Kripasindhu Sarkar
TeGA: Texture Space Gaussian Avatars for High-Resolution Dynamic Head Modeling
May 08, 2025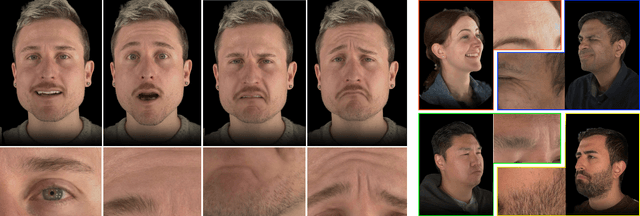
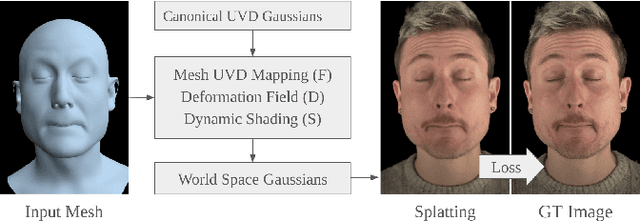
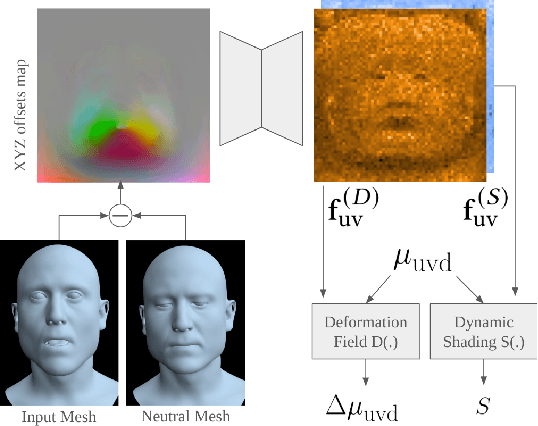
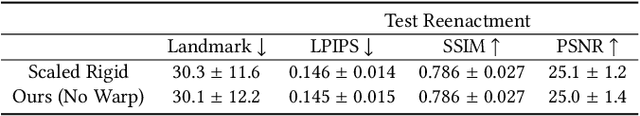
Abstract:Sparse volumetric reconstruction and rendering via 3D Gaussian splatting have recently enabled animatable 3D head avatars that are rendered under arbitrary viewpoints with impressive photorealism. Today, such photoreal avatars are seen as a key component in emerging applications in telepresence, extended reality, and entertainment. Building a photoreal avatar requires estimating the complex non-rigid motion of different facial components as seen in input video images; due to inaccurate motion estimation, animatable models typically present a loss of fidelity and detail when compared to their non-animatable counterparts, built from an individual facial expression. Also, recent state-of-the-art models are often affected by memory limitations that reduce the number of 3D Gaussians used for modeling, leading to lower detail and quality. To address these problems, we present a new high-detail 3D head avatar model that improves upon the state of the art, largely increasing the number of 3D Gaussians and modeling quality for rendering at 4K resolution. Our high-quality model is reconstructed from multiview input video and builds on top of a mesh-based 3D morphable model, which provides a coarse deformation layer for the head. Photoreal appearance is modelled by 3D Gaussians embedded within the continuous UVD tangent space of this mesh, allowing for more effective densification where most needed. Additionally, these Gaussians are warped by a novel UVD deformation field to capture subtle, localized motion. Our key contribution is the novel deformable Gaussian encoding and overall fitting procedure that allows our head model to preserve appearance detail, while capturing facial motion and other transient high-frequency features such as skin wrinkling.
Cafca: High-quality Novel View Synthesis of Expressive Faces from Casual Few-shot Captures
Oct 01, 2024
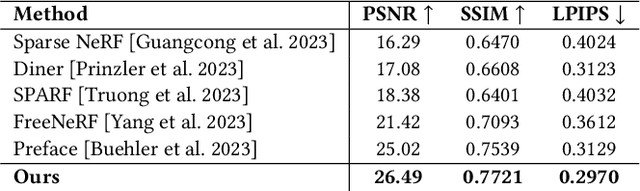
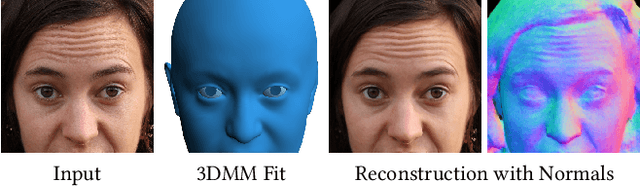
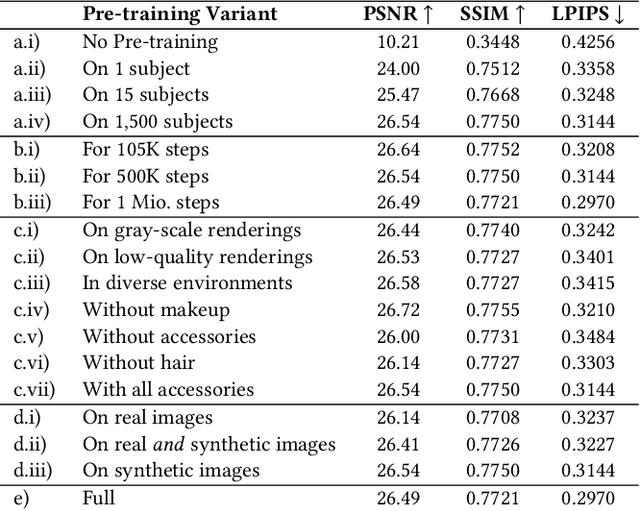
Abstract:Volumetric modeling and neural radiance field representations have revolutionized 3D face capture and photorealistic novel view synthesis. However, these methods often require hundreds of multi-view input images and are thus inapplicable to cases with less than a handful of inputs. We present a novel volumetric prior on human faces that allows for high-fidelity expressive face modeling from as few as three input views captured in the wild. Our key insight is that an implicit prior trained on synthetic data alone can generalize to extremely challenging real-world identities and expressions and render novel views with fine idiosyncratic details like wrinkles and eyelashes. We leverage a 3D Morphable Face Model to synthesize a large training set, rendering each identity with different expressions, hair, clothing, and other assets. We then train a conditional Neural Radiance Field prior on this synthetic dataset and, at inference time, fine-tune the model on a very sparse set of real images of a single subject. On average, the fine-tuning requires only three inputs to cross the synthetic-to-real domain gap. The resulting personalized 3D model reconstructs strong idiosyncratic facial expressions and outperforms the state-of-the-art in high-quality novel view synthesis of faces from sparse inputs in terms of perceptual and photo-metric quality.
Egocentric Whole-Body Motion Capture with FisheyeViT and Diffusion-Based Motion Refinement
Dec 02, 2023
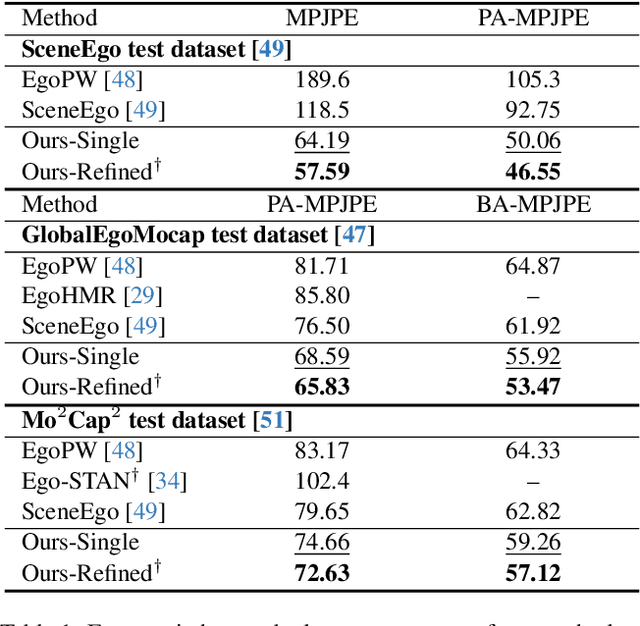
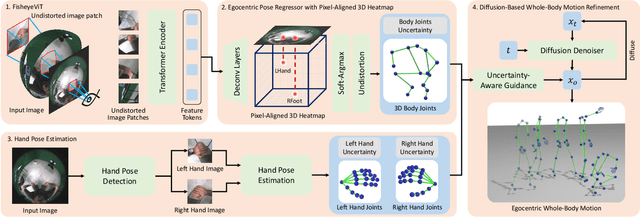
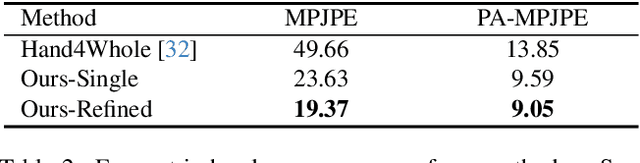
Abstract:In this work, we explore egocentric whole-body motion capture using a single fisheye camera, which simultaneously estimates human body and hand motion. This task presents significant challenges due to three factors: the lack of high-quality datasets, fisheye camera distortion, and human body self-occlusion. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that leverages FisheyeViT to extract fisheye image features, which are subsequently converted into pixel-aligned 3D heatmap representations for 3D human body pose prediction. For hand tracking, we incorporate dedicated hand detection and hand pose estimation networks for regressing 3D hand poses. Finally, we develop a diffusion-based whole-body motion prior model to refine the estimated whole-body motion while accounting for joint uncertainties. To train these networks, we collect a large synthetic dataset, EgoWholeBody, comprising 840,000 high-quality egocentric images captured across a diverse range of whole-body motion sequences. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing high-quality whole-body motion estimates from a single egocentric camera.
Preface: A Data-driven Volumetric Prior for Few-shot Ultra High-resolution Face Synthesis
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:NeRFs have enabled highly realistic synthesis of human faces including complex appearance and reflectance effects of hair and skin. These methods typically require a large number of multi-view input images, making the process hardware intensive and cumbersome, limiting applicability to unconstrained settings. We propose a novel volumetric human face prior that enables the synthesis of ultra high-resolution novel views of subjects that are not part of the prior's training distribution. This prior model consists of an identity-conditioned NeRF, trained on a dataset of low-resolution multi-view images of diverse humans with known camera calibration. A simple sparse landmark-based 3D alignment of the training dataset allows our model to learn a smooth latent space of geometry and appearance despite a limited number of training identities. A high-quality volumetric representation of a novel subject can be obtained by model fitting to 2 or 3 camera views of arbitrary resolution. Importantly, our method requires as few as two views of casually captured images as input at inference time.
Learning Personalized High Quality Volumetric Head Avatars from Monocular RGB Videos
Apr 04, 2023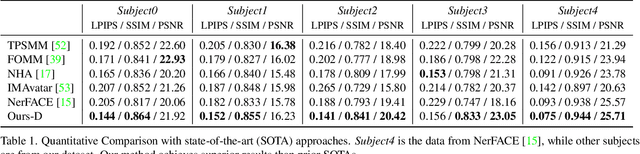
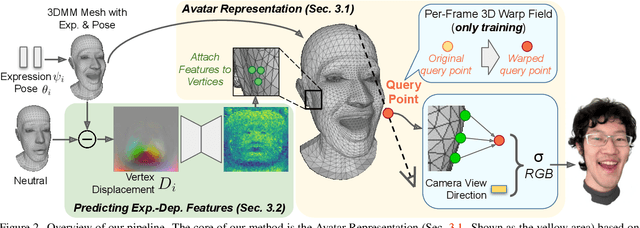
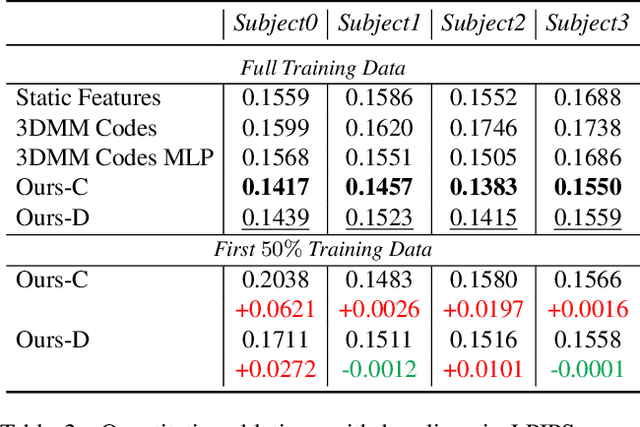
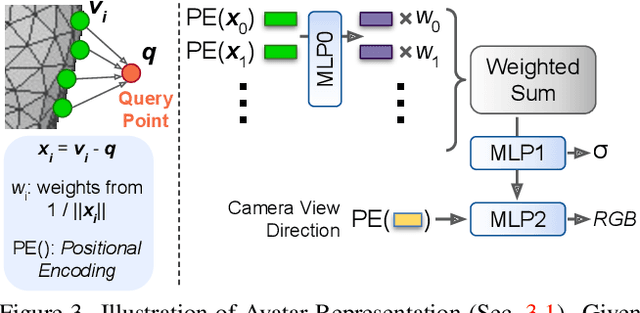
Abstract:We propose a method to learn a high-quality implicit 3D head avatar from a monocular RGB video captured in the wild. The learnt avatar is driven by a parametric face model to achieve user-controlled facial expressions and head poses. Our hybrid pipeline combines the geometry prior and dynamic tracking of a 3DMM with a neural radiance field to achieve fine-grained control and photorealism. To reduce over-smoothing and improve out-of-model expressions synthesis, we propose to predict local features anchored on the 3DMM geometry. These learnt features are driven by 3DMM deformation and interpolated in 3D space to yield the volumetric radiance at a designated query point. We further show that using a Convolutional Neural Network in the UV space is critical in incorporating spatial context and producing representative local features. Extensive experiments show that we are able to reconstruct high-quality avatars, with more accurate expression-dependent details, good generalization to out-of-training expressions, and quantitatively superior renderings compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
Scene-aware Egocentric 3D Human Pose Estimation
Dec 20, 2022
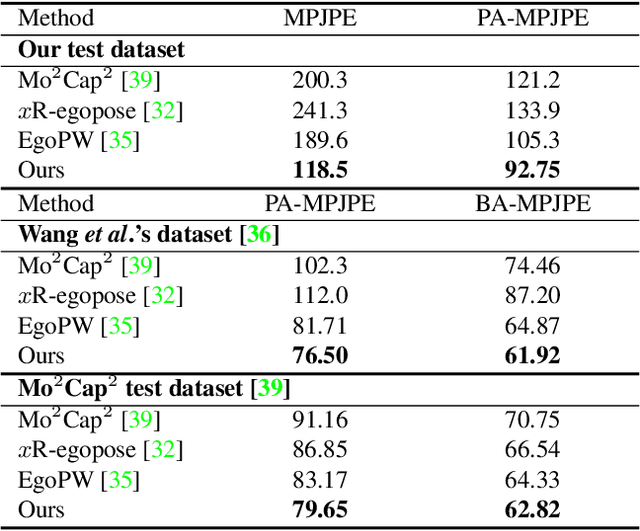
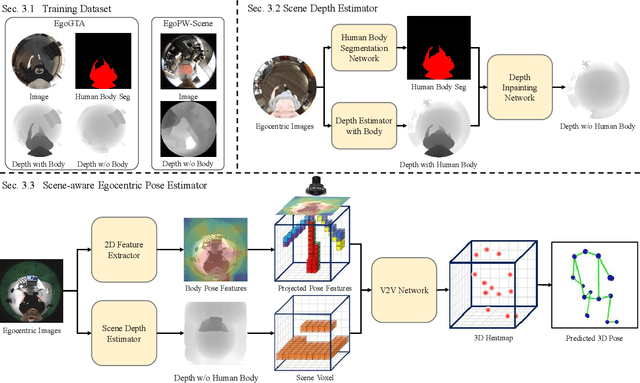

Abstract:Egocentric 3D human pose estimation with a single head-mounted fisheye camera has recently attracted attention due to its numerous applications in virtual and augmented reality. Existing methods still struggle in challenging poses where the human body is highly occluded or is closely interacting with the scene. To address this issue, we propose a scene-aware egocentric pose estimation method that guides the prediction of the egocentric pose with scene constraints. To this end, we propose an egocentric depth estimation network to predict the scene depth map from a wide-view egocentric fisheye camera while mitigating the occlusion of the human body with a depth-inpainting network. Next, we propose a scene-aware pose estimation network that projects the 2D image features and estimated depth map of the scene into a voxel space and regresses the 3D pose with a V2V network. The voxel-based feature representation provides the direct geometric connection between 2D image features and scene geometry, and further facilitates the V2V network to constrain the predicted pose based on the estimated scene geometry. To enable the training of the aforementioned networks, we also generated a synthetic dataset, called EgoGTA, and an in-the-wild dataset based on EgoPW, called EgoPW-Scene. The experimental results of our new evaluation sequences show that the predicted 3D egocentric poses are accurate and physically plausible in terms of human-scene interaction, demonstrating that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Estimating Egocentric 3D Human Pose in the Wild with External Weak Supervision
Jan 20, 2022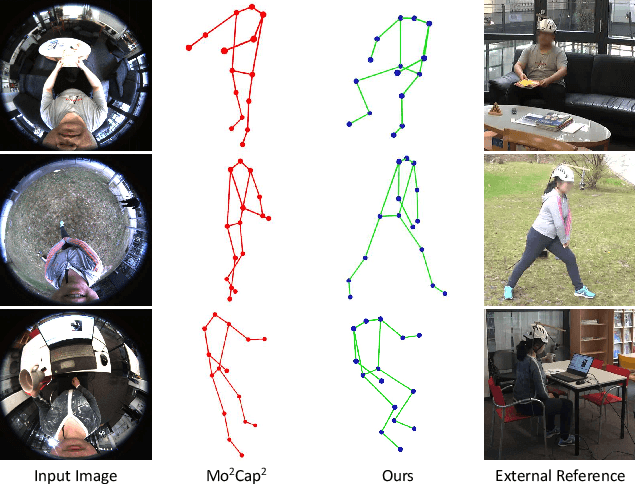
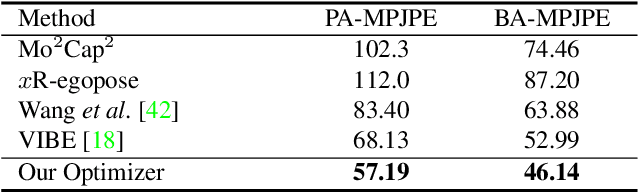
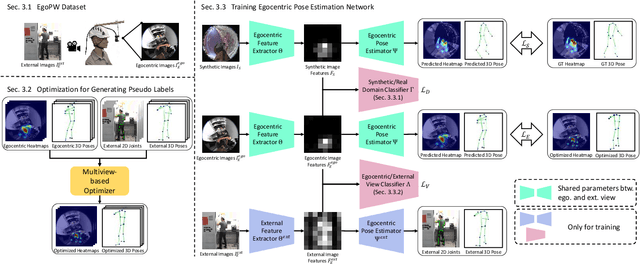
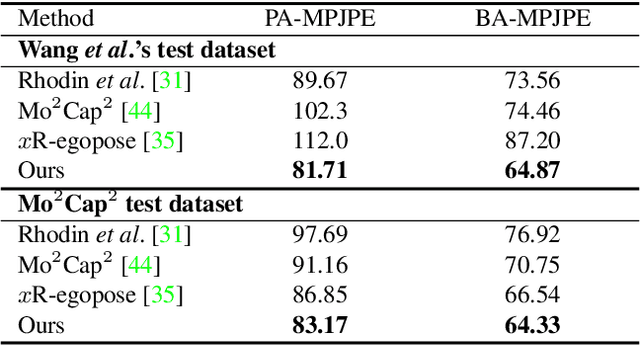
Abstract:Egocentric 3D human pose estimation with a single fisheye camera has drawn a significant amount of attention recently. However, existing methods struggle with pose estimation from in-the-wild images, because they can only be trained on synthetic data due to the unavailability of large-scale in-the-wild egocentric datasets. Furthermore, these methods easily fail when the body parts are occluded by or interacting with the surrounding scene. To address the shortage of in-the-wild data, we collect a large-scale in-the-wild egocentric dataset called Egocentric Poses in the Wild (EgoPW). This dataset is captured by a head-mounted fisheye camera and an auxiliary external camera, which provides an additional observation of the human body from a third-person perspective during training. We present a new egocentric pose estimation method, which can be trained on the new dataset with weak external supervision. Specifically, we first generate pseudo labels for the EgoPW dataset with a spatio-temporal optimization method by incorporating the external-view supervision. The pseudo labels are then used to train an egocentric pose estimation network. To facilitate the network training, we propose a novel learning strategy to supervise the egocentric features with the high-quality features extracted by a pretrained external-view pose estimation model. The experiments show that our method predicts accurate 3D poses from a single in-the-wild egocentric image and outperforms the state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively.
EgoRenderer: Rendering Human Avatars from Egocentric Camera Images
Nov 24, 2021
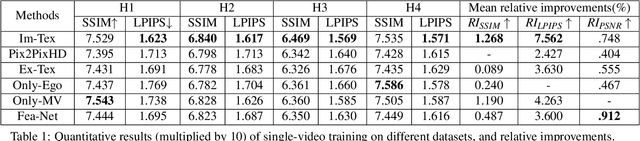
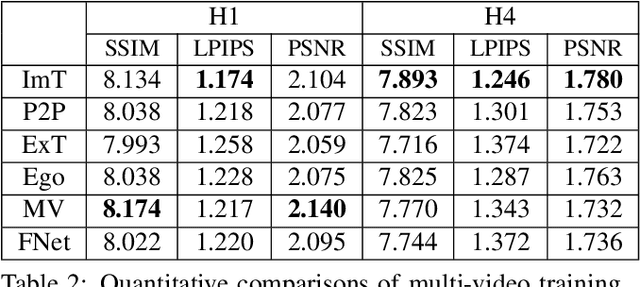
Abstract:We present EgoRenderer, a system for rendering full-body neural avatars of a person captured by a wearable, egocentric fisheye camera that is mounted on a cap or a VR headset. Our system renders photorealistic novel views of the actor and her motion from arbitrary virtual camera locations. Rendering full-body avatars from such egocentric images come with unique challenges due to the top-down view and large distortions. We tackle these challenges by decomposing the rendering process into several steps, including texture synthesis, pose construction, and neural image translation. For texture synthesis, we propose Ego-DPNet, a neural network that infers dense correspondences between the input fisheye images and an underlying parametric body model, and to extract textures from egocentric inputs. In addition, to encode dynamic appearances, our approach also learns an implicit texture stack that captures detailed appearance variation across poses and viewpoints. For correct pose generation, we first estimate body pose from the egocentric view using a parametric model. We then synthesize an external free-viewpoint pose image by projecting the parametric model to the user-specified target viewpoint. We next combine the target pose image and the textures into a combined feature image, which is transformed into the output color image using a neural image translation network. Experimental evaluations show that EgoRenderer is capable of generating realistic free-viewpoint avatars of a person wearing an egocentric camera. Comparisons to several baselines demonstrate the advantages of our approach.
Neural Actor: Neural Free-view Synthesis of Human Actors with Pose Control
Jun 03, 2021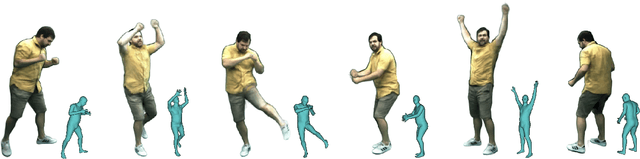
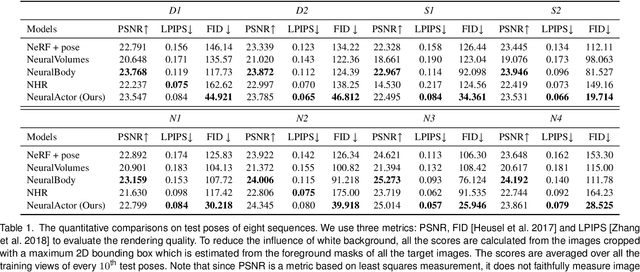
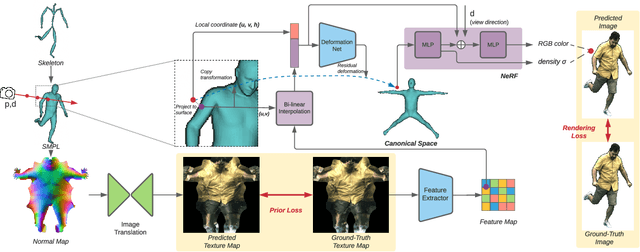
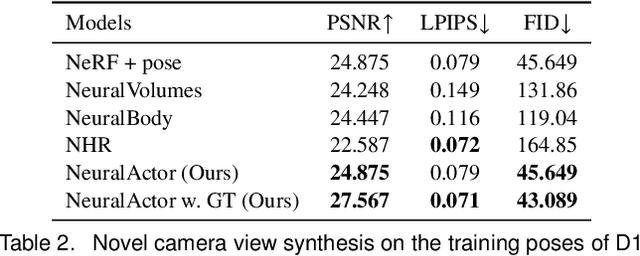
Abstract:We propose Neural Actor (NA), a new method for high-quality synthesis of humans from arbitrary viewpoints and under arbitrary controllable poses. Our method is built upon recent neural scene representation and rendering works which learn representations of geometry and appearance from only 2D images. While existing works demonstrated compelling rendering of static scenes and playback of dynamic scenes, photo-realistic reconstruction and rendering of humans with neural implicit methods, in particular under user-controlled novel poses, is still difficult. To address this problem, we utilize a coarse body model as the proxy to unwarp the surrounding 3D space into a canonical pose. A neural radiance field learns pose-dependent geometric deformations and pose- and view-dependent appearance effects in the canonical space from multi-view video input. To synthesize novel views of high fidelity dynamic geometry and appearance, we leverage 2D texture maps defined on the body model as latent variables for predicting residual deformations and the dynamic appearance. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves better quality than the state-of-the-arts on playback as well as novel pose synthesis, and can even generalize well to new poses that starkly differ from the training poses. Furthermore, our method also supports body shape control of the synthesized results.
Estimating Egocentric 3D Human Pose in Global Space
Apr 30, 2021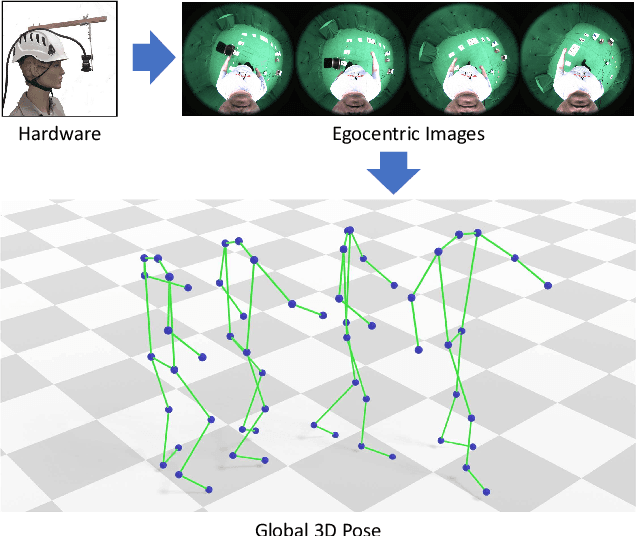
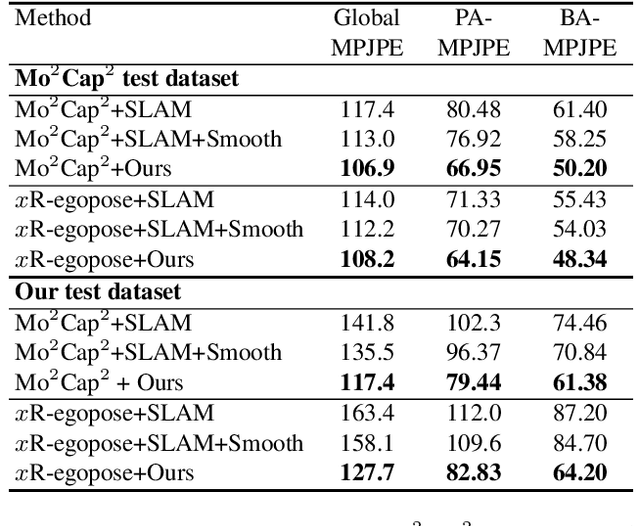
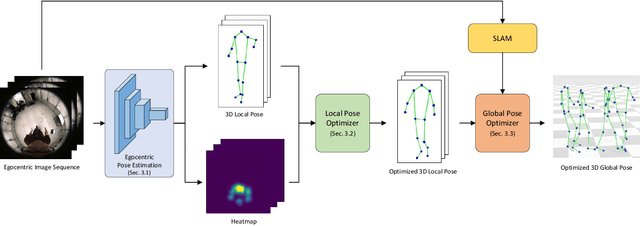
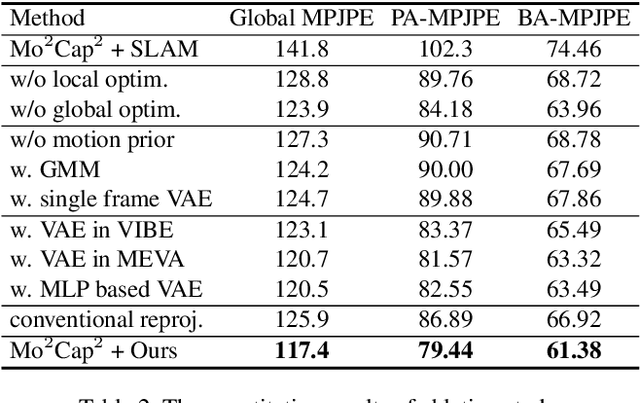
Abstract:Egocentric 3D human pose estimation using a single fisheye camera has become popular recently as it allows capturing a wide range of daily activities in unconstrained environments, which is difficult for traditional outside-in motion capture with external cameras. However, existing methods have several limitations. A prominent problem is that the estimated poses lie in the local coordinate system of the fisheye camera, rather than in the world coordinate system, which is restrictive for many applications. Furthermore, these methods suffer from limited accuracy and temporal instability due to ambiguities caused by the monocular setup and the severe occlusion in a strongly distorted egocentric perspective. To tackle these limitations, we present a new method for egocentric global 3D body pose estimation using a single head-mounted fisheye camera. To achieve accurate and temporally stable global poses, a spatio-temporal optimization is performed over a sequence of frames by minimizing heatmap reprojection errors and enforcing local and global body motion priors learned from a mocap dataset. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods both quantitatively and qualitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge