Mohan Zhang
Advancing MoE Efficiency: A Collaboration-Constrained Routing (C2R) Strategy for Better Expert Parallelism Design
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) has successfully scaled up models while maintaining nearly constant computing costs. By employing a gating network to route input tokens, it selectively activates a subset of expert networks to process the corresponding token embeddings. However, in practice, the efficiency of MoE is challenging to achieve due to two key reasons: imbalanced expert activation, which leads to substantial idle time during model or expert parallelism, and insufficient capacity utilization; massive communication overhead, induced by numerous expert routing combinations in expert parallelism at the system level. Previous works typically formulate it as the load imbalance issue characterized by the gating network favoring certain experts over others or attribute it to static execution which fails to adapt to the dynamic expert workload at runtime. In this paper, we exploit it from a brand new perspective, a higher-order view and analysis of MoE routing policies: expert collaboration and specialization where some experts tend to activate broadly with others (collaborative), while others are more likely to activate only with a specific subset of experts (specialized). Our experiments reveal that most experts tend to be overly collaborative, leading to increased communication overhead from repeatedly sending tokens to different accelerators. To this end, we propose a novel collaboration-constrained routing (C2R) strategy to encourage more specialized expert groups, as well as to improve expert utilization, and present an efficient implementation of MoE that further leverages expert specialization. We achieve an average performance improvement of 0.51% and 0.33% on LLaMA-MoE and Qwen-MoE respectively across ten downstream NLP benchmarks, and reduce the all2all communication costs between GPUs, bringing an extra 20%-30% total running time savings on top of the existing SoTA, i.e. MegaBlocks.
Symbiotic Cooperation for Web Agents: Harnessing Complementary Strengths of Large and Small LLMs
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Web browsing agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have shown tremendous potential in automating complex web-based tasks. Existing approaches typically rely on large LLMs (e.g., GPT-4o) to explore web environments and generate trajectory data, which is then used either for demonstration retrieval (for large LLMs) or to distill small LLMs (e.g., Llama3) in a process that remains decoupled from the exploration. In this paper, we propose AgentSymbiotic, an iterative framework that couples data synthesis with task-performance, yielding a "symbiotic improvement" for both large and small LLMs. Our study uncovers a complementary dynamic between LLM types: while large LLMs excel at generating high-quality trajectories for distillation, the distilled small LLMs-owing to their distinct reasoning capabilities-often choose actions that diverge from those of their larger counterparts. This divergence drives the exploration of novel trajectories, thereby enriching the synthesized data. However, we also observe that the performance of small LLMs becomes a bottleneck in this iterative enhancement process. To address this, we propose two innovations in LLM distillation: a speculative data synthesis strategy that mitigates off-policy bias, and a multi-task learning approach designed to boost the reasoning capabilities of the student LLM. Furthermore, we introduce a Hybrid Mode for Privacy Preservation to address user privacy concerns. Evaluated on the WEBARENA benchmark, AgentSymbiotic achieves SOTA performance with both LLM types. Our best Large LLM agent reaches 52%, surpassing the previous best of 45%, while our 8B distilled model demonstrates a competitive 49%, exceeding the prior best of 28%. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Continually Evolved Multimodal Foundation Models for Cancer Prognosis
Jan 30, 2025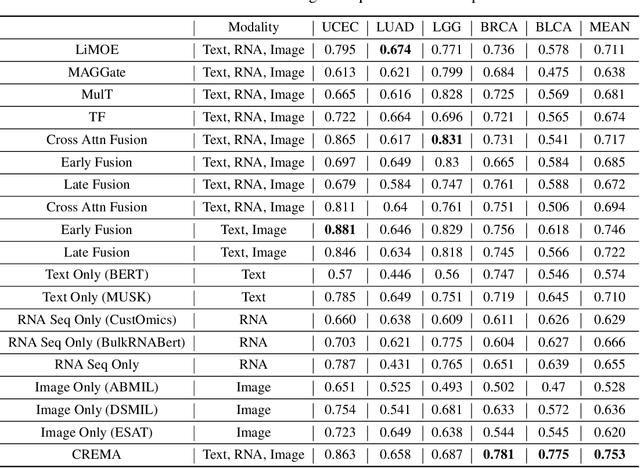
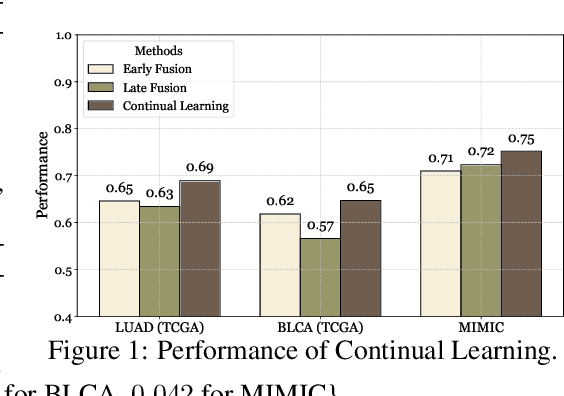
Abstract:Cancer prognosis is a critical task that involves predicting patient outcomes and survival rates. To enhance prediction accuracy, previous studies have integrated diverse data modalities, such as clinical notes, medical images, and genomic data, leveraging their complementary information. However, existing approaches face two major limitations. First, they struggle to incorporate newly arrived data with varying distributions into training, such as patient records from different hospitals, thus rendering sub-optimal generalizability and limited utility in real-world applications. Second, most multimodal integration methods rely on simplistic concatenation or task-specific pipelines, which fail to capture the complex interdependencies across modalities. To address these, we propose a continually evolving multi-modal foundation model. Extensive experiments on the TCGA dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, highlighting its potential to advance cancer prognosis by enabling robust and adaptive multimodal integration.
SMPL: Simulated Industrial Manufacturing and Process Control Learning Environments
Jun 17, 2022
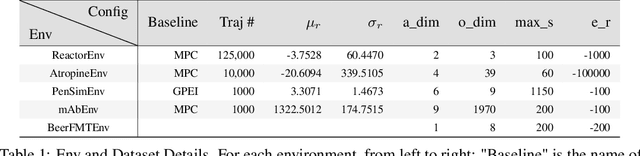
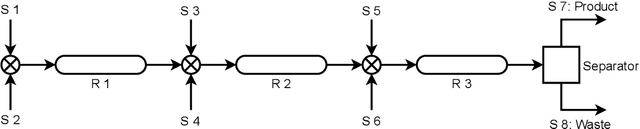

Abstract:Traditional biological and pharmaceutical manufacturing plants are controlled by human workers or pre-defined thresholds. Modernized factories have advanced process control algorithms such as model predictive control (MPC). However, there is little exploration of applying deep reinforcement learning to control manufacturing plants. One of the reasons is the lack of high fidelity simulations and standard APIs for benchmarking. To bridge this gap, we develop an easy-to-use library that includes five high-fidelity simulation environments: BeerFMTEnv, ReactorEnv, AtropineEnv, PenSimEnv and mAbEnv, which cover a wide range of manufacturing processes. We build these environments on published dynamics models. Furthermore, we benchmark online and offline, model-based and model-free reinforcement learning algorithms for comparisons of follow-up research.
To Paraphrase or Not To Paraphrase: User-Controllable Selective Paraphrase Generation
Aug 21, 2020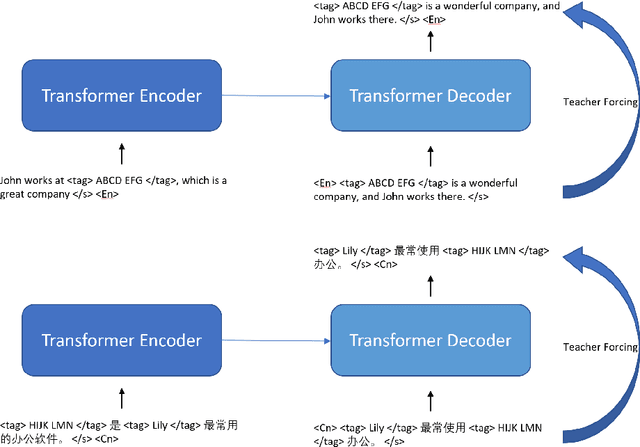
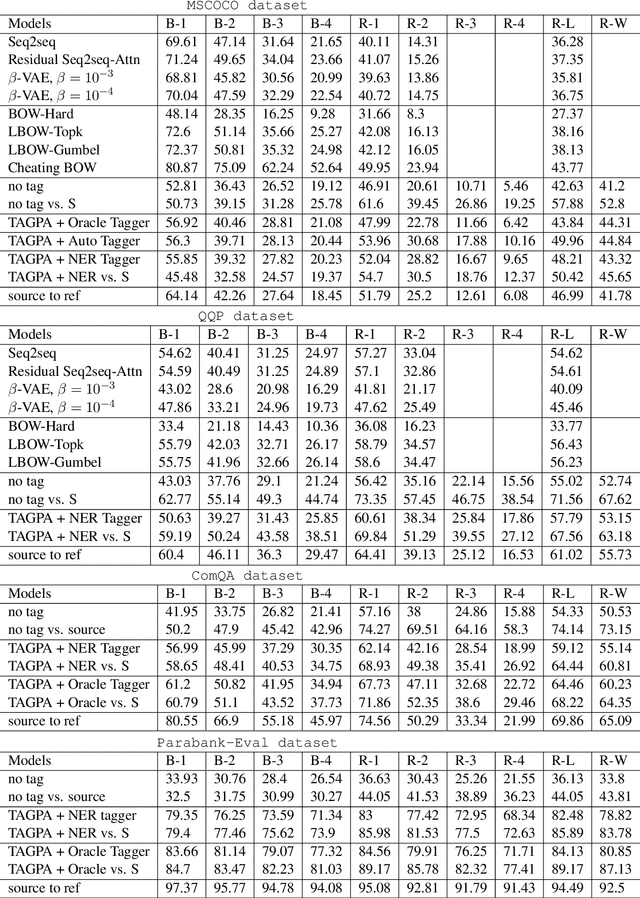
Abstract:In this article, we propose a paraphrase generation technique to keep the key phrases in source sentences during paraphrasing. We also develop a model called TAGPA with such technique, which has multiple pre-configured or trainable key phrase detector and a paraphrase generator. The paraphrase generator aims to keep the key phrases and increase the diversity of the paraphrased sentences. The key phrases can be entities provided by our user, like company names, people's names, domain-specific terminologies, etc., or can be learned from a given dataset.
Latent Dirichlet Allocation with Residual Convolutional Neural Network Applied in Evaluating Credibility of Chinese Listed Companies
Nov 24, 2018

Abstract:This project demonstrated a methodology to estimating cooperate credibility with a Natural Language Processing approach. As cooperate transparency impacts both the credibility and possible future earnings of the firm, it is an important factor to be considered by banks and investors on risk assessments of listed firms. This approach of estimating cooperate credibility can bypass human bias and inconsistency in the risk assessment, the use of large quantitative data and neural network models provides more accurate estimation in a more efficient manner compare to manual assessment. At the beginning, the model will employs Latent Dirichlet Allocation and THU Open Chinese Lexicon from Tsinghua University to classify topics in articles which are potentially related to corporate credibility. Then with the keywords related to each topics, we trained a residual convolutional neural network with data labeled according to surveys of fund manager and accountant's opinion on corporate credibility. After the training, we run the model with preprocessed news reports regarding to all of the 3065 listed companies, the model is supposed to give back companies ranking based on the level of their transparency.
Representation Learning Models for Entity Search
Jan 15, 2017



Abstract:We focus on the problem of learning distributed representations for entity search queries, named entities, and their short descriptions. With our representation learning models, the entity search query, named entity and description can be represented as low-dimensional vectors. Our goal is to develop a simple but effective model that can make the distributed representations of query related entities similar to the query in the vector space. Hence, we propose three kinds of learning strategies, and the difference between them mainly lies in how to deal with the relationship between an entity and its description. We analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each learning strategy and validate our methods on public datasets which contain four kinds of named entities, i.e., movies, TV shows, restaurants and celebrities. The experimental results indicate that our proposed methods can adapt to different types of entity search queries, and outperform the current state-of-the-art methods based on keyword matching and vanilla word2vec models. Besides, the proposed methods can be trained fast and be easily extended to other similar tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge