Minjie Cai
Unit-Based Agent for Semi-Cascaded Full-Duplex Dialogue Systems
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Full-duplex voice interaction is crucial for natural human computer interaction. We present a framework that decomposes complex dialogue into minimal conversational units, enabling the system to process each unit independently and predict when to transit to the next. This framework is instantiated as a semi-cascaded full-duplex dialogue system built around a multimodal large language model, supported by auxiliary modules such as voice activity detection (VAD) and text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis. The resulting system operates in a train-free, plug-and-play manner. Experiments on the HumDial dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework, which ranks second among all teams on the test set of the Human-like Spoken Dialogue Systems Challenge (Track 2: Full-Duplex Interaction). Code is available at the GitHub repository https://github.com/yu-haoyuan/fd-badcat.
SiMHand: Mining Similar Hands for Large-Scale 3D Hand Pose Pre-training
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:We present a framework for pre-training of 3D hand pose estimation from in-the-wild hand images sharing with similar hand characteristics, dubbed SimHand. Pre-training with large-scale images achieves promising results in various tasks, but prior methods for 3D hand pose pre-training have not fully utilized the potential of diverse hand images accessible from in-the-wild videos. To facilitate scalable pre-training, we first prepare an extensive pool of hand images from in-the-wild videos and design our pre-training method with contrastive learning. Specifically, we collect over 2.0M hand images from recent human-centric videos, such as 100DOH and Ego4D. To extract discriminative information from these images, we focus on the similarity of hands: pairs of non-identical samples with similar hand poses. We then propose a novel contrastive learning method that embeds similar hand pairs closer in the feature space. Our method not only learns from similar samples but also adaptively weights the contrastive learning loss based on inter-sample distance, leading to additional performance gains. Our experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms conventional contrastive learning approaches that produce positive pairs sorely from a single image with data augmentation. We achieve significant improvements over the state-of-the-art method (PeCLR) in various datasets, with gains of 15% on FreiHand, 10% on DexYCB, and 4% on AssemblyHands. Our code is available at https://github.com/ut-vision/SiMHand.
EPIC-KITCHENS-100 Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Challenge for Action Recognition 2022: Team HNU-FPV Technical Report
Jul 07, 2022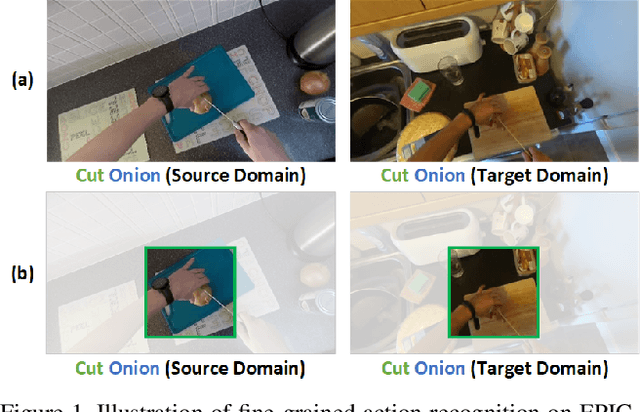
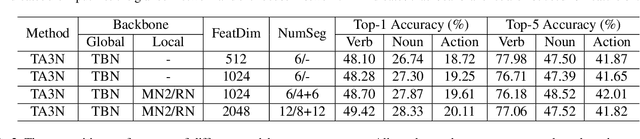
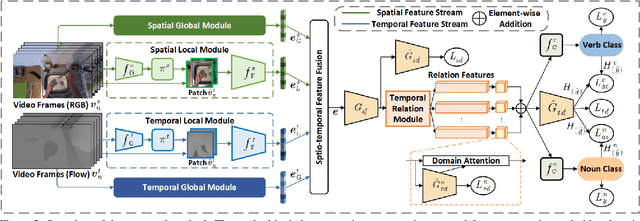
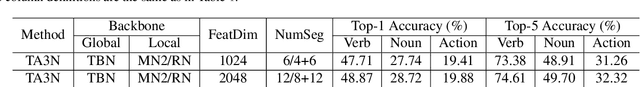
Abstract:In this report, we present the technical details of our submission to the 2022 EPIC-Kitchens Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) Challenge. Existing UDA methods align the global features extracted from the whole video clips across the source and target domains but suffer from the spatial redundancy of feature matching in video recognition. Motivated by the observation that in most cases a small image region in each video frame can be informative enough for the action recognition task, we propose to exploit informative image regions to perform efficient domain alignment. Specifically, we first use lightweight CNNs to extract the global information of the input two-stream video frames and select the informative image patches by a differentiable interpolation-based selection strategy. Then the global information from videos frames and local information from image patches are processed by an existing video adaptation method, i.e., TA3N, in order to perform feature alignment for the source domain and the target domain. Our method (without model ensemble) ranks 4th among this year's teams on the test set of EPIC-KITCHENS-100.
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Efficient Super-Resolution: Methods and Results
May 11, 2022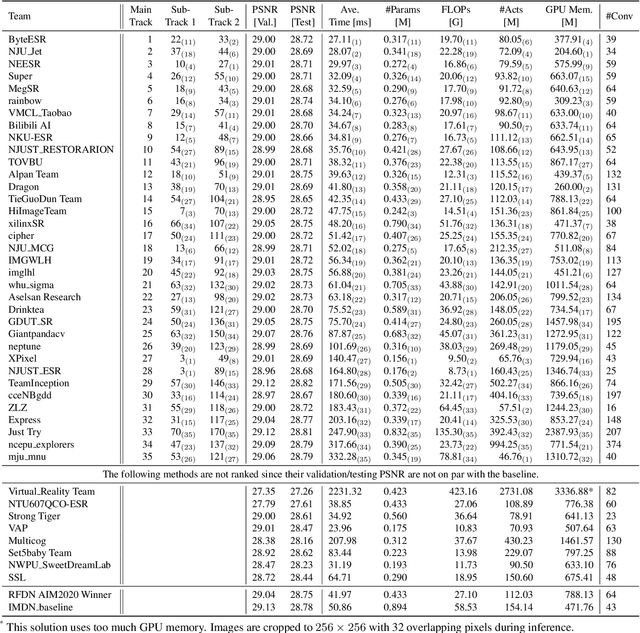
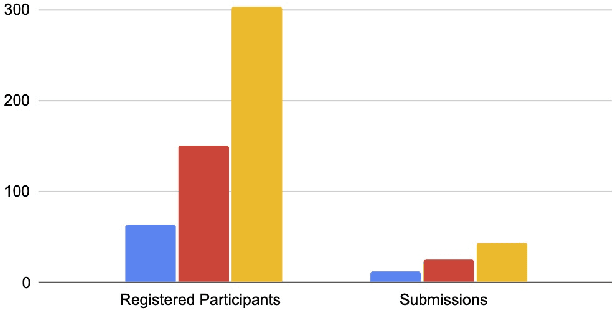
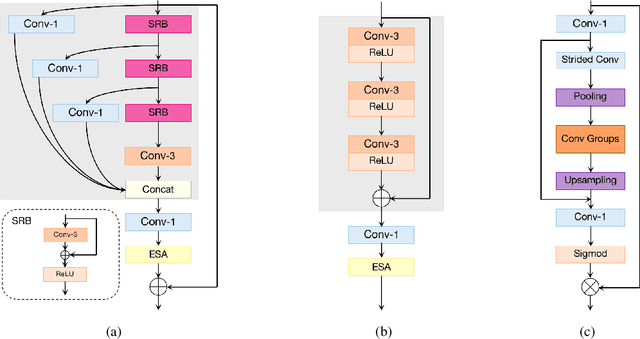
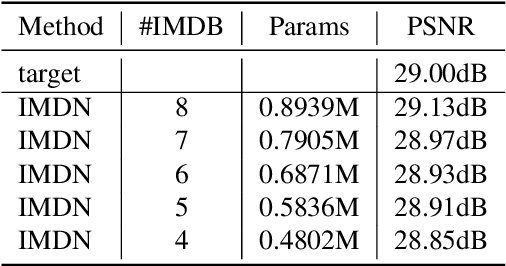
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2022 challenge on efficient single image super-resolution with focus on the proposed solutions and results. The task of the challenge was to super-resolve an input image with a magnification factor of $\times$4 based on pairs of low and corresponding high resolution images. The aim was to design a network for single image super-resolution that achieved improvement of efficiency measured according to several metrics including runtime, parameters, FLOPs, activations, and memory consumption while at least maintaining the PSNR of 29.00dB on DIV2K validation set. IMDN is set as the baseline for efficiency measurement. The challenge had 3 tracks including the main track (runtime), sub-track one (model complexity), and sub-track two (overall performance). In the main track, the practical runtime performance of the submissions was evaluated. The rank of the teams were determined directly by the absolute value of the average runtime on the validation set and test set. In sub-track one, the number of parameters and FLOPs were considered. And the individual rankings of the two metrics were summed up to determine a final ranking in this track. In sub-track two, all of the five metrics mentioned in the description of the challenge including runtime, parameter count, FLOPs, activations, and memory consumption were considered. Similar to sub-track one, the rankings of five metrics were summed up to determine a final ranking. The challenge had 303 registered participants, and 43 teams made valid submissions. They gauge the state-of-the-art in efficient single image super-resolution.
Uncertainty-Aware Model Adaptation for Unsupervised Cross-Domain Object Detection
Aug 28, 2021



Abstract:This work tackles the unsupervised cross-domain object detection problem which aims to generalize a pre-trained object detector to a new target domain without labels. We propose an uncertainty-aware model adaptation method, which is based on two motivations: 1) the estimation and exploitation of model uncertainty in a new domain is critical for reliable domain adaptation; and 2) the joint alignment of distributions for inputs (feature alignment) and outputs (self-training) is needed. To this end, we compose a Bayesian CNN-based framework for uncertainty estimation in object detection, and propose an algorithm for generation of uncertainty-aware pseudo-labels. We also devise a scheme for joint feature alignment and self-training of the object detection model with uncertainty-aware pseudo-labels. Experiments on multiple cross-domain object detection benchmarks show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
NTIRE 2021 Challenge on Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Methods and Results
May 02, 2021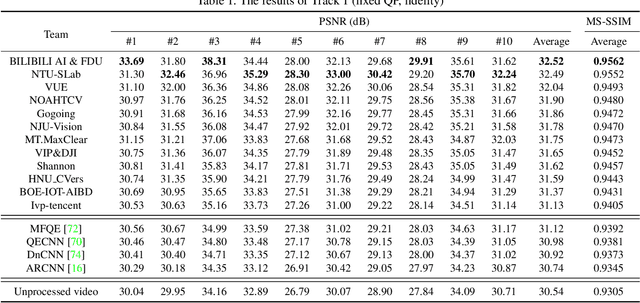
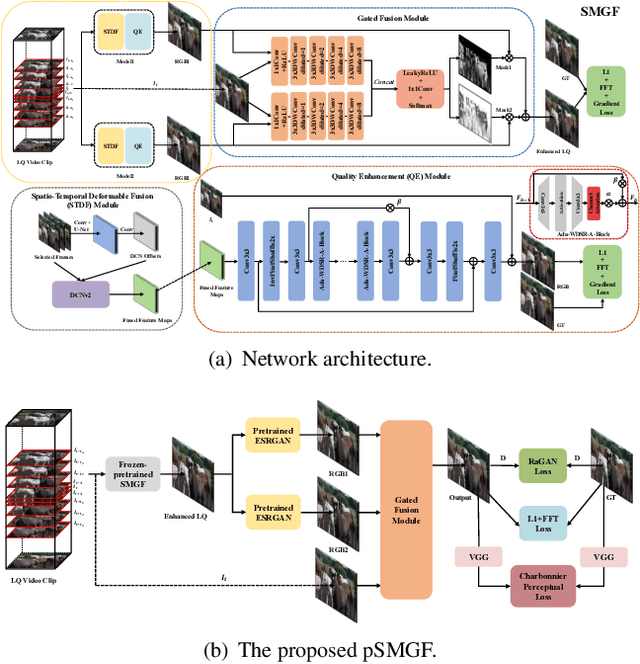
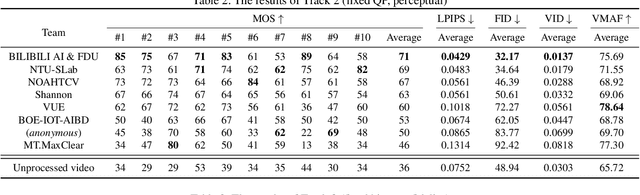
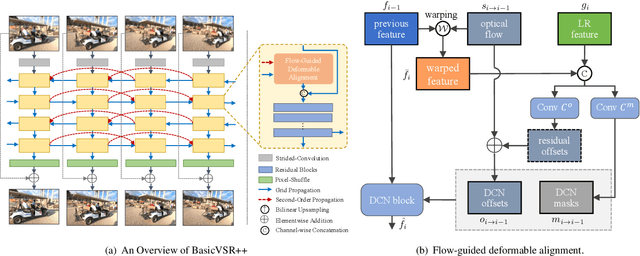
Abstract:This paper reviews the first NTIRE challenge on quality enhancement of compressed video, with a focus on the proposed methods and results. In this challenge, the new Large-scale Diverse Video (LDV) dataset is employed. The challenge has three tracks. Tracks 1 and 2 aim at enhancing the videos compressed by HEVC at a fixed QP, while Track 3 is designed for enhancing the videos compressed by x265 at a fixed bit-rate. Besides, the quality enhancement of Tracks 1 and 3 targets at improving the fidelity (PSNR), and Track 2 targets at enhancing the perceptual quality. The three tracks totally attract 482 registrations. In the test phase, 12 teams, 8 teams and 11 teams submitted the final results of Tracks 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of video quality enhancement. The homepage of the challenge: https://github.com/RenYang-home/NTIRE21_VEnh
What I See Is What You See: Joint Attention Learning for First and Third Person Video Co-analysis
Apr 16, 2019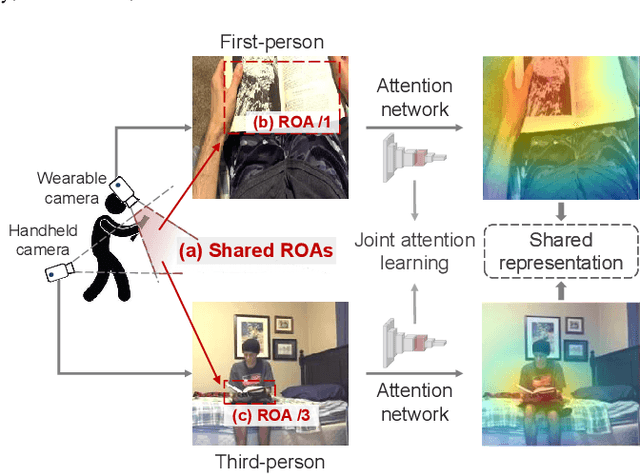
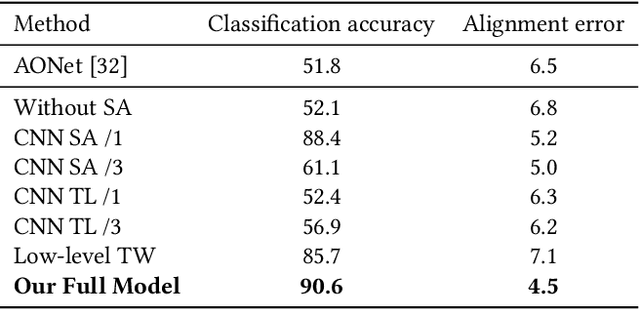

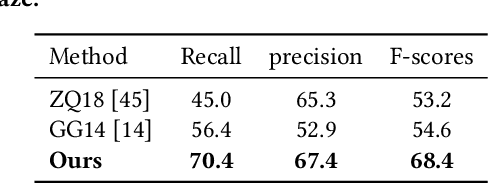
Abstract:In recent years, more and more videos are captured from the first-person viewpoint by wearable cameras. Such first-person video provides additional information besides the traditional third-person video, and thus has a wide range of applications. However, techniques for analyzing the first-person video can be fundamentally different from those for the third-person video, and it is even more difficult to explore the shared information from both viewpoints. In this paper, we propose a novel method for first- and third-person video co-analysis. At the core of our method is the notion of "joint attention", indicating the learnable representation that corresponds to the shared attention regions in different viewpoints and thus links the two viewpoints. To this end, we develop a multi-branch deep network with a triplet loss to extract the joint attention from the first- and third-person videos via self-supervised learning. We evaluate our method on the public dataset with cross-viewpoint video matching tasks. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art both qualitatively and quantitatively. We also demonstrate how the learned joint attention can benefit various applications through a set of additional experiments.
Manipulation-skill Assessment from Videos with Spatial Attention Network
Jan 09, 2019



Abstract:Recent advances in computer vision have made it possible to automatically assess from videos the manipulation skills of humans in performing a task, which has many important applications in domains such as health rehabilitation and manufacturing. However, previous methods used all video appearance as input and did not consider the attention mechanism humans use in assessing videos, which may limit their performance since only a part of video regions is critical for skill assessment. Our motivation here is to model human attention in videos that helps to focus on most relevant video regions for better skill assessment. In particular, we propose a novel deep model that learns spatial attention automatically from videos in an end-to-end manner. We evaluate our approach on a newly collected dataset of infant grasping task and four existing datasets of hand manipulation tasks. Experiment results demonstrate that state-of-the-art performance can be achieved by considering attention in automatic skill assessment.
Mutual Context Network for Jointly Estimating Egocentric Gaze and Actions
Jan 07, 2019



Abstract:In this work, we address two coupled tasks of gaze prediction and action recognition in egocentric videos by exploring their mutual context. Our assumption is that in the procedure of performing a manipulation task, what a person is doing determines where the person is looking at, and the gaze point reveals gaze and non-gaze regions which contain important and complementary information about the undergoing action. We propose a novel mutual context network (MCN) that jointly learns action-dependent gaze prediction and gaze-guided action recognition in an end-to-end manner. Experiments on public egocentric video datasets demonstrate that our MCN achieves state-of-the-art performance of both gaze prediction and action recognition.
Understanding hand-object manipulation by modeling the contextual relationship between actions, grasp types and object attributes
Jul 22, 2018



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel method for understanding daily hand-object manipulation by developing computer vision-based techniques. Specifically, we focus on recognizing hand grasp types, object attributes and manipulation actions within an unified framework by exploring their contextual relationships. Our hypothesis is that it is necessary to jointly model hands, objects and actions in order to accurately recognize multiple tasks that are correlated to each other in hand-object manipulation. In the proposed model, we explore various semantic relationships between actions, grasp types and object attributes, and show how the context can be used to boost the recognition of each component. We also explore the spatial relationship between the hand and object in order to detect the manipulated object from hand in cluttered environment. Experiment results on all three recognition tasks show that our proposed method outperforms traditional appearance-based methods which are not designed to take into account contextual relationships involved in hand-object manipulation. The visualization and generalizability study of the learned context further supports our hypothesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge