Youngjoon Jang
FastAV: Efficient Token Pruning for Audio-Visual Large Language Model Inference
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:In this work, we present FastAV, the first token pruning framework tailored for audio-visual large language models (AV-LLMs). While token pruning has been actively explored in standard large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (LVLMs), its application to AV-LLMs has received little attention, even though multimodal integration substantially increases their token demands. To address this gap, we introduce a pruning strategy that utilizes attention weights to identify tokens emphasized at different stages and estimates their importance. Building on this analysis, FastAV applies a two-stage pruning strategy: (1) global pruning in intermediate layers to remove broadly less influential tokens, and (2) fine pruning in later layers considering the impact on next token generation. Notably, our method does not rely on full attention maps, which makes it fully compatible with efficient attention mechanisms such as FlashAttention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FastAV reduces FLOPs by more than 40% on two representative AV-LLMs, while preserving or even improving model performance.
LP-CFM: Perceptual Invariance-Aware Conditional Flow Matching for Speech Modeling
Dec 23, 2025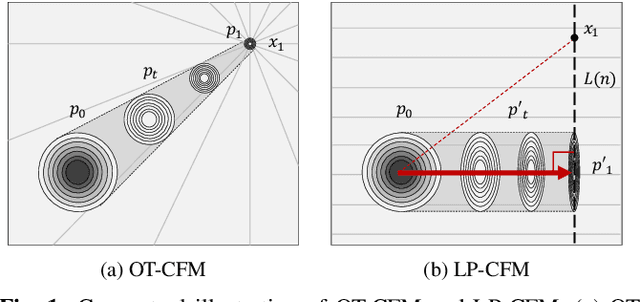
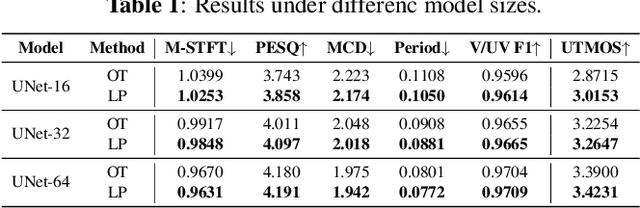
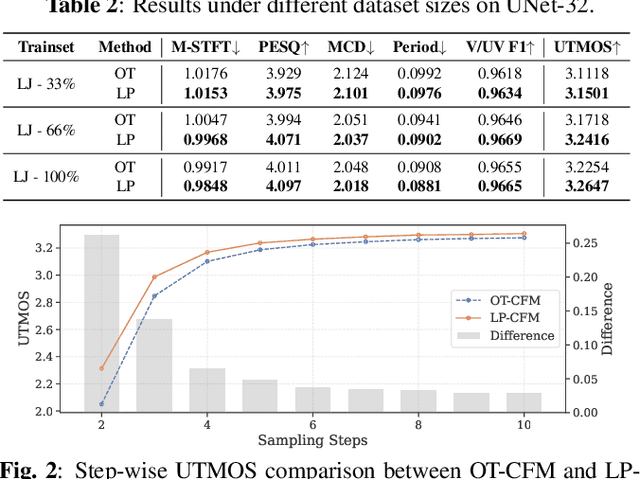
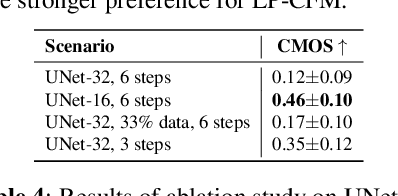
Abstract:The goal of this paper is to provide a new perspective on speech modeling by incorporating perceptual invariances such as amplitude scaling and temporal shifts. Conventional generative formulations often treat each dataset sample as a fixed representative of the target distribution. From a generative standpoint, however, such samples are only one among many perceptually equivalent variants within the true speech distribution. To address this, we propose Linear Projection Conditional Flow Matching (LP-CFM), which models targets as projection-aligned elongated Gaussians along perceptually equivalent variants. We further introduce Vector Calibrated Sampling (VCS) to keep the sampling process aligned with the line-projection path. In neural vocoding experiments across model sizes, data scales, and sampling steps, the proposed approach consistently improves over the conventional optimal transport CFM, with particularly strong gains in low-resource and few-step scenarios. These results highlight the potential of LP-CFM and VCS to provide more robust and perceptually grounded generative modeling of speech.
Segment, Embed, and Align: A Universal Recipe for Aligning Subtitles to Signing
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:The goal of this work is to develop a universal approach for aligning subtitles (i.e., spoken language text with corresponding timestamps) to continuous sign language videos. Prior approaches typically rely on end-to-end training tied to a specific language or dataset, which limits their generality. In contrast, our method Segment, Embed, and Align (SEA) provides a single framework that works across multiple languages and domains. SEA leverages two pretrained models: the first to segment a video frame sequence into individual signs and the second to embed the video clip of each sign into a shared latent space with text. Alignment is subsequently performed with a lightweight dynamic programming procedure that runs efficiently on CPUs within a minute, even for hour-long episodes. SEA is flexible and can adapt to a wide range of scenarios, utilizing resources from small lexicons to large continuous corpora. Experiments on four sign language datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art alignment performance, highlighting the potential of SEA to generate high-quality parallel data for advancing sign language processing. SEA's code and models are openly available.
Lost in Translation, Found in Embeddings: Sign Language Translation and Alignment
Dec 08, 2025
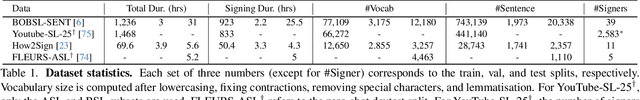
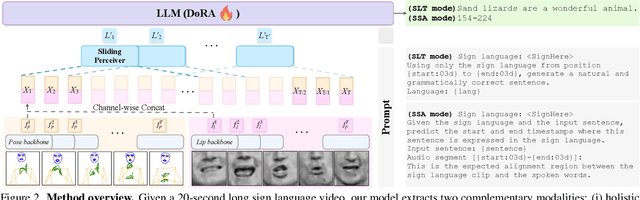
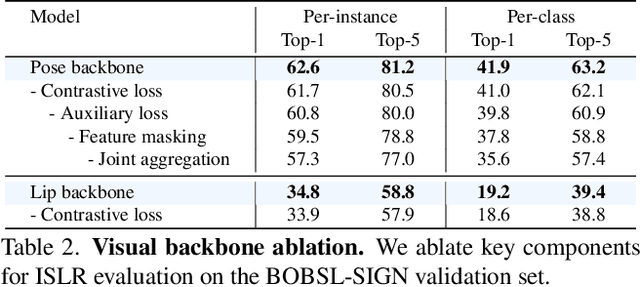
Abstract:Our aim is to develop a unified model for sign language understanding, that performs sign language translation (SLT) and sign-subtitle alignment (SSA). Together, these two tasks enable the conversion of continuous signing videos into spoken language text and also the temporal alignment of signing with subtitles -- both essential for practical communication, large-scale corpus construction, and educational applications. To achieve this, our approach is built upon three components: (i) a lightweight visual backbone that captures manual and non-manual cues from human keypoints and lip-region images while preserving signer privacy; (ii) a Sliding Perceiver mapping network that aggregates consecutive visual features into word-level embeddings to bridge the vision-text gap; and (iii) a multi-task scalable training strategy that jointly optimises SLT and SSA, reinforcing both linguistic and temporal alignment. To promote cross-linguistic generalisation, we pretrain our model on large-scale sign-text corpora covering British Sign Language (BSL) and American Sign Language (ASL) from the BOBSL and YouTube-SL-25 datasets. With this multilingual pretraining and strong model design, we achieve state-of-the-art results on the challenging BOBSL (BSL) dataset for both SLT and SSA. Our model also demonstrates robust zero-shot generalisation and finetuned SLT performance on How2Sign (ASL), highlighting the potential of scalable translation across different sign languages.
From Ambiguity to Accuracy: The Transformative Effect of Coreference Resolution on Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a crucial framework in natural language processing (NLP), improving factual consistency and reducing hallucinations by integrating external document retrieval with large language models (LLMs). However, the effectiveness of RAG is often hindered by coreferential complexity in retrieved documents, introducing ambiguity that disrupts in-context learning. In this study, we systematically investigate how entity coreference affects both document retrieval and generative performance in RAG-based systems, focusing on retrieval relevance, contextual understanding, and overall response quality. We demonstrate that coreference resolution enhances retrieval effectiveness and improves question-answering (QA) performance. Through comparative analysis of different pooling strategies in retrieval tasks, we find that mean pooling demonstrates superior context capturing ability after applying coreference resolution. In QA tasks, we discover that smaller models benefit more from the disambiguation process, likely due to their limited inherent capacity for handling referential ambiguity. With these findings, this study aims to provide a deeper understanding of the challenges posed by coreferential complexity in RAG, providing guidance for improving retrieval and generation in knowledge-intensive AI applications.
Fork-Merge Decoding: Enhancing Multimodal Understanding in Audio-Visual Large Language Models
May 27, 2025Abstract:The goal of this work is to enhance balanced multimodal understanding in audio-visual large language models (AV-LLMs) by addressing modality bias without requiring additional training. In current AV-LLMs, audio and video features are typically processed jointly in the decoder. While this strategy facilitates unified multimodal understanding, it may introduce modality bias, where the model tends to over-rely on one modality due to imbalanced training signals. To mitigate this, we propose Fork-Merge Decoding (FMD), a simple yet effective inference-time strategy that requires no additional training or architectural modifications. FMD first performs modality-specific reasoning by processing audio-only and video-only inputs through the early decoder layers (a fork phase), and then merges the resulting hidden states for joint reasoning in the remaining layers (a merge phase). This approach promotes balanced modality contributions and leverages complementary information across modalities. We evaluate our method on two representative AV-LLMs, VideoLLaMA2 and video-SALMONN, using three benchmark datasets. Experimental results demonstrate consistent performance improvements on tasks focused on audio, video, and combined audio-visual reasoning, demonstrating the effectiveness of inference-time interventions for robust multimodal understanding.
AVCD: Mitigating Hallucinations in Audio-Visual Large Language Models through Contrastive Decoding
May 27, 2025Abstract:Hallucination remains a major challenge in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). To address this, various contrastive decoding (CD) methods have been proposed that contrasts original logits with hallucinated logits generated from perturbed inputs. While CD has shown promise in vision-language models (VLMs), it is not well-suited for AV-LLMs, where hallucinations often emerge from both unimodal and cross-modal combinations involving audio, video, and language. These intricate interactions call for a more adaptive and modality-aware decoding strategy. In this paper, we propose Audio-Visual Contrastive Decoding (AVCD)-a novel, training-free decoding framework designed to model trimodal interactions and suppress modality-induced hallucinations in AV-LLMs. Unlike previous CD methods in VLMs that corrupt a fixed modality, AVCD leverages attention distributions to dynamically identify less dominant modalities and applies attentive masking to generate perturbed output logits. To support CD in a trimodal setting, we also reformulate the original CD framework to jointly handle audio, visual, and textual inputs. Finally, to improve efficiency, we introduce entropy-guided adaptive decoding, which selectively skips unnecessary decoding steps based on the model's confidence in its predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AVCD consistently outperforms existing decoding methods. Especially, on the AVHBench dataset, it improves accuracy by 6% for VideoLLaMA2 and 11% for video-SALMONN, demonstrating strong robustness and generalizability.
Test-Time Augmentation for Pose-invariant Face Recognition
May 14, 2025Abstract:The goal of this paper is to enhance face recognition performance by augmenting head poses during the testing phase. Existing methods often rely on training on frontalised images or learning pose-invariant representations, yet both approaches typically require re-training and testing for each dataset, involving a substantial amount of effort. In contrast, this study proposes Pose-TTA, a novel approach that aligns faces at inference time without additional training. To achieve this, we employ a portrait animator that transfers the source image identity into the pose of a driving image. Instead of frontalising a side-profile face -- which can introduce distortion -- Pose-TTA generates matching side-profile images for comparison, thereby reducing identity information loss. Furthermore, we propose a weighted feature aggregation strategy to address any distortions or biases arising from the synthetic data, thus enhancing the reliability of the augmented images. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets and with various pre-trained face recognition models demonstrate that Pose-TTA consistently improves inference performance. Moreover, our method is straightforward to integrate into existing face recognition pipelines, as it requires no retraining or fine-tuning of the underlying recognition models.
Deep Understanding of Sign Language for Sign to Subtitle Alignment
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:The objective of this work is to align asynchronous subtitles in sign language videos with limited labelled data. To achieve this goal, we propose a novel framework with the following contributions: (1) we leverage fundamental grammatical rules of British Sign Language (BSL) to pre-process the input subtitles, (2) we design a selective alignment loss to optimise the model for predicting the temporal location of signs only when the queried sign actually occurs in a scene, and (3) we conduct self-training with refined pseudo-labels which are more accurate than the heuristic audio-aligned labels. From this, our model not only better understands the correlation between the text and the signs, but also holds potential for application in the translation of sign languages, particularly in scenarios where manual labelling of large-scale sign data is impractical or challenging. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results, surpassing previous baselines by substantial margins in terms of both frame-level accuracy and F1-score. This highlights the effectiveness and practicality of our framework in advancing the field of sign language video alignment and translation.
Lost in Translation, Found in Context: Sign Language Translation with Contextual Cues
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Our objective is to translate continuous sign language into spoken language text. Inspired by the way human interpreters rely on context for accurate translation, we incorporate additional contextual cues together with the signing video, into a new translation framework. Specifically, besides visual sign recognition features that encode the input video, we integrate complementary textual information from (i) captions describing the background show, (ii) translation of previous sentences, as well as (iii) pseudo-glosses transcribing the signing. These are automatically extracted and inputted along with the visual features to a pre-trained large language model (LLM), which we fine-tune to generate spoken language translations in text form. Through extensive ablation studies, we show the positive contribution of each input cue to the translation performance. We train and evaluate our approach on BOBSL -- the largest British Sign Language dataset currently available. We show that our contextual approach significantly enhances the quality of the translations compared to previously reported results on BOBSL, and also to state-of-the-art methods that we implement as baselines. Furthermore, we demonstrate the generality of our approach by applying it also to How2Sign, an American Sign Language dataset, and achieve competitive results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge