Guangyin Jin
M3-Net: A Cost-Effective Graph-Free MLP-Based Model for Traffic Prediction
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Achieving accurate traffic prediction is a fundamental but crucial task in the development of current intelligent transportation systems.Most of the mainstream methods that have made breakthroughs in traffic prediction rely on spatio-temporal graph neural networks, spatio-temporal attention mechanisms, etc. The main challenges of the existing deep learning approaches are that they either depend on a complete traffic network structure or require intricate model designs to capture complex spatio-temporal dependencies. These limitations pose significant challenges for the efficient deployment and operation of deep learning models on large-scale datasets. To address these challenges, we propose a cost-effective graph-free Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) based model M3-Net for traffic prediction. Our proposed model not only employs time series and spatio-temporal embeddings for efficient feature processing but also first introduces a novel MLP-Mixer architecture with a mixture of experts (MoE) mechanism. Extensive experiments conducted on multiple real datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model in terms of prediction performance and lightweight deployment.
Synergistic Prompting for Robust Visual Recognition with Missing Modalities
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Large-scale multi-modal models have demonstrated remarkable performance across various visual recognition tasks by leveraging extensive paired multi-modal training data. However, in real-world applications, the presence of missing or incomplete modality inputs often leads to significant performance degradation. Recent research has focused on prompt-based strategies to tackle this issue; however, existing methods are hindered by two major limitations: (1) static prompts lack the flexibility to adapt to varying missing-data conditions, and (2) basic prompt-tuning methods struggle to ensure reliable performance when critical modalities are missing.To address these challenges, we propose a novel Synergistic Prompting (SyP) framework for robust visual recognition with missing modalities. The proposed SyP introduces two key innovations: (I) a Dynamic Adapter, which computes adaptive scaling factors to dynamically generate prompts, replacing static parameters for flexible multi-modal adaptation, and (II) a Synergistic Prompting Strategy, which combines static and dynamic prompts to balance information across modalities, ensuring robust reasoning even when key modalities are missing. The proposed SyP achieves significant performance improvements over existing approaches across three widely-used visual recognition datasets, demonstrating robustness under diverse missing rates and conditions. Extensive experiments and ablation studies validate its effectiveness in handling missing modalities, highlighting its superior adaptability and reliability.
Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Point Process for Traffic Congestion Event Prediction
Nov 15, 2023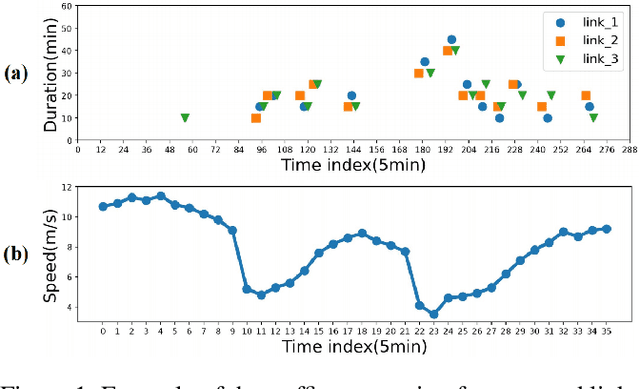
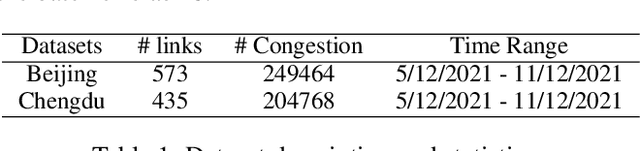
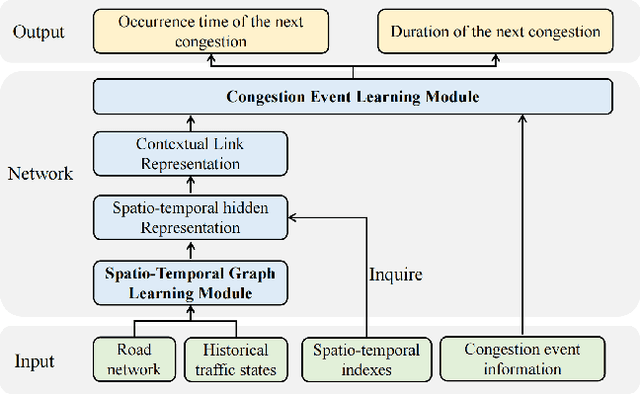
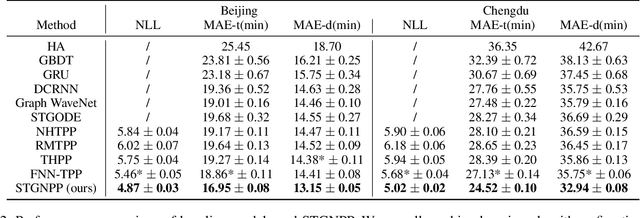
Abstract:Traffic congestion event prediction is an important yet challenging task in intelligent transportation systems. Many existing works about traffic prediction integrate various temporal encoders and graph convolution networks (GCNs), called spatio-temporal graph-based neural networks, which focus on predicting dense variables such as flow, speed and demand in time snapshots, but they can hardly forecast the traffic congestion events that are sparsely distributed on the continuous time axis. In recent years, neural point process (NPP) has emerged as an appropriate framework for event prediction in continuous time scenarios. However, most conventional works about NPP cannot model the complex spatio-temporal dependencies and congestion evolution patterns. To address these limitations, we propose a spatio-temporal graph neural point process framework, named STGNPP for traffic congestion event prediction. Specifically, we first design the spatio-temporal graph learning module to fully capture the long-range spatio-temporal dependencies from the historical traffic state data along with the road network. The extracted spatio-temporal hidden representation and congestion event information are then fed into a continuous gated recurrent unit to model the congestion evolution patterns. In particular, to fully exploit the periodic information, we also improve the intensity function calculation of the point process with a periodic gated mechanism. Finally, our model simultaneously predicts the occurrence time and duration of the next congestion. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance in comparison to existing state-of-the-art approaches.
Exploring Progress in Multivariate Time Series Forecasting: Comprehensive Benchmarking and Heterogeneity Analysis
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Multivariate Time Series (MTS) widely exists in real-word complex systems, such as traffic and energy systems, making their forecasting crucial for understanding and influencing these systems. Recently, deep learning-based approaches have gained much popularity for effectively modeling temporal and spatial dependencies in MTS, specifically in Long-term Time Series Forecasting (LTSF) and Spatial-Temporal Forecasting (STF). However, the fair benchmarking issue and the choice of technical approaches have been hotly debated in related work. Such controversies significantly hinder our understanding of progress in this field. Thus, this paper aims to address these controversies to present insights into advancements achieved. To resolve benchmarking issues, we introduce BasicTS, a benchmark designed for fair comparisons in MTS forecasting. BasicTS establishes a unified training pipeline and reasonable evaluation settings, enabling an unbiased evaluation of over 30 popular MTS forecasting models on more than 18 datasets. Furthermore, we highlight the heterogeneity among MTS datasets and classify them based on temporal and spatial characteristics. We further prove that neglecting heterogeneity is the primary reason for generating controversies in technical approaches. Moreover, based on the proposed BasicTS and rich heterogeneous MTS datasets, we conduct an exhaustive and reproducible performance and efficiency comparison of popular models, providing insights for researchers in selecting and designing MTS forecasting models.
A Survey on Service Route and Time Prediction in Instant Delivery: Taxonomy, Progress, and Prospects
Sep 03, 2023



Abstract:Instant delivery services, such as food delivery and package delivery, have achieved explosive growth in recent years by providing customers with daily-life convenience. An emerging research area within these services is service Route\&Time Prediction (RTP), which aims to estimate the future service route as well as the arrival time of a given worker. As one of the most crucial tasks in those service platforms, RTP stands central to enhancing user satisfaction and trimming operational expenditures on these platforms. Despite a plethora of algorithms developed to date, there is no systematic, comprehensive survey to guide researchers in this domain. To fill this gap, our work presents the first comprehensive survey that methodically categorizes recent advances in service route and time prediction. We start by defining the RTP challenge and then delve into the metrics that are often employed. Following that, we scrutinize the existing RTP methodologies, presenting a novel taxonomy of them. We categorize these methods based on three criteria: (i) type of task, subdivided into only-route prediction, only-time prediction, and joint route\&time prediction; (ii) model architecture, which encompasses sequence-based and graph-based models; and (iii) learning paradigm, including Supervised Learning (SL) and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). Conclusively, we highlight the limitations of current research and suggest prospective avenues. We believe that the taxonomy, progress, and prospects introduced in this paper can significantly promote the development of this field.
HUTFormer: Hierarchical U-Net Transformer for Long-Term Traffic Forecasting
Jul 27, 2023



Abstract:Traffic forecasting, which aims to predict traffic conditions based on historical observations, has been an enduring research topic and is widely recognized as an essential component of intelligent transportation. Recent proposals on Spatial-Temporal Graph Neural Networks (STGNNs) have made significant progress by combining sequential models with graph convolution networks. However, due to high complexity issues, STGNNs only focus on short-term traffic forecasting, e.g., 1-hour forecasting, while ignoring more practical long-term forecasting. In this paper, we make the first attempt to explore long-term traffic forecasting, e.g., 1-day forecasting. To this end, we first reveal its unique challenges in exploiting multi-scale representations. Then, we propose a novel Hierarchical U-net TransFormer (HUTFormer) to address the issues of long-term traffic forecasting. HUTFormer consists of a hierarchical encoder and decoder to jointly generate and utilize multi-scale representations of traffic data. Specifically, for the encoder, we propose window self-attention and segment merging to extract multi-scale representations from long-term traffic data. For the decoder, we design a cross-scale attention mechanism to effectively incorporate multi-scale representations. In addition, HUTFormer employs an efficient input embedding strategy to address the complexity issues. Extensive experiments on four traffic datasets show that the proposed HUTFormer significantly outperforms state-of-the-art traffic forecasting and long time series forecasting baselines.
Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Networks for Predictive Learning in Urban Computing: A Survey
Mar 25, 2023



Abstract:With the development of sophisticated sensors and large database technologies, more and more spatio-temporal data in urban systems are recorded and stored. Predictive learning for the evolution patterns of these spatio-temporal data is a basic but important loop in urban computing, which can better support urban intelligent management decisions, especially in the fields of transportation, environment, security, public health, etc. Since traditional statistical learning and deep learning methods can hardly capture the complex correlations in the urban spatio-temporal data, the framework of spatio-temporal graph neural network (STGNN) has been proposed in recent years. STGNNs enable the extraction of complex spatio-temporal dependencies by integrating graph neural networks (GNNs) and various temporal learning methods. However, for different predictive learning tasks, it is a challenging problem to effectively design the spatial dependencies learning modules, temporal dependencies learning modules and spatio-temporal dependencies fusion methods in STGNN framework. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive survey on recent progress on STGNN technologies for predictive learning in urban computing. We first briefly introduce the construction methods of spatio-temporal graph data and popular deep learning models that are employed in STGNNs. Then we sort out the main application domains and specific predictive learning tasks from the existing literature. Next we analyze the design approaches of STGNN framework and the combination with some advanced technologies in recent years. Finally, we conclude the limitations of the existing research and propose some potential directions.
Automated Dilated Spatio-Temporal Synchronous Graph Modeling for Traffic Prediction
Jul 22, 2022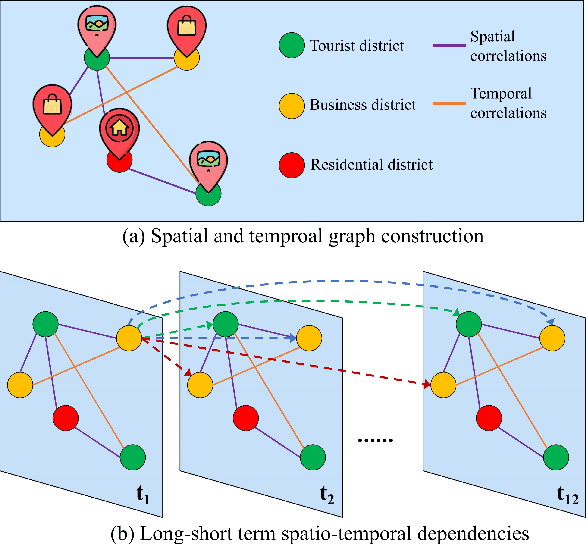
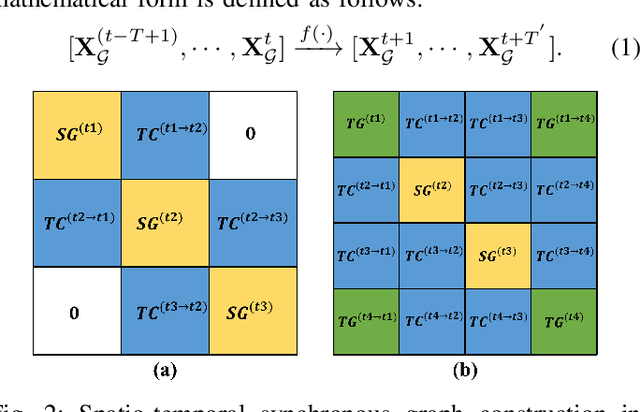
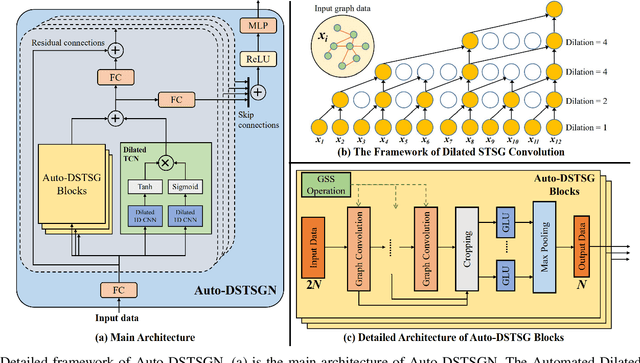
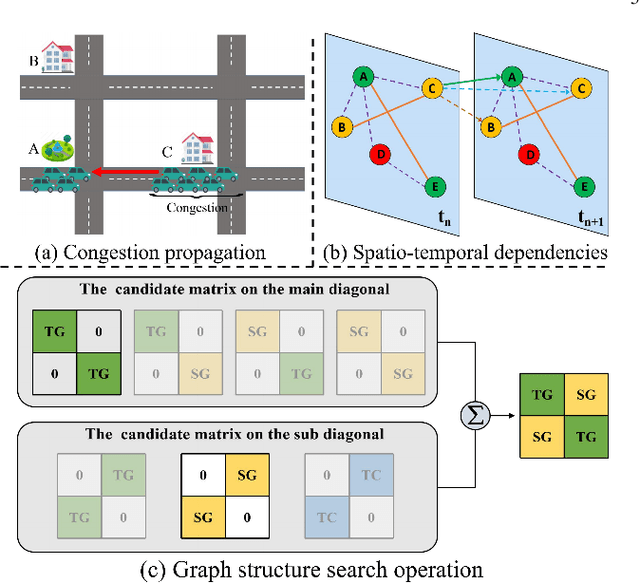
Abstract:Accurate traffic prediction is a challenging task in intelligent transportation systems because of the complex spatio-temporal dependencies in transportation networks. Many existing works utilize sophisticated temporal modeling approaches to incorporate with graph convolution networks (GCNs) for capturing short-term and long-term spatio-temporal dependencies. However, these separated modules with complicated designs could restrict effectiveness and efficiency of spatio-temporal representation learning. Furthermore, most previous works adopt the fixed graph construction methods to characterize the global spatio-temporal relations, which limits the learning capability of the model for different time periods and even different data scenarios. To overcome these limitations, we propose an automated dilated spatio-temporal synchronous graph network, named Auto-DSTSGN for traffic prediction. Specifically, we design an automated dilated spatio-temporal synchronous graph (Auto-DSTSG) module to capture the short-term and long-term spatio-temporal correlations by stacking deeper layers with dilation factors in an increasing order. Further, we propose a graph structure search approach to automatically construct the spatio-temporal synchronous graph that can adapt to different data scenarios. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate that our model can achieve about 10% improvements compared with the state-of-art methods. Source codes are available at https://github.com/jinguangyin/Auto-DSTSGN.
Network-wide link travel time and station waiting time estimation using automatic fare collection data: A computational graph approach
Aug 19, 2021



Abstract:Urban rail transit (URT) system plays a dominating role in many megacities like Beijing and Hong Kong. Due to its important role and complex nature, it is always in great need for public agencies to better understand the performance of the URT system. This paper focuses on an essential and hard problem to estimate the network-wide link travel time and station waiting time using the automatic fare collection (AFC) data in the URT system, which is beneficial to better understand the system-wide real-time operation state. The emerging data-driven techniques, such as computational graph (CG) models in the machine learning field, provide a new solution for solving this problem. In this study, we first formulate a data-driven estimation optimization framework to estimate the link travel time and station waiting time. Then, we cast the estimation optimization model into a CG framework to solve the optimization problem and obtain the estimation results. The methodology is verified on a synthetic URT network and applied to a real-world URT network using the synthetic and real-world AFC data, respectively. Results show the robustness and effectiveness of the CG-based framework. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that the CG is applied to the URT. This study can provide critical insights to better understand the operational state in URT.
Spatial-Temporal Dual Graph Neural Networks for Travel Time Estimation
May 28, 2021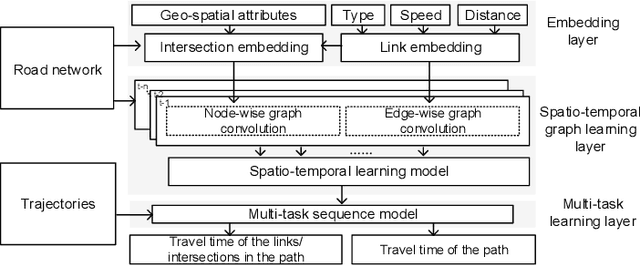
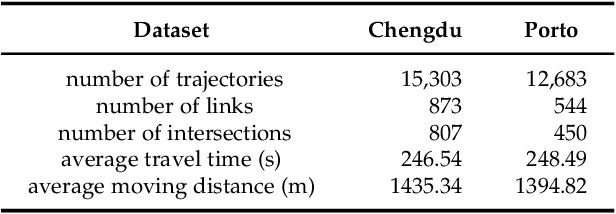
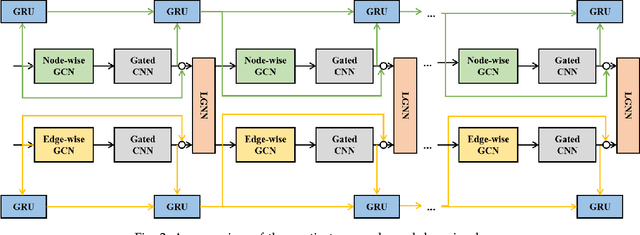
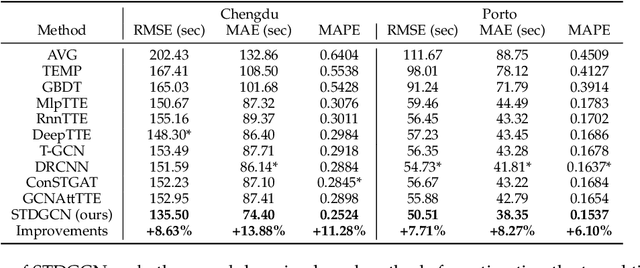
Abstract:Travel time estimation is a basic but important part in intelligent transportation systems, especially widely applied in online map services to help travel navigation and route planning. Most previous works commonly model the road segments or intersections separately and obtain their spatial-temporal characteristics for travel time estimation. However, due to the continuous alternation of the road segments and intersections, the dynamic features of them are supposed to be coupled and interactive. Therefore, modeling one of them limits further improvement in accuracy of estimating travel time. To address the above problems, we propose a novel graph-based deep learning framework for travel time estimation, namely Spatial-Temporal Dual Graph Neural Networks (STDGNN). Specifically, we first establish the spatial-temporal dual graph architecture to capture the complex correlations of both intersections and road segments. The adjacency relations of intersections and that of road segments are respectively characterized by node-wise graph and edge-wise graph. In order to capture the joint spatial-temporal dynamics of the intersections and road segments, we adopt the spatial-temporal learning layer that incorporates the multi-scale spatial-temporal graph convolution networks and dual graph interaction networks. Followed by the spatial-temporal learning layer, we also employ the multi-task learning layer to estimate the travel time of a given whole route and each road segment simultaneously. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate our proposed model on two real-world trajectory datasets, and the experimental results show that STDGNN significantly outperforms several state-of-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge