Jiaxi Liu
HERMES: A Holistic End-to-End Risk-Aware Multimodal Embodied System with Vision-Language Models for Long-Tail Autonomous Driving
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving models increasingly benefit from large vision--language models for semantic understanding, yet ensuring safe and accurate operation under long-tail conditions remains challenging. These challenges are particularly prominent in long-tail mixed-traffic scenarios, where autonomous vehicles must interact with heterogeneous road users, including human-driven vehicles and vulnerable road users, under complex and uncertain conditions. This paper proposes HERMES, a holistic risk-aware end-to-end multimodal driving framework designed to inject explicit long-tail risk cues into trajectory planning. HERMES employs a foundation-model-assisted annotation pipeline to produce structured Long-Tail Scene Context and Long-Tail Planning Context, capturing hazard-centric cues together with maneuver intent and safety preference, and uses these signals to guide end-to-end planning. HERMES further introduces a Tri-Modal Driving Module that fuses multi-view perception, historical motion cues, and semantic guidance, ensuring risk-aware accurate trajectory planning under long-tail scenarios. Experiments on the real-world long-tail dataset demonstrate that HERMES consistently outperforms representative end-to-end and VLM-driven baselines under long-tail mixed-traffic scenarios. Ablation studies verify the complementary contributions of key components.
Towards Practical Large-scale Dynamical Heterogeneous Graph Embedding: Cold-start Resilient Recommendation
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Deploying dynamic heterogeneous graph embeddings in production faces key challenges of scalability, data freshness, and cold-start. This paper introduces a practical, two-stage solution that balances deep graph representation with low-latency incremental updates. Our framework combines HetSGFormer, a scalable graph transformer for static learning, with Incremental Locally Linear Embedding (ILLE), a lightweight, CPU-based algorithm for real-time updates. HetSGFormer captures global structure with linear scalability, while ILLE provides rapid, targeted updates to incorporate new data, thus avoiding costly full retraining. This dual approach is cold-start resilient, leveraging the graph to create meaningful embeddings from sparse data. On billion-scale graphs, A/B tests show HetSGFormer achieved up to a 6.11% lift in Advertiser Value over previous methods, while the ILLE module added another 3.22% lift and improved embedding refresh timeliness by 83.2%. Our work provides a validated framework for deploying dynamic graph learning in production environments.
CATS-V2V: A Real-World Vehicle-to-Vehicle Cooperative Perception Dataset with Complex Adverse Traffic Scenarios
Nov 14, 2025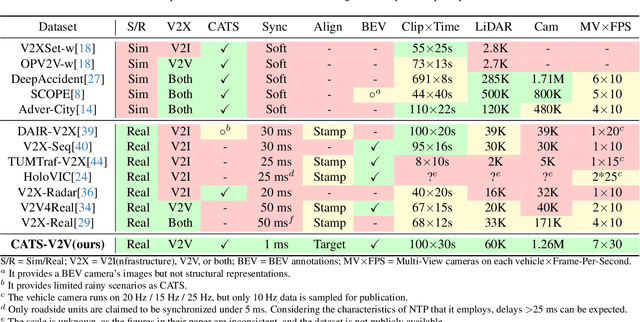

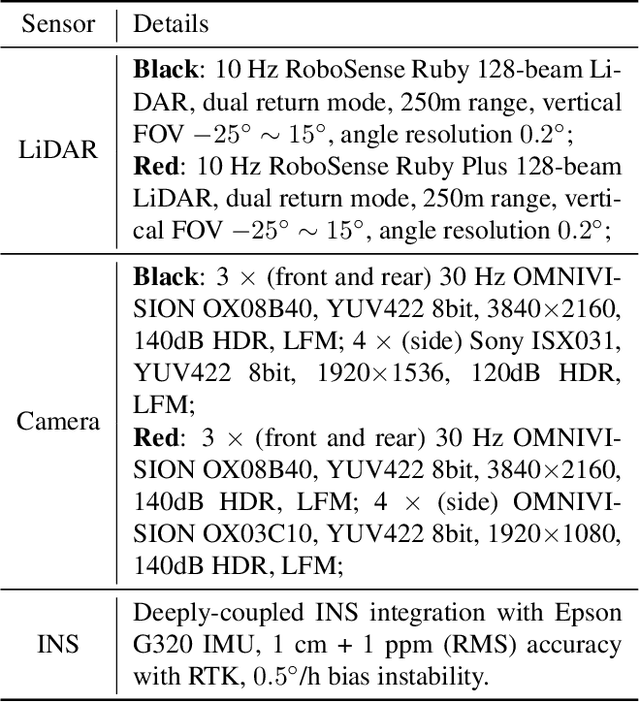
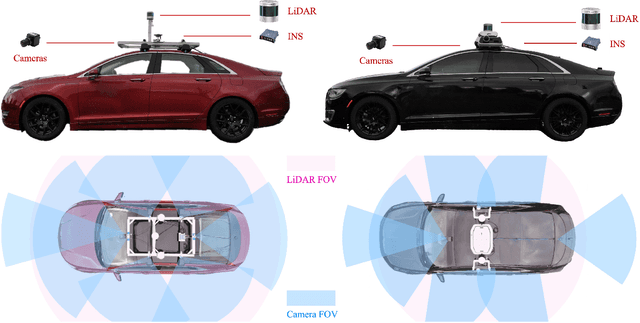
Abstract:Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) cooperative perception has great potential to enhance autonomous driving performance by overcoming perception limitations in complex adverse traffic scenarios (CATS). Meanwhile, data serves as the fundamental infrastructure for modern autonomous driving AI. However, due to stringent data collection requirements, existing datasets focus primarily on ordinary traffic scenarios, constraining the benefits of cooperative perception. To address this challenge, we introduce CATS-V2V, the first-of-its-kind real-world dataset for V2V cooperative perception under complex adverse traffic scenarios. The dataset was collected by two hardware time-synchronized vehicles, covering 10 weather and lighting conditions across 10 diverse locations. The 100-clip dataset includes 60K frames of 10 Hz LiDAR point clouds and 1.26M multi-view 30 Hz camera images, along with 750K anonymized yet high-precision RTK-fixed GNSS and IMU records. Correspondingly, we provide time-consistent 3D bounding box annotations for objects, as well as static scenes to construct a 4D BEV representation. On this basis, we propose a target-based temporal alignment method, ensuring that all objects are precisely aligned across all sensor modalities. We hope that CATS-V2V, the largest-scale, most supportive, and highest-quality dataset of its kind to date, will benefit the autonomous driving community in related tasks.
FollowGen: A Scaled Noise Conditional Diffusion Model for Car-Following Trajectory Prediction
Nov 23, 2024



Abstract:Vehicle trajectory prediction is crucial for advancing autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Although deep learning-based approaches - especially those utilizing transformer-based and generative models - have markedly improved prediction accuracy by capturing complex, non-linear patterns in vehicle dynamics and traffic interactions, they frequently overlook detailed car-following behaviors and the inter-vehicle interactions critical for real-world driving applications, particularly in fully autonomous or mixed traffic scenarios. To address the issue, this study introduces a scaled noise conditional diffusion model for car-following trajectory prediction, which integrates detailed inter-vehicular interactions and car-following dynamics into a generative framework, improving both the accuracy and plausibility of predicted trajectories. The model utilizes a novel pipeline to capture historical vehicle dynamics by scaling noise with encoded historical features within the diffusion process. Particularly, it employs a cross-attention-based transformer architecture to model intricate inter-vehicle dependencies, effectively guiding the denoising process and enhancing prediction accuracy. Experimental results on diverse real-world driving scenarios demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance and robustness of the proposed method.
Local map Construction Methods with SD map: A Novel Survey
Sep 04, 2024Abstract:In recent years, significant academic advancements have been made in the field of autonomous vehicles, with Local maps emerging as a crucial component of autonomous driving technology. Local maps not only provide intricate details of road networks but also serve as fundamental inputs for critical tasks such as vehicle localization, navigation, and decision-making. Given the characteristics of SD map (Standard Definition Map), which include low cost, ease of acquisition, and high versatility, perception methods that integrate SD map as prior information have demonstrated significant potential in the field of Local map perception. The purpose of this paper is to provide researchers with a comprehensive overview and summary of the latest advancements in the integration of SD map as prior information for Local map perception methods. This review begins by introducing the task definition and general pipeline of local map perception methods that incorporate SD maps as prior information, along with relevant public datasets. And then it focuses on the representation and encoding methods of multi-source information, as well as the methods for fusing multi-source information. In response to this burgeoning trend, this article presents a comprehensive and meticulous overview of the diverse research efforts in this particular field. Finally, the article addresses pertinent issues and future challenges with the aim of guiding researchers in understanding the current trends and methodologies prevalent in the field.
Risk Occupancy: A New and Efficient Paradigm through Vehicle-Road-Cloud Collaboration
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:This study introduces the 4D Risk Occupancy within a vehicle-road-cloud architecture, integrating the road surface spatial, risk, and temporal dimensions, and endowing the algorithm with beyond-line-of-sight, all-angles, and efficient abilities. The algorithm simplifies risk modeling by focusing on directly observable information and key factors, drawing on the concept of Occupancy Grid Maps (OGM), and incorporating temporal prediction to effectively map current and future risk occupancy. Compared to conventional driving risk fields and grid occupancy maps, this algorithm can map global risks more efficiently, simply, and reliably. It can integrate future risk information, adapting to dynamic traffic environments. The 4D Risk Occupancy also unifies the expression of BEV detection and lane line detection results, enhancing the intuitiveness and unity of environmental perception. Using DAIR-V2X data, this paper validates the 4D Risk Occupancy algorithm and develops a local path planning model based on it. Qualitative experiments under various road conditions demonstrate the practicality and robustness of this local path planning model. Quantitative analysis shows that the path planning based on risk occupation significantly improves trajectory planning performance, increasing safety redundancy by 12.5% and reducing average deceleration by 5.41% at an initial braking speed of 8 m/s, thereby improving safety and comfort. This work provides a new global perception method and local path planning method through Vehicle-Road-Cloud architecture, offering a new perceptual paradigm for achieving safer and more efficient autonomous driving.
VLM-MPC: Vision Language Foundation Model (VLM)-Guided Model Predictive Controller (MPC) for Autonomous Driving
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Motivated by the emergent reasoning capabilities of Vision Language Models (VLMs) and its potential to improve the comprehensibility of autonomous driving systems, this paper introduces a closed-loop autonomous driving controller called VLM-MPC, which combines a VLM for high-level decision-making and a Model Predictive Controller (MPC) for low-level vehicle control. The proposed VLM-MPC system is structurally divided into two asynchronous components: an upper-level VLM and a lower-level MPC. The upper layer VLM generates driving parameters for lower-level control based on front camera images, ego vehicle state, traffic environment conditions, and reference memory. The lower-level MPC controls the vehicle in real-time using these parameters, considering engine lag and providing state feedback to the entire system. Experiments based on the nuScenes dataset validated the effectiveness of the proposed VLM-MPC system across various scenarios (e.g., night, rain, intersections). Results showed that the VLM-MPC system consistently outperformed baseline models in terms of safety and driving comfort. By comparing behaviors under different weather conditions and scenarios, we demonstrated the VLM's ability to understand the environment and make reasonable inferences.
AI-powered Covert Botnet Command and Control on OSNs
Sep 22, 2020

Abstract:Botnet is one of the major threats to computer security. In previous botnet command and control (C&C) scenarios using online social networks (OSNs), methods for finding botmasters (e.g. ids, links, DGAs, etc.) are hardcoded into bots. Once a bot is reverse engineered, botmaster is exposed. Meanwhile, abnormal contents from explicit commands may expose botmaster and raise anomalies on OSNs. To overcome these deficiencies, we propose an AI-powered covert C&C channel. On leverage of neural networks, bots can find botmasters by avatars, which are converted into feature vectors. Commands are embedded into normal contents (e.g. tweets, comments, etc.) using text data augmentation and hash collision. Experiment on Twitter shows that the command-embedded contents can be generated efficiently, and bots can find botmaster and obtain commands accurately. By demonstrating how AI may help promote a covert communication on OSNs, this work provides a new perspective on botnet detection and confrontation.
Dynamic Pricing on E-commerce Platform with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 05, 2019



Abstract:In this paper we present an end-to-end framework for addressing the problem of dynamic pricing on E-commerce platform using methods based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL). By using four groups of different business data to represent the states of each time period, we model the dynamic pricing problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP). Compared with the state-of-the-art DRL-based dynamic pricing algorithms, our approaches make the following three contributions. First, we extend the discrete set problem to the continuous price set. Second, instead of using revenue as the reward function directly, we define a new function named difference of revenue conversion rates (DRCR). Third, the cold-start problem of MDP is tackled by pre-training and evaluation using some carefully chosen historical sales data. Our approaches are evaluated by both offline evaluation method using real dataset of Alibaba Inc., and online field experiments on Tmall.com, a major online shopping website owned by Alibaba Inc.. In particular, experiment results suggest that DRCR is a more appropriate reward function than revenue, which is widely used by current literature. In the end, field experiments, which last for months on 1000 stock keeping units (SKUs) of products demonstrate that continuous price sets have better performance than discrete sets and show that our approaches significantly outperformed the manual pricing by operation experts.
Context-Based Dynamic Pricing with Online Clustering
Feb 17, 2019



Abstract:We consider a context-based dynamic pricing problem of online products which have low sales. Sales data from Alibaba, a major global online retailer, illustrate the prevalence of low-sale products. For these products, existing single-product dynamic pricing algorithms do not work well due to insufficient data samples. To address this challenge, we propose pricing policies that concurrently perform clustering over products and set individual pricing decisions on the fly. By clustering data and identifying products that have similar demand patterns, we utilize sales data from products within the same cluster to improve demand estimation and allow for better pricing decisions. We evaluate the algorithms using the regret, and the result shows that when product demand functions come from multiple clusters, our algorithms significantly outperform traditional single-product pricing policies. Numerical experiments using a real dataset from Alibaba demonstrate that the proposed policies, compared with several benchmark policies, increase the revenue. The results show that online clustering is an effective approach to tackling dynamic pricing problems associated with low-sale products. Our algorithms were further implemented in a field study at Alibaba with 40 products for 30 consecutive days, and compared to the products which use business-as-usual pricing policy of Alibaba. The results from the field experiment show that the overall revenue increased by 10.14%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge