Garrison Cottrell
Speech Recognition and Multi-Speaker Diarization of Long Conversations
May 16, 2020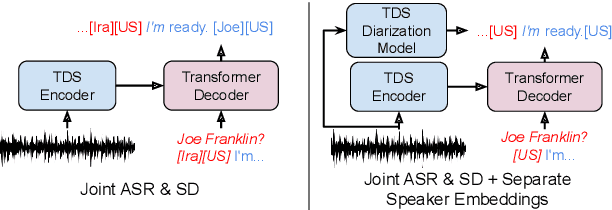
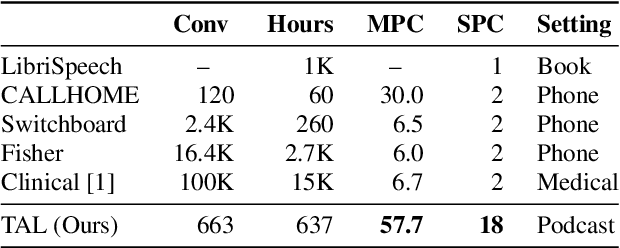
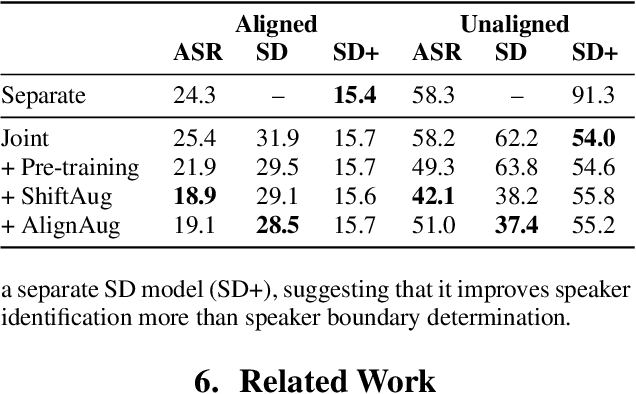
Abstract:Speech recognition (ASR) and speaker diarization (SD) models have traditionally been trained separately to produce rich conversation transcripts with speaker labels. Recent advances have shown that joint ASR and SD models can learn to leverage audio-lexical inter-dependencies to improve word diarization performance. We introduce a new benchmark of hour-long podcasts collected from the weekly This American Life radio program to better compare these approaches when applied to extended multi-speaker conversations. We find that training separate ASR and SD models perform better when utterance boundaries are known but otherwise joint models can perform better. To handle long conversations with unknown utterance boundaries, we introduce a striding attention decoding algorithm and data augmentation techniques which, combined with model pre-training, improves ASR and SD.
Deflecting Adversarial Attacks
Feb 18, 2020

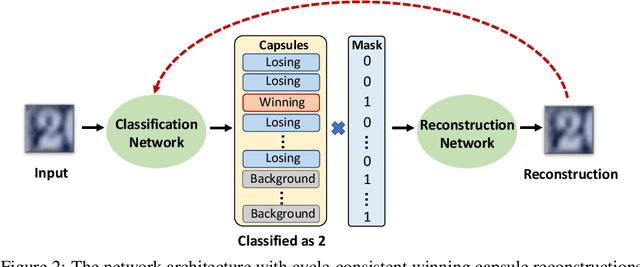

Abstract:There has been an ongoing cycle where stronger defenses against adversarial attacks are subsequently broken by a more advanced defense-aware attack. We present a new approach towards ending this cycle where we "deflect'' adversarial attacks by causing the attacker to produce an input that semantically resembles the attack's target class. To this end, we first propose a stronger defense based on Capsule Networks that combines three detection mechanisms to achieve state-of-the-art detection performance on both standard and defense-aware attacks. We then show that undetected attacks against our defense often perceptually resemble the adversarial target class by performing a human study where participants are asked to label images produced by the attack. These attack images can no longer be called "adversarial'' because our network classifies them the same way as humans do.
Detecting and Diagnosing Adversarial Images with Class-Conditional Capsule Reconstructions
Jul 05, 2019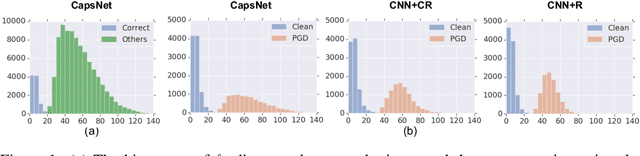
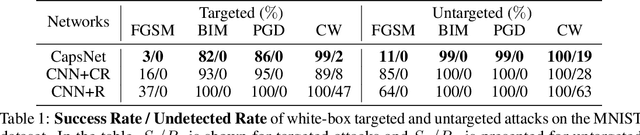
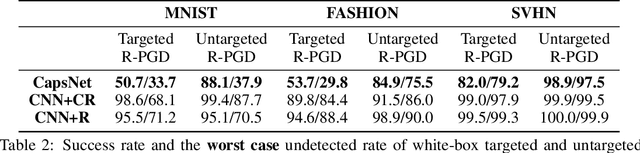
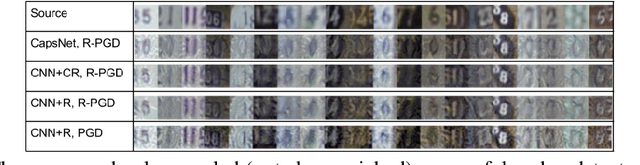
Abstract:Adversarial examples raise questions about whether neural network models are sensitive to the same visual features as humans. Most of the proposed methods for mitigating adversarial examples have subsequently been defeated by stronger attacks. Motivated by these issues, we take a different approach and propose to instead detect adversarial examples based on class-conditional reconstructions of the input. Our method uses the reconstruction network proposed as part of Capsule Networks (CapsNets), but is general enough to be applied to standard convolutional networks. We find that adversarial or otherwise corrupted images result in much larger reconstruction errors than normal inputs, prompting a simple detection method by thresholding the reconstruction error. Based on these findings, we propose the Reconstructive Attack which seeks both to cause a misclassification and a low reconstruction error. While this attack produces undetected adversarial examples, we find that for CapsNets the resulting perturbations can cause the images to appear visually more like the target class. This suggests that CapsNets utilize features that are more aligned with human perception and address the central issue raised by adversarial examples.
Imperceptible, Robust, and Targeted Adversarial Examples for Automatic Speech Recognition
Mar 22, 2019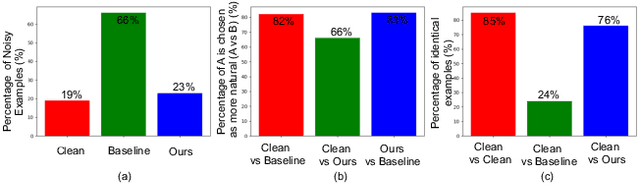
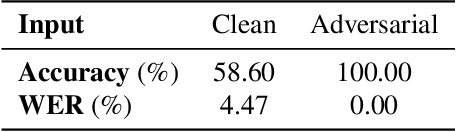
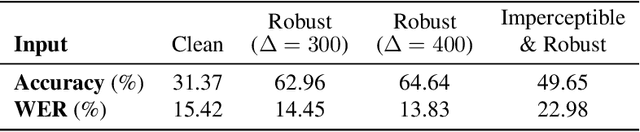
Abstract:Adversarial examples are inputs to machine learning models designed by an adversary to cause an incorrect output. So far, adversarial examples have been studied most extensively in the image domain. In this domain, adversarial examples can be constructed by imperceptibly modifying images to cause misclassification, and are practical in the physical world. In contrast, current targeted adversarial examples applied to speech recognition systems have neither of these properties: humans can easily identify the adversarial perturbations, and they are not effective when played over-the-air. This paper makes advances on both of these fronts. First, we develop effectively imperceptible audio adversarial examples (verified through a human study) by leveraging the psychoacoustic principle of auditory masking, while retaining 100% targeted success rate on arbitrary full-sentence targets. Next, we make progress towards physical-world over-the-air audio adversarial examples by constructing perturbations which remain effective even after applying realistic simulated environmental distortions.
Autofocus Layer for Semantic Segmentation
Jun 11, 2018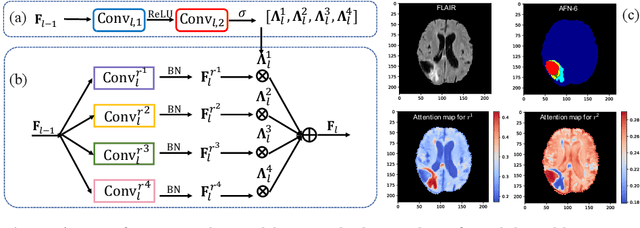
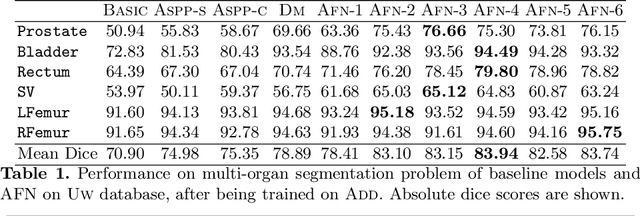
Abstract:We propose the autofocus convolutional layer for semantic segmentation with the objective of enhancing the capabilities of neural networks for multi-scale processing. Autofocus layers adaptively change the size of the effective receptive field based on the processed context to generate more powerful features. This is achieved by parallelising multiple convolutional layers with different dilation rates, combined by an attention mechanism that learns to focus on the optimal scales driven by context. By sharing the weights of the parallel convolutions we make the network scale-invariant, with only a modest increase in the number of parameters. The proposed autofocus layer can be easily integrated into existing networks to improve a model's representational power. We evaluate our models on the challenging tasks of multi-organ segmentation in pelvic CT and brain tumor segmentation in MRI and achieve very promising performance.
Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
Jun 01, 2018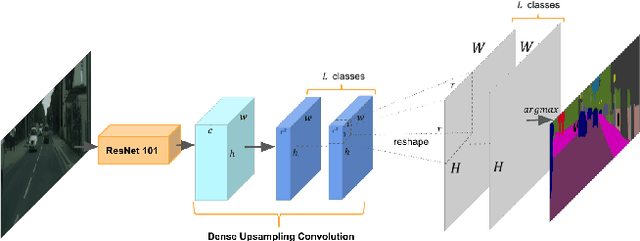
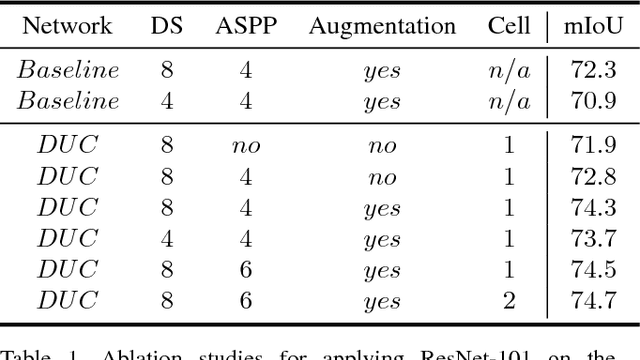
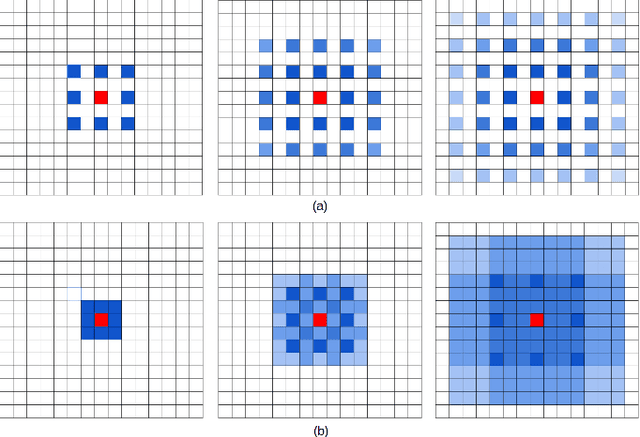
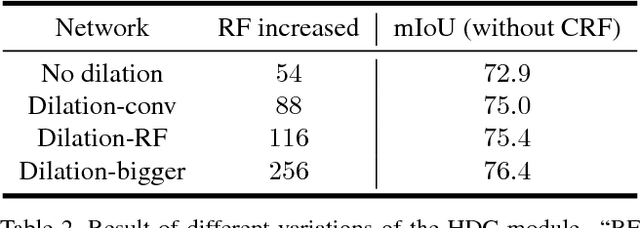
Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning, especially deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have led to significant improvement over previous semantic segmentation systems. Here we show how to improve pixel-wise semantic segmentation by manipulating convolution-related operations that are of both theoretical and practical value. First, we design dense upsampling convolution (DUC) to generate pixel-level prediction, which is able to capture and decode more detailed information that is generally missing in bilinear upsampling. Second, we propose a hybrid dilated convolution (HDC) framework in the encoding phase. This framework 1) effectively enlarges the receptive fields (RF) of the network to aggregate global information; 2) alleviates what we call the "gridding issue" caused by the standard dilated convolution operation. We evaluate our approaches thoroughly on the Cityscapes dataset, and achieve a state-of-art result of 80.1% mIOU in the test set at the time of submission. We also have achieved state-of-the-art overall on the KITTI road estimation benchmark and the PASCAL VOC2012 segmentation task. Our source code can be found at https://github.com/TuSimple/TuSimple-DUC .
A Dual-Stage Attention-Based Recurrent Neural Network for Time Series Prediction
Aug 14, 2017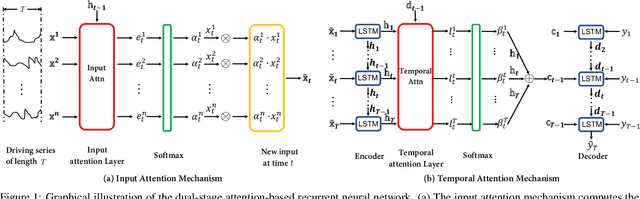
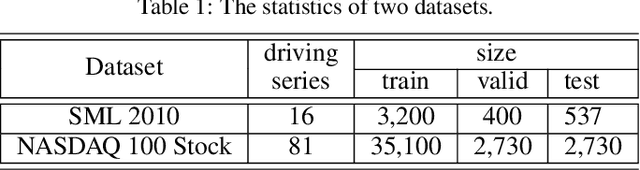
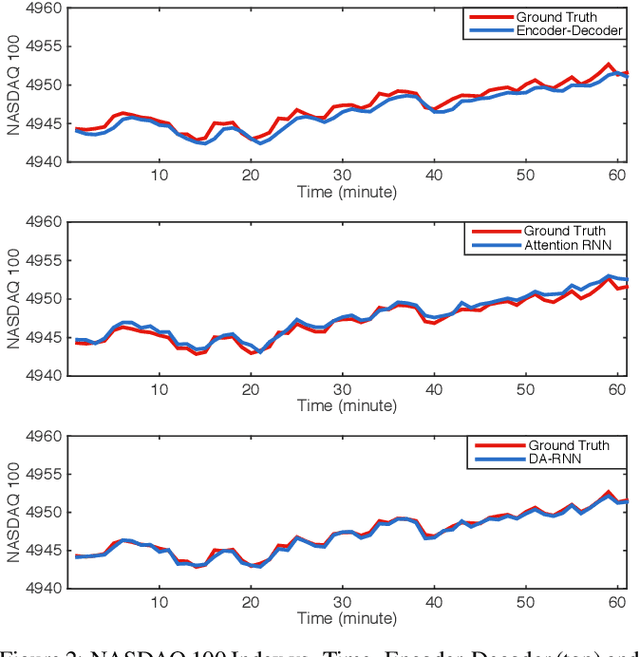
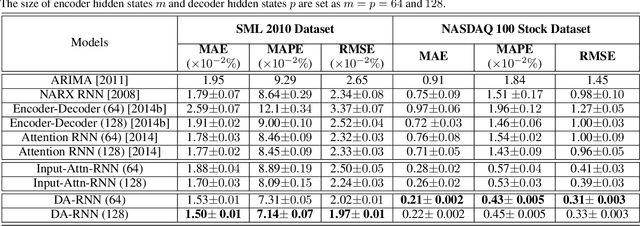
Abstract:The Nonlinear autoregressive exogenous (NARX) model, which predicts the current value of a time series based upon its previous values as well as the current and past values of multiple driving (exogenous) series, has been studied for decades. Despite the fact that various NARX models have been developed, few of them can capture the long-term temporal dependencies appropriately and select the relevant driving series to make predictions. In this paper, we propose a dual-stage attention-based recurrent neural network (DA-RNN) to address these two issues. In the first stage, we introduce an input attention mechanism to adaptively extract relevant driving series (a.k.a., input features) at each time step by referring to the previous encoder hidden state. In the second stage, we use a temporal attention mechanism to select relevant encoder hidden states across all time steps. With this dual-stage attention scheme, our model can not only make predictions effectively, but can also be easily interpreted. Thorough empirical studies based upon the SML 2010 dataset and the NASDAQ 100 Stock dataset demonstrate that the DA-RNN can outperform state-of-the-art methods for time series prediction.
Learning to see people like people
May 05, 2017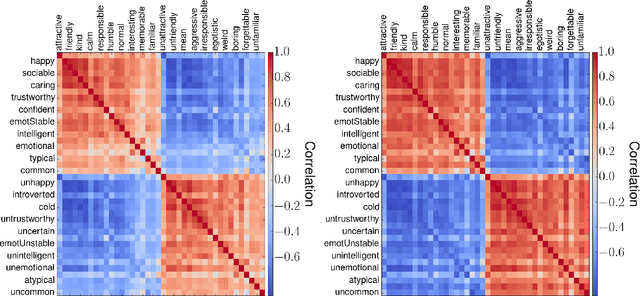

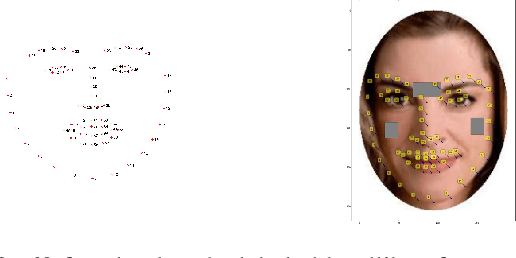
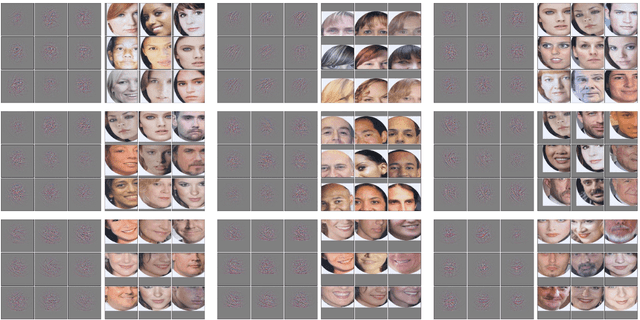
Abstract:Humans make complex inferences on faces, ranging from objective properties (gender, ethnicity, expression, age, identity, etc) to subjective judgments (facial attractiveness, trustworthiness, sociability, friendliness, etc). While the objective aspects of face perception have been extensively studied, relatively fewer computational models have been developed for the social impressions of faces. Bridging this gap, we develop a method to predict human impressions of faces in 40 subjective social dimensions, using deep representations from state-of-the-art neural networks. We find that model performance grows as the human consensus on a face trait increases, and that model predictions outperform human groups in correlation with human averages. This illustrates the learnability of subjective social perception of faces, especially when there is high human consensus. Our system can be used to decide which photographs from a personal collection will make the best impression. The results are significant for the field of social robotics, demonstrating that robots can learn the subjective judgments defining the underlying fabric of human interaction.
Are Face and Object Recognition Independent? A Neurocomputational Modeling Exploration
Apr 26, 2016Abstract:Are face and object recognition abilities independent? Although it is commonly believed that they are, Gauthier et al.(2014) recently showed that these abilities become more correlated as experience with nonface categories increases. They argued that there is a single underlying visual ability, v, that is expressed in performance with both face and nonface categories as experience grows. Using the Cambridge Face Memory Test and the Vanderbilt Expertise Test, they showed that the shared variance between Cambridge Face Memory Test and Vanderbilt Expertise Test performance increases monotonically as experience increases. Here, we address why a shared resource across different visual domains does not lead to competition and to an inverse correlation in abilities? We explain this conundrum using our neurocomputational model of face and object processing (The Model, TM). Our results show that, as in the behavioral data, the correlation between subordinate level face and object recognition accuracy increases as experience grows. We suggest that different domains do not compete for resources because the relevant features are shared between faces and objects. The essential power of experience is to generate a "spreading transform" for faces that generalizes to objects that must be individuated. Interestingly, when the task of the network is basic level categorization, no increase in the correlation between domains is observed. Hence, our model predicts that it is the type of experience that matters and that the source of the correlation is in the fusiform face area, rather than in cortical areas that subserve basic level categorization. This result is consistent with our previous modeling elucidating why the FFA is recruited for novel domains of expertise (Tong et al., 2008).
Modeling the Contribution of Central Versus Peripheral Vision in Scene, Object, and Face Recognition
Apr 25, 2016
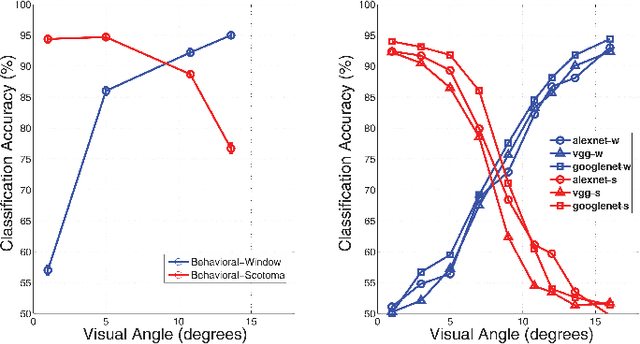
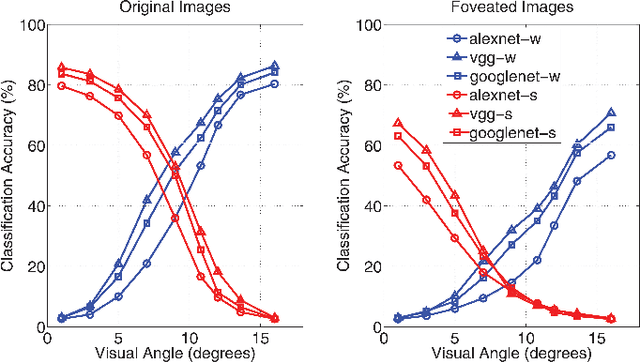

Abstract:It is commonly believed that the central visual field is important for recognizing objects and faces, and the peripheral region is useful for scene recognition. However, the relative importance of central versus peripheral information for object, scene, and face recognition is unclear. In a behavioral study, Larson and Loschky (2009) investigated this question by measuring the scene recognition accuracy as a function of visual angle, and demonstrated that peripheral vision was indeed more useful in recognizing scenes than central vision. In this work, we modeled and replicated the result of Larson and Loschky (2009), using deep convolutional neural networks. Having fit the data for scenes, we used the model to predict future data for large-scale scene recognition as well as for objects and faces. Our results suggest that the relative order of importance of using central visual field information is face recognition>object recognition>scene recognition, and vice-versa for peripheral information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge