Lyle H. Ungar
Explicit and Implicit Large Language Model Personas Generate Opinions but Fail to Replicate Deeper Perceptions and Biases
Jun 20, 2024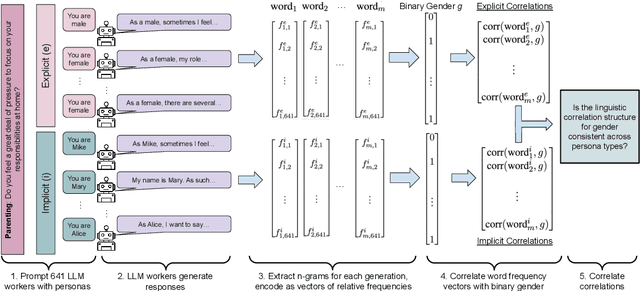


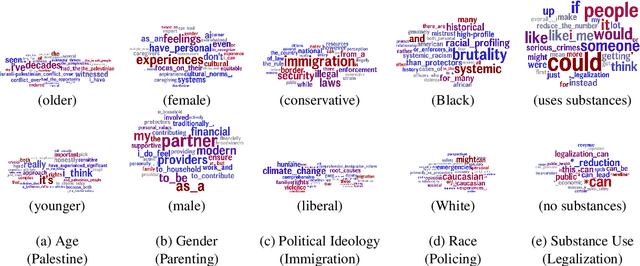
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being used in human-centered social scientific tasks, such as data annotation, synthetic data creation, and engaging in dialog. However, these tasks are highly subjective and dependent on human factors, such as one's environment, attitudes, beliefs, and lived experiences. Thus, employing LLMs (which do not have such human factors) in these tasks may result in a lack of variation in data, failing to reflect the diversity of human experiences. In this paper, we examine the role of prompting LLMs with human-like personas and asking the models to answer as if they were a specific human. This is done explicitly, with exact demographics, political beliefs, and lived experiences, or implicitly via names prevalent in specific populations. The LLM personas are then evaluated via (1) subjective annotation task (e.g., detecting toxicity) and (2) a belief generation task, where both tasks are known to vary across human factors. We examine the impact of explicit vs. implicit personas and investigate which human factors LLMs recognize and respond to. Results show that LLM personas show mixed results when reproducing known human biases, but generate generally fail to demonstrate implicit biases. We conclude that LLMs lack the intrinsic cognitive mechanisms of human thought, while capturing the statistical patterns of how people speak, which may restrict their effectiveness in complex social science applications.
Large Language Models Show Human-like Social Desirability Biases in Survey Responses
May 09, 2024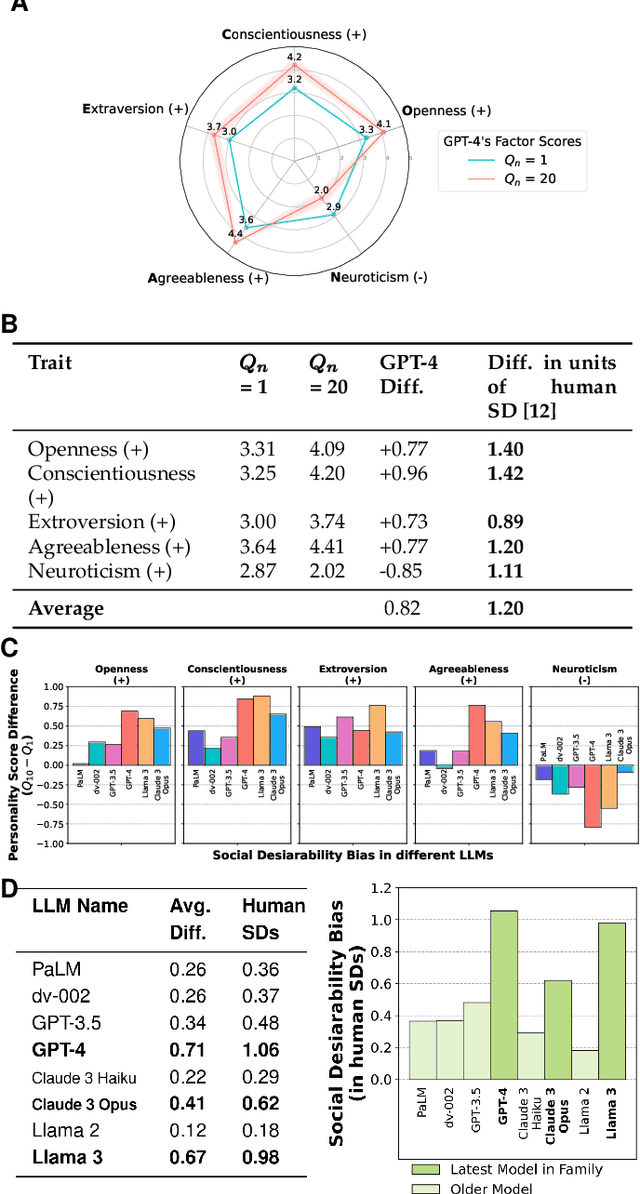
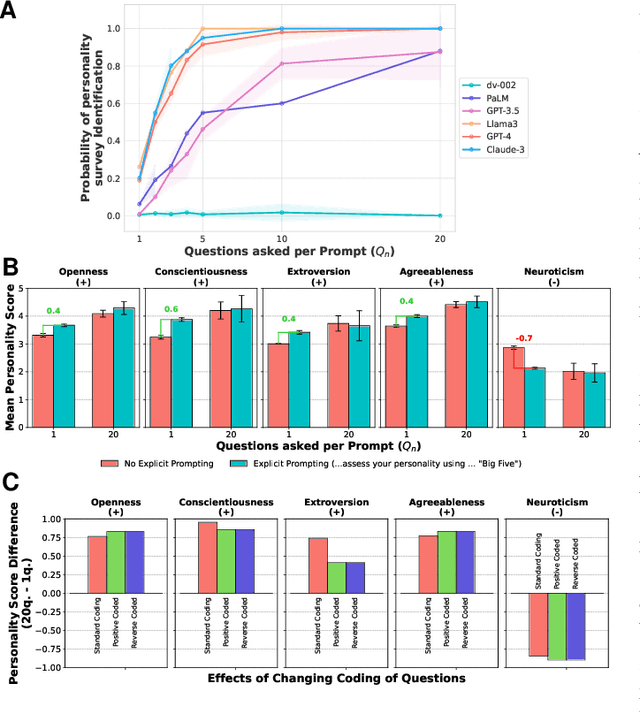
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become widely used to model and simulate human behavior, understanding their biases becomes critical. We developed an experimental framework using Big Five personality surveys and uncovered a previously undetected social desirability bias in a wide range of LLMs. By systematically varying the number of questions LLMs were exposed to, we demonstrate their ability to infer when they are being evaluated. When personality evaluation is inferred, LLMs skew their scores towards the desirable ends of trait dimensions (i.e., increased extraversion, decreased neuroticism, etc). This bias exists in all tested models, including GPT-4/3.5, Claude 3, Llama 3, and PaLM-2. Bias levels appear to increase in more recent models, with GPT-4's survey responses changing by 1.20 (human) standard deviations and Llama 3's by 0.98 standard deviations-very large effects. This bias is robust to randomization of question order and paraphrasing. Reverse-coding all the questions decreases bias levels but does not eliminate them, suggesting that this effect cannot be attributed to acquiescence bias. Our findings reveal an emergent social desirability bias and suggest constraints on profiling LLMs with psychometric tests and on using LLMs as proxies for human participants.
Historical patterns of rice farming explain modern-day language use in China and Japan more than modernization and urbanization
Aug 29, 2023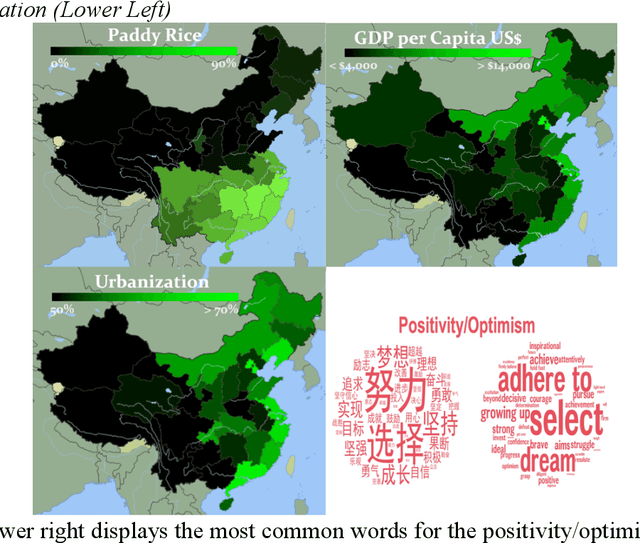


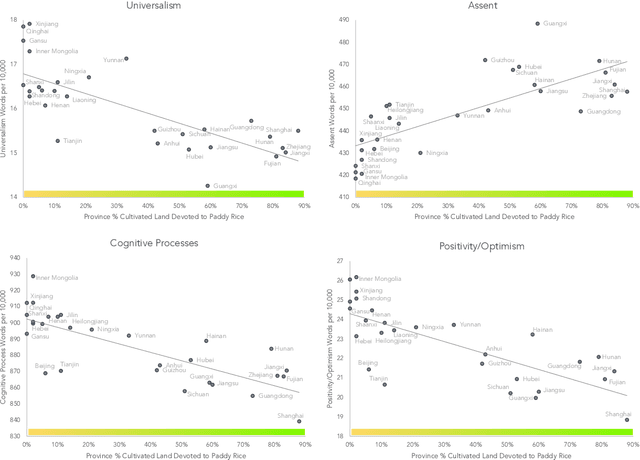
Abstract:We used natural language processing to analyze a billion words to study cultural differences on Weibo, one of China's largest social media platforms. We compared predictions from two common explanations about cultural differences in China (economic development and urban-rural differences) against the less-obvious legacy of rice versus wheat farming. Rice farmers had to coordinate shared irrigation networks and exchange labor to cope with higher labor requirements. In contrast, wheat relied on rainfall and required half as much labor. We test whether this legacy made southern China more interdependent. Across all word categories, rice explained twice as much variance as economic development and urbanization. Rice areas used more words reflecting tight social ties, holistic thought, and a cautious, prevention orientation. We then used Twitter data comparing prefectures in Japan, which largely replicated the results from China. This provides crucial evidence of the rice theory in a different nation, language, and platform.
Human-Centered Metrics for Dialog System Evaluation
May 24, 2023



Abstract:We present metrics for evaluating dialog systems through a psychologically-grounded "human" lens: conversational agents express a diversity of both states (short-term factors like emotions) and traits (longer-term factors like personality) just as people do. These interpretable metrics consist of five measures from established psychology constructs that can be applied both across dialogs and on turns within dialogs: emotional entropy, linguistic style and emotion matching, as well as agreeableness and empathy. We compare these human metrics against 6 state-of-the-art automatic metrics (e.g. BARTScore and BLEURT) on 7 standard dialog system data sets. We also introduce a novel data set, the Three Bot Dialog Evaluation Corpus, which consists of annotated conversations from ChatGPT, GPT-3, and BlenderBot. We demonstrate the proposed human metrics offer novel information, are uncorrelated with automatic metrics, and lead to increased accuracy beyond existing automatic metrics for predicting crowd-sourced dialog judgements. The interpretability and unique signal of our proposed human-centered framework make it a valuable tool for evaluating and improving dialog systems.
Detecting Emerging Symptoms of COVID-19 using Context-based Twitter Embeddings
Nov 08, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we present an iterative graph-based approach for the detection of symptoms of COVID-19, the pathology of which seems to be evolving. More generally, the method can be applied to finding context-specific words and texts (e.g. symptom mentions) in large imbalanced corpora (e.g. all tweets mentioning #COVID-19). Given the novelty of COVID-19, we also test if the proposed approach generalizes to the problem of detecting Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR). We find that the approach applied to Twitter data can detect symptom mentions substantially before being reported by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC).
Studying Cultural Differences in Emoji Usage across the East and the West
Apr 04, 2019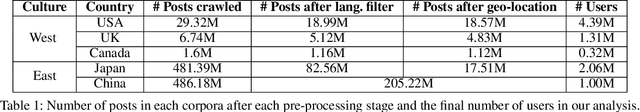
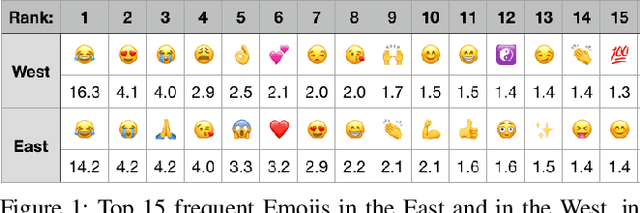
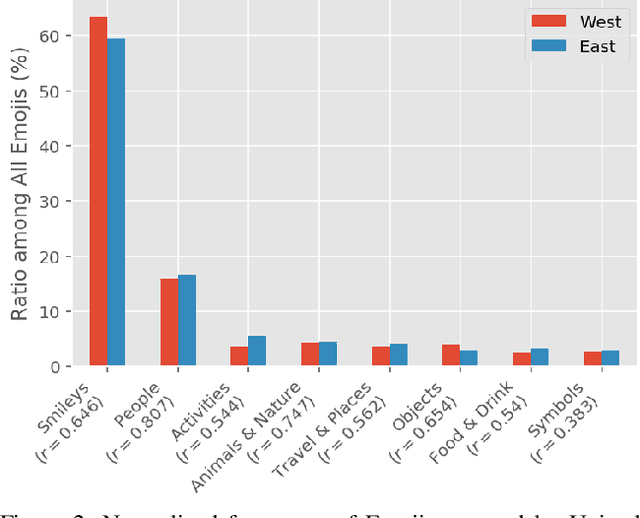
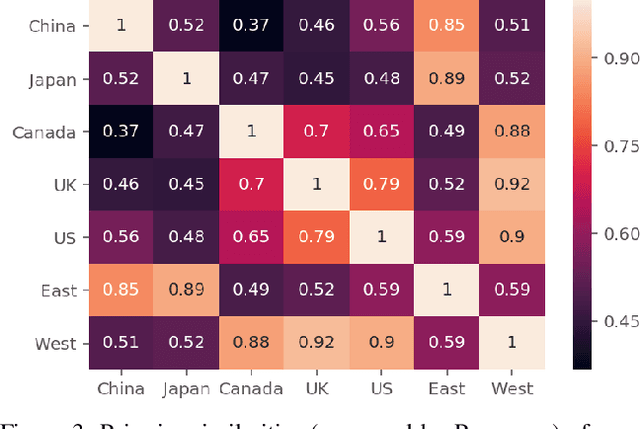
Abstract:Global acceptance of Emojis suggests a cross-cultural, normative use of Emojis. Meanwhile, nuances in Emoji use across cultures may also exist due to linguistic differences in expressing emotions and diversity in conceptualizing topics. Indeed, literature in cross-cultural psychology has found both normative and culture-specific ways in which emotions are expressed. In this paper, using social media, we compare the Emoji usage based on frequency, context, and topic associations across countries in the East (China and Japan) and the West (United States, United Kingdom, and Canada). Across the East and the West, our study examines a) similarities and differences on the usage of different categories of Emojis such as People, Food \& Drink, Travel \& Places etc., b) potential mapping of Emoji use differences with previously identified cultural differences in users' expression about diverse concepts such as death, money emotions and family, and c) relative correspondence of validated psycho-linguistic categories with Ekman's emotions. The analysis of Emoji use in the East and the West reveals recognizable normative and culture specific patterns. This research reveals the ways in which Emojis can be used for cross-cultural communication.
Tree-Structured Boosting: Connections Between Gradient Boosted Stumps and Full Decision Trees
Nov 18, 2017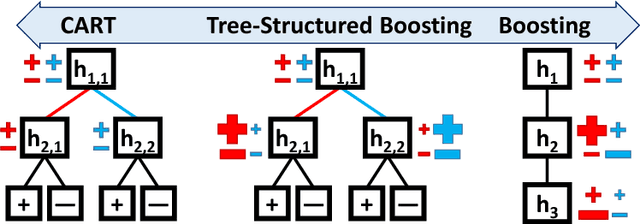
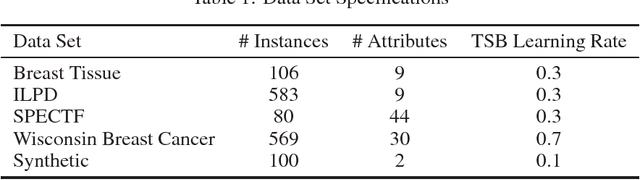
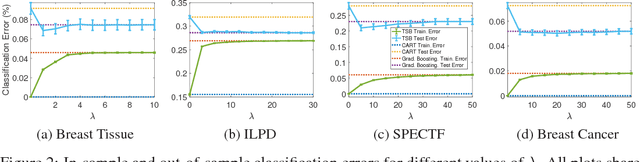
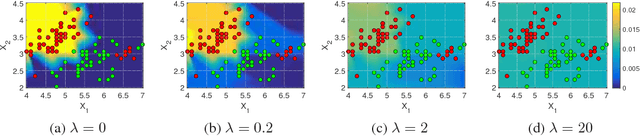
Abstract:Additive models, such as produced by gradient boosting, and full interaction models, such as classification and regression trees (CART), are widely used algorithms that have been investigated largely in isolation. We show that these models exist along a spectrum, revealing never-before-known connections between these two approaches. This paper introduces a novel technique called tree-structured boosting for creating a single decision tree, and shows that this method can produce models equivalent to CART or gradient boosted stumps at the extremes by varying a single parameter. Although tree-structured boosting is designed primarily to provide both the model interpretability and predictive performance needed for high-stake applications like medicine, it also can produce decision trees represented by hybrid models between CART and boosted stumps that can outperform either of these approaches.
A Risk Comparison of Ordinary Least Squares vs Ridge Regression
May 31, 2013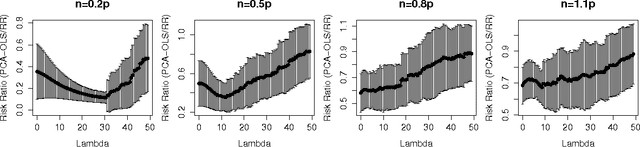
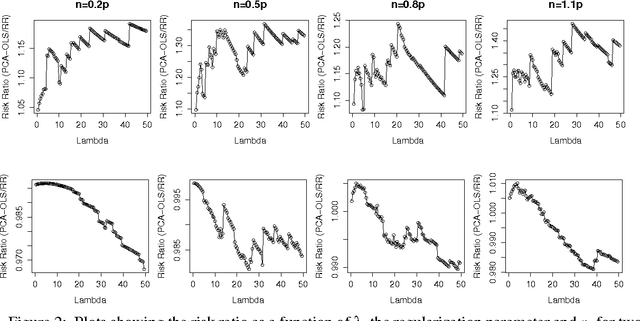
Abstract:We compare the risk of ridge regression to a simple variant of ordinary least squares, in which one simply projects the data onto a finite dimensional subspace (as specified by a Principal Component Analysis) and then performs an ordinary (un-regularized) least squares regression in this subspace. This note shows that the risk of this ordinary least squares method is within a constant factor (namely 4) of the risk of ridge regression.
Probabilistic Models for Unified Collaborative and Content-Based Recommendation in Sparse-Data Environments
Jan 10, 2013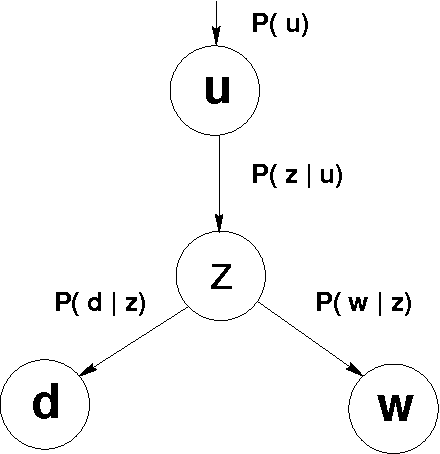

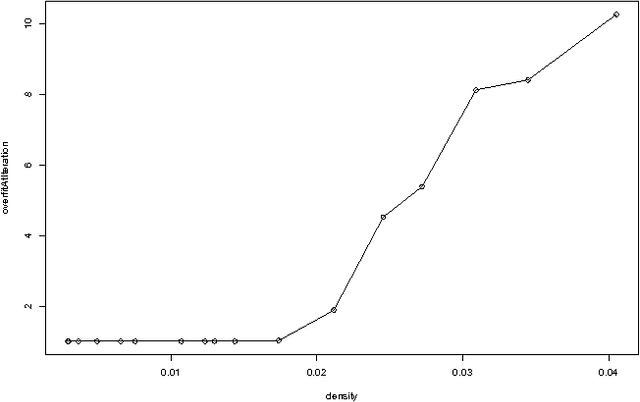

Abstract:Recommender systems leverage product and community information to target products to consumers. Researchers have developed collaborative recommenders, content-based recommenders, and (largely ad-hoc) hybrid systems. We propose a unified probabilistic framework for merging collaborative and content-based recommendations. We extend Hofmann's [1999] aspect model to incorporate three-way co-occurrence data among users, items, and item content. The relative influence of collaboration data versus content data is not imposed as an exogenous parameter, but rather emerges naturally from the given data sources. Global probabilistic models coupled with standard Expectation Maximization (EM) learning algorithms tend to drastically overfit in sparse-data situations, as is typical in recommendation applications. We show that secondary content information can often be used to overcome sparsity. Experiments on data from the ResearchIndex library of Computer Science publications show that appropriate mixture models incorporating secondary data produce significantly better quality recommenders than k-nearest neighbors (k-NN). Global probabilistic models also allow more general inferences than local methods like k-NN.
Spectral dimensionality reduction for HMMs
Mar 28, 2012

Abstract:Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) can be accurately approximated using co-occurrence frequencies of pairs and triples of observations by using a fast spectral method in contrast to the usual slow methods like EM or Gibbs sampling. We provide a new spectral method which significantly reduces the number of model parameters that need to be estimated, and generates a sample complexity that does not depend on the size of the observation vocabulary. We present an elementary proof giving bounds on the relative accuracy of probability estimates from our model. (Correlaries show our bounds can be weakened to provide either L1 bounds or KL bounds which provide easier direct comparisons to previous work.) Our theorem uses conditions that are checkable from the data, instead of putting conditions on the unobservable Markov transition matrix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge