Sunny Rai
HATS: Hindi Analogy Test Set for Evaluating Reasoning in Large Language Models
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Analogies test a model's ability to infer implicit relationships between concepts, making them a key benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities. While large language models (LLMs) are widely evaluated for reasoning in English, their abilities in Indic languages remain understudied, limiting our understanding of whether these models generalize across languages. To address this gap, we introduce a new Hindi Analogy Test Set (HATS), comprising 405 multiple-choice questions sourced from Indian government exams. We benchmark state-of-the-art multilingual LLMs using various prompting strategies and introduce a grounded Chain of Thought approach that leverages cognitive theories of analogical reasoning. This approach improves model performance on Hindi analogy questions. Our experiments show that models perform best with English prompts, irrespective of the prompting strategy. Our test set addresses the lack of a critical resource to evaluate LLM reasoning capabilities in Hindi.
Building Knowledge-Guided Lexica to Model Cultural Variation
Jun 17, 2024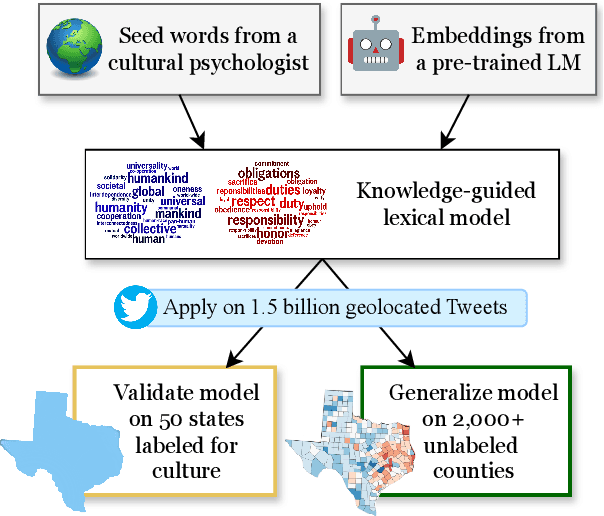

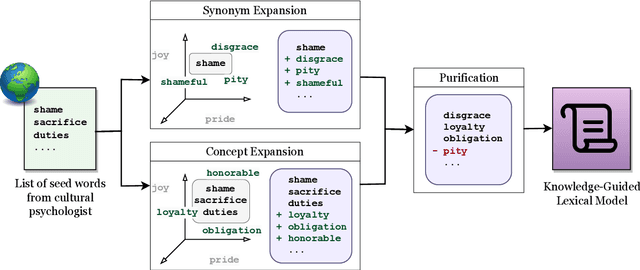
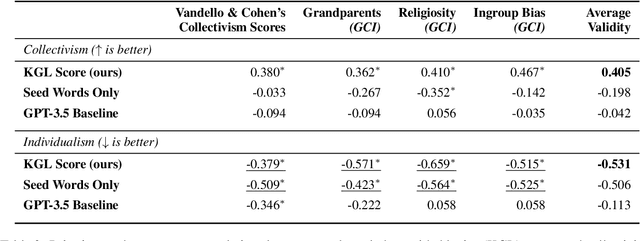
Abstract:Cultural variation exists between nations (e.g., the United States vs. China), but also within regions (e.g., California vs. Texas, Los Angeles vs. San Francisco). Measuring this regional cultural variation can illuminate how and why people think and behave differently. Historically, it has been difficult to computationally model cultural variation due to a lack of training data and scalability constraints. In this work, we introduce a new research problem for the NLP community: How do we measure variation in cultural constructs across regions using language? We then provide a scalable solution: building knowledge-guided lexica to model cultural variation, encouraging future work at the intersection of NLP and cultural understanding. We also highlight modern LLMs' failure to measure cultural variation or generate culturally varied language.
An Integrative Survey on Mental Health Conversational Agents to Bridge Computer Science and Medical Perspectives
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Mental health conversational agents (a.k.a. chatbots) are widely studied for their potential to offer accessible support to those experiencing mental health challenges. Previous surveys on the topic primarily consider papers published in either computer science or medicine, leading to a divide in understanding and hindering the sharing of beneficial knowledge between both domains. To bridge this gap, we conduct a comprehensive literature review using the PRISMA framework, reviewing 534 papers published in both computer science and medicine. Our systematic review reveals 136 key papers on building mental health-related conversational agents with diverse characteristics of modeling and experimental design techniques. We find that computer science papers focus on LLM techniques and evaluating response quality using automated metrics with little attention to the application while medical papers use rule-based conversational agents and outcome metrics to measure the health outcomes of participants. Based on our findings on transparency, ethics, and cultural heterogeneity in this review, we provide a few recommendations to help bridge the disciplinary divide and enable the cross-disciplinary development of mental health conversational agents.
Multilingual Language Models are not Multicultural: A Case Study in Emotion
Jul 09, 2023



Abstract:Emotions are experienced and expressed differently across the world. In order to use Large Language Models (LMs) for multilingual tasks that require emotional sensitivity, LMs must reflect this cultural variation in emotion. In this study, we investigate whether the widely-used multilingual LMs in 2023 reflect differences in emotional expressions across cultures and languages. We find that embeddings obtained from LMs (e.g., XLM-RoBERTa) are Anglocentric, and generative LMs (e.g., ChatGPT) reflect Western norms, even when responding to prompts in other languages. Our results show that multilingual LMs do not successfully learn the culturally appropriate nuances of emotion and we highlight possible research directions towards correcting this.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge