Jianfeng Zhu
Understanding Risk and Dependency in AI Chatbot Use from User Discourse
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Generative AI systems are increasingly embedded in everyday life, yet empirical understanding of how psychological risk associated with AI use emerges, is experienced, and is regulated by users remains limited. We present a large-scale computational thematic analysis of posts collected between 2023 and 2025 from two Reddit communities, r/AIDangers and r/ChatbotAddiction, explicitly focused on AI-related harm and distress. Using a multi-agent, LLM-assisted thematic analysis grounded in Braun and Clarke's reflexive framework, we identify 14 recurring thematic categories and synthesize them into five higher-order experiential dimensions. To further characterize affective patterns, we apply emotion labeling using a BERT-based classifier and visualize emotional profiles across dimensions. Our findings reveal five empirically derived experiential dimensions of AI-related psychological risk grounded in real-world user discourse, with self-regulation difficulties emerging as the most prevalent and fear concentrated in concerns related to autonomy, control, and technical risk. These results provide early empirical evidence from lived user experience of how AI safety is perceived and emotionally experienced outside laboratory or speculative contexts, offering a foundation for future AI safety research, evaluation, and responsible governance.
A Unified Geometric Field Theory Framework for Transformers: From Manifold Embeddings to Kernel Modulation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:The Transformer architecture has achieved tremendous success in natural language processing, computer vision, and scientific computing through its self-attention mechanism. However, its core components-positional encoding and attention mechanisms-have lacked a unified physical or mathematical interpretation. This paper proposes a structural theoretical framework that integrates positional encoding, kernel integral operators, and attention mechanisms for in-depth theoretical investigation. We map discrete positions (such as text token indices and image pixel coordinates) to spatial functions on continuous manifolds, enabling a field-theoretic interpretation of Transformer layers as kernel-modulated operators acting over embedded manifolds.
Evaluating LLM Alignment on Personality Inference from Real-World Interview Data
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in roles requiring nuanced psychological understanding, such as emotional support agents, counselors, and decision-making assistants. However, their ability to interpret human personality traits, a critical aspect of such applications, remains unexplored, particularly in ecologically valid conversational settings. While prior work has simulated LLM "personas" using discrete Big Five labels on social media data, the alignment of LLMs with continuous, ground-truth personality assessments derived from natural interactions is largely unexamined. To address this gap, we introduce a novel benchmark comprising semi-structured interview transcripts paired with validated continuous Big Five trait scores. Using this dataset, we systematically evaluate LLM performance across three paradigms: (1) zero-shot and chain-of-thought prompting with GPT-4.1 Mini, (2) LoRA-based fine-tuning applied to both RoBERTa and Meta-LLaMA architectures, and (3) regression using static embeddings from pretrained BERT and OpenAI's text-embedding-3-small. Our results reveal that all Pearson correlations between model predictions and ground-truth personality traits remain below 0.26, highlighting the limited alignment of current LLMs with validated psychological constructs. Chain-of-thought prompting offers minimal gains over zero-shot, suggesting that personality inference relies more on latent semantic representation than explicit reasoning. These findings underscore the challenges of aligning LLMs with complex human attributes and motivate future work on trait-specific prompting, context-aware modeling, and alignment-oriented fine-tuning.
Can Large Language Models Understand Intermediate Representations?
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Intermediate Representations (IRs) are essential in compiler design and program analysis, yet their comprehension by Large Language Models (LLMs) remains underexplored. This paper presents a pioneering empirical study to investigate the capabilities of LLMs, including GPT-4, GPT-3, Gemma 2, LLaMA 3.1, and Code Llama, in understanding IRs. We analyze their performance across four tasks: Control Flow Graph (CFG) reconstruction, decompilation, code summarization, and execution reasoning. Our results indicate that while LLMs demonstrate competence in parsing IR syntax and recognizing high-level structures, they struggle with control flow reasoning, execution semantics, and loop handling. Specifically, they often misinterpret branching instructions, omit critical IR operations, and rely on heuristic-based reasoning, leading to errors in CFG reconstruction, IR decompilation, and execution reasoning. The study underscores the necessity for IR-specific enhancements in LLMs, recommending fine-tuning on structured IR datasets and integration of explicit control flow models to augment their comprehension and handling of IR-related tasks.
Leveraging Large Language Models to Analyze Emotional and Contextual Drivers of Teen Substance Use in Online Discussions
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:Adolescence is a critical stage often linked to risky behaviors, including substance use, with significant developmental and public health implications. Social media provides a lens into adolescent self-expression, but interpreting emotional and contextual signals remains complex. This study applies Large Language Models (LLMs) to analyze adolescents' social media posts, uncovering emotional patterns (e.g., sadness, guilt, fear, joy) and contextual factors (e.g., family, peers, school) related to substance use. Heatmap and machine learning analyses identified key predictors of substance use-related posts. Negative emotions like sadness and guilt were significantly more frequent in substance use contexts, with guilt acting as a protective factor, while shame and peer influence heightened substance use risk. Joy was more common in non-substance use discussions. Peer influence correlated strongly with sadness, fear, and disgust, while family and school environments aligned with non-substance use. Findings underscore the importance of addressing emotional vulnerabilities and contextual influences, suggesting that collaborative interventions involving families, schools, and communities can reduce risk factors and foster healthier adolescent development.
Investigating Large Language Models in Inferring Personality Traits from User Conversations
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are demonstrating remarkable human like capabilities across diverse domains, including psychological assessment. This study evaluates whether LLMs, specifically GPT-4o and GPT-4o mini, can infer Big Five personality traits and generate Big Five Inventory-10 (BFI-10) item scores from user conversations under zero-shot prompting conditions. Our findings reveal that incorporating an intermediate step--prompting for BFI-10 item scores before calculating traits--enhances accuracy and aligns more closely with the gold standard than direct trait inference. This structured approach underscores the importance of leveraging psychological frameworks in improving predictive precision. Additionally, a group comparison based on depressive symptom presence revealed differential model performance. Participants were categorized into two groups: those experiencing at least one depressive symptom and those without symptoms. GPT-4o mini demonstrated heightened sensitivity to depression-related shifts in traits such as Neuroticism and Conscientiousness within the symptom-present group, whereas GPT-4o exhibited strengths in nuanced interpretation across groups. These findings underscore the potential of LLMs to analyze real-world psychological data effectively, offering a valuable foundation for interdisciplinary research at the intersection of artificial intelligence and psychology.
Multi-scale GCN-assisted two-stage network for joint segmentation of retinal layers and disc in peripapillary OCT images
Feb 09, 2021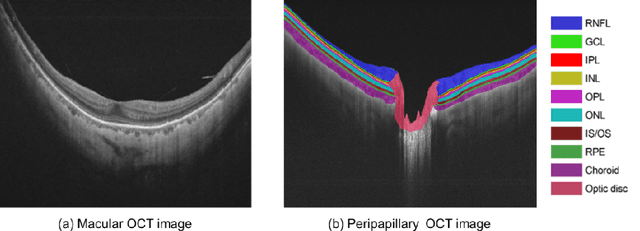
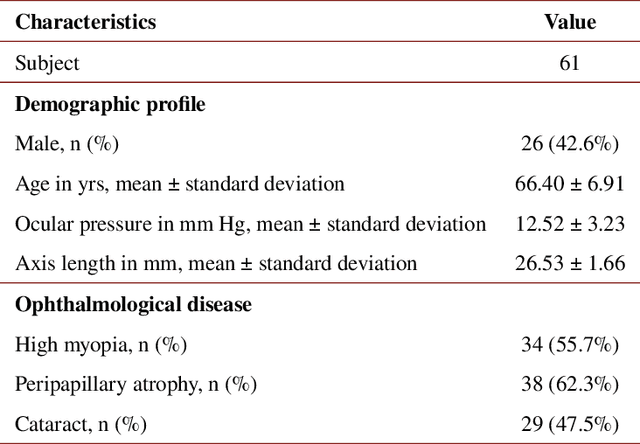
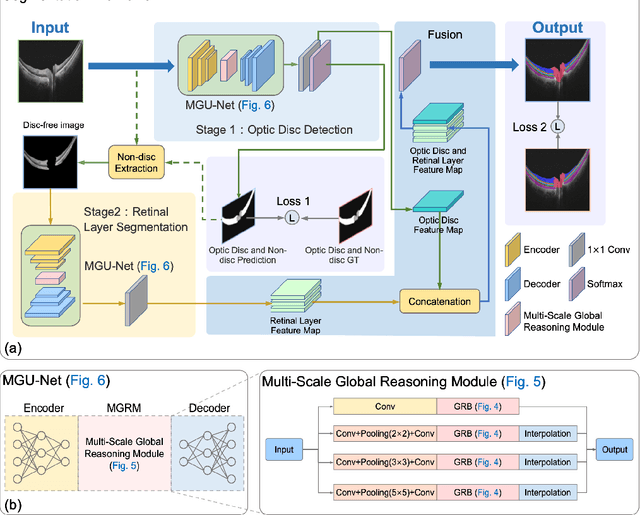
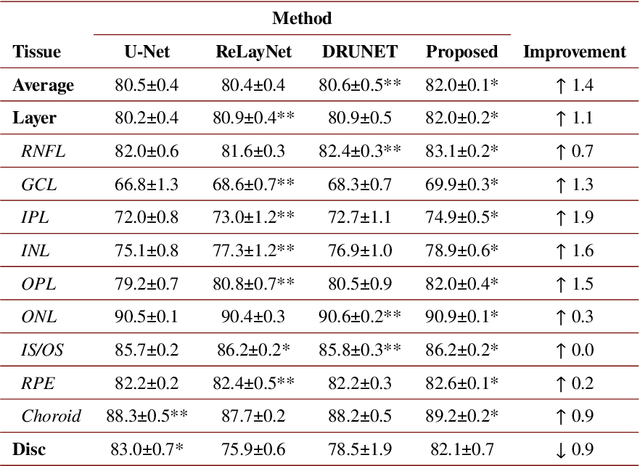
Abstract:An accurate and automated tissue segmentation algorithm for retinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) images is crucial for the diagnosis of glaucoma. However, due to the presence of the optic disc, the anatomical structure of the peripapillary region of the retina is complicated and is challenging for segmentation. To address this issue, we developed a novel graph convolutional network (GCN)-assisted two-stage framework to simultaneously label the nine retinal layers and the optic disc. Specifically, a multi-scale global reasoning module is inserted between the encoder and decoder of a U-shape neural network to exploit anatomical prior knowledge and perform spatial reasoning. We conducted experiments on human peripapillary retinal OCT images. The Dice score of the proposed segmentation network is 0.820$\pm$0.001 and the pixel accuracy is 0.830$\pm$0.002, both of which outperform those from other state-of-the-art techniques.
2nd Place Solution in Google AI Open Images Object Detection Track 2019
Nov 17, 2019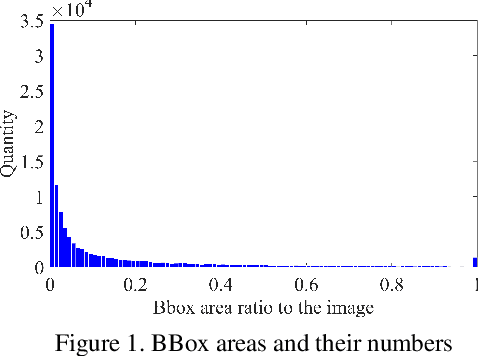
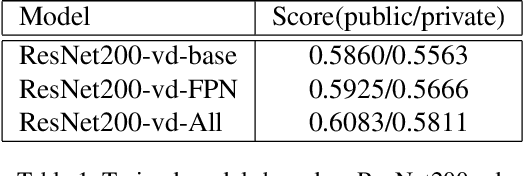


Abstract:We present an object detection framework based on PaddlePaddle. We put all the strategies together (multi-scale training, FPN, Cascade, Dcnv2, Non-local, libra loss) based on ResNet200-vd backbone. Our model score on public leaderboard comes to 0.6269 with single scale test. We proposed a new voting method called top-k voting-nms, based on the SoftNMS detection results. The voting method helps us merge all the models' results more easily and achieve 2nd place in the Google AI Open Images Object Detection Track 2019.
Learning from Large-scale Noisy Web Data with Ubiquitous Reweighting for Image Classification
Nov 02, 2018
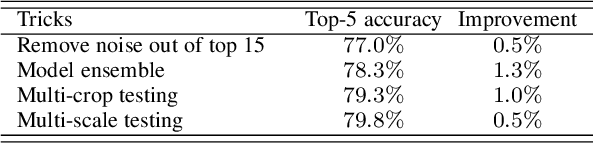
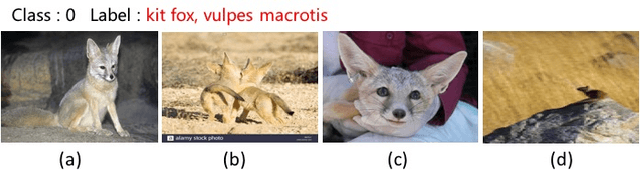

Abstract:Many advances of deep learning techniques originate from the efforts of addressing the image classification task on large-scale datasets. However, the construction of such clean datasets is costly and time-consuming since the Internet is overwhelmed by noisy images with inadequate and inaccurate tags. In this paper, we propose a Ubiquitous Reweighting Network (URNet) that learns an image classification model from large-scale noisy data. By observing the web data, we find that there are five key challenges, \ie, imbalanced class sizes, high intra-classes diversity and inter-class similarity, imprecise instances, insufficient representative instances, and ambiguous class labels. To alleviate these challenges, we assume that every training instance has the potential to contribute positively by alleviating the data bias and noise via reweighting the influence of each instance according to different class sizes, large instance clusters, its confidence, small instance bags and the labels. In this manner, the influence of bias and noise in the web data can be gradually alleviated, leading to the steadily improving performance of URNet. Experimental results in the WebVision 2018 challenge with 16 million noisy training images from 5000 classes show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art models and ranks the first place in the image classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge