Guoyu Lu
Automated Genomic Interpretation via Concept Bottleneck Models for Medical Robotics
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:We propose an automated genomic interpretation module that transforms raw DNA sequences into actionable, interpretable decisions suitable for integration into medical automation and robotic systems. Our framework combines Chaos Game Representation (CGR) with a Concept Bottleneck Model (CBM), enforcing predictions to flow through biologically meaningful concepts such as GC content, CpG density, and k mer motifs. To enhance reliability, we incorporate concept fidelity supervision, prior consistency alignment, KL distribution matching, and uncertainty calibration. Beyond accurate classification of HIV subtypes across both in-house and LANL datasets, our module delivers interpretable evidence that can be directly validated against biological priors. A cost aware recommendation layer further translates predictive outputs into decision policies that balance accuracy, calibration, and clinical utility, reducing unnecessary retests and improving efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed system achieves state of the art classification performance, superior concept prediction fidelity, and more favorable cost benefit trade-offs compared to existing baselines. By bridging the gap between interpretable genomic modeling and automated decision-making, this work establishes a reliable foundation for robotic and clinical automation in genomic medicine.
Graph Integrated Multimodal Concept Bottleneck Model
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:With growing demand for interpretability in deep learning, especially in high stakes domains, Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) address this by inserting human understandable concepts into the prediction pipeline, but they are generally single modal and ignore structured concept relationships. To overcome these limitations, we present MoE-SGT, a reasoning driven framework that augments CBMs with a structure injecting Graph Transformer and a Mixture of Experts (MoE) module. We construct answer-concept and answer-question graphs for multimodal inputs to explicitly model the structured relationships among concepts. Subsequently, we integrate Graph Transformer to capture multi level dependencies, addressing the limitations of traditional Concept Bottleneck Models in modeling concept interactions. However, it still encounters bottlenecks in adapting to complex concept patterns. Therefore, we replace the feed forward layers with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) module, enabling the model to have greater capacity in learning diverse concept relationships while dynamically allocating reasoning tasks to different sub experts, thereby significantly enhancing the model's adaptability to complex concept reasoning. MoE-SGT achieves higher accuracy than other concept bottleneck networks on multiple datasets by modeling structured relationships among concepts and utilizing a dynamic expert selection mechanism.
Adaptive Event Stream Slicing for Open-Vocabulary Event-Based Object Detection via Vision-Language Knowledge Distillation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Event cameras offer advantages in object detection tasks due to high-speed response, low latency, and robustness to motion blur. However, event cameras lack texture and color information, making open-vocabulary detection particularly challenging. Current event-based detection methods are typically trained on predefined categories, limiting their ability to generalize to novel objects, where encountering previously unseen objects is common. Vision-language models (VLMs) have enabled open-vocabulary object detection in RGB images. However, the modality gap between images and event streams makes it ineffective to directly transfer CLIP to event data, as CLIP was not designed for event streams. To bridge this gap, we propose an event-image knowledge distillation framework that leverages CLIP's semantic understanding to achieve open-vocabulary object detection on event data. Instead of training CLIP directly on event streams, we use image frames as inputs to a teacher model, guiding the event-based student model to learn CLIP's rich visual representations. Through spatial attention-based distillation, the student network learns meaningful visual features directly from raw event inputs while inheriting CLIP's broad visual knowledge. Furthermore, to prevent information loss due to event data segmentation, we design a hybrid spiking neural network (SNN) and convolutional neural network (CNN) framework. Unlike fixed-group event segmentation methods, which often discard crucial temporal information, our SNN adaptively determines the optimal event segmentation moments, ensuring that key temporal features are extracted. The extracted event features are then processed by CNNs for object detection.
3D Plant Root Skeleton Detection and Extraction
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Plant roots typically exhibit a highly complex and dense architecture, incorporating numerous slender lateral roots and branches, which significantly hinders the precise capture and modeling of the entire root system. Additionally, roots often lack sufficient texture and color information, making it difficult to identify and track root traits using visual methods. Previous research on roots has been largely confined to 2D studies; however, exploring the 3D architecture of roots is crucial in botany. Since roots grow in real 3D space, 3D phenotypic information is more critical for studying genetic traits and their impact on root development. We have introduced a 3D root skeleton extraction method that efficiently derives the 3D architecture of plant roots from a few images. This method includes the detection and matching of lateral roots, triangulation to extract the skeletal structure of lateral roots, and the integration of lateral and primary roots. We developed a highly complex root dataset and tested our method on it. The extracted 3D root skeletons showed considerable similarity to the ground truth, validating the effectiveness of the model. This method can play a significant role in automated breeding robots. Through precise 3D root structure analysis, breeding robots can better identify plant phenotypic traits, especially root structure and growth patterns, helping practitioners select seeds with superior root systems. This automated approach not only improves breeding efficiency but also reduces manual intervention, making the breeding process more intelligent and efficient, thus advancing modern agriculture.
Vision-Language Embodiment for Monocular Depth Estimation
Mar 18, 2025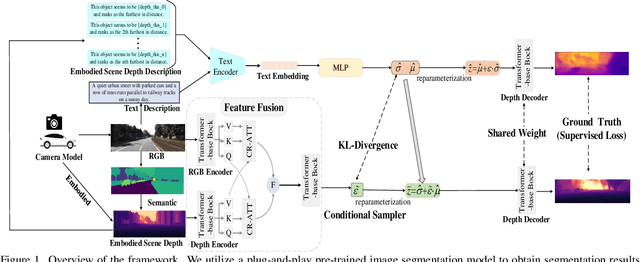
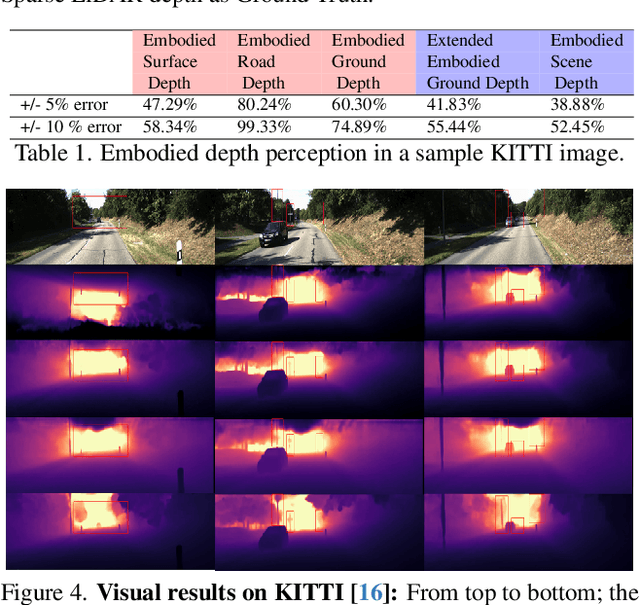
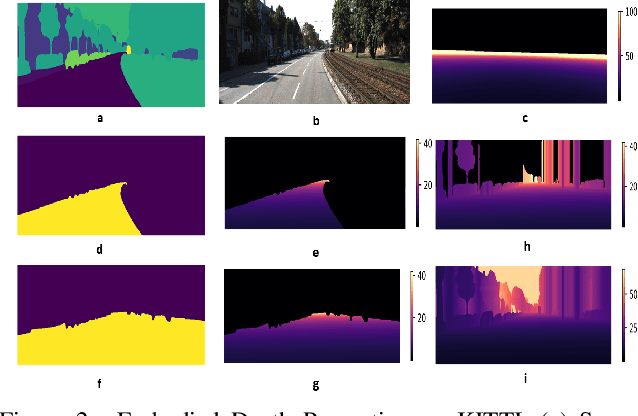
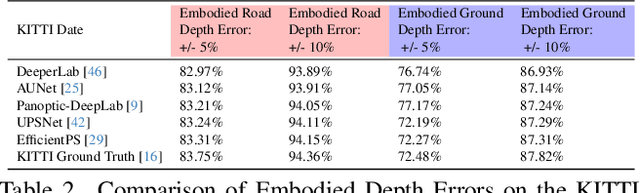
Abstract:Depth estimation is a core problem in robotic perception and vision tasks, but 3D reconstruction from a single image presents inherent uncertainties. Current depth estimation models primarily rely on inter-image relationships for supervised training, often overlooking the intrinsic information provided by the camera itself. We propose a method that embodies the camera model and its physical characteristics into a deep learning model, computing embodied scene depth through real-time interactions with road environments. The model can calculate embodied scene depth in real-time based on immediate environmental changes using only the intrinsic properties of the camera, without any additional equipment. By combining embodied scene depth with RGB image features, the model gains a comprehensive perspective on both geometric and visual details. Additionally, we incorporate text descriptions containing environmental content and depth information as priors for scene understanding, enriching the model's perception of objects. This integration of image and language - two inherently ambiguous modalities - leverages their complementary strengths for monocular depth estimation. The real-time nature of the embodied language and depth prior model ensures that the model can continuously adjust its perception and behavior in dynamic environments. Experimental results show that the embodied depth estimation method enhances model performance across different scenes.
Language-Depth Navigated Thermal and Visible Image Fusion
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Depth-guided multimodal fusion combines depth information from visible and infrared images, significantly enhancing the performance of 3D reconstruction and robotics applications. Existing thermal-visible image fusion mainly focuses on detection tasks, ignoring other critical information such as depth. By addressing the limitations of single modalities in low-light and complex environments, the depth information from fused images not only generates more accurate point cloud data, improving the completeness and precision of 3D reconstruction, but also provides comprehensive scene understanding for robot navigation, localization, and environmental perception. This supports precise recognition and efficient operations in applications such as autonomous driving and rescue missions. We introduce a text-guided and depth-driven infrared and visible image fusion network. The model consists of an image fusion branch for extracting multi-channel complementary information through a diffusion model, equipped with a text-guided module, and two auxiliary depth estimation branches. The fusion branch uses CLIP to extract semantic information and parameters from depth-enriched image descriptions to guide the diffusion model in extracting multi-channel features and generating fused images. These fused images are then input into the depth estimation branches to calculate depth-driven loss, optimizing the image fusion network. This framework aims to integrate vision-language and depth to directly generate color-fused images from multimodal inputs.
Keypoint Detection and Description for Raw Bayer Images
Mar 11, 2025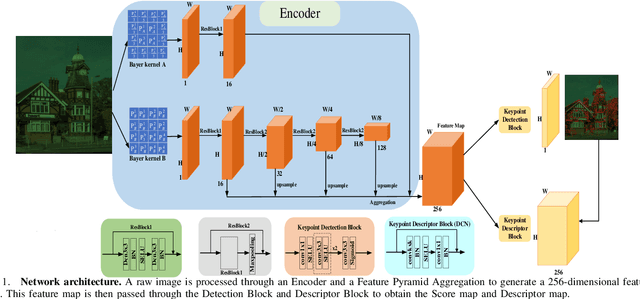
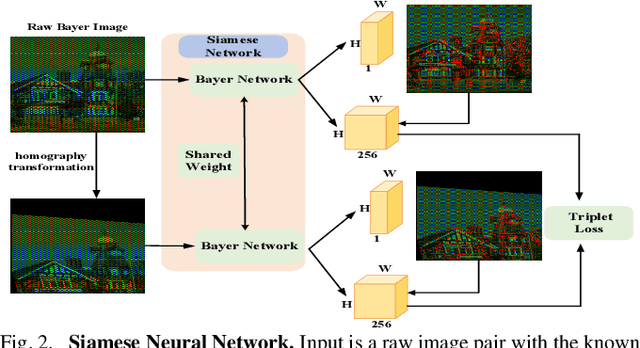
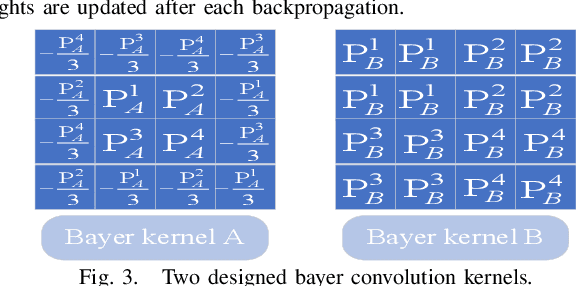
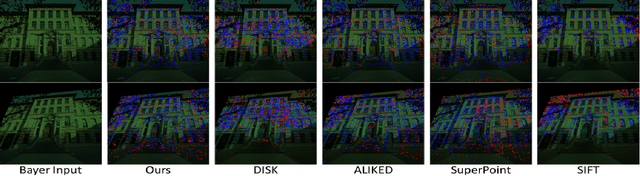
Abstract:Keypoint detection and local feature description are fundamental tasks in robotic perception, critical for applications such as SLAM, robot localization, feature matching, pose estimation, and 3D mapping. While existing methods predominantly operate on RGB images, we propose a novel network that directly processes raw images, bypassing the need for the Image Signal Processor (ISP). This approach significantly reduces hardware requirements and memory consumption, which is crucial for robotic vision systems. Our method introduces two custom-designed convolutional kernels capable of performing convolutions directly on raw images, preserving inter-channel information without converting to RGB. Experimental results show that our network outperforms existing algorithms on raw images, achieving higher accuracy and stability under large rotations and scale variations. This work represents the first attempt to develop a keypoint detection and feature description network specifically for raw images, offering a more efficient solution for resource-constrained environments.
Evaluation of OpenAI o1: Opportunities and Challenges of AGI
Sep 27, 2024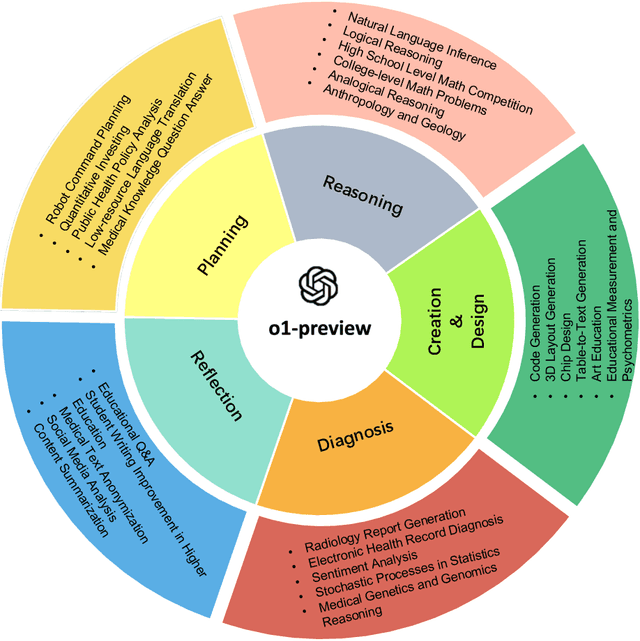
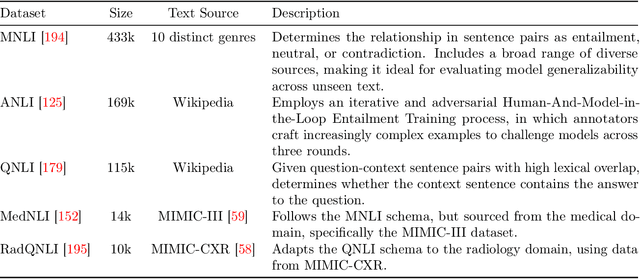
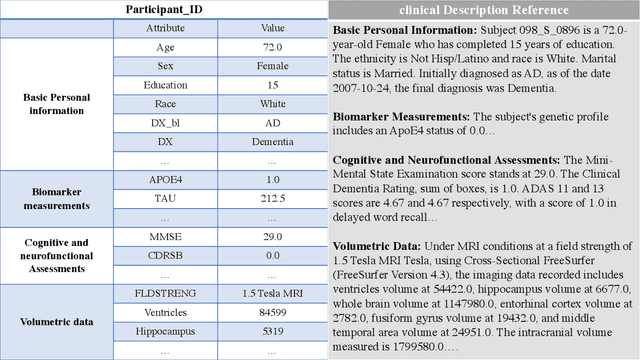
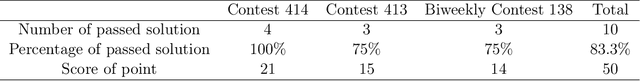
Abstract:This comprehensive study evaluates the performance of OpenAI's o1-preview large language model across a diverse array of complex reasoning tasks, spanning multiple domains, including computer science, mathematics, natural sciences, medicine, linguistics, and social sciences. Through rigorous testing, o1-preview demonstrated remarkable capabilities, often achieving human-level or superior performance in areas ranging from coding challenges to scientific reasoning and from language processing to creative problem-solving. Key findings include: -83.3% success rate in solving complex competitive programming problems, surpassing many human experts. -Superior ability in generating coherent and accurate radiology reports, outperforming other evaluated models. -100% accuracy in high school-level mathematical reasoning tasks, providing detailed step-by-step solutions. -Advanced natural language inference capabilities across general and specialized domains like medicine. -Impressive performance in chip design tasks, outperforming specialized models in areas such as EDA script generation and bug analysis. -Remarkable proficiency in anthropology and geology, demonstrating deep understanding and reasoning in these specialized fields. -Strong capabilities in quantitative investing. O1 has comprehensive financial knowledge and statistical modeling skills. -Effective performance in social media analysis, including sentiment analysis and emotion recognition. The model excelled particularly in tasks requiring intricate reasoning and knowledge integration across various fields. While some limitations were observed, including occasional errors on simpler problems and challenges with certain highly specialized concepts, the overall results indicate significant progress towards artificial general intelligence.
Underground Mapping and Localization Based on Ground-Penetrating Radar
Sep 24, 2024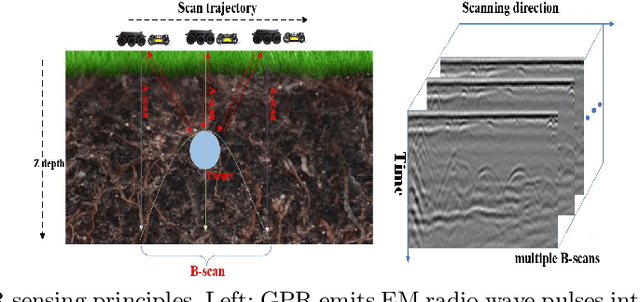
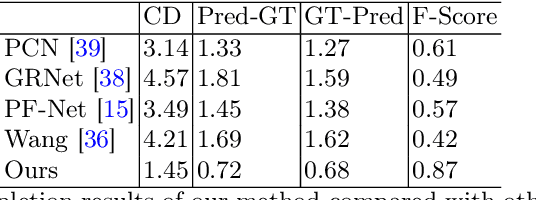
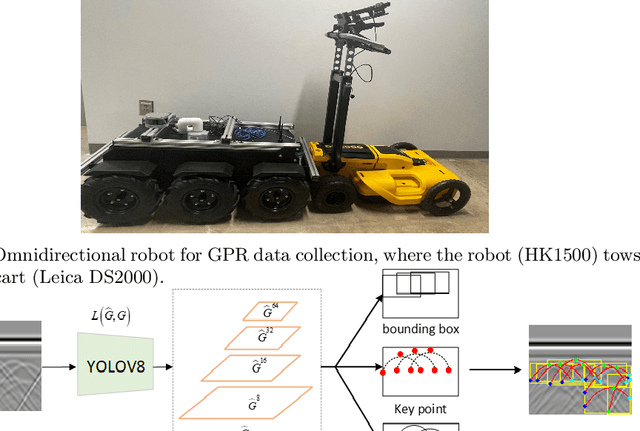
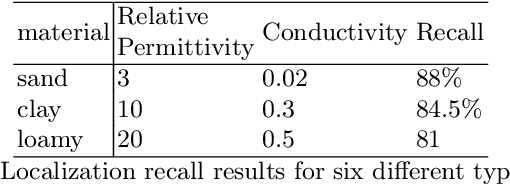
Abstract:3D object reconstruction based on deep neural networks has gained increasing attention in recent years. However, 3D reconstruction of underground objects to generate point cloud maps remains a challenge. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is one of the most powerful and extensively used tools for detecting and locating underground objects such as plant root systems and pipelines, with its cost-effectiveness and continuously evolving technology. This paper introduces a parabolic signal detection network based on deep convolutional neural networks, utilizing B-scan images from GPR sensors. The detected keypoints can aid in accurately fitting parabolic curves used to interpret the original GPR B-scan images as cross-sections of the object model. Additionally, a multi-task point cloud network was designed to perform both point cloud segmentation and completion simultaneously, filling in sparse point cloud maps. For unknown locations, GPR A-scan data can be used to match corresponding A-scan data in the constructed map, pinpointing the position to verify the accuracy of the map construction by the model. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Self-Supervised Depth Estimation Based on Camera Models
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Depth estimationn is a critical topic for robotics and vision-related tasks. In monocular depth estimation, in comparison with supervised learning that requires expensive ground truth labeling, self-supervised methods possess great potential due to no labeling cost. However, self-supervised learning still has a large gap with supervised learning in depth estimation performance. Meanwhile, scaling is also a major issue for monocular unsupervised depth estimation, which commonly still needs ground truth scale from GPS, LiDAR, or existing maps to correct. In deep learning era, while existing methods mainly rely on the exploration of image relationships to train the unsupervised neural networks, fundamental information provided by the camera itself has been generally ignored, which can provide extensive supervision information for free, without the need for any extra equipment to provide supervision signals. Utilizing the camera itself's intrinsics and extrinsics, depth information can be calculated for ground regions and regions connecting ground based on physical principles, providing free supervision information without any other sensors. The method is easy to realize and can be a component to enhance the effects of all the unsupervised methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge