Lei Luo
LaVR: Scene Latent Conditioned Generative Video Trajectory Re-Rendering using Large 4D Reconstruction Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Given a monocular video, the goal of video re-rendering is to generate views of the scene from a novel camera trajectory. Existing methods face two distinct challenges. Geometrically unconditioned models lack spatial awareness, leading to drift and deformation under viewpoint changes. On the other hand, geometrically-conditioned models depend on estimated depth and explicit reconstruction, making them susceptible to depth inaccuracies and calibration errors. We propose to address these challenges by using the implicit geometric knowledge embedded in the latent space of a large 4D reconstruction model to condition the video generation process. These latents capture scene structure in a continuous space without explicit reconstruction. Therefore, they provide a flexible representation that allows the pretrained diffusion prior to regularize errors more effectively. By jointly conditioning on these latents and source camera poses, we demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art results on the video re-rendering task. Project webpage is https://lavr-4d-scene-rerender.github.io/
Small but Mighty: Dynamic Wavelet Expert-Guided Fine-Tuning of Large-Scale Models for Optical Remote Sensing Object Segmentation
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Accurately localizing and segmenting relevant objects from optical remote sensing images (ORSIs) is critical for advancing remote sensing applications. Existing methods are typically built upon moderate-scale pre-trained models and employ diverse optimization strategies to achieve promising performance under full-parameter fine-tuning. In fact, deeper and larger-scale foundation models can provide stronger support for performance improvement. However, due to their massive number of parameters, directly adopting full-parameter fine-tuning leads to pronounced training difficulties, such as excessive GPU memory consumption and high computational costs, which result in extremely limited exploration of large-scale models in existing works. In this paper, we propose a novel dynamic wavelet expert-guided fine-tuning paradigm with fewer trainable parameters, dubbed WEFT, which efficiently adapts large-scale foundation models to ORSIs segmentation tasks by leveraging the guidance of wavelet experts. Specifically, we introduce a task-specific wavelet expert extractor to model wavelet experts from different perspectives and dynamically regulate their outputs, thereby generating trainable features enriched with task-specific information for subsequent fine-tuning. Furthermore, we construct an expert-guided conditional adapter that first enhances the fine-grained perception of frozen features for specific tasks by injecting trainable features, and then iteratively updates the information of both types of feature, allowing for efficient fine-tuning. Extensive experiments show that our WEFT not only outperforms 21 state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on three ORSIs datasets, but also achieves optimal results in camouflage, natural, and medical scenarios. The source code is available at: https://github.com/CSYSI/WEFT.
A General Anchor-Based Framework for Scalable Fair Clustering
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Fair clustering is crucial for mitigating bias in unsupervised learning, yet existing algorithms often suffer from quadratic or super-quadratic computational complexity, rendering them impractical for large-scale datasets. To bridge this gap, we introduce the Anchor-based Fair Clustering Framework (AFCF), a novel, general, and plug-and-play framework that empowers arbitrary fair clustering algorithms with linear-time scalability. Our approach first selects a small but representative set of anchors using a novel fair sampling strategy. Then, any off-the-shelf fair clustering algorithm can be applied to this small anchor set. The core of our framework lies in a novel anchor graph construction module, where we formulate an optimization problem to propagate labels while preserving fairness. This is achieved through a carefully designed group-label joint constraint, which we prove theoretically ensures that the fairness of the final clustering on the entire dataset matches that of the anchor clustering. We solve this optimization efficiently using an ADMM-based algorithm. Extensive experiments on multiple large-scale benchmarks demonstrate that AFCF drastically accelerates state-of-the-art methods, which reduces computational time by orders of magnitude while maintaining strong clustering performance and fairness guarantees.
QoE Optimization for Semantic Self-Correcting Video Transmission in Multi-UAV Networks
Jul 09, 2025
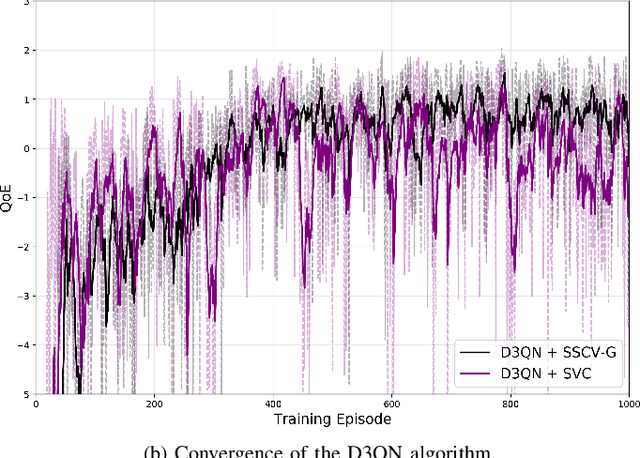
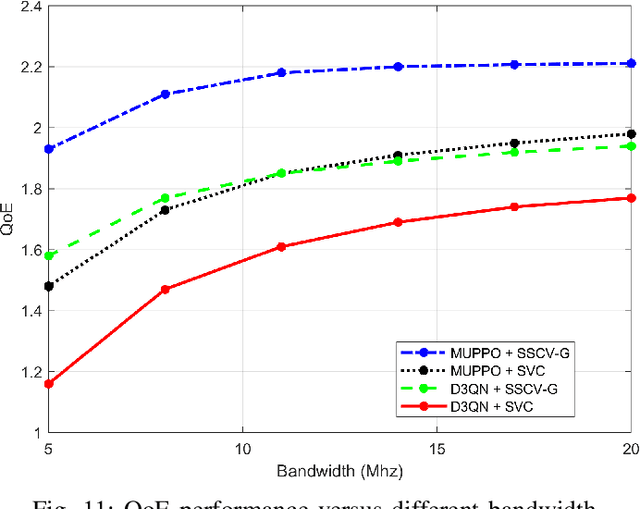
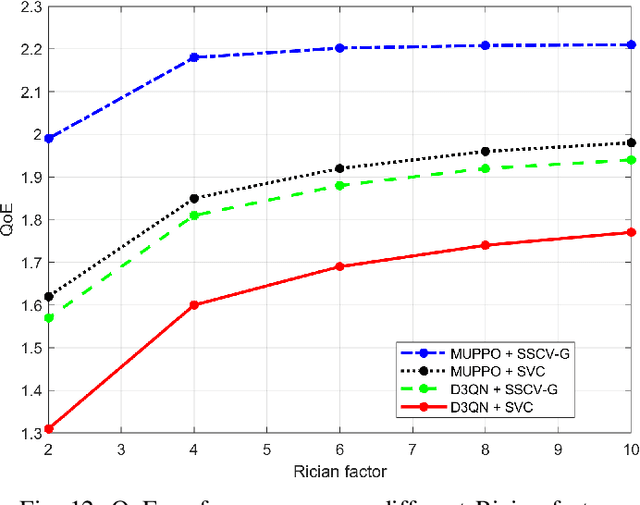
Abstract:Real-time unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) video streaming is essential for time-sensitive applications, including remote surveillance, emergency response, and environmental monitoring. However, it faces challenges such as limited bandwidth, latency fluctuations, and high packet loss. To address these issues, we propose a novel semantic self-correcting video transmission framework with ultra-fine bitrate granularity (SSCV-G). In SSCV-G, video frames are encoded into a compact semantic codebook space, and the transmitter adaptively sends a subset of semantic indices based on bandwidth availability, enabling fine-grained bitrate control for improved bandwidth efficiency. At the receiver, a spatio-temporal vision transformer (ST-ViT) performs multi-frame joint decoding to reconstruct dropped semantic indices by modeling intra- and inter-frame dependencies. To further improve performance under dynamic network conditions, we integrate a multi-user proximal policy optimization (MUPPO) reinforcement learning scheme that jointly optimizes communication resource allocation and semantic bitrate selection to maximize user Quality of Experience (QoE). Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SSCV-G significantly outperforms state-of-the-art video codecs in coding efficiency, bandwidth adaptability, and packet loss robustness. Moreover, the proposed MUPPO-based QoE optimization consistently surpasses existing benchmarks.
M4-SAR: A Multi-Resolution, Multi-Polarization, Multi-Scene, Multi-Source Dataset and Benchmark for Optical-SAR Fusion Object Detection
May 16, 2025Abstract:Single-source remote sensing object detection using optical or SAR images struggles in complex environments. Optical images offer rich textural details but are often affected by low-light, cloud-obscured, or low-resolution conditions, reducing the detection performance. SAR images are robust to weather, but suffer from speckle noise and limited semantic expressiveness. Optical and SAR images provide complementary advantages, and fusing them can significantly improve the detection accuracy. However, progress in this field is hindered by the lack of large-scale, standardized datasets. To address these challenges, we propose the first comprehensive dataset for optical-SAR fusion object detection, named Multi-resolution, Multi-polarization, Multi-scene, Multi-source SAR dataset (M4-SAR). It contains 112,184 precisely aligned image pairs and nearly one million labeled instances with arbitrary orientations, spanning six key categories. To enable standardized evaluation, we develop a unified benchmarking toolkit that integrates six state-of-the-art multi-source fusion methods. Furthermore, we propose E2E-OSDet, a novel end-to-end multi-source fusion detection framework that mitigates cross-domain discrepancies and establishes a robust baseline for future studies. Extensive experiments on M4-SAR demonstrate that fusing optical and SAR data can improve $mAP$ by 5.7\% over single-source inputs, with particularly significant gains in complex environments. The dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/wchao0601/M4-SAR.
Remote Photoplethysmography in Real-World and Extreme Lighting Scenarios
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Physiological activities can be manifested by the sensitive changes in facial imaging. While they are barely observable to our eyes, computer vision manners can, and the derived remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) has shown considerable promise. However, existing studies mainly rely on spatial skin recognition and temporal rhythmic interactions, so they focus on identifying explicit features under ideal light conditions, but perform poorly in-the-wild with intricate obstacles and extreme illumination exposure. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end video transformer model for rPPG. It strives to eliminate complex and unknown external time-varying interferences, whether they are sufficient to occupy subtle biosignal amplitudes or exist as periodic perturbations that hinder network training. In the specific implementation, we utilize global interference sharing, subject background reference, and self-supervised disentanglement to eliminate interference, and further guide learning based on spatiotemporal filtering, reconstruction guidance, and frequency domain and biological prior constraints to achieve effective rPPG. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first robust rPPG model for real outdoor scenarios based on natural face videos, and is lightweight to deploy. Extensive experiments show the competitiveness and performance of our model in rPPG prediction across datasets and scenes.
Diff-Reg v2: Diffusion-Based Matching Matrix Estimation for Image Matching and 3D Registration
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:Establishing reliable correspondences is crucial for all registration tasks, including 2D image registration, 3D point cloud registration, and 2D-3D image-to-point cloud registration. However, these tasks are often complicated by challenges such as scale inconsistencies, symmetry, and large deformations, which can lead to ambiguous matches. Previous feature-based and correspondence-based methods typically rely on geometric or semantic features to generate or polish initial potential correspondences. Some methods typically leverage specific geometric priors, such as topological preservation, to devise diverse and innovative strategies tailored to a given enhancement goal, which cannot be exhaustively enumerated. Additionally, many previous approaches rely on a single-step prediction head, which can struggle with local minima in complex matching scenarios. To address these challenges, we introduce an innovative paradigm that leverages a diffusion model in matrix space for robust matching matrix estimation. Our model treats correspondence estimation as a denoising diffusion process in the matching matrix space, gradually refining the intermediate matching matrix to the optimal one. Specifically, we apply the diffusion model in the doubly stochastic matrix space for 3D-3D and 2D-3D registration tasks. In the 2D image registration task, we deploy the diffusion model in a matrix subspace where dual-softmax projection regularization is applied. For all three registration tasks, we provide adaptive matching matrix embedding implementations tailored to the specific characteristics of each task while maintaining a consistent "match-to-warp" encoding pattern. Furthermore, we adopt a lightweight design for the denoising module. In inference, once points or image features are extracted and fixed, this module performs multi-step denoising predictions through reverse sampling.
Towards Better Spherical Sliced-Wasserstein Distance Learning with Data-Adaptive Discriminative Projection Direction
Dec 26, 2024



Abstract:Spherical Sliced-Wasserstein (SSW) has recently been proposed to measure the discrepancy between spherical data distributions in various fields, such as geology, medical domains, computer vision, and deep representation learning. However, in the original SSW, all projection directions are treated equally, which is too idealistic and cannot accurately reflect the importance of different projection directions for various data distributions. To address this issue, we propose a novel data-adaptive Discriminative Spherical Sliced-Wasserstein (DSSW) distance, which utilizes a projected energy function to determine the discriminative projection direction for SSW. In our new DSSW, we introduce two types of projected energy functions to generate the weights for projection directions with complete theoretical guarantees. The first type employs a non-parametric deterministic function that transforms the projected Wasserstein distance into its corresponding weight in each projection direction. This improves the performance of the original SSW distance with negligible additional computational overhead. The second type utilizes a neural network-induced function that learns the projection direction weight through a parameterized neural network based on data projections. This further enhances the performance of the original SSW distance with less extra computational overhead. Finally, we evaluate the performance of our proposed DSSW by comparing it with several state-of-the-art methods across a variety of machine learning tasks, including gradient flows, density estimation on real earth data, and self-supervised learning.
United Domain Cognition Network for Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images
Nov 11, 2024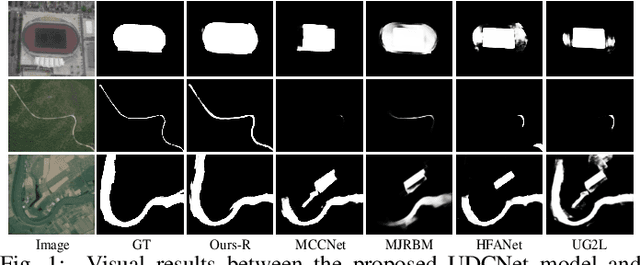



Abstract:Recently, deep learning-based salient object detection (SOD) in optical remote sensing images (ORSIs) have achieved significant breakthroughs. We observe that existing ORSIs-SOD methods consistently center around optimizing pixel features in the spatial domain, progressively distinguishing between backgrounds and objects. However, pixel information represents local attributes, which are often correlated with their surrounding context. Even with strategies expanding the local region, spatial features remain biased towards local characteristics, lacking the ability of global perception. To address this problem, we introduce the Fourier transform that generate global frequency features and achieve an image-size receptive field. To be specific, we propose a novel United Domain Cognition Network (UDCNet) to jointly explore the global-local information in the frequency and spatial domains. Technically, we first design a frequency-spatial domain transformer block that mutually amalgamates the complementary local spatial and global frequency features to strength the capability of initial input features. Furthermore, a dense semantic excavation module is constructed to capture higher-level semantic for guiding the positioning of remote sensing objects. Finally, we devise a dual-branch joint optimization decoder that applies the saliency and edge branches to generate high-quality representations for predicting salient objects. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed UDCNet method over 24 state-of-the-art models, through extensive quantitative and qualitative comparisons in three widely-used ORSIs-SOD datasets. The source code is available at: \href{https://github.com/CSYSI/UDCNet}{\color{blue} https://github.com/CSYSI/UDCNet}.
The ISCSLP 2024 Conversational Voice Clone (CoVoC) Challenge: Tasks, Results and Findings
Oct 31, 2024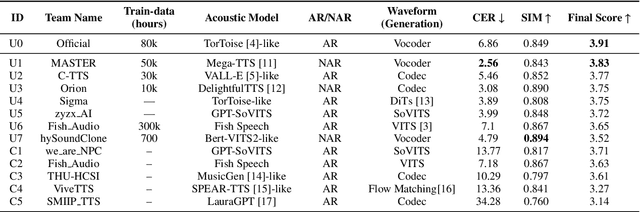
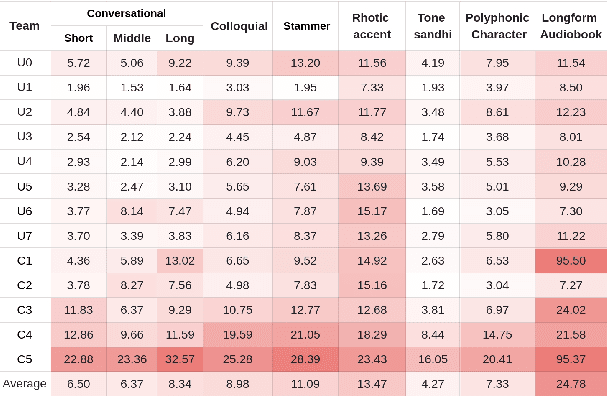
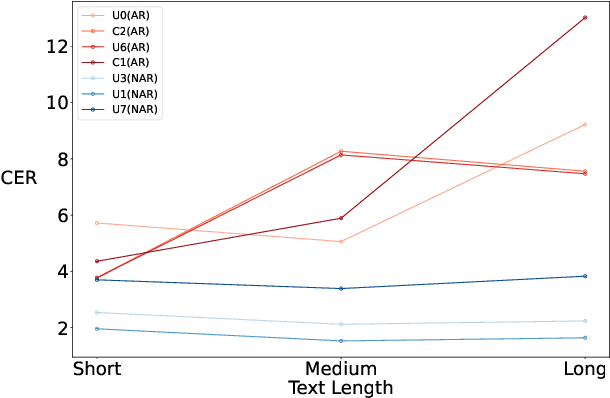
Abstract:The ISCSLP 2024 Conversational Voice Clone (CoVoC) Challenge aims to benchmark and advance zero-shot spontaneous style voice cloning, particularly focusing on generating spontaneous behaviors in conversational speech. The challenge comprises two tracks: an unconstrained track without limitation on data and model usage, and a constrained track only allowing the use of constrained open-source datasets. A 100-hour high-quality conversational speech dataset is also made available with the challenge. This paper details the data, tracks, submitted systems, evaluation results, and findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge