Fayyaz Minhas
Tissue Image Analytics Centre, Department of Computer Science, University of Warwick, Coven-try, UK
Beer-Lambert Autoencoder for Unsupervised Stain Representation Learning and Deconvolution in Multi-immunohistochemical Brightfield Histology Images
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Separating the contributions of individual chromogenic stains in RGB histology whole slide images (WSIs) is essential for stain normalization, quantitative assessment of marker expression, and cell-level readouts in immunohistochemistry (IHC). Classical Beer-Lambert (BL) color deconvolution is well-established for two- or three-stain settings, but becomes under-determined and unstable for multiplex IHC (mIHC) with K>3 chromogens. We present a simple, data-driven encoder-decoder architecture that learns cohort-specific stain characteristics for mIHC RGB WSIs and yields crisp, well-separated per-stain concentration maps. The encoder is a compact U-Net that predicts K nonnegative concentration channels; the decoder is a differentiable BL forward model with a learnable stain matrix initialized from typical chromogen hues. Training is unsupervised with a perceptual reconstruction objective augmented by loss terms that discourage unnecessary stain mixing. On a colorectal mIHC panel comprising 5 stains (H, CDX2, MUC2, MUC5, CD8) we show excellent RGB reconstruction, and significantly reduced inter-channel bleed-through compared with matrix-based deconvolution. Code and model are available at https://github.com/measty/StainQuant.git.
INSIGHT: Spatially resolved survival modelling from routine histology crosslinked with molecular profiling reveals prognostic epithelial-immune axes in stage II/III colorectal cancer
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Routine histology contains rich prognostic information in stage II/III colorectal cancer, much of which is embedded in complex spatial tissue organisation. We present INSIGHT, a graph neural network that predicts survival directly from routine histology images. Trained and cross-validated on TCGA (n=342) and SURGEN (n=336), INSIGHT produces patient-level spatially resolved risk scores. Large independent validation showed superior prognostic performance compared with pTNM staging (C-index 0.68-0.69 vs 0.44-0.58). INSIGHT spatial risk maps recapitulated canonical prognostic histopathology and identified nuclear solidity and circularity as quantitative risk correlates. Integrating spatial risk with data-driven spatial transcriptomic signatures, spatial proteomics, bulk RNA-seq, and single-cell references revealed an epithelium-immune risk manifold capturing epithelial dedifferentiation and fetal programs, myeloid-driven stromal states including $\mathrm{SPP1}^{+}$ macrophages and $\mathrm{LAMP3}^{+}$ dendritic cells, and adaptive immune dysfunction. This analysis exposed patient-specific epithelial heterogeneity, stratification within MSI-High tumours, and high-risk routes of CDX2/HNF4A loss and CEACAM5/6-associated proliferative programs, highlighting coordinated therapeutic vulnerabilities.
From Traditional to Deep Learning Approaches in Whole Slide Image Registration: A Methodological Review
Feb 26, 2025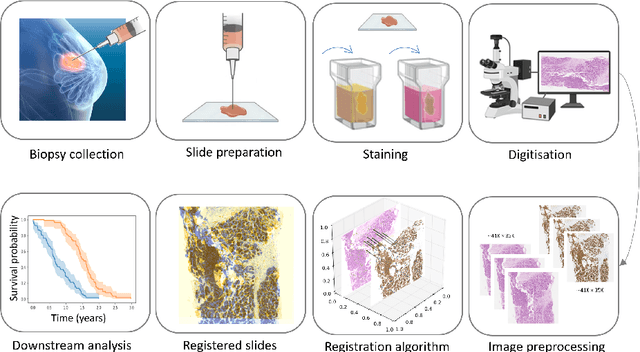
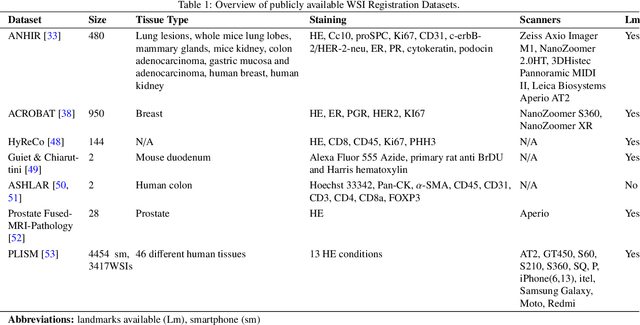
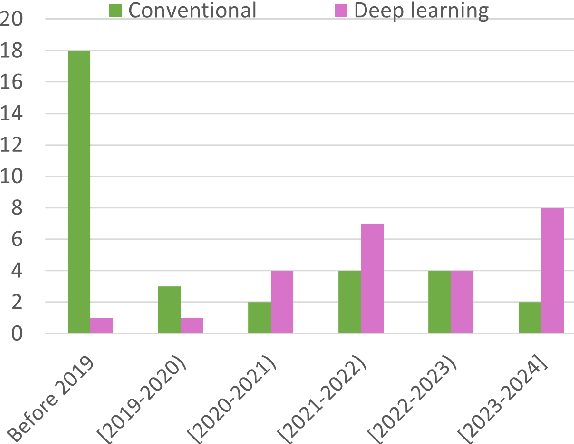
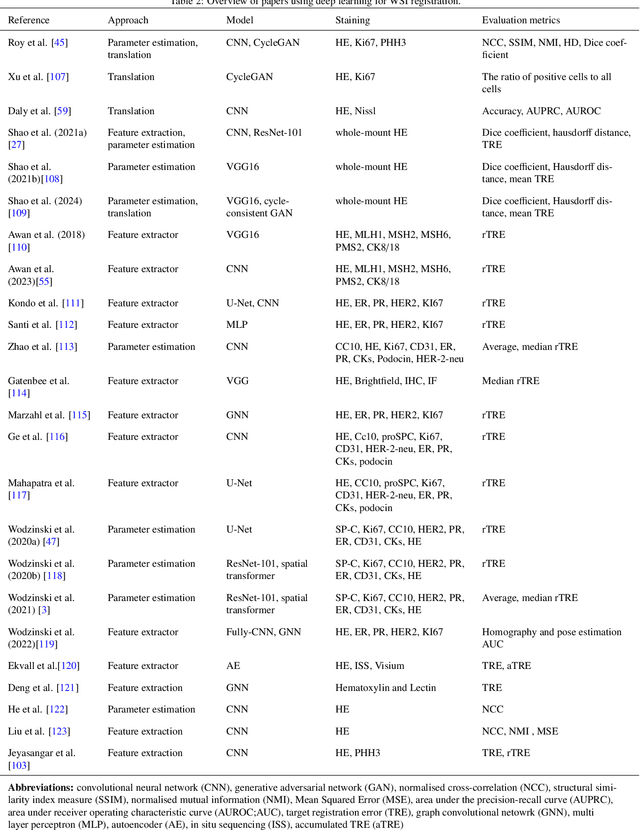
Abstract:Whole slide image (WSI) registration is an essential task for analysing the tumour microenvironment (TME) in histopathology. It involves the alignment of spatial information between WSIs of the same section or serial sections of a tissue sample. The tissue sections are usually stained with single or multiple biomarkers before imaging, and the goal is to identify neighbouring nuclei along the Z-axis for creating a 3D image or identifying subclasses of cells in the TME. This task is considerably more challenging compared to radiology image registration, such as magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography, due to various factors. These include gigapixel size of images, variations in appearance between differently stained tissues, changes in structure and morphology between non-consecutive sections, and the presence of artefacts, tears, and deformations. Currently, there is a noticeable gap in the literature regarding a review of the current approaches and their limitations, as well as the challenges and opportunities they present. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the available approaches and their application for various purposes. Furthermore, we investigate current deep learning methods used for WSI registration, emphasising their diverse methodologies. We examine the available datasets and explore tools and software employed in the field. Finally, we identify open challenges and potential future trends in this area of research.
Large Multimodal Model based Standardisation of Pathology Reports with Confidence and their Prognostic Significance
May 03, 2024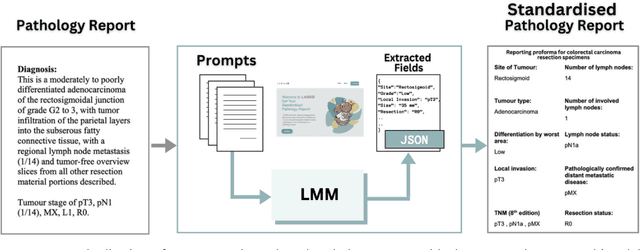
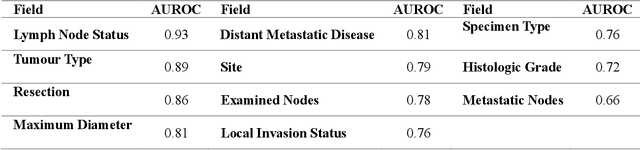
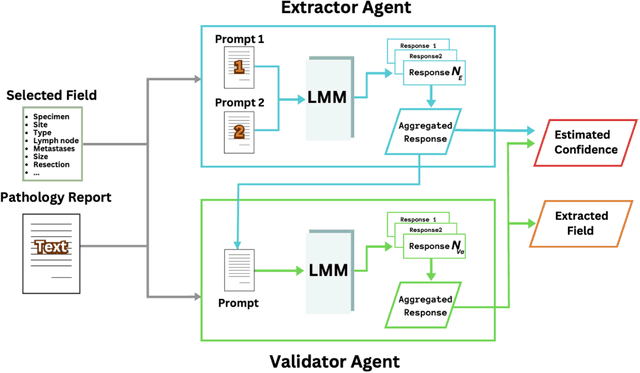
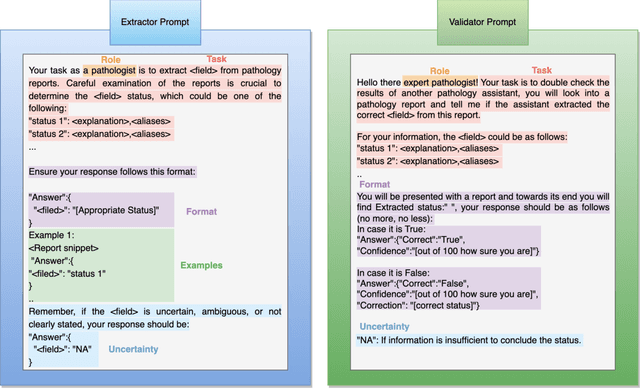
Abstract:Pathology reports are rich in clinical and pathological details but are often presented in free-text format. The unstructured nature of these reports presents a significant challenge limiting the accessibility of their content. In this work, we present a practical approach based on the use of large multimodal models (LMMs) for automatically extracting information from scanned images of pathology reports with the goal of generating a standardised report specifying the value of different fields along with estimated confidence about the accuracy of the extracted fields. The proposed approach overcomes limitations of existing methods which do not assign confidence scores to extracted fields limiting their practical use. The proposed framework uses two stages of prompting a Large Multimodal Model (LMM) for information extraction and validation. The framework generalises to textual reports from multiple medical centres as well as scanned images of legacy pathology reports. We show that the estimated confidence is an effective indicator of the accuracy of the extracted information that can be used to select only accurately extracted fields. We also show the prognostic significance of structured and unstructured data from pathology reports and show that the automatically extracted field values significant prognostic value for patient stratification. The framework is available for evaluation via the URL: https://labieb.dcs.warwick.ac.uk/.
TIAViz: A Browser-based Visualization Tool for Computational Pathology Models
Feb 15, 2024


Abstract:Digital pathology has gained significant traction in modern healthcare systems. This shift from optical microscopes to digital imagery brings with it the potential for improved diagnosis, efficiency, and the integration of AI tools into the pathologists workflow. A critical aspect of this is visualization. Throughout the development of a machine learning (ML) model in digital pathology, it is crucial to have flexible, openly available tools to visualize models, from their outputs and predictions to the underlying annotations and images used to train or test a model. We introduce TIAViz, a Python-based visualization tool built into TIAToolbox which allows flexible, interactive, fully zoomable overlay of a wide variety of information onto whole slide images, including graphs, heatmaps, segmentations, annotations and other WSIs. The UI is browser-based, allowing use either locally, on a remote machine, or on a server to provide publicly available demos. This tool is open source and is made available at: https://github.com/TissueImageAnalytics/tiatoolbox and via pip installation (pip install tiatoolbox) and conda as part of TIAToolbox.
Efficient Parameter Optimisation for Quantum Kernel Alignment: A Sub-sampling Approach in Variational Training
Jan 05, 2024



Abstract:Quantum machine learning with quantum kernels for classification problems is a growing area of research. Recently, quantum kernel alignment techniques that parameterise the kernel have been developed, allowing the kernel to be trained and therefore aligned with a specific dataset. While quantum kernel alignment is a promising technique, it has been hampered by considerable training costs because the full kernel matrix must be constructed at every training iteration. Addressing this challenge, we introduce a novel method that seeks to balance efficiency and performance. We present a sub-sampling training approach that uses a subset of the kernel matrix at each training step, thereby reducing the overall computational cost of the training. In this work, we apply the sub-sampling method to synthetic datasets and a real-world breast cancer dataset and demonstrate considerable reductions in the number of circuits required to train the quantum kernel while maintaining classification accuracy.
Domain Generalization in Computational Pathology: Survey and Guidelines
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning models have exhibited exceptional effectiveness in Computational Pathology (CPath) by tackling intricate tasks across an array of histology image analysis applications. Nevertheless, the presence of out-of-distribution data (stemming from a multitude of sources such as disparate imaging devices and diverse tissue preparation methods) can cause \emph{domain shift} (DS). DS decreases the generalization of trained models to unseen datasets with slightly different data distributions, prompting the need for innovative \emph{domain generalization} (DG) solutions. Recognizing the potential of DG methods to significantly influence diagnostic and prognostic models in cancer studies and clinical practice, we present this survey along with guidelines on achieving DG in CPath. We rigorously define various DS types, systematically review and categorize existing DG approaches and resources in CPath, and provide insights into their advantages, limitations, and applicability. We also conduct thorough benchmarking experiments with 28 cutting-edge DG algorithms to address a complex DG problem. Our findings suggest that careful experiment design and CPath-specific Stain Augmentation technique can be very effective. However, there is no one-size-fits-all solution for DG in CPath. Therefore, we establish clear guidelines for detecting and managing DS depending on different scenarios. While most of the concepts, guidelines, and recommendations are given for applications in CPath, we believe that they are applicable to most medical image analysis tasks as well.
A Fully Automated and Explainable Algorithm for the Prediction of Malignant Transformation in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia
Jul 06, 2023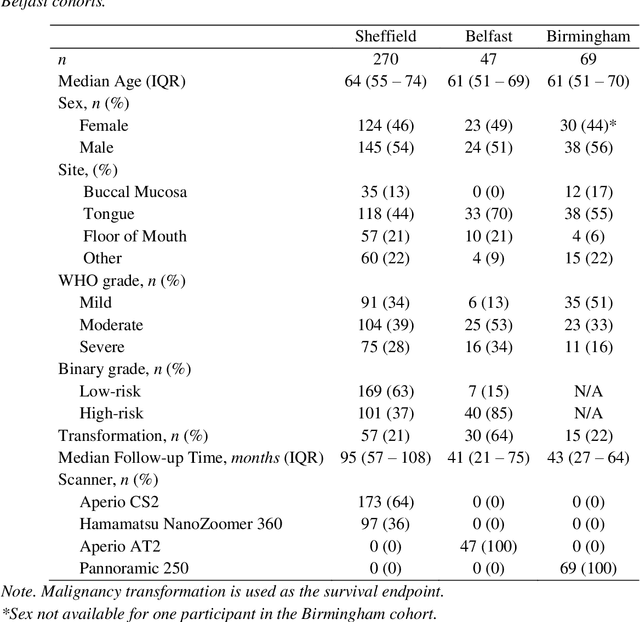
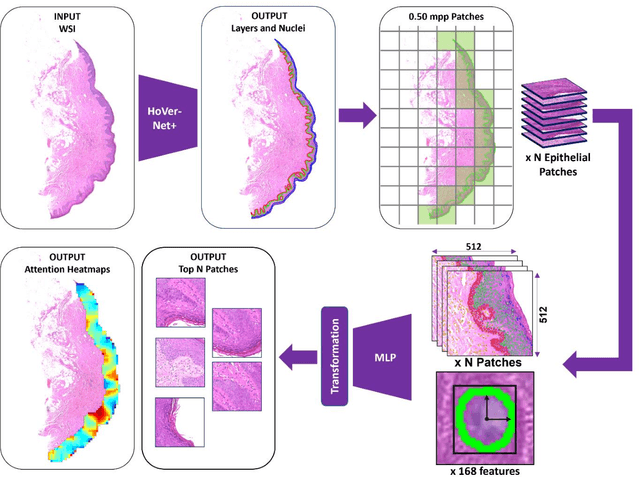
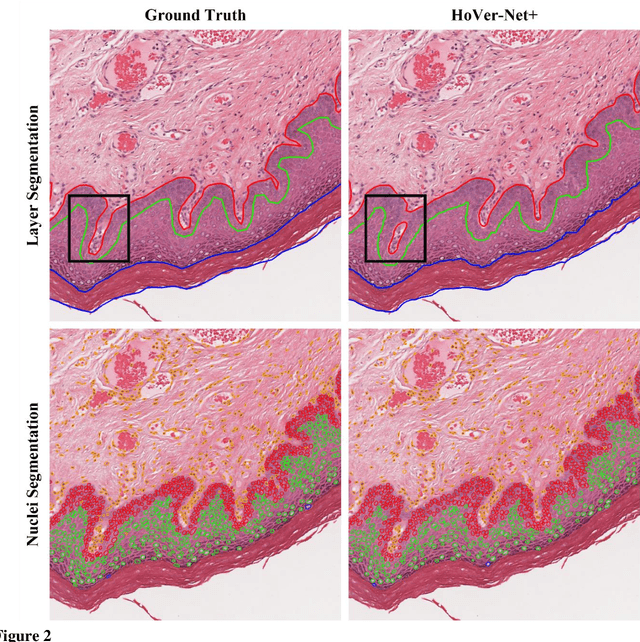
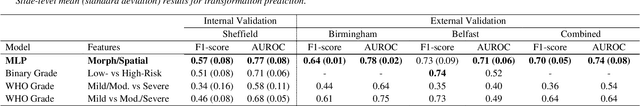
Abstract:Oral epithelial dysplasia (OED) is a premalignant histopathological diagnosis given to lesions of the oral cavity. Its grading suffers from significant inter-/intra- observer variability, and does not reliably predict malignancy progression, potentially leading to suboptimal treatment decisions. To address this, we developed a novel artificial intelligence algorithm that can assign an Oral Malignant Transformation (OMT) risk score, based on histological patterns in the in Haematoxylin and Eosin stained whole slide images, to quantify the risk of OED progression. The algorithm is based on the detection and segmentation of nuclei within (and around) the epithelium using an in-house segmentation model. We then employed a shallow neural network fed with interpretable morphological/spatial features, emulating histological markers. We conducted internal cross-validation on our development cohort (Sheffield; n = 193 cases) followed by independent validation on two external cohorts (Birmingham and Belfast; n = 92 cases). The proposed OMTscore yields an AUROC = 0.74 in predicting whether an OED progresses to malignancy or not. Survival analyses showed the prognostic value of our OMTscore for predicting malignancy transformation, when compared to the manually-assigned WHO and binary grades. Analysis of the correctly predicted cases elucidated the presence of peri-epithelial and epithelium-infiltrating lymphocytes in the most predictive patches of cases that transformed (p < 0.0001). This is the first study to propose a completely automated algorithm for predicting OED transformation based on interpretable nuclear features, whilst being validated on external datasets. The algorithm shows better-than-human-level performance for prediction of OED malignant transformation and offers a promising solution to the challenges of grading OED in routine clinical practice.
Synthesis of Annotated Colorectal Cancer Tissue Images from Gland Layout
May 08, 2023Abstract:Generating annotated pairs of realistic tissue images along with their annotations is a challenging task in computational histopathology. Such synthetic images and their annotations can be useful in training and evaluation of algorithms in the domain of computational pathology. To address this, we present an interactive framework to generate pairs of realistic colorectal cancer histology images with corresponding tissue component masks from the input gland layout. The framework shows the ability to generate realistic qualitative tissue images preserving morphological characteristics including stroma, goblet cells and glandular lumen. We show the appearance of glands can be controlled by user inputs such as number of glands, their locations and sizes. We also validate the quality of generated annotated pair with help of the gland segmentation algorithm.
CoNIC Challenge: Pushing the Frontiers of Nuclear Detection, Segmentation, Classification and Counting
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:Nuclear detection, segmentation and morphometric profiling are essential in helping us further understand the relationship between histology and patient outcome. To drive innovation in this area, we setup a community-wide challenge using the largest available dataset of its kind to assess nuclear segmentation and cellular composition. Our challenge, named CoNIC, stimulated the development of reproducible algorithms for cellular recognition with real-time result inspection on public leaderboards. We conducted an extensive post-challenge analysis based on the top-performing models using 1,658 whole-slide images of colon tissue. With around 700 million detected nuclei per model, associated features were used for dysplasia grading and survival analysis, where we demonstrated that the challenge's improvement over the previous state-of-the-art led to significant boosts in downstream performance. Our findings also suggest that eosinophils and neutrophils play an important role in the tumour microevironment. We release challenge models and WSI-level results to foster the development of further methods for biomarker discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge