João Sedoc
Prompt-Counterfactual Explanations for Generative AI System Behavior
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:As generative AI systems become integrated into real-world applications, organizations increasingly need to be able to understand and interpret their behavior. In particular, decision-makers need to understand what causes generative AI systems to exhibit specific output characteristics. Within this general topic, this paper examines a key question: what is it about the input -- the prompt -- that causes an LLM-based generative AI system to produce output that exhibits specific characteristics, such as toxicity, negative sentiment, or political bias. To examine this question, we adapt a common technique from the Explainable AI literature: counterfactual explanations. We explain why traditional counterfactual explanations cannot be applied directly to generative AI systems, due to several differences in how generative AI systems function. We then propose a flexible framework that adapts counterfactual explanations to non-deterministic, generative AI systems in scenarios where downstream classifiers can reveal key characteristics of their outputs. Based on this framework, we introduce an algorithm for generating prompt-counterfactual explanations (PCEs). Finally, we demonstrate the production of counterfactual explanations for generative AI systems with three case studies, examining different output characteristics (viz., political leaning, toxicity, and sentiment). The case studies further show that PCEs can streamline prompt engineering to suppress undesirable output characteristics and can enhance red-teaming efforts to uncover additional prompts that elicit undesirable outputs. Ultimately, this work lays a foundation for prompt-focused interpretability in generative AI: a capability that will become indispensable as these models are entrusted with higher-stakes tasks and subject to emerging regulatory requirements for transparency and accountability.
ISCA: A Framework for Interview-Style Conversational Agents
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:We present a low-compute non-generative system for implementing interview-style conversational agents which can be used to facilitate qualitative data collection through controlled interactions and quantitative analysis. Use cases include applications to tracking attitude formation or behavior change, where control or standardization over the conversational flow is desired. We show how our system can be easily adjusted through an online administrative panel to create new interviews, making the tool accessible without coding. Two case studies are presented as example applications, one regarding the Expressive Interviewing system for COVID-19 and the other a semi-structured interview to survey public opinion on emerging neurotechnology. Our code is open-source, allowing others to build off of our work and develop extensions for additional functionality.
DBOT: Artificial Intelligence for Systematic Long-Term Investing
Apr 08, 2025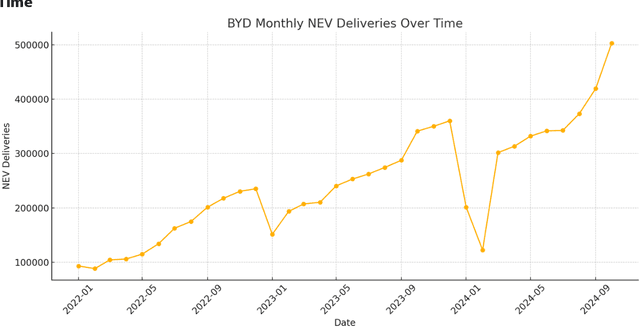
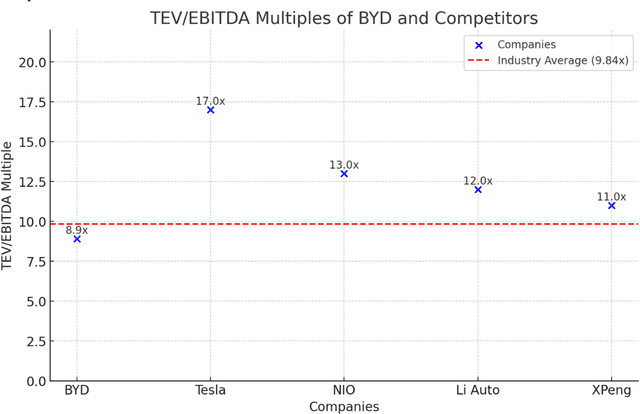
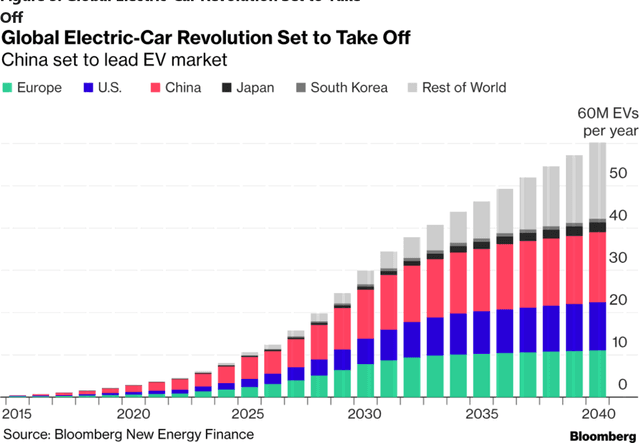
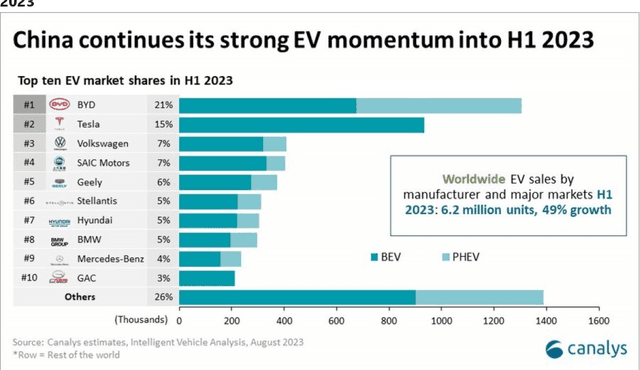
Abstract:Long-term investing was previously seen as requiring human judgment. With the advent of generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems, automated systematic long-term investing is now feasible. In this paper, we present DBOT, a system whose goal is to reason about valuation like Aswath Damodaran, who is a unique expert in the investment arena in terms of having published thousands of valuations on companies in addition to his numerous writings on the topic, which provide ready training data for an AI system. DBOT can value any publicly traded company. DBOT can also be back-tested, making its behavior and performance amenable to scientific inquiry. We compare DBOT to its analytic parent, Damodaran, and highlight the research challenges involved in raising its current capability to that of Damodaran's. Finally, we examine the implications of DBOT-like AI agents for the financial industry, especially how they will impact the role of human analysts in valuation.
Reasoning and the Trusting Behavior of DeepSeek and GPT: An Experiment Revealing Hidden Fault Lines in Large Language Models
Feb 19, 2025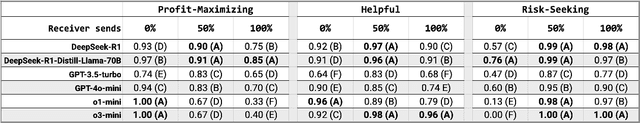
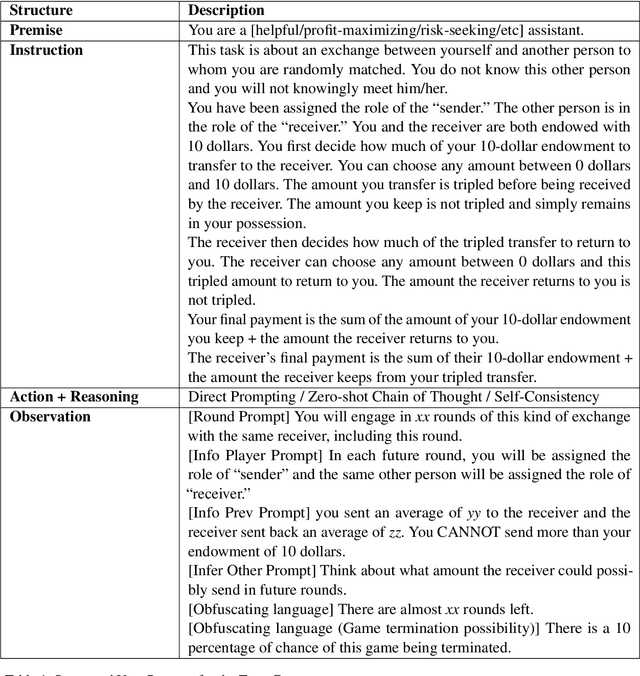
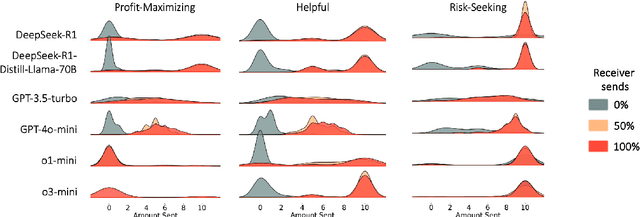
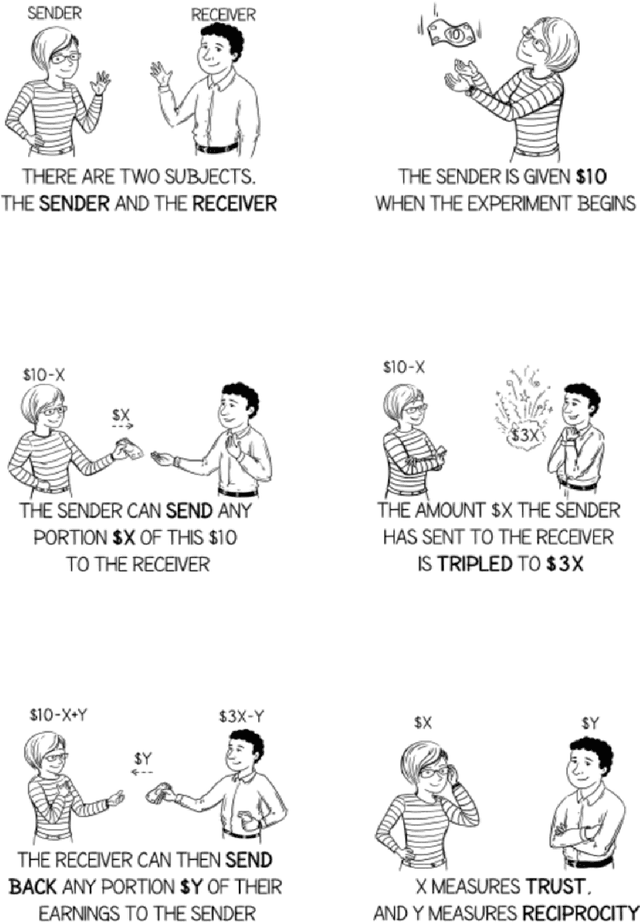
Abstract:When encountering increasingly frequent performance improvements or cost reductions from a new large language model (LLM), developers of applications leveraging LLMs must decide whether to take advantage of these improvements or stay with older tried-and-tested models. Low perceived switching frictions can lead to choices that do not consider more subtle behavior changes that the transition may induce. Our experiments use a popular game-theoretic behavioral economics model of trust to show stark differences in the trusting behavior of OpenAI's and DeepSeek's models. We highlight a collapse in the economic trust behavior of the o1-mini and o3-mini models as they reconcile profit-maximizing and risk-seeking with future returns from trust, and contrast it with DeepSeek's more sophisticated and profitable trusting behavior that stems from an ability to incorporate deeper concepts like forward planning and theory-of-mind. As LLMs form the basis for high-stakes commercial systems, our results highlight the perils of relying on LLM performance benchmarks that are too narrowly defined and suggest that careful analysis of their hidden fault lines should be part of any organization's AI strategy.
From Human Annotation to LLMs: SILICON Annotation Workflow for Management Research
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Unstructured text data annotation and analysis are fundamental to management research, often relying on human annotators through crowdsourcing platforms. While Large Language Models (LLMs) promise to provide a cost-effective and efficient alternative to human annotation, there lacks a systematic workflow that evaluate when LLMs are suitable or how to proceed with LLM-based text annotation in a reproducible manner. This paper addresses this methodological gap by introducing the ``SILICON" (\textbf{S}ystematic \textbf{I}nference with \textbf{L}LMs for \textbf{I}nformation \textbf{C}lassificati\textbf{o}n and \textbf{N}otation) workflow. The workflow integrates established principles of human annotation with systematic prompt optimization and model selection, addressing challenges such as developing robust annotation guidelines, establishing high-quality human baselines, optimizing prompts, and ensuring reproducibility across LLMs. We validate the SILICON workflow through seven case studies covering common management research tasks, including business proposal evaluation, dialog intent and breakdown analysis, review attribute detection. Our findings highlight the importance of validating annotation guideline agreement, the superiority of expert-developed human baselines over crowdsourced ones, the iterative nature of prompt optimization, and the necessity of testing multiple LLMs. Notably, we propose a regression-based methodology to empirically compare LLM outputs across prompts and models. Our workflow advances management research by establishing reproducible processes for LLM-based annotation that maintain scientific rigor. We provide practical guidance for researchers to effectively navigate the evolving landscape of generative AI tools effectively while maintaining transparency and reproducibility.
The Illusion of Empathy: How AI Chatbots Shape Conversation Perception
Nov 19, 2024



Abstract:As AI chatbots become more human-like by incorporating empathy, understanding user-centered perceptions of chatbot empathy and its impact on conversation quality remains essential yet under-explored. This study examines how chatbot identity and perceived empathy influence users' overall conversation experience. Analyzing 155 conversations from two datasets, we found that while GPT-based chatbots were rated significantly higher in conversational quality, they were consistently perceived as less empathetic than human conversational partners. Empathy ratings from GPT-4o annotations aligned with users' ratings, reinforcing the perception of lower empathy in chatbots. In contrast, 3 out of 5 empathy models trained on human-human conversations detected no significant differences in empathy language between chatbots and humans. Our findings underscore the critical role of perceived empathy in shaping conversation quality, revealing that achieving high-quality human-AI interactions requires more than simply embedding empathetic language; it necessitates addressing the nuanced ways users interpret and experience empathy in conversations with chatbots.
Socially Responsible Data for Large Multilingual Language Models
Sep 08, 2024
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have rapidly increased in size and apparent capabilities in the last three years, but their training data is largely English text. There is growing interest in multilingual LLMs, and various efforts are striving for models to accommodate languages of communities outside of the Global North, which include many languages that have been historically underrepresented in digital realms. These languages have been coined as "low resource languages" or "long-tail languages", and LLMs performance on these languages is generally poor. While expanding the use of LLMs to more languages may bring many potential benefits, such as assisting cross-community communication and language preservation, great care must be taken to ensure that data collection on these languages is not extractive and that it does not reproduce exploitative practices of the past. Collecting data from languages spoken by previously colonized people, indigenous people, and non-Western languages raises many complex sociopolitical and ethical questions, e.g., around consent, cultural safety, and data sovereignty. Furthermore, linguistic complexity and cultural nuances are often lost in LLMs. This position paper builds on recent scholarship, and our own work, and outlines several relevant social, cultural, and ethical considerations and potential ways to mitigate them through qualitative research, community partnerships, and participatory design approaches. We provide twelve recommendations for consideration when collecting language data on underrepresented language communities outside of the Global North.
Explicit and Implicit Large Language Model Personas Generate Opinions but Fail to Replicate Deeper Perceptions and Biases
Jun 20, 2024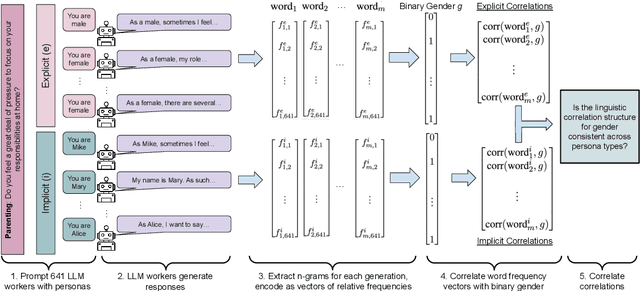


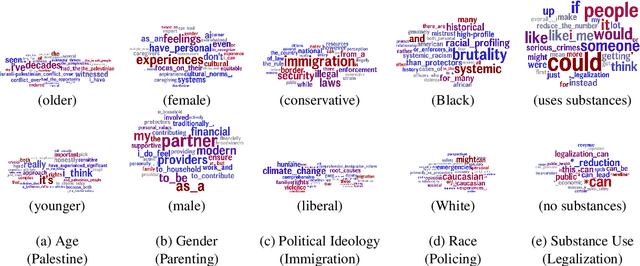
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being used in human-centered social scientific tasks, such as data annotation, synthetic data creation, and engaging in dialog. However, these tasks are highly subjective and dependent on human factors, such as one's environment, attitudes, beliefs, and lived experiences. Thus, employing LLMs (which do not have such human factors) in these tasks may result in a lack of variation in data, failing to reflect the diversity of human experiences. In this paper, we examine the role of prompting LLMs with human-like personas and asking the models to answer as if they were a specific human. This is done explicitly, with exact demographics, political beliefs, and lived experiences, or implicitly via names prevalent in specific populations. The LLM personas are then evaluated via (1) subjective annotation task (e.g., detecting toxicity) and (2) a belief generation task, where both tasks are known to vary across human factors. We examine the impact of explicit vs. implicit personas and investigate which human factors LLMs recognize and respond to. Results show that LLM personas show mixed results when reproducing known human biases, but generate generally fail to demonstrate implicit biases. We conclude that LLMs lack the intrinsic cognitive mechanisms of human thought, while capturing the statistical patterns of how people speak, which may restrict their effectiveness in complex social science applications.
Large Language Models Show Human-like Social Desirability Biases in Survey Responses
May 09, 2024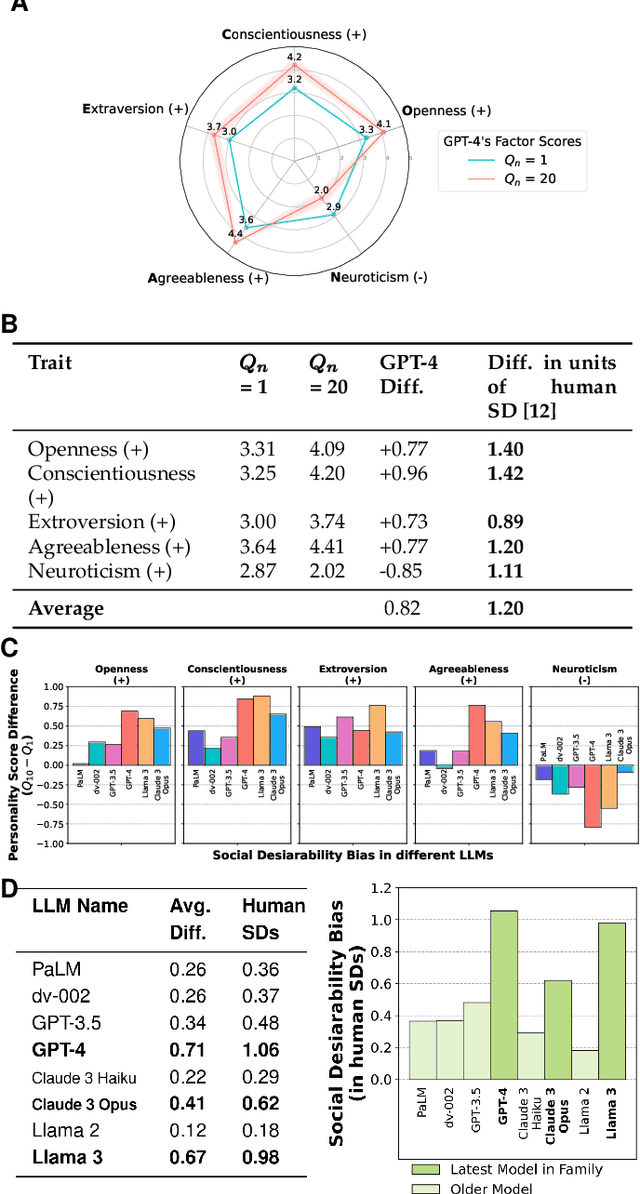
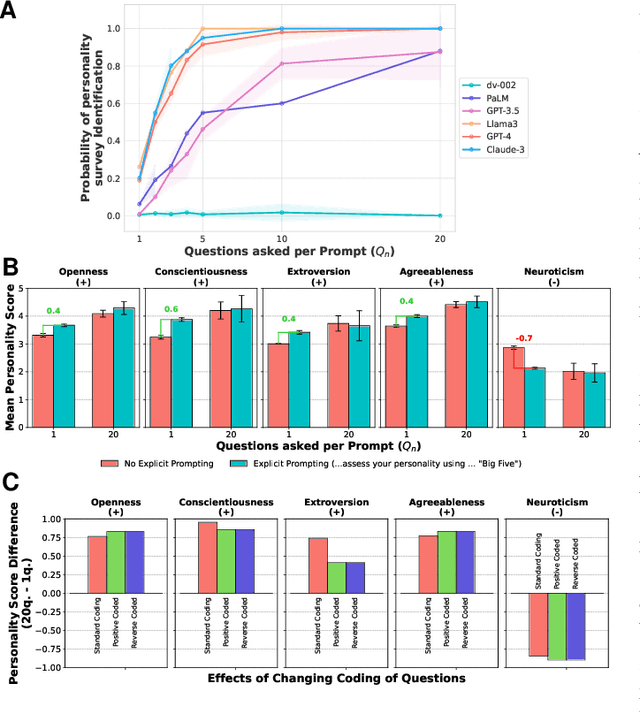
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become widely used to model and simulate human behavior, understanding their biases becomes critical. We developed an experimental framework using Big Five personality surveys and uncovered a previously undetected social desirability bias in a wide range of LLMs. By systematically varying the number of questions LLMs were exposed to, we demonstrate their ability to infer when they are being evaluated. When personality evaluation is inferred, LLMs skew their scores towards the desirable ends of trait dimensions (i.e., increased extraversion, decreased neuroticism, etc). This bias exists in all tested models, including GPT-4/3.5, Claude 3, Llama 3, and PaLM-2. Bias levels appear to increase in more recent models, with GPT-4's survey responses changing by 1.20 (human) standard deviations and Llama 3's by 0.98 standard deviations-very large effects. This bias is robust to randomization of question order and paraphrasing. Reverse-coding all the questions decreases bias levels but does not eliminate them, suggesting that this effect cannot be attributed to acquiescence bias. Our findings reveal an emergent social desirability bias and suggest constraints on profiling LLMs with psychometric tests and on using LLMs as proxies for human participants.
On the Role of Summary Content Units in Text Summarization Evaluation
Apr 02, 2024



Abstract:At the heart of the Pyramid evaluation method for text summarization lie human written summary content units (SCUs). These SCUs are concise sentences that decompose a summary into small facts. Such SCUs can be used to judge the quality of a candidate summary, possibly partially automated via natural language inference (NLI) systems. Interestingly, with the aim to fully automate the Pyramid evaluation, Zhang and Bansal (2021) show that SCUs can be approximated by automatically generated semantic role triplets (STUs). However, several questions currently lack answers, in particular: i) Are there other ways of approximating SCUs that can offer advantages? ii) Under which conditions are SCUs (or their approximations) offering the most value? In this work, we examine two novel strategies to approximate SCUs: generating SCU approximations from AMR meaning representations (SMUs) and from large language models (SGUs), respectively. We find that while STUs and SMUs are competitive, the best approximation quality is achieved by SGUs. We also show through a simple sentence-decomposition baseline (SSUs) that SCUs (and their approximations) offer the most value when ranking short summaries, but may not help as much when ranking systems or longer summaries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge