Tree-Structured Boosting: Connections Between Gradient Boosted Stumps and Full Decision Trees
Paper and Code
Nov 18, 2017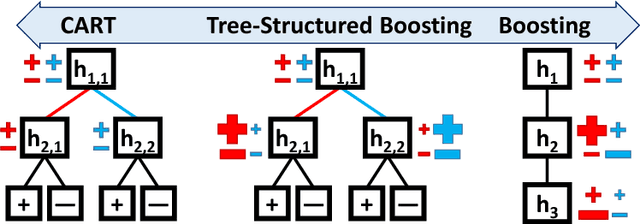
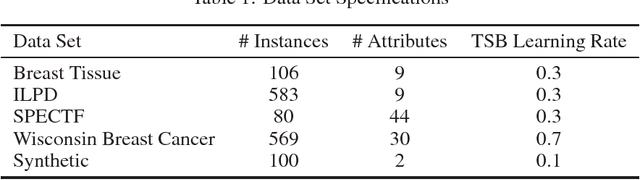
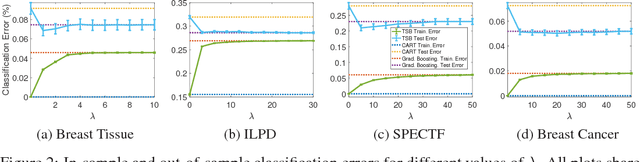
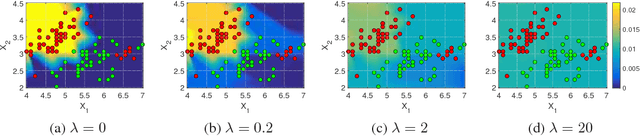
Additive models, such as produced by gradient boosting, and full interaction models, such as classification and regression trees (CART), are widely used algorithms that have been investigated largely in isolation. We show that these models exist along a spectrum, revealing never-before-known connections between these two approaches. This paper introduces a novel technique called tree-structured boosting for creating a single decision tree, and shows that this method can produce models equivalent to CART or gradient boosted stumps at the extremes by varying a single parameter. Although tree-structured boosting is designed primarily to provide both the model interpretability and predictive performance needed for high-stake applications like medicine, it also can produce decision trees represented by hybrid models between CART and boosted stumps that can outperform either of these approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge