Vitaly Protasov
BRIGHTER: BRIdging the Gap in Human-Annotated Textual Emotion Recognition Datasets for 28 Languages
Feb 17, 2025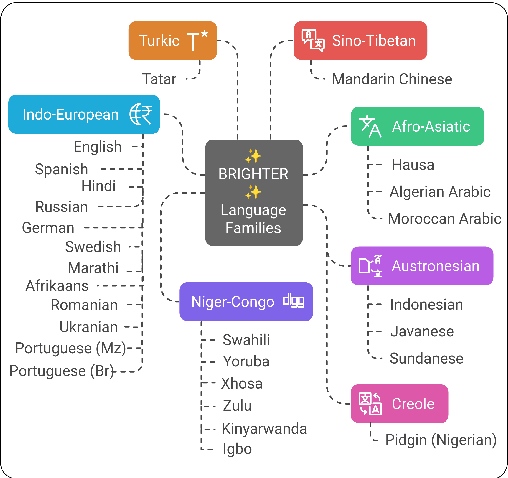
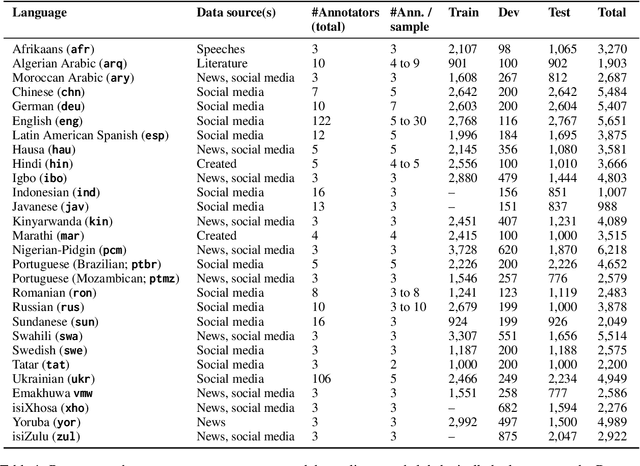
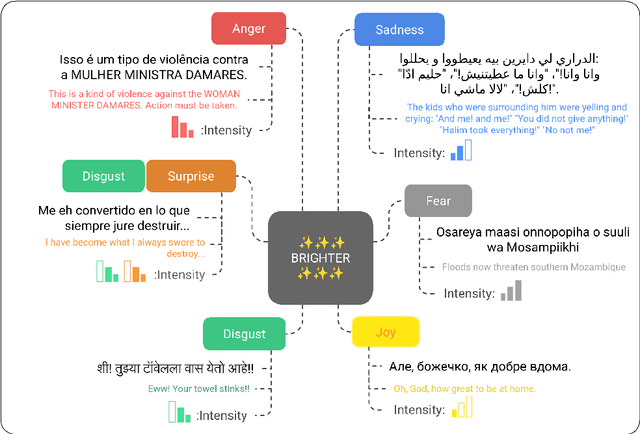
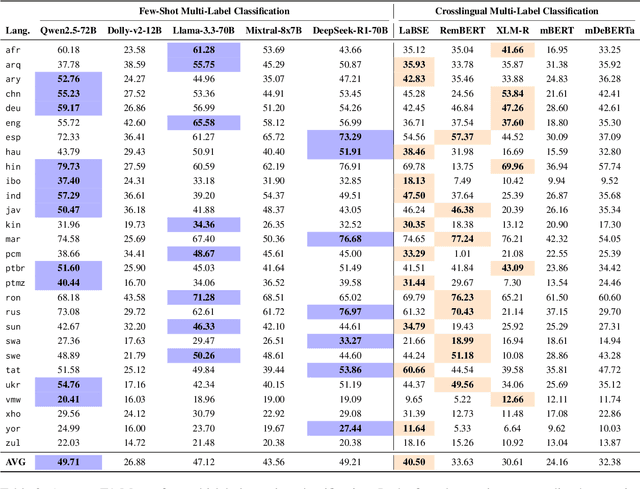
Abstract:People worldwide use language in subtle and complex ways to express emotions. While emotion recognition -- an umbrella term for several NLP tasks -- significantly impacts different applications in NLP and other fields, most work in the area is focused on high-resource languages. Therefore, this has led to major disparities in research and proposed solutions, especially for low-resource languages that suffer from the lack of high-quality datasets. In this paper, we present BRIGHTER-- a collection of multilabeled emotion-annotated datasets in 28 different languages. BRIGHTER covers predominantly low-resource languages from Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, with instances from various domains annotated by fluent speakers. We describe the data collection and annotation processes and the challenges of building these datasets. Then, we report different experimental results for monolingual and crosslingual multi-label emotion identification, as well as intensity-level emotion recognition. We investigate results with and without using LLMs and analyse the large variability in performance across languages and text domains. We show that BRIGHTER datasets are a step towards bridging the gap in text-based emotion recognition and discuss their impact and utility.
BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be able to perform new tasks based on a few demonstrations or natural language instructions. While these capabilities have led to widespread adoption, most LLMs are developed by resource-rich organizations and are frequently kept from the public. As a step towards democratizing this powerful technology, we present BLOOM, a 176B-parameter open-access language model designed and built thanks to a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. BLOOM is a decoder-only Transformer language model that was trained on the ROOTS corpus, a dataset comprising hundreds of sources in 46 natural and 13 programming languages (59 in total). We find that BLOOM achieves competitive performance on a wide variety of benchmarks, with stronger results after undergoing multitask prompted finetuning. To facilitate future research and applications using LLMs, we publicly release our models and code under the Responsible AI License.
Universal and Independent: Multilingual Probing Framework for Exhaustive Model Interpretation and Evaluation
Oct 24, 2022



Abstract:Linguistic analysis of language models is one of the ways to explain and describe their reasoning, weaknesses, and limitations. In the probing part of the model interpretability research, studies concern individual languages as well as individual linguistic structures. The question arises: are the detected regularities linguistically coherent, or on the contrary, do they dissonate at the typological scale? Moreover, the majority of studies address the inherent set of languages and linguistic structures, leaving the actual typological diversity knowledge out of scope. In this paper, we present and apply the GUI-assisted framework allowing us to easily probe a massive number of languages for all the morphosyntactic features present in the Universal Dependencies data. We show that reflecting the anglo-centric trend in NLP over the past years, most of the regularities revealed in the mBERT model are typical for the western-European languages. Our framework can be integrated with the existing probing toolboxes, model cards, and leaderboards, allowing practitioners to use and share their standard probing methods to interpret multilingual models. Thus we propose a toolkit to systematize the multilingual flaws in multilingual models, providing a reproducible experimental setup for 104 languages and 80 morphosyntactic features. https://github.com/AIRI-Institute/Probing_framework
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge