Jeongsoo Choi
Semantic-VAE: Semantic-Alignment Latent Representation for Better Speech Synthesis
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:While mel-spectrograms have been widely utilized as intermediate representations in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS), their inherent redundancy leads to inefficiency in learning text-speech alignment. Compact VAE-based latent representations have recently emerged as a stronger alternative, but they also face a fundamental optimization dilemma: higher-dimensional latent spaces improve reconstruction quality and speaker similarity, but degrade intelligibility, while lower-dimensional spaces improve intelligibility at the expense of reconstruction fidelity. To overcome this dilemma, we propose Semantic-VAE, a novel VAE framework that utilizes semantic alignment regularization in the latent space. This design alleviates the reconstruction-generation trade-off by capturing semantic structure in high-dimensional latent representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Semantic-VAE significantly improves synthesis quality and training efficiency. When integrated into F5-TTS, our method achieves 2.10% WER and 0.64 speaker similarity on LibriSpeech-PC, outperforming mel-based systems (2.23%, 0.60) and vanilla acoustic VAE baselines (2.65%, 0.59). We also release the code and models to facilitate further research.
Dub-S2ST: Textless Speech-to-Speech Translation for Seamless Dubbing
May 27, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces a cross-lingual dubbing system that translates speech from one language to another while preserving key characteristics such as duration, speaker identity, and speaking speed. Despite the strong translation quality of existing speech translation approaches, they often overlook the transfer of speech patterns, leading to mismatches with source speech and limiting their suitability for dubbing applications. To address this, we propose a discrete diffusion-based speech-to-unit translation model with explicit duration control, enabling time-aligned translation. We then synthesize speech based on the predicted units and source identity with a conditional flow matching model. Additionally, we introduce a unit-based speed adaptation mechanism that guides the translation model to produce speech at a rate consistent with the source, without relying on any text. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework generates natural and fluent translations that align with the original speech's duration and speaking pace, while achieving competitive translation performance.
Accelerating Diffusion-based Text-to-Speech Model Training with Dual Modality Alignment
May 26, 2025Abstract:The goal of this paper is to optimize the training process of diffusion-based text-to-speech models. While recent studies have achieved remarkable advancements, their training demands substantial time and computational costs, largely due to the implicit guidance of diffusion models in learning complex intermediate representations. To address this, we propose A-DMA, an effective strategy for Accelerating training with Dual Modality Alignment. Our method introduces a novel alignment pipeline leveraging both text and speech modalities: text-guided alignment, which incorporates contextual representations, and speech-guided alignment, which refines semantic representations. By aligning hidden states with discriminative features, our training scheme reduces the reliance on diffusion models for learning complex representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that A-DMA doubles the convergence speed while achieving superior performance over baselines. Code and demo samples are available at: https://github.com/ZhikangNiu/A-DMA
AlignDiT: Multimodal Aligned Diffusion Transformer for Synchronized Speech Generation
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we address the task of multimodal-to-speech generation, which aims to synthesize high-quality speech from multiple input modalities: text, video, and reference audio. This task has gained increasing attention due to its wide range of applications, such as film production, dubbing, and virtual avatars. Despite recent progress, existing methods still suffer from limitations in speech intelligibility, audio-video synchronization, speech naturalness, and voice similarity to the reference speaker. To address these challenges, we propose AlignDiT, a multimodal Aligned Diffusion Transformer that generates accurate, synchronized, and natural-sounding speech from aligned multimodal inputs. Built upon the in-context learning capability of the DiT architecture, AlignDiT explores three effective strategies to align multimodal representations. Furthermore, we introduce a novel multimodal classifier-free guidance mechanism that allows the model to adaptively balance information from each modality during speech synthesis. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AlignDiT significantly outperforms existing methods across multiple benchmarks in terms of quality, synchronization, and speaker similarity. Moreover, AlignDiT exhibits strong generalization capability across various multimodal tasks, such as video-to-speech synthesis and visual forced alignment, consistently achieving state-of-the-art performance. The demo page is available at https://mm.kaist.ac.kr/projects/AlignDiT .
VoiceCraft-Dub: Automated Video Dubbing with Neural Codec Language Models
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:We present VoiceCraft-Dub, a novel approach for automated video dubbing that synthesizes high-quality speech from text and facial cues. This task has broad applications in filmmaking, multimedia creation, and assisting voice-impaired individuals. Building on the success of Neural Codec Language Models (NCLMs) for speech synthesis, our method extends their capabilities by incorporating video features, ensuring that synthesized speech is time-synchronized and expressively aligned with facial movements while preserving natural prosody. To inject visual cues, we design adapters to align facial features with the NCLM token space and introduce audio-visual fusion layers to merge audio-visual information within the NCLM framework. Additionally, we curate CelebV-Dub, a new dataset of expressive, real-world videos specifically designed for automated video dubbing. Extensive experiments show that our model achieves high-quality, intelligible, and natural speech synthesis with accurate lip synchronization, outperforming existing methods in human perception and performing favorably in objective evaluations. We also adapt VoiceCraft-Dub for the video-to-speech task, demonstrating its versatility for various applications.
MAVFlow: Preserving Paralinguistic Elements with Conditional Flow Matching for Zero-Shot AV2AV Multilingual Translation
Mar 14, 2025



Abstract:Despite recent advances in text-to-speech (TTS) models, audio-visual to audio-visual (AV2AV) translation still faces a critical challenge: maintaining speaker consistency between the original and translated vocal and facial features. To address this issue, we propose a conditional flow matching (CFM) zero-shot audio-visual renderer that utilizes strong dual guidance from both audio and visual modalities. By leveraging multi-modal guidance with CFM, our model robustly preserves speaker-specific characteristics and significantly enhances zero-shot AV2AV translation abilities. For the audio modality, we enhance the CFM process by integrating robust speaker embeddings with x-vectors, which serve to bolster speaker consistency. Additionally, we convey emotional nuances to the face rendering module. The guidance provided by both audio and visual cues remains independent of semantic or linguistic content, allowing our renderer to effectively handle zero-shot translation tasks for monolingual speakers in different languages. We empirically demonstrate that the inclusion of high-quality mel-spectrograms conditioned on facial information not only enhances the quality of the synthesized speech but also positively influences facial generation, leading to overall performance improvements.
Deep Understanding of Sign Language for Sign to Subtitle Alignment
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:The objective of this work is to align asynchronous subtitles in sign language videos with limited labelled data. To achieve this goal, we propose a novel framework with the following contributions: (1) we leverage fundamental grammatical rules of British Sign Language (BSL) to pre-process the input subtitles, (2) we design a selective alignment loss to optimise the model for predicting the temporal location of signs only when the queried sign actually occurs in a scene, and (3) we conduct self-training with refined pseudo-labels which are more accurate than the heuristic audio-aligned labels. From this, our model not only better understands the correlation between the text and the signs, but also holds potential for application in the translation of sign languages, particularly in scenarios where manual labelling of large-scale sign data is impractical or challenging. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results, surpassing previous baselines by substantial margins in terms of both frame-level accuracy and F1-score. This highlights the effectiveness and practicality of our framework in advancing the field of sign language video alignment and translation.
V2SFlow: Video-to-Speech Generation with Speech Decomposition and Rectified Flow
Nov 29, 2024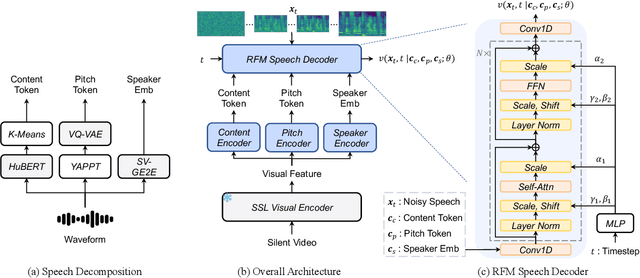
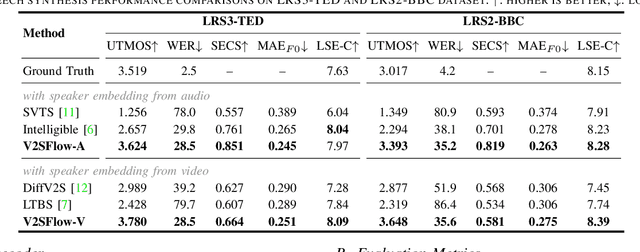
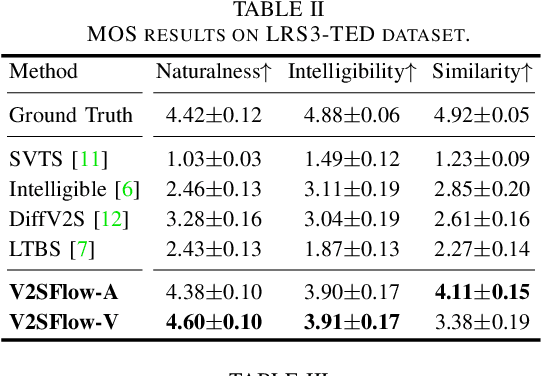
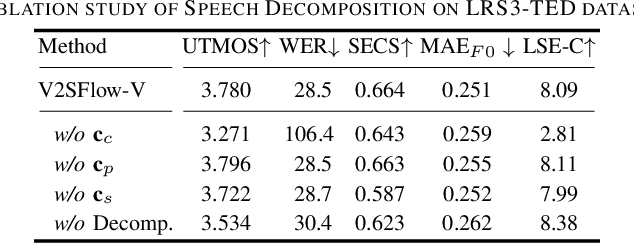
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce V2SFlow, a novel Video-to-Speech (V2S) framework designed to generate natural and intelligible speech directly from silent talking face videos. While recent V2S systems have shown promising results on constrained datasets with limited speakers and vocabularies, their performance often degrades on real-world, unconstrained datasets due to the inherent variability and complexity of speech signals. To address these challenges, we decompose the speech signal into manageable subspaces (content, pitch, and speaker information), each representing distinct speech attributes, and predict them directly from the visual input. To generate coherent and realistic speech from these predicted attributes, we employ a rectified flow matching decoder built on a Transformer architecture, which models efficient probabilistic pathways from random noise to the target speech distribution. Extensive experiments demonstrate that V2SFlow significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, even surpassing the naturalness of ground truth utterances.
ARLON: Boosting Diffusion Transformers with Autoregressive Models for Long Video Generation
Oct 27, 2024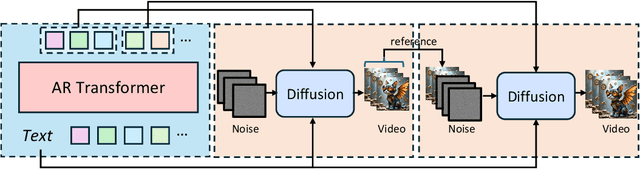
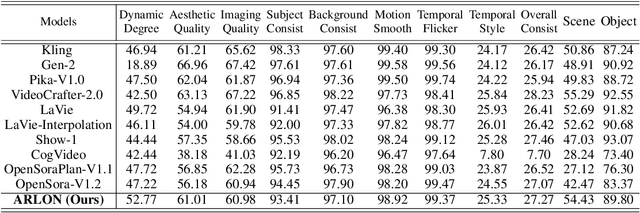
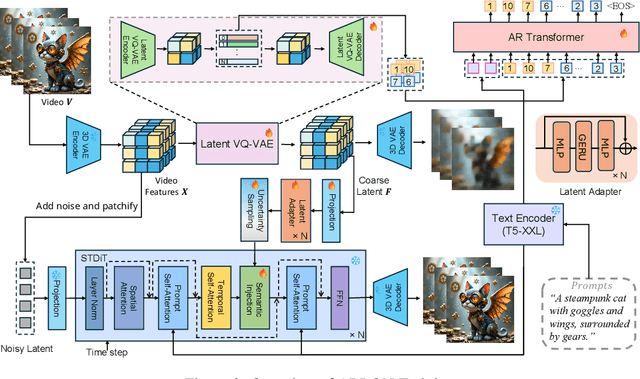
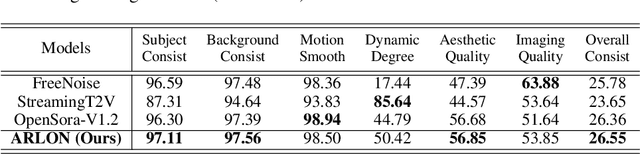
Abstract:Text-to-video models have recently undergone rapid and substantial advancements. Nevertheless, due to limitations in data and computational resources, achieving efficient generation of long videos with rich motion dynamics remains a significant challenge. To generate high-quality, dynamic, and temporally consistent long videos, this paper presents ARLON, a novel framework that boosts diffusion Transformers with autoregressive models for long video generation, by integrating the coarse spatial and long-range temporal information provided by the AR model to guide the DiT model. Specifically, ARLON incorporates several key innovations: 1) A latent Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) compresses the input latent space of the DiT model into compact visual tokens, bridging the AR and DiT models and balancing the learning complexity and information density; 2) An adaptive norm-based semantic injection module integrates the coarse discrete visual units from the AR model into the DiT model, ensuring effective guidance during video generation; 3) To enhance the tolerance capability of noise introduced from the AR inference, the DiT model is trained with coarser visual latent tokens incorporated with an uncertainty sampling module. Experimental results demonstrate that ARLON significantly outperforms the baseline OpenSora-V1.2 on eight out of eleven metrics selected from VBench, with notable improvements in dynamic degree and aesthetic quality, while delivering competitive results on the remaining three and simultaneously accelerating the generation process. In addition, ARLON achieves state-of-the-art performance in long video generation. Detailed analyses of the improvements in inference efficiency are presented, alongside a practical application that demonstrates the generation of long videos using progressive text prompts. See demos of ARLON at \url{http://aka.ms/arlon}.
Accelerating Codec-based Speech Synthesis with Multi-Token Prediction and Speculative Decoding
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:The goal of this paper is to accelerate codec-based speech synthesis systems with minimum sacrifice to speech quality. We propose an enhanced inference method that allows for flexible trade-offs between speed and quality during inference without requiring additional training. Our core idea is to predict multiple tokens per inference step of the AR module using multiple prediction heads, resulting in a linear reduction in synthesis time as the number of heads increases. Furthermore, we introduce a novel speculative decoding technique that utilises a Viterbi-based algorithm to select the optimal sequence of generated tokens at each decoding step. In our experiments, we demonstrate that the time required to predict each token is reduced by a factor of 4 to 5 compared to baseline models, with minimal quality trade-off or even improvement in terms of speech intelligibility. Audio samples are available at: multpletokensprediction.github.io/multipletokensprediction.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge