Xiaozhou Wang
SMPL: Simulated Industrial Manufacturing and Process Control Learning Environments
Jun 17, 2022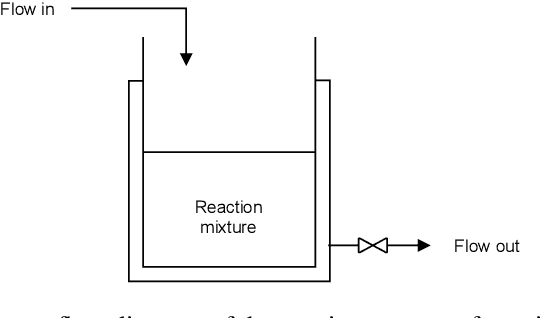
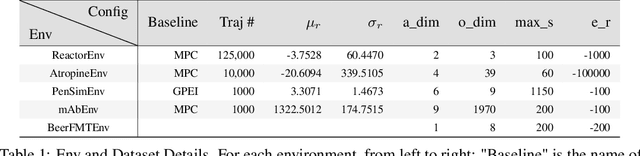
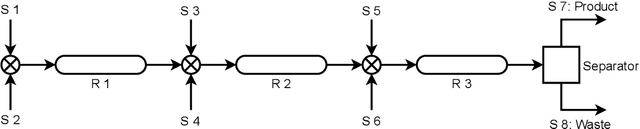

Abstract:Traditional biological and pharmaceutical manufacturing plants are controlled by human workers or pre-defined thresholds. Modernized factories have advanced process control algorithms such as model predictive control (MPC). However, there is little exploration of applying deep reinforcement learning to control manufacturing plants. One of the reasons is the lack of high fidelity simulations and standard APIs for benchmarking. To bridge this gap, we develop an easy-to-use library that includes five high-fidelity simulation environments: BeerFMTEnv, ReactorEnv, AtropineEnv, PenSimEnv and mAbEnv, which cover a wide range of manufacturing processes. We build these environments on published dynamics models. Furthermore, we benchmark online and offline, model-based and model-free reinforcement learning algorithms for comparisons of follow-up research.
Distributed Inference for Linear Support Vector Machine
Nov 29, 2018



Abstract:The growing size of modern data brings many new challenges to existing statistical inference methodologies and theories, and calls for the development of distributed inferential approaches. This paper studies distributed inference for linear support vector machine (SVM) for the binary classification task. Despite a vast literature on SVM, much less is known about the inferential properties of SVM, especially in a distributed setting. In this paper, we propose a multi-round distributed linear-type (MDL) estimator for conducting inference for linear SVM. The proposed estimator is computationally efficient. In particular, it only requires an initial SVM estimator and then successively refines the estimator by solving simple weighted least squares problem. Theoretically, we establish the Bahadur representation of the estimator. Based on the representation, the asymptotic normality is further derived, which shows that the MDL estimator achieves the optimal statistical efficiency, i.e., the same efficiency as the classical linear SVM applying to the entire dataset in a single machine setup. Moreover, our asymptotic result avoids the condition on the number of machines or data batches, which is commonly assumed in distributed estimation literature, and allows the case of diverging dimension. We provide simulation studies to demonstrate the performance of the proposed MDL estimator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge