What I See Is What You See: Joint Attention Learning for First and Third Person Video Co-analysis
Paper and Code
Apr 16, 2019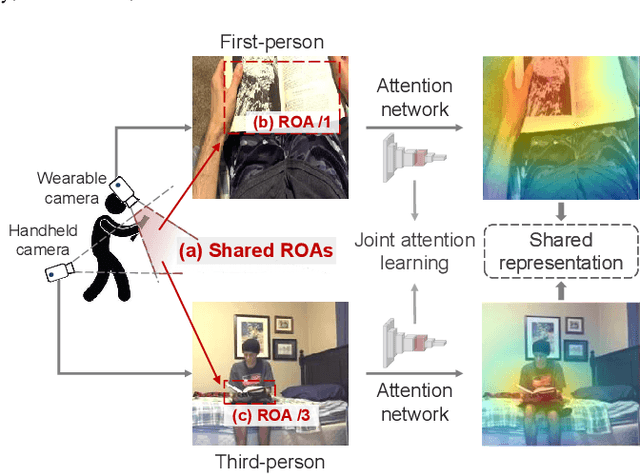
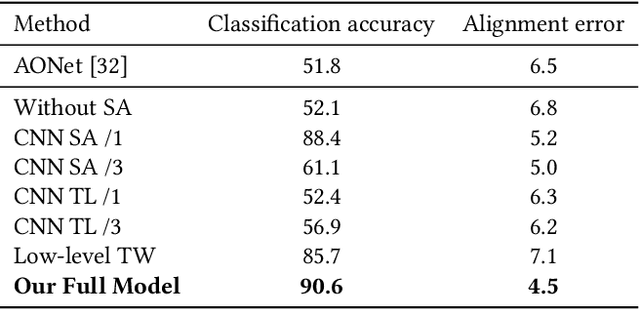

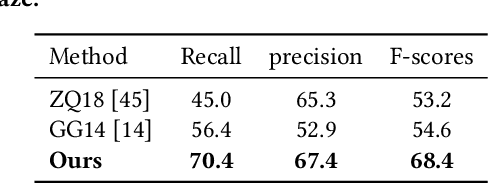
In recent years, more and more videos are captured from the first-person viewpoint by wearable cameras. Such first-person video provides additional information besides the traditional third-person video, and thus has a wide range of applications. However, techniques for analyzing the first-person video can be fundamentally different from those for the third-person video, and it is even more difficult to explore the shared information from both viewpoints. In this paper, we propose a novel method for first- and third-person video co-analysis. At the core of our method is the notion of "joint attention", indicating the learnable representation that corresponds to the shared attention regions in different viewpoints and thus links the two viewpoints. To this end, we develop a multi-branch deep network with a triplet loss to extract the joint attention from the first- and third-person videos via self-supervised learning. We evaluate our method on the public dataset with cross-viewpoint video matching tasks. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art both qualitatively and quantitatively. We also demonstrate how the learned joint attention can benefit various applications through a set of additional experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge