Haiquan Lu
Joint Sparsity and Beamforming Design for RDARS-Aided Systems
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Reconfigurable distributed antennas and reflecting surface (RDARS) has emerged as a promising architecture for communication and sensing performance enhancement. In particular, the new selection gain can be achieved by leveraging the dynamic working mode selection between connection and reflection modes, whereas low-complexity element configuration remains an open issue. In this paper, we consider a RDARS-assisted communication system, where the connected elements are formed as a uniform sparse array for simplified mode configuration while achieving enlarged physical array aperture. The sum rate maximization problem is then formulated by jointly optimizing the active and passive beamforming matrices and sparsity of connected element array. For the special cases of a single user equipment (UE) and two UEs, the optimal sparsity designs are derived in closed-form. Then, for an arbitrary number of UEs, a weighted minimum mean-square error-based alternating optimization (AO) algorithm is proposed to tackle the non-convex optimization problem. Numerical results demonstrate the importance of optimizing the sparsity and the effectiveness of low-complexity sparsity optimization.
Model-Driven Deep Learning Enhanced Joint Beamforming and Mode Switching for RDARS-Aided MIMO Systems
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable distributed antenna and reflecting surface (RDARS) is a promising architecture for future sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. In particular, the dynamic working mode configuration for the RDARS-aided system brings an extra selection gain compared to the existing reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided system and distributed antenna system (DAS). In this paper, we consider the RDARS-aided downlink multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system and aim to maximize the weighted sum rate (WSR) by jointly optimizing the beamforming matrices at the based station (BS) and RDARS, as well as mode switching matrix at RDARS. The optimization problem is challenging to be solved due to the non-convex objective function and mixed integer binary constraint. To this end, a penalty term-based weight minimum mean square error (PWM) algorithm is proposed by integrating the majorization-minimization (MM) and weight minimum mean square error (WMMSE) methods. To further escape the local optimum point in the PWM algorithm, a model-driven DL method is integrated into this algorithm, where the key variables related to the convergence of PWM algorithm are trained to accelerate the convergence speed and improve the system performance. Simulation results are provided to show that the PWM-based beamforming network (PWM-BFNet) can reduce the number of iterations by half and achieve performance improvements of 26.53% and 103.2% at the scenarios of high total transmit power and a large number of RDARS transmit elements (TEs), respectively.
Wireless Communication for Low-Altitude Economy with UAV Swarm Enabled Two-Level Movable Antenna System
May 28, 2025Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is regarded as a key enabling platform for low-altitude economy, due to its advantages such as 3D maneuverability, flexible deployment, and LoS air-to-air/ground communication links. In particular, the intrinsic high mobility renders UAV especially suitable for operating as a movable antenna (MA) from the sky. In this paper, by exploiting the flexible mobility of UAV swarm and antenna position adjustment of MA, we propose a novel UAV swarm enabled two-level MA system, where UAVs not only individually deploy a local MA array, but also form a larger-scale MA system with their individual MA arrays via swarm coordination. We formulate a general optimization problem to maximize the minimum achievable rate over all ground UEs, by jointly optimizing the 3D UAV swarm placement positions, their individual MAs' positions, and receive beamforming for different UEs. We first consider the special case where each UAV has only one antenna, under different scenarios of one single UE, two UEs, and arbitrary number of UEs. In particular, for the two-UE case, we derive the optimal UAV swarm placement positions in closed-form that achieves IUI-free communication, where the UAV swarm forms a uniform sparse array (USA) satisfying collision avoidance constraint. While for the general case with arbitrary number of UEs, we propose an efficient alternating optimization algorithm to solve the formulated non-convex optimization problem. Then, we extend the results to the case where each UAV is equipped with multiple antennas. Numerical results verify that the proposed low-altitude UAV swarm enabled MA system significantly outperforms various benchmark schemes, thanks to the exploitation of two-level mobility to create more favorable channel conditions for multi-UE communications.
A Model Zoo on Phase Transitions in Neural Networks
Apr 25, 2025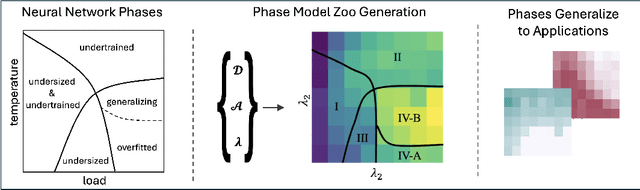
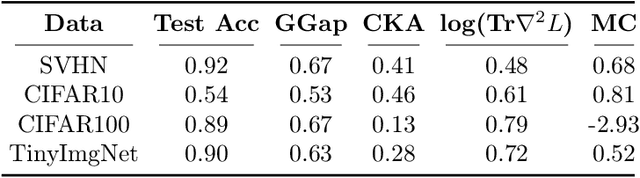
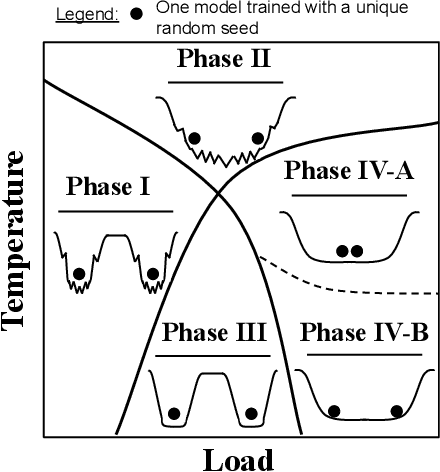
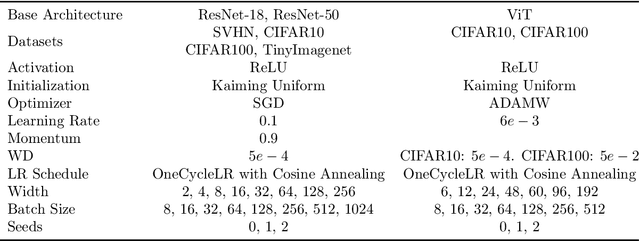
Abstract:Using the weights of trained Neural Network (NN) models as data modality has recently gained traction as a research field - dubbed Weight Space Learning (WSL). Multiple recent works propose WSL methods to analyze models, evaluate methods, or synthesize weights. Weight space learning methods require populations of trained models as datasets for development and evaluation. However, existing collections of models - called `model zoos' - are unstructured or follow a rudimentary definition of diversity. In parallel, work rooted in statistical physics has identified phases and phase transitions in NN models. Models are homogeneous within the same phase but qualitatively differ from one phase to another. We combine the idea of `model zoos' with phase information to create a controlled notion of diversity in populations. We introduce 12 large-scale zoos that systematically cover known phases and vary over model architecture, size, and datasets. These datasets cover different modalities, such as computer vision, natural language processing, and scientific ML. For every model, we compute loss landscape metrics and validate full coverage of the phases. With this dataset, we provide the community with a resource with a wide range of potential applications for WSL and beyond. Evidence suggests the loss landscape phase plays a role in applications such as model training, analysis, or sparsification. We demonstrate this in an exploratory study of the downstream methods like transfer learning or model weights averaging.
Reconfigurable Codebook-Based Beamforming for RDARS-Aided mmWave MU-MIMO Systems
Apr 02, 2025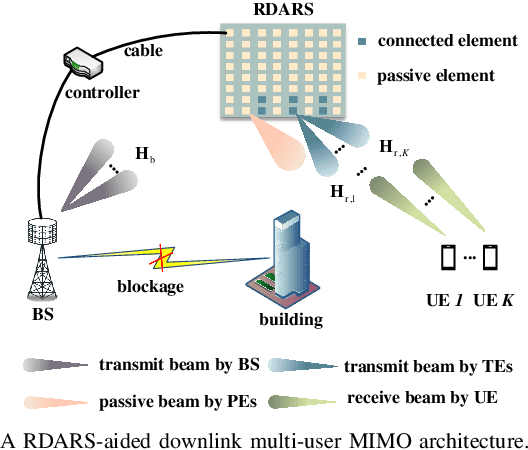
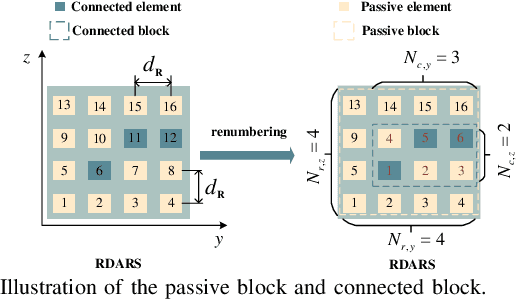
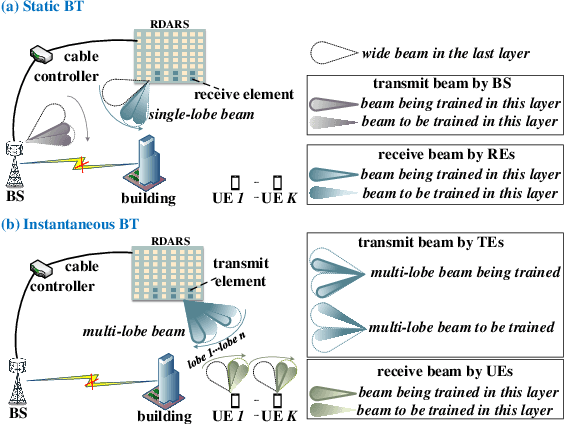
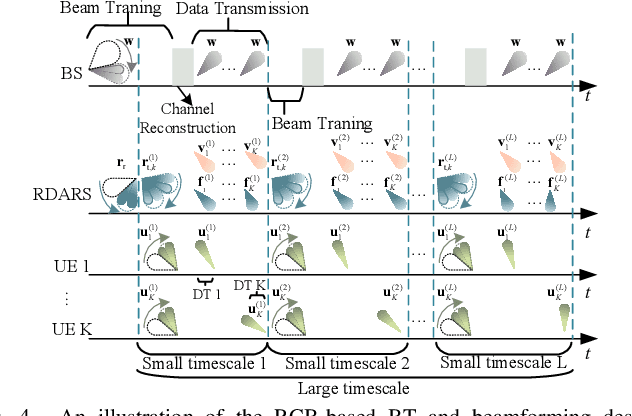
Abstract:Reconfigurable distributed antenna and reflecting surface (RDARS) is a new architecture for the sixth-generation (6G) millimeter wave (mmWave) communications. In RDARS-aided mmWave systems, the active and passive beamforming design and working mode configuration for reconfigurable elements are crucial for system performance. In this paper, we aim to maximize the weighted sum rate (WSR) in the RDARS-aided mmWave system. To take advantage of RDARS, we first design a reconfigurable codebook (RCB) in which the number and dimension of the codeword can be flexibly adjusted. Then, a low overhead beam training scheme based on hierarchical search is proposed. Accordingly, the active and passive beamforming for data transmission is designed to achieve the maximum WSR for both space-division multiple access (SDMA) and time-division multiple access (TDMA) schemes. For the TDMA scheme, the optimal number of RDARS transmit elements and the allocated power budget for WSR maximization are derived in closed form. Besides, the superiority of the RDARS is verified and the conditions under which RDARS outperforms RIS and DAS are given. For the SDMA scheme, we characterize the relationship between the number of RDARS connected elements and the user distribution, followed by the derivation of the optimal placement positions of the RDARS transmit elements. High-quality beamforming design solutions are derived to minimize the inter-user interference (IUI) at the base station and RDARS side respectively, which nearly leads to the maximal WSR. Finally, simulation results confirm our theoretical findings and the superiority of the proposed schemes.
Wireless Communication with Flexible Reflector: Joint Placement and Rotation Optimization for Coverage Enhancement
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:Passive metal reflectors for communication enhancement have appealing advantages such as ultra low cost, zero energy expenditure, maintenance-free operation, long life span, and full compatibility with legacy wireless systems. To unleash the full potential of passive reflectors for wireless communications, this paper proposes a new passive reflector architecture, termed flexible reflector (FR), for enabling the flexible adjustment of beamforming direction via the FR placement and rotation optimization. We consider the multi-FR aided area coverage enhancement and aim to maximize the minimum expected receive power over all locations within the target coverage area, by jointly optimizing the placement positions and rotation angles of multiple FRs. To gain useful insights, the special case of movable reflector (MR) with fixed rotation is first studied to maximize the expected receive power at a target location, where the optimal single-MR placement positions for electrically large and small reflectors are derived in closed-form, respectively. It is shown that the reflector should be placed at the specular reflection point for electrically large reflector. While for area coverage enhancement, the optimal placement is obtained for the single-MR case and a sequential placement algorithm is proposed for the multi-MR case. Moreover, for the general case of FR, joint placement and rotation design is considered for the single-/multi-FR aided coverage enhancement, respectively. Numerical results are presented which demonstrate significant performance gains of FRs over various benchmark schemes under different practical setups in terms of receive power enhancement.
Double-Side Delay Alignment Modulation for Multi-User Millimeter Wave and TeraHertz Communications
Oct 22, 2024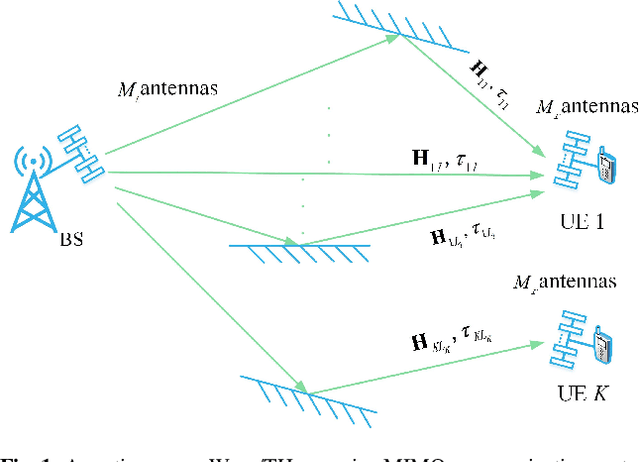
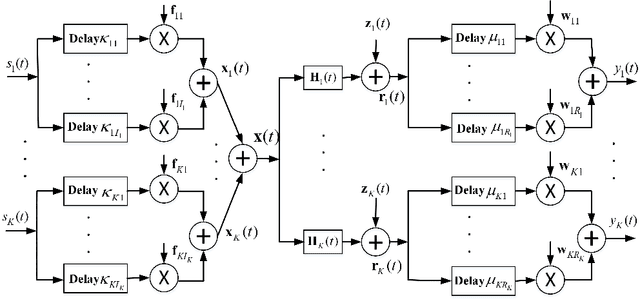
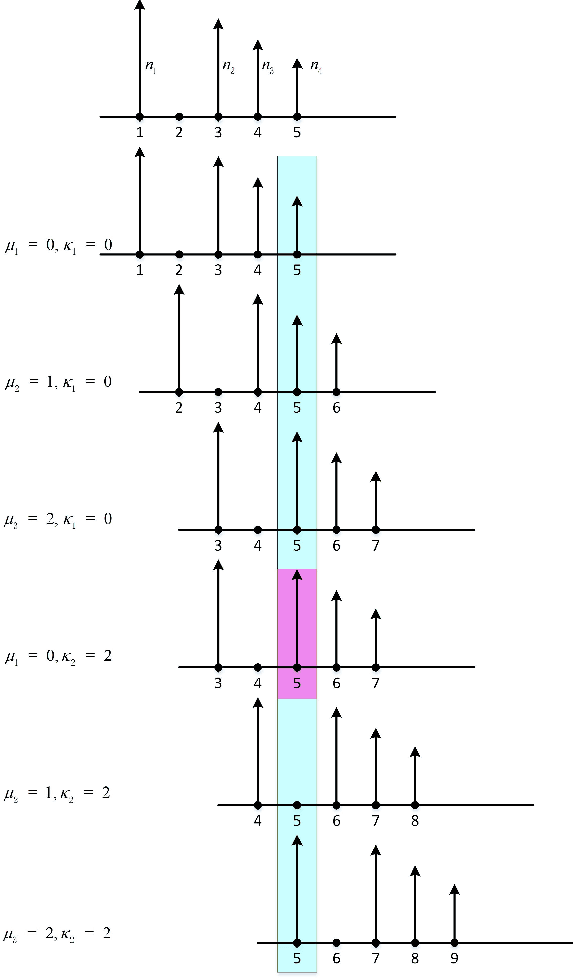
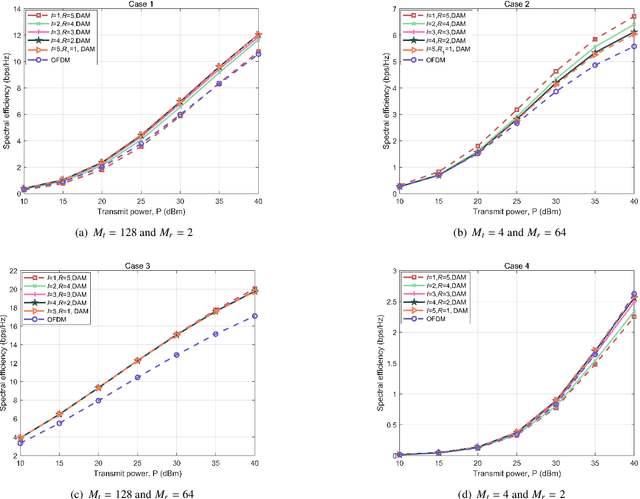
Abstract:Delay alignment modulation (DAM) is an innovative broadband modulation technique well suited for millimeter wave (mmWave) and terahertz (THz) massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication systems. Leveraging the high spatial resolution and sparsity of multi-path channels, DAM mitigates inter-symbol interference (ISI) effectively, by aligning all multi-path components through a combination of delay pre/post-compensation and path-based beamforming. As such, ISI is eliminated while preserving multi-path power gains. In this paper, we explore multi-user double-side DAM with both delay pre-compensation at the transmitter and post-compensation at the receiver, contrasting with prior one-side DAM that primarily focuses on delay pre-compensation only. Firstly, we reveal the constraint for the introduced delays and the delay pre/post-compensation vectors tailored for multi-user double-side DAM, given a specific number of delay pre/post-compensations. Furthermore, we show that as long as the number of base station (BS)/user equipment (UE) antennas is sufficiently large, single-side DAM, where delay compensation is only performed at the BS/UE, is preferred than double-side DAM since the former results in less ISI to be spatially eliminated. Next, we propose two low-complexity path-based beamforming strategies based on the eigen-beamforming transmission and ISI-zero forcing (ZF) principles, respectively, based on which the achievable sum rates are studied. Simulation results verify that with sufficiently large BS/UE antennas, single-side DAM is sufficient. Furthermore, compared to the benchmark scheme of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), multi-user BS-side DAM achieves higher spectral efficiency and/or lower peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR).
AlphaPruning: Using Heavy-Tailed Self Regularization Theory for Improved Layer-wise Pruning of Large Language Models
Oct 14, 2024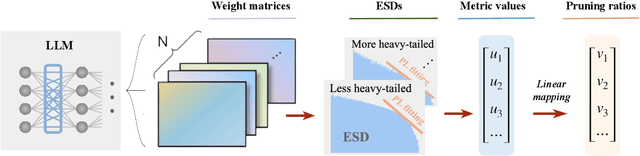
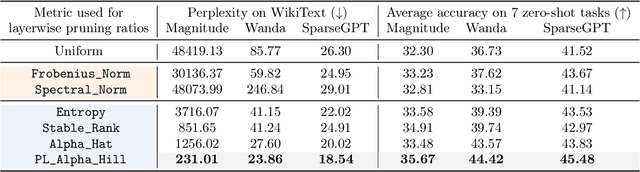
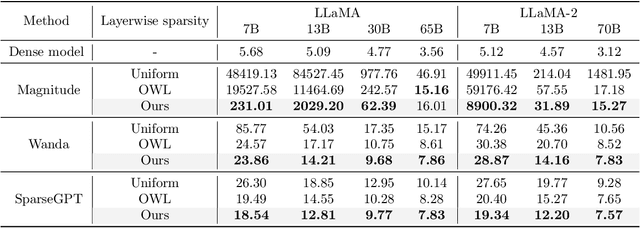
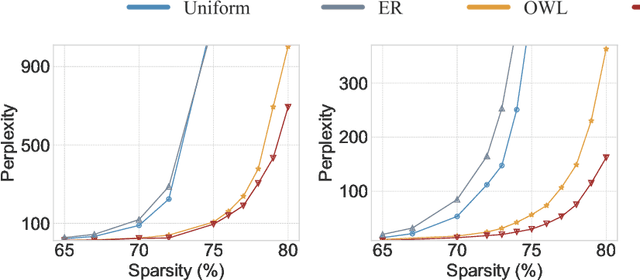
Abstract:Recent work on pruning large language models (LLMs) has shown that one can eliminate a large number of parameters without compromising performance, making pruning a promising strategy to reduce LLM model size. Existing LLM pruning strategies typically assign uniform pruning ratios across layers, limiting overall pruning ability; and recent work on layerwise pruning of LLMs is often based on heuristics that can easily lead to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we leverage Heavy-Tailed Self-Regularization (HT-SR) Theory, in particular the shape of empirical spectral densities (ESDs) of weight matrices, to design improved layerwise pruning ratios for LLMs. Our analysis reveals a wide variability in how well-trained, and thus relatedly how prunable, different layers of an LLM are. Based on this, we propose AlphaPruning, which uses shape metrics to allocate layerwise sparsity ratios in a more theoretically principled manner. AlphaPruning can be used in conjunction with multiple existing LLM pruning methods. Our empirical results show that AlphaPruning prunes LLaMA-7B to 80% sparsity while maintaining reasonable perplexity, marking a first in the literature on LLMs. We have open-sourced our code at https://github.com/haiquanlu/AlphaPruning.
Early Preparation Pays Off: New Classifier Pre-tuning for Class Incremental Semantic Segmentation
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Class incremental semantic segmentation aims to preserve old knowledge while learning new tasks, however, it is impeded by catastrophic forgetting and background shift issues. Prior works indicate the pivotal importance of initializing new classifiers and mainly focus on transferring knowledge from the background classifier or preparing classifiers for future classes, neglecting the flexibility and variance of new classifiers. In this paper, we propose a new classifier pre-tuning~(NeST) method applied before the formal training process, learning a transformation from old classifiers to generate new classifiers for initialization rather than directly tuning the parameters of new classifiers. Our method can make new classifiers align with the backbone and adapt to the new data, preventing drastic changes in the feature extractor when learning new classes. Besides, we design a strategy considering the cross-task class similarity to initialize matrices used in the transformation, helping achieve the stability-plasticity trade-off. Experiments on Pascal VOC 2012 and ADE20K datasets show that the proposed strategy can significantly improve the performance of previous methods. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/zhengyuan-xie/ECCV24_NeST}.
Group Movable Antenna With Flexible Sparsity: Joint Array Position and Sparsity Optimization
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Movable antenna (MA) is a promising technology to exploit the spatial variation of wireless channel for performance enhancement, by dynamically varying the antenna position within a certain region. However, for multi-antenna communication systems, moving each antenna independently not only requires prohibitive complexity to find the optimal antenna positions, but also incurs sophisticated movement control in practice. To address this issue, this letter proposes a new MA architecture termed group MA (GMA), enabling the group movement of all elements collectively in a continuous manner, and simultaneously achieving flexible array architecture by antenna selection (AS). In this letter, we focus on the uniform sparse array based GMA, where equally spaced antenna elements are selected to achieve desired array sparsity. The array position and sparsity level are jointly optimized to maximize the sum rate of the multi-user communication system. Numerical results verify the necessity to optimize the position and sparsity of GMA, and considerable performance gain is achieved as compared to the conventional fixed-position antenna (FPA).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge