James L. McClelland
Stanford University
Neural Computation Without Slots: Steps Towards Biologically Plausible Memory and Attention in Natural and Artificial Intelligence
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Many models used in artificial intelligence and cognitive science rely on multi-element patterns stored in "slots" - dedicated storage locations - in a digital computer. As biological brains likely lack slots, we consider how they might achieve similar functional outcomes without them by building on the neurally-inspired modern Hopfield network (MHN; Krotov & Hopfield, 2021), which stores patterns in the connection weights of an individual neuron. We propose extensions of this approach to increase its biological plausibility as a model of memory and to capture an important advantage of slot-based computation in contemporary language models. For memory, neuroscience research suggests that the weights of overlapping sparse ensembles of neurons, rather than a dedicated individual neuron, are used to store a memory. We introduce the K-winner MHN, extending the approach to ensembles, and find that within a continual learning regime, the ensemble-based MHN exhibits greater retention of older memories, as measured by the graded sensitivity measure d', than a standard (one-neuron) MHN. Next, we consider the powerful use of slot-based memory in contemporary language models. These models use slots to store long sequences of past inputs and their learned encodings, supporting later predictions and allowing error signals to be transported backward in time to adjust weights underlying the learned encodings of these past inputs. Inspired by these models' successes, we show how the MHN can be extended to capture both of these important functional outcomes. Collectively, our modeling approaches constitute steps towards understanding how biologically plausible mechanisms can support computations that have enabled AI systems to capture human-like abilities that no prior models have been able to achieve.
Latent learning: episodic memory complements parametric learning by enabling flexible reuse of experiences
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:When do machine learning systems fail to generalize, and what mechanisms could improve their generalization? Here, we draw inspiration from cognitive science to argue that one weakness of machine learning systems is their failure to exhibit latent learning -- learning information that is not relevant to the task at hand, but that might be useful in a future task. We show how this perspective links failures ranging from the reversal curse in language modeling to new findings on agent-based navigation. We then highlight how cognitive science points to episodic memory as a potential part of the solution to these issues. Correspondingly, we show that a system with an oracle retrieval mechanism can use learning experiences more flexibly to generalize better across many of these challenges. We also identify some of the essential components for effectively using retrieval, including the importance of within-example in-context learning for acquiring the ability to use information across retrieved examples. In summary, our results illustrate one possible contributor to the relative data inefficiency of current machine learning systems compared to natural intelligence, and help to understand how retrieval methods can complement parametric learning to improve generalization.
On the generalization of language models from in-context learning and finetuning: a controlled study
May 01, 2025Abstract:Large language models exhibit exciting capabilities, yet can show surprisingly narrow generalization from finetuning -- from failing to generalize to simple reversals of relations they are trained on, to missing logical deductions that can be made from trained information. These failures to generalize from fine-tuning can hinder practical application of these models. However, language models' in-context learning shows different inductive biases, and can generalize better in some of these cases. Here, we explore these differences in generalization between in-context- and fine-tuning-based learning. To do so, we constructed several novel datasets to evaluate and improve models' ability to generalize from finetuning data. The datasets are constructed to isolate the knowledge in the dataset from that in pretraining, to create clean tests of generalization. We expose pretrained large models to controlled subsets of the information in these datasets -- either in context, or through fine-tuning -- and evaluate their performance on test sets that require various types of generalization. We find overall that in data-matched settings, in-context learning can generalize more flexibly than fine-tuning (though we also find some qualifications of prior findings, such as cases when fine-tuning can generalize to reversals embedded in a larger structure of knowledge). We build on these findings to propose a method to enable improved generalization from fine-tuning: adding in-context inferences to finetuning data. We show that this method improves generalization across various splits of our datasets and other benchmarks. Our results have implications for understanding the inductive biases of different modes of learning in language models, and practically improving their performance.
Emergent Symbol-like Number Variables in Artificial Neural Networks
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:What types of numeric representations emerge in Neural Networks (NNs)? To what degree do NNs induce abstract, mutable, slot-like numeric variables, and in what situations do these representations emerge? How do these representations change over learning, and how can we understand the neural implementations in ways that are unified across different NNs? In this work, we approach these questions by first training sequence based neural systems using Next Token Prediction (NTP) objectives on numeric tasks. We then seek to understand the neural solutions through the lens of causal abstractions or symbolic algorithms. We use a combination of causal interventions and visualization methods to find that artificial neural models do indeed develop analogs of interchangeable, mutable, latent number variables purely from the NTP objective. We then ask how variations on the tasks and model architectures affect the models' learned solutions to find that these symbol-like numeric representations do not form for every variant of the task, and transformers solve the problem in a notably different way than their recurrent counterparts. We then show how the symbol-like variables change over the course of training to find a strong correlation between the models' task performance and the alignment of their symbol-like representations. Lastly, we show that in all cases, some degree of gradience exists in these neural symbols, highlighting the difficulty of finding simple, interpretable symbolic stories of how neural networks perform numeric tasks. Taken together, our results are consistent with the view that neural networks can approximate interpretable symbolic programs of number cognition, but the particular program they approximate and the extent to which they approximate it can vary widely, depending on the network architecture, training data, extent of training, and network size.
SODA: Bottleneck Diffusion Models for Representation Learning
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:We introduce SODA, a self-supervised diffusion model, designed for representation learning. The model incorporates an image encoder, which distills a source view into a compact representation, that, in turn, guides the generation of related novel views. We show that by imposing a tight bottleneck between the encoder and a denoising decoder, and leveraging novel view synthesis as a self-supervised objective, we can turn diffusion models into strong representation learners, capable of capturing visual semantics in an unsupervised manner. To the best of our knowledge, SODA is the first diffusion model to succeed at ImageNet linear-probe classification, and, at the same time, it accomplishes reconstruction, editing and synthesis tasks across a wide range of datasets. Further investigation reveals the disentangled nature of its emergent latent space, that serves as an effective interface to control and manipulate the model's produced images. All in all, we aim to shed light on the exciting and promising potential of diffusion models, not only for image generation, but also for learning rich and robust representations.
Causal interventions expose implicit situation models for commonsense language understanding
Jun 07, 2023



Abstract:Accounts of human language processing have long appealed to implicit ``situation models'' that enrich comprehension with relevant but unstated world knowledge. Here, we apply causal intervention techniques to recent transformer models to analyze performance on the Winograd Schema Challenge (WSC), where a single context cue shifts interpretation of an ambiguous pronoun. We identify a relatively small circuit of attention heads that are responsible for propagating information from the context word that guides which of the candidate noun phrases the pronoun ultimately attends to. We then compare how this circuit behaves in a closely matched ``syntactic'' control where the situation model is not strictly necessary. These analyses suggest distinct pathways through which implicit situation models are constructed to guide pronoun resolution.
Out-of-Distribution Generalization in Algorithmic Reasoning Through Curriculum Learning
Oct 07, 2022


Abstract:Out-of-distribution generalization (OODG) is a longstanding challenge for neural networks, and is quite apparent in tasks with well-defined variables and rules, where explicit use of the rules can solve problems independently of the particular values of the variables. Large transformer-based language models have pushed the boundaries on how well neural networks can generalize to novel inputs, but their complexity obfuscates they achieve such robustness. As a step toward understanding how transformer-based systems generalize, we explore the question of OODG in smaller scale transformers. Using a reasoning task based on the puzzle Sudoku, we show that OODG can occur on complex problems if the training set includes examples sampled from the whole distribution of simpler component tasks.
Learning to Reason With Relational Abstractions
Oct 06, 2022



Abstract:Large language models have recently shown promising progress in mathematical reasoning when fine-tuned with human-generated sequences walking through a sequence of solution steps. However, the solution sequences are not formally structured and the resulting model-generated sequences may not reflect the kind of systematic reasoning we might expect an expert human to produce. In this paper, we study how to build stronger reasoning capability in language models using the idea of relational abstractions. We introduce new types of sequences that more explicitly provide an abstract characterization of the transitions through intermediate solution steps to the goal state. We find that models that are supplied with such sequences as prompts can solve tasks with a significantly higher accuracy, and models that are trained to produce such sequences solve problems better than those that are trained with previously used human-generated sequences and other baselines. Our work thus takes several steps toward elucidating and improving how language models perform on tasks requiring multi-step mathematical reasoning.
Systematic Generalization and Emergent Structures in Transformers Trained on Structured Tasks
Oct 02, 2022



Abstract:Transformer networks have seen great success in natural language processing and machine vision, where task objectives such as next word prediction and image classification benefit from nuanced context sensitivity across high-dimensional inputs. However, there is an ongoing debate about how and when transformers can acquire highly structured behavior and achieve systematic generalization. Here, we explore how well a causal transformer can perform a set of algorithmic tasks, including copying, sorting, and hierarchical compositions of these operations. We demonstrate strong generalization to sequences longer than those used in training by replacing the standard positional encoding typically used in transformers with labels arbitrarily paired with items in the sequence. By finding the layer and head configuration sufficient to solve the task, then performing ablation experiments and representation analysis, we show that two-layer transformers learn generalizable solutions to multi-level problems and develop signs of systematic task decomposition. They also exploit shared computation across related tasks. These results provide key insights into how transformer models may be capable of decomposing complex decisions into reusable, multi-level policies in tasks requiring structured behavior.
Language models show human-like content effects on reasoning
Jul 14, 2022

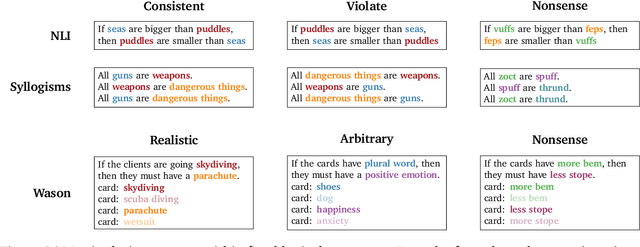

Abstract:Abstract reasoning is a key ability for an intelligent system. Large language models achieve above-chance performance on abstract reasoning tasks, but exhibit many imperfections. However, human abstract reasoning is also imperfect, and depends on our knowledge and beliefs about the content of the reasoning problem. For example, humans reason much more reliably about logical rules that are grounded in everyday situations than arbitrary rules about abstract attributes. The training experiences of language models similarly endow them with prior expectations that reflect human knowledge and beliefs. We therefore hypothesized that language models would show human-like content effects on abstract reasoning problems. We explored this hypothesis across three logical reasoning tasks: natural language inference, judging the logical validity of syllogisms, and the Wason selection task (Wason, 1968). We find that state of the art large language models (with 7 or 70 billion parameters; Hoffman et al., 2022) reflect many of the same patterns observed in humans across these tasks -- like humans, models reason more effectively about believable situations than unrealistic or abstract ones. Our findings have implications for understanding both these cognitive effects, and the factors that contribute to language model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge