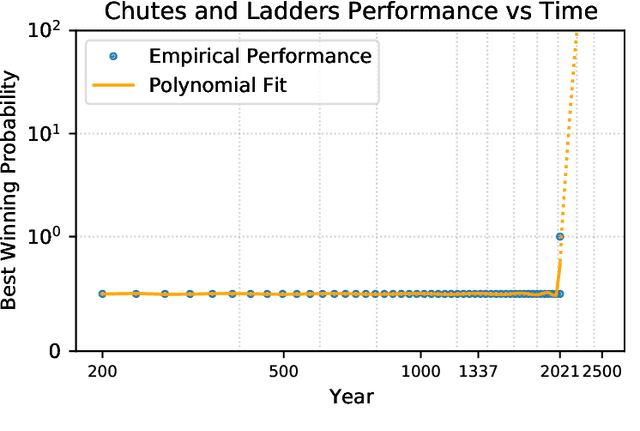
Abstract:We present AlphaChute: a state-of-the-art algorithm that achieves superhuman performance in the ancient game of Chutes and Ladders. We prove that our algorithm converges to the Nash equilibrium in constant time, and therefore is -- to the best of our knowledge -- the first such formal solution to this game. Surprisingly, despite all this, our implementation of AlphaChute remains relatively straightforward due to domain-specific adaptations. We provide the source code for AlphaChute here in our Appendix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge