Weidong Liu
Robust Variational Bayes by Min-Max Median Aggregation
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:We propose a robust and scalable variational Bayes (VB) framework designed to effectively handle contamination and outliers in dataset. Our approach partitions the data into $m$ disjoint subsets and formulates a joint optimization problem based on robust aggregation principles. A key insight is that the full posterior distribution is equivalent to the minimizer of the mean Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence from the $m$-powered local posterior distributions. To enhance robustness, we replace the mean KL divergence with a min-max median formulation. The min-max formulation not only ensures consistency between the KL minimizer and the Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO) maximizer but also facilitates the establishment of improved statistical rates for the mean of variational posterior. We observe a notable discrepancy in the $m$-powered marginal log likelihood function contingent on the presence of local latent variables. To address this, we treat these two scenarios separately to guarantee the consistency of the aggregated variational posterior. Specifically, when local latent variables are present, we introduce an aggregate-and-rescale strategy. Theoretically, we provide a non-asymptotic analysis of our proposed posterior, incorporating a refined analysis of Bernstein-von Mises (BvM) theorem to accommodate a diverging number of subsets $m$. Our findings indicate that the two-stage approach yields a smaller approximation error compared to directly aggregating the $m$-powered local posteriors. Furthermore, we establish a nearly optimal statistical rate for the mean of the proposed posterior, advancing existing theories related to min-max median estimators. The efficacy of our method is demonstrated through extensive simulation studies.
A Bias-Correction Decentralized Stochastic Gradient Algorithm with Momentum Acceleration
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Distributed stochastic optimization algorithms can handle large-scale data simultaneously and accelerate model training. However, the sparsity of distributed networks and the heterogeneity of data limit these advantages. This paper proposes a momentum-accelerated distributed stochastic gradient algorithm, referred to as Exact-Diffusion with Momentum (EDM), which can correct the bias caused by data heterogeneity and introduces the momentum method commonly used in deep learning to accelerate the convergence of the algorithm. We theoretically demonstrate that this algorithm converges to the neighborhood of the optimum sub-linearly irrelevant to data heterogeneity when applied to non-convex objective functions and linearly under the Polyak-{\L}ojasiewicz condition (a weaker assumption than $\mu$-strongly convexity). Finally, we evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm by simulation, comparing it with a range of existing decentralized optimization algorithms to demonstrate its effectiveness in addressing data heterogeneity and network sparsity.
A Short Review for Ontology Learning from Text: Stride from Shallow Learning, Deep Learning to Large Language Models Trend
Apr 23, 2024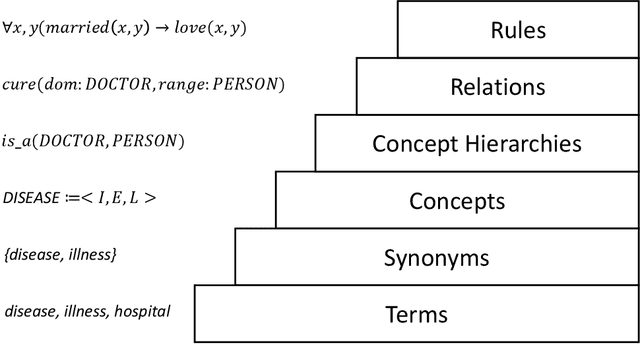
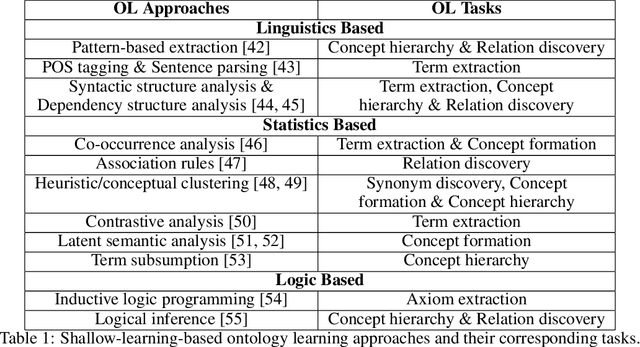
Abstract:Ontologies provide formal representation of knowledge shared within Semantic Web applications and Ontology learning from text involves the construction of ontologies from a given corpus of text. In the past years, ontology learning has traversed through shallow learning and deep learning methodologies, each offering distinct advantages and limitations in the quest for knowledge extraction and representation. A new trend of these approaches is relying on large language models to enhance ontology learning. This paper gives a review in approaches and challenges of ontology learning. It analyzes the methodologies and limitations of shallow-learning-based and deep-learning-based techniques for ontology learning, and provides comprehensive knowledge for the frontier work of using large language models to enhance ontology learning. In addition, it proposes several noteworthy future directions for further exploration into the integration of large language models with ontology learning tasks.
OneBit: Towards Extremely Low-bit Large Language Models
Feb 17, 2024Abstract:Model quantification uses low bit-width values to represent the weight matrices of models, which is a promising approach to reduce both storage and computational overheads of deploying highly anticipated LLMs. However, existing quantization methods suffer severe performance degradation when the bit-width is extremely reduced, and thus focus on utilizing 4-bit or 8-bit values to quantize models. This paper boldly quantizes the weight matrices of LLMs to 1-bit, paving the way for the extremely low bit-width deployment of LLMs. For this target, we introduce a 1-bit quantization-aware training (QAT) framework named OneBit, including a novel 1-bit parameter representation method to better quantize LLMs as well as an effective parameter initialization method based on matrix decomposition to improve the convergence speed of the QAT framework. Sufficient experimental results indicate that OneBit achieves good performance (at least 83% of the non-quantized performance) with robust training processes when only using 1-bit weight matrices.
Efficient Sparse Least Absolute Deviation Regression with Differential Privacy
Jan 02, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, privacy-preserving machine learning algorithms have attracted increasing attention because of their important applications in many scientific fields. However, in the literature, most privacy-preserving algorithms demand learning objectives to be strongly convex and Lipschitz smooth, which thus cannot cover a wide class of robust loss functions (e.g., quantile/least absolute loss). In this work, we aim to develop a fast privacy-preserving learning solution for a sparse robust regression problem. Our learning loss consists of a robust least absolute loss and an $\ell_1$ sparse penalty term. To fast solve the non-smooth loss under a given privacy budget, we develop a Fast Robust And Privacy-Preserving Estimation (FRAPPE) algorithm for least absolute deviation regression. Our algorithm achieves a fast estimation by reformulating the sparse LAD problem as a penalized least square estimation problem and adopts a three-stage noise injection to guarantee the $(\epsilon,\delta)$-differential privacy. We show that our algorithm can achieve better privacy and statistical accuracy trade-off compared with the state-of-the-art privacy-preserving regression algorithms. In the end, we conduct experiments to verify the efficiency of our proposed FRAPPE algorithm.
Vision-language Assisted Attribute Learning
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:Attribute labeling at large scale is typically incomplete and partial, posing significant challenges to model optimization. Existing attribute learning methods often treat the missing labels as negative or simply ignore them all during training, either of which could hamper the model performance to a great extent. To overcome these limitations, in this paper we leverage the available vision-language knowledge to explicitly disclose the missing labels for enhancing model learning. Given an image, we predict the likelihood of each missing attribute label assisted by an off-the-shelf vision-language model, and randomly select to ignore those with high scores in training. Our strategy strikes a good balance between fully ignoring and negatifying the missing labels, as these high scores are found to be informative on revealing label ambiguity. Extensive experiments show that our proposed vision-language assisted loss can achieve state-of-the-art performance on the newly cleaned VAW dataset. Qualitative evaluation demonstrates the ability of the proposed method in predicting more complete attributes.
Online Estimation and Inference for Robust Policy Evaluation in Reinforcement Learning
Oct 04, 2023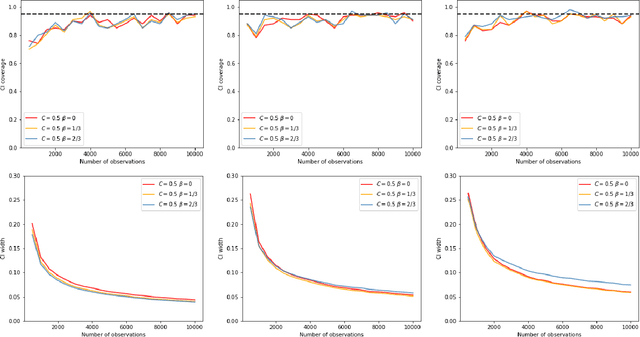
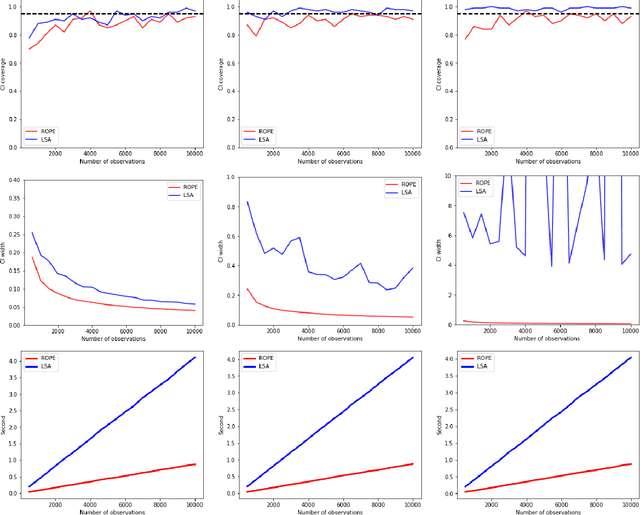
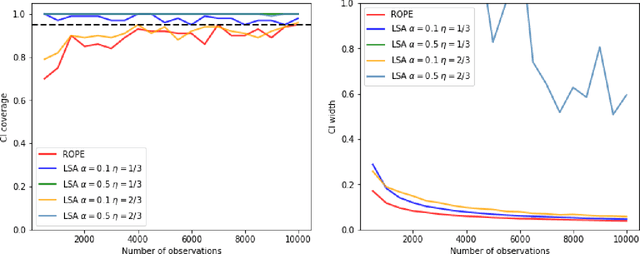
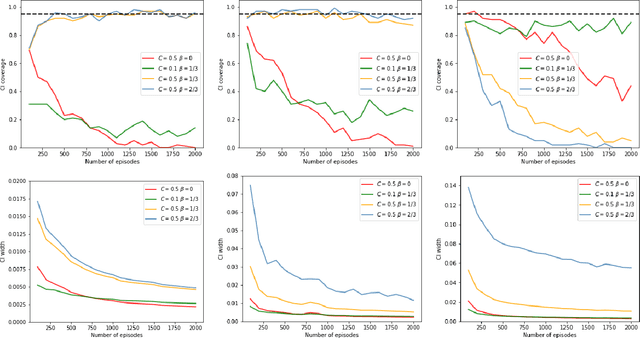
Abstract:Recently, reinforcement learning has gained prominence in modern statistics, with policy evaluation being a key component. Unlike traditional machine learning literature on this topic, our work places emphasis on statistical inference for the parameter estimates computed using reinforcement learning algorithms. While most existing analyses assume random rewards to follow standard distributions, limiting their applicability, we embrace the concept of robust statistics in reinforcement learning by simultaneously addressing issues of outlier contamination and heavy-tailed rewards within a unified framework. In this paper, we develop an online robust policy evaluation procedure, and establish the limiting distribution of our estimator, based on its Bahadur representation. Furthermore, we develop a fully-online procedure to efficiently conduct statistical inference based on the asymptotic distribution. This paper bridges the gap between robust statistics and statistical inference in reinforcement learning, offering a more versatile and reliable approach to policy evaluation. Finally, we validate the efficacy of our algorithm through numerical experiments conducted in real-world reinforcement learning experiments.
Exploring Large Language Models for Communication Games: An Empirical Study on Werewolf
Sep 09, 2023Abstract:Communication games, which we refer to as incomplete information games that heavily depend on natural language communication, hold significant research value in fields such as economics, social science, and artificial intelligence. In this work, we explore the problem of how to engage large language models (LLMs) in communication games, and in response, propose a tuning-free framework. Our approach keeps LLMs frozen, and relies on the retrieval and reflection on past communications and experiences for improvement. An empirical study on the representative and widely-studied communication game, ``Werewolf'', demonstrates that our framework can effectively play Werewolf game without tuning the parameters of the LLMs. More importantly, strategic behaviors begin to emerge in our experiments, suggesting that it will be a fruitful journey to engage LLMs in communication games and associated domains.
Pluggable Neural Machine Translation Models via Memory-augmented Adapters
Jul 12, 2023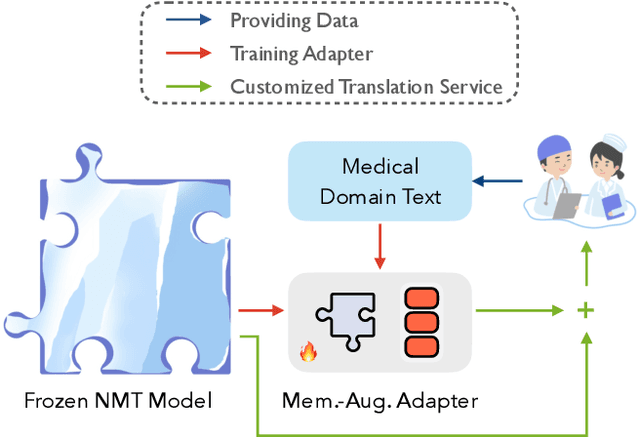
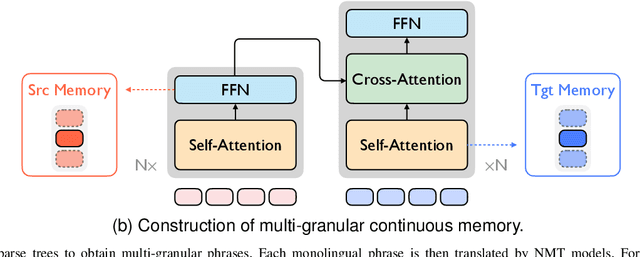
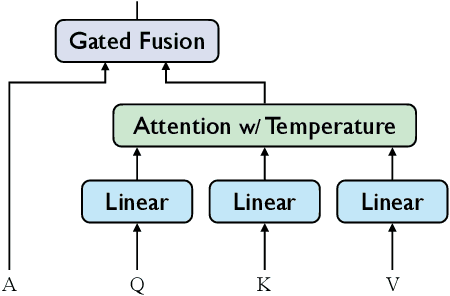
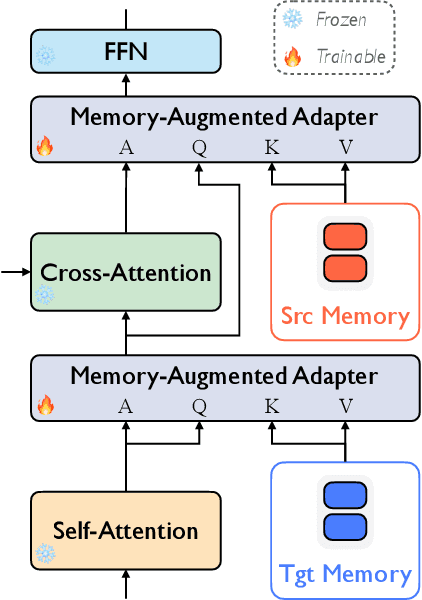
Abstract:Although neural machine translation (NMT) models perform well in the general domain, it remains rather challenging to control their generation behavior to satisfy the requirement of different users. Given the expensive training cost and the data scarcity challenge of learning a new model from scratch for each user requirement, we propose a memory-augmented adapter to steer pretrained NMT models in a pluggable manner. Specifically, we construct a multi-granular memory based on the user-provided text samples and propose a new adapter architecture to combine the model representations and the retrieved results. We also propose a training strategy using memory dropout to reduce spurious dependencies between the NMT model and the memory. We validate our approach on both style- and domain-specific experiments and the results indicate that our method can outperform several representative pluggable baselines.
Distributed Semi-Supervised Sparse Statistical Inference
Jun 17, 2023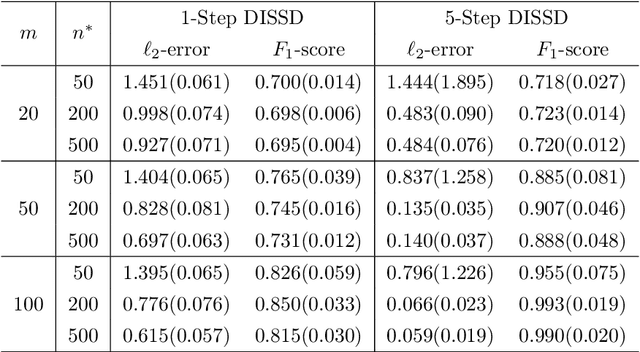
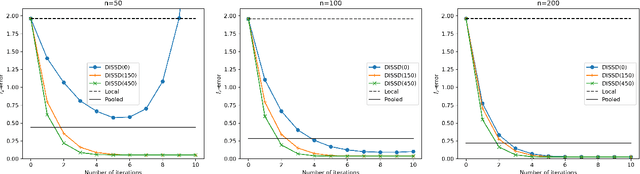
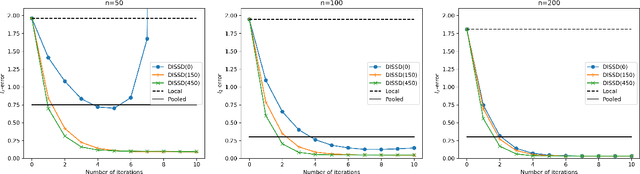
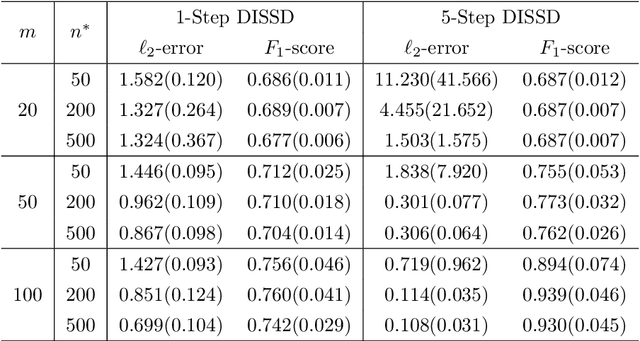
Abstract:This paper is devoted to studying the semi-supervised sparse statistical inference in a distributed setup. An efficient multi-round distributed debiased estimator, which integrates both labeled and unlabelled data, is developed. We will show that the additional unlabeled data helps to improve the statistical rate of each round of iteration. Our approach offers tailored debiasing methods for $M$-estimation and generalized linear model according to the specific form of the loss function. Our method also applies to a non-smooth loss like absolute deviation loss. Furthermore, our algorithm is computationally efficient since it requires only one estimation of a high-dimensional inverse covariance matrix. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method by presenting simulation studies and real data applications that highlight the benefits of incorporating unlabeled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge