Dingyuan Zhang
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
Extending Large Vision-Language Model for Diverse Interactive Tasks in Autonomous Driving
May 13, 2025



Abstract:The Large Visual-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly advanced image understanding. Their comprehension and reasoning capabilities enable promising applications in autonomous driving scenarios. However, existing research typically focuses on front-view perspectives and partial objects within scenes, struggling to achieve comprehensive scene understanding. Meanwhile, existing LVLMs suffer from the lack of mapping relationship between 2D and 3D and insufficient integration of 3D object localization and instruction understanding. To tackle these limitations, we first introduce NuInteract, a large-scale dataset with over 1.5M multi-view image language pairs spanning dense scene captions and diverse interactive tasks. Furthermore, we propose DriveMonkey, a simple yet effective framework that seamlessly integrates LVLMs with a spatial processor using a series of learnable queries. The spatial processor, designed as a plug-and-play component, can be initialized with pre-trained 3D detectors to improve 3D perception. Our experiments show that DriveMonkey outperforms general LVLMs, especially achieving a 9.86% notable improvement on the 3D visual grounding task. The dataset and code will be released at https://github.com/zc-zhao/DriveMonkey.
ORION: A Holistic End-to-End Autonomous Driving Framework by Vision-Language Instructed Action Generation
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving methods still struggle to make correct decisions in interactive closed-loop evaluation due to limited causal reasoning capability. Current methods attempt to leverage the powerful understanding and reasoning abilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to resolve this dilemma. However, the problem is still open that few VLMs for E2E methods perform well in the closed-loop evaluation due to the gap between the semantic reasoning space and the purely numerical trajectory output in the action space. To tackle this issue, we propose ORION, a holistic E2E autonomous driving framework by vision-language instructed action generation. ORION uniquely combines a QT-Former to aggregate long-term history context, a Large Language Model (LLM) for driving scenario reasoning, and a generative planner for precision trajectory prediction. ORION further aligns the reasoning space and the action space to implement a unified E2E optimization for both visual question-answering (VQA) and planning tasks. Our method achieves an impressive closed-loop performance of 77.74 Driving Score (DS) and 54.62% Success Rate (SR) on the challenge Bench2Drive datasets, which outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods by a large margin of 14.28 DS and 19.61% SR.
Seeing the Future, Perceiving the Future: A Unified Driving World Model for Future Generation and Perception
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:We present UniFuture, a simple yet effective driving world model that seamlessly integrates future scene generation and perception within a single framework. Unlike existing models focusing solely on pixel-level future prediction or geometric reasoning, our approach jointly models future appearance (i.e., RGB image) and geometry (i.e., depth), ensuring coherent predictions. Specifically, during the training, we first introduce a Dual-Latent Sharing scheme, which transfers image and depth sequence in a shared latent space, allowing both modalities to benefit from shared feature learning. Additionally, we propose a Multi-scale Latent Interaction mechanism, which facilitates bidirectional refinement between image and depth features at multiple spatial scales, effectively enhancing geometry consistency and perceptual alignment. During testing, our UniFuture can easily predict high-consistency future image-depth pairs by only using the current image as input. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that UniFuture outperforms specialized models on future generation and perception tasks, highlighting the advantages of a unified, structurally-aware world model. The project page is at https://github.com/dk-liang/UniFuture.
HERMES: A Unified Self-Driving World Model for Simultaneous 3D Scene Understanding and Generation
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Driving World Models (DWMs) have become essential for autonomous driving by enabling future scene prediction. However, existing DWMs are limited to scene generation and fail to incorporate scene understanding, which involves interpreting and reasoning about the driving environment. In this paper, we present a unified Driving World Model named HERMES. We seamlessly integrate 3D scene understanding and future scene evolution (generation) through a unified framework in driving scenarios. Specifically, HERMES leverages a Bird's-Eye View (BEV) representation to consolidate multi-view spatial information while preserving geometric relationships and interactions. We also introduce world queries, which incorporate world knowledge into BEV features via causal attention in the Large Language Model (LLM), enabling contextual enrichment for understanding and generation tasks. We conduct comprehensive studies on nuScenes and OmniDrive-nuScenes datasets to validate the effectiveness of our method. HERMES achieves state-of-the-art performance, reducing generation error by 32.4% and improving understanding metrics such as CIDEr by 8.0%. The model and code will be publicly released at https://github.com/LMD0311/HERMES.
Make Your ViT-based Multi-view 3D Detectors Faster via Token Compression
Sep 01, 2024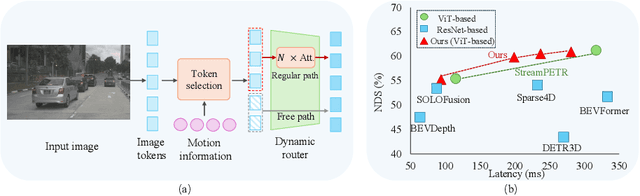
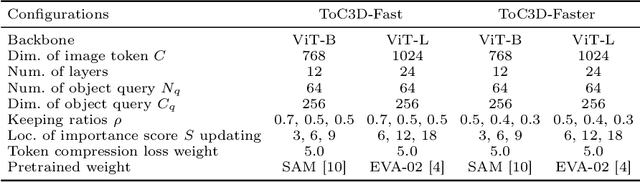
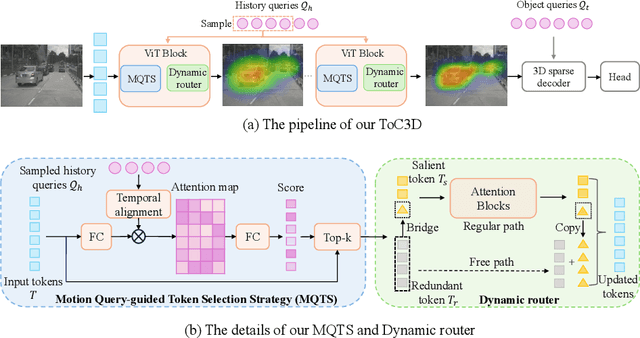
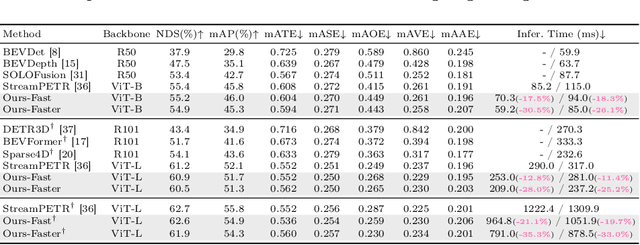
Abstract:Slow inference speed is one of the most crucial concerns for deploying multi-view 3D detectors to tasks with high real-time requirements like autonomous driving. Although many sparse query-based methods have already attempted to improve the efficiency of 3D detectors, they neglect to consider the backbone, especially when using Vision Transformers (ViT) for better performance. To tackle this problem, we explore the efficient ViT backbones for multi-view 3D detection via token compression and propose a simple yet effective method called TokenCompression3D (ToC3D). By leveraging history object queries as foreground priors of high quality, modeling 3D motion information in them, and interacting them with image tokens through the attention mechanism, ToC3D can effectively determine the magnitude of information densities of image tokens and segment the salient foreground tokens. With the introduced dynamic router design, ToC3D can weigh more computing resources to important foreground tokens while compressing the information loss, leading to a more efficient ViT-based multi-view 3D detector. Extensive results on the large-scale nuScenes dataset show that our method can nearly maintain the performance of recent SOTA with up to 30% inference speedup, and the improvements are consistent after scaling up the ViT and input resolution. The code will be made at https://github.com/DYZhang09/ToC3D.
AVS-Net: Point Sampling with Adaptive Voxel Size for 3D Point Cloud Analysis
Feb 27, 2024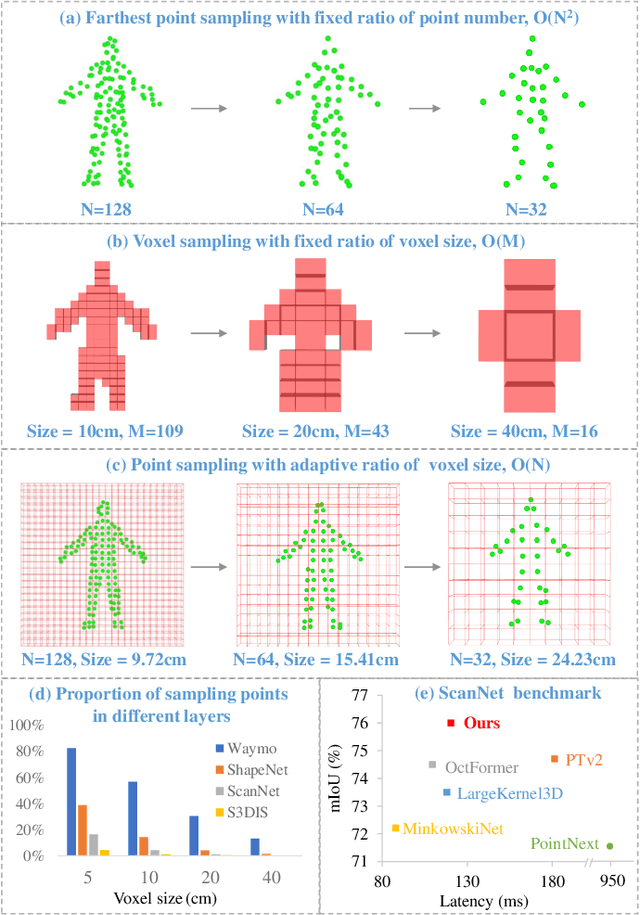
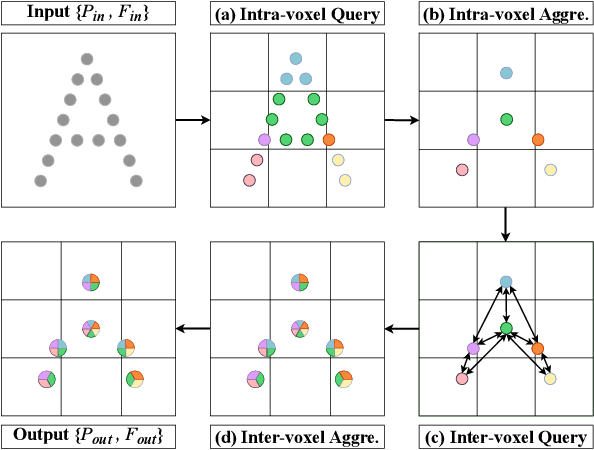
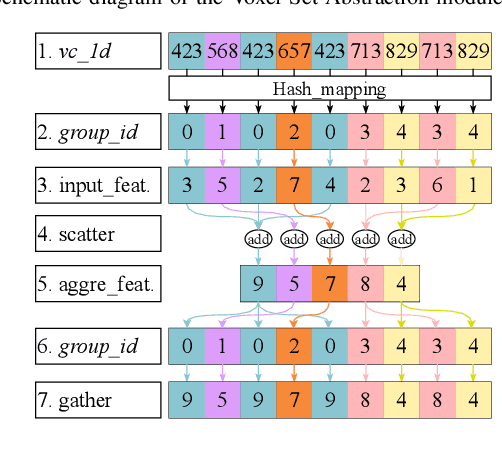
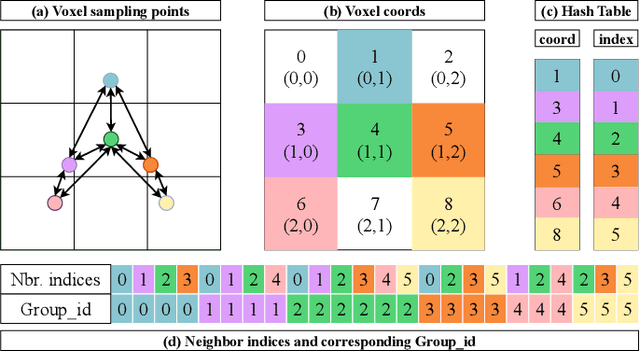
Abstract:Efficient downsampling plays a crucial role in point cloud learning, particularly for large-scale 3D scenes. Existing downsampling methods either require a huge computational burden or sacrifice fine-grained geometric information. This paper presents an advanced sampler that achieves both high accuracy and efficiency. The proposed method utilizes voxel-based sampling as a foundation, but effectively addresses the challenges regarding voxel size determination and the preservation of critical geometric cues. Specifically, we propose a Voxel Adaptation Module that adaptively adjusts voxel sizes with the reference of point-based downsampling ratio. This ensures the sampling results exhibit a favorable distribution for comprehending various 3D objects or scenes. Additionally, we introduce a network compatible with arbitrary voxel sizes for sampling and feature extraction while maintaining high efficiency. Our method achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on the ShapeNetPart and ScanNet benchmarks with promising efficiency. Code will be available at https://github.com/yhc2021/AVS-Net.
You Only Look Bottom-Up for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Jan 27, 2024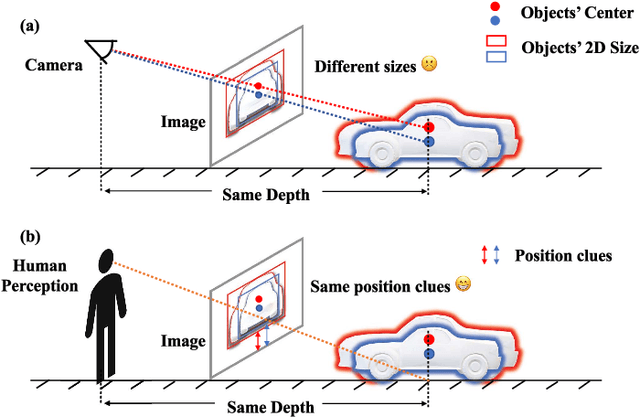
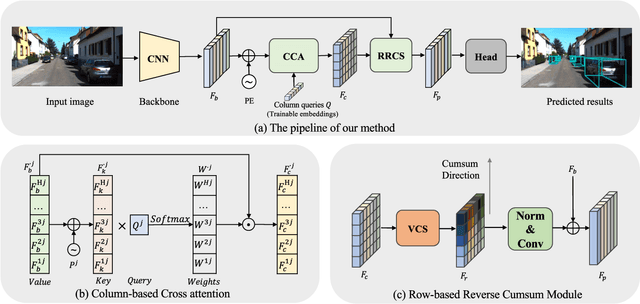
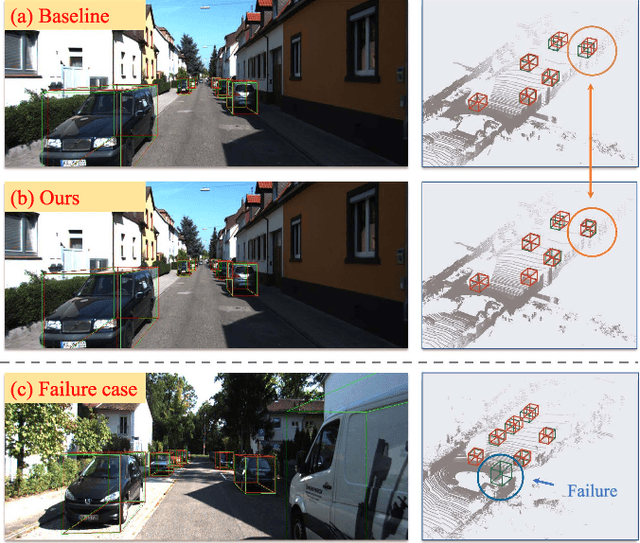
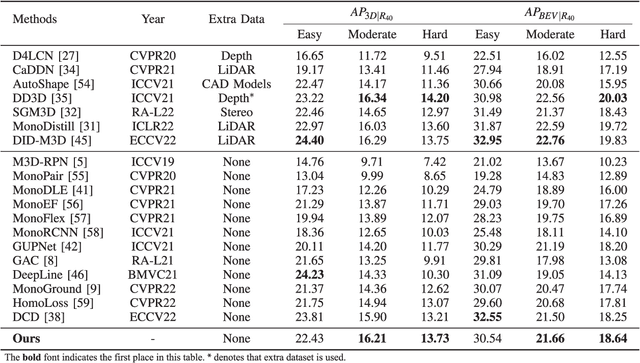
Abstract:Monocular 3D Object Detection is an essential task for autonomous driving. Meanwhile, accurate 3D object detection from pure images is very challenging due to the loss of depth information. Most existing image-based methods infer objects' location in 3D space based on their 2D sizes on the image plane, which usually ignores the intrinsic position clues from images, leading to unsatisfactory performances. Motivated by the fact that humans could leverage the bottom-up positional clues to locate objects in 3D space from a single image, in this paper, we explore the position modeling from the image feature column and propose a new method named You Only Look Bottum-Up (YOLOBU). Specifically, our YOLOBU leverages Column-based Cross Attention to determine how much a pixel contributes to pixels above it. Next, the Row-based Reverse Cumulative Sum (RRCS) is introduced to build the connections of pixels in the bottom-up direction. Our YOLOBU fully explores the position clues for monocular 3D detection via building the relationship of pixels from the bottom-up way. Extensive experiments on the KITTI dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
SAM3D: Zero-Shot 3D Object Detection via Segment Anything Model
Jun 04, 2023Abstract:With the development of large language models, many remarkable linguistic systems like ChatGPT have thrived and achieved astonishing success on many tasks, showing the incredible power of foundation models. In the spirit of unleashing the capability of foundation models on vision tasks, the Segment Anything Model (SAM), a vision foundation model for image segmentation, has been proposed recently and presents strong zero-shot ability on many downstream 2D tasks. However, whether SAM can be adapted to 3D vision tasks has yet to be explored, especially 3D object detection. With this inspiration, we explore adapting the zero-shot ability of SAM to 3D object detection in this paper. We propose a SAM-powered BEV processing pipeline to detect objects and get promising results on the large-scale Waymo open dataset. As an early attempt, our method takes a step toward 3D object detection with vision foundation models and presents the opportunity to unleash their power on 3D vision tasks. The code is released at https://github.com/DYZhang09/SAM3D.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge