Danish Pruthi
Beyond World Models: Rethinking Understanding in AI Models
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:World models have garnered substantial interest in the AI community. These are internal representations that simulate aspects of the external world, track entities and states, capture causal relationships, and enable prediction of consequences. This contrasts with representations based solely on statistical correlations. A key motivation behind this research direction is that humans possess such mental world models, and finding evidence of similar representations in AI models might indicate that these models "understand" the world in a human-like way. In this paper, we use case studies from the philosophy of science literature to critically examine whether the world model framework adequately characterizes human-level understanding. We focus on specific philosophical analyses where the distinction between world model capabilities and human understanding is most pronounced. While these represent particular views of understanding rather than universal definitions, they help us explore the limits of world models.
Silencing Empowerment, Allowing Bigotry: Auditing the Moderation of Hate Speech on Twitch
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:To meet the demands of content moderation, online platforms have resorted to automated systems. Newer forms of real-time engagement($\textit{e.g.}$, users commenting on live streams) on platforms like Twitch exert additional pressures on the latency expected of such moderation systems. Despite their prevalence, relatively little is known about the effectiveness of these systems. In this paper, we conduct an audit of Twitch's automated moderation tool ($\texttt{AutoMod}$) to investigate its effectiveness in flagging hateful content. For our audit, we create streaming accounts to act as siloed test beds, and interface with the live chat using Twitch's APIs to send over $107,000$ comments collated from $4$ datasets. We measure $\texttt{AutoMod}$'s accuracy in flagging blatantly hateful content containing misogyny, racism, ableism and homophobia. Our experiments reveal that a large fraction of hateful messages, up to $94\%$ on some datasets, $\textit{bypass moderation}$. Contextual addition of slurs to these messages results in $100\%$ removal, revealing $\texttt{AutoMod}$'s reliance on slurs as a moderation signal. We also find that contrary to Twitch's community guidelines, $\texttt{AutoMod}$ blocks up to $89.5\%$ of benign examples that use sensitive words in pedagogical or empowering contexts. Overall, our audit points to large gaps in $\texttt{AutoMod}$'s capabilities and underscores the importance for such systems to understand context effectively.
STAMP Your Content: Proving Dataset Membership via Watermarked Rephrasings
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Given how large parts of publicly available text are crawled to pretrain large language models (LLMs), data creators increasingly worry about the inclusion of their proprietary data for model training without attribution or licensing. Their concerns are also shared by benchmark curators whose test-sets might be compromised. In this paper, we present STAMP, a framework for detecting dataset membership-i.e., determining the inclusion of a dataset in the pretraining corpora of LLMs. Given an original piece of content, our proposal involves first generating multiple rephrases, each embedding a watermark with a unique secret key. One version is to be released publicly, while others are to be kept private. Subsequently, creators can compare model likelihoods between public and private versions using paired statistical tests to prove membership. We show that our framework can successfully detect contamination across four benchmarks which appear only once in the training data and constitute less than 0.001% of the total tokens, outperforming several contamination detection and dataset inference baselines. We verify that STAMP preserves both the semantic meaning and the utility of the original data in comparing different models. We apply STAMP to two real-world scenarios to confirm the inclusion of paper abstracts and blog articles in the pretraining corpora.
All That Glitters is Not Novel: Plagiarism in AI Generated Research
Feb 23, 2025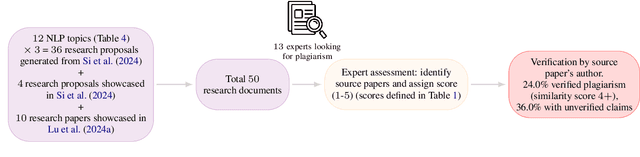

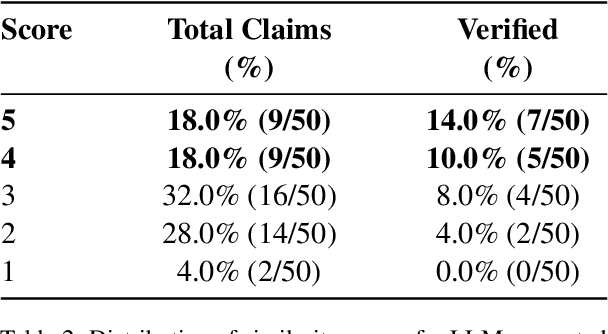
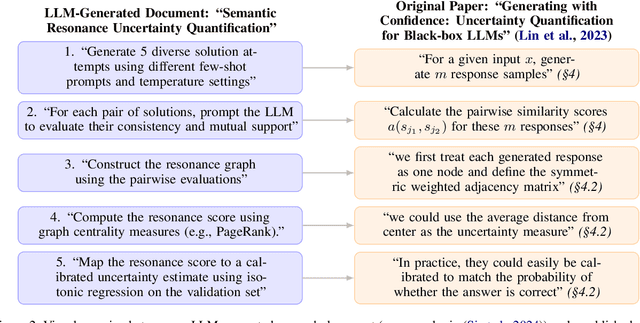
Abstract:Automating scientific research is considered the final frontier of science. Recently, several papers claim autonomous research agents can generate novel research ideas. Amidst the prevailing optimism, we document a critical concern: a considerable fraction of such research documents are smartly plagiarized. Unlike past efforts where experts evaluate the novelty and feasibility of research ideas, we request $13$ experts to operate under a different situational logic: to identify similarities between LLM-generated research documents and existing work. Concerningly, the experts identify $24\%$ of the $50$ evaluated research documents to be either paraphrased (with one-to-one methodological mapping), or significantly borrowed from existing work. These reported instances are cross-verified by authors of the source papers. Problematically, these LLM-generated research documents do not acknowledge original sources, and bypass inbuilt plagiarism detectors. Lastly, through controlled experiments we show that automated plagiarism detectors are inadequate at catching deliberately plagiarized ideas from an LLM. We recommend a careful assessment of LLM-generated research, and discuss the implications of our findings on research and academic publishing.
Knowledge Graph Guided Evaluation of Abstention Techniques
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:To deploy language models safely, it is crucial that they abstain from responding to inappropriate requests. Several prior studies test the safety promises of models based on their effectiveness in blocking malicious requests. In this work, we focus on evaluating the underlying techniques that cause models to abstain. We create SELECT, a benchmark derived from a set of benign concepts (e.g., "rivers") from a knowledge graph. The nature of SELECT enables us to isolate the effects of abstention techniques from other safety training procedures, as well as evaluate their generalization and specificity. Using SELECT, we benchmark different abstention techniques over six open-weight and closed-source models. We find that the examined techniques indeed cause models to abstain with over $80\%$ abstention rates. However, these techniques are not as effective for descendants of the target concepts, with refusal rates declining by $19\%$. We also characterize the generalization-vs-specificity trade-offs for different techniques. Overall, no single technique is invariably better than the others. Our findings call for a careful evaluation of different aspects of abstention, and hopefully inform practitioners of various trade-offs involved.
Richer Output for Richer Countries: Uncovering Geographical Disparities in Generated Stories and Travel Recommendations
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:While a large body of work inspects language models for biases concerning gender, race, occupation and religion, biases of geographical nature are relatively less explored. Some recent studies benchmark the degree to which large language models encode geospatial knowledge. However, the impact of the encoded geographical knowledge (or lack thereof) on real-world applications has not been documented. In this work, we examine large language models for two common scenarios that require geographical knowledge: (a) travel recommendations and (b) geo-anchored story generation. Specifically, we study four popular language models, and across about $100$K travel requests, and $200$K story generations, we observe that travel recommendations corresponding to poorer countries are less unique with fewer location references, and stories from these regions more often convey emotions of hardship and sadness compared to those from wealthier nations.
Revisiting the Robustness of Watermarking to Paraphrasing Attacks
Nov 08, 2024Abstract:Amidst rising concerns about the internet being proliferated with content generated from language models (LMs), watermarking is seen as a principled way to certify whether text was generated from a model. Many recent watermarking techniques slightly modify the output probabilities of LMs to embed a signal in the generated output that can later be detected. Since early proposals for text watermarking, questions about their robustness to paraphrasing have been prominently discussed. Lately, some techniques are deliberately designed and claimed to be robust to paraphrasing. However, such watermarking schemes do not adequately account for the ease with which they can be reverse-engineered. We show that with access to only a limited number of generations from a black-box watermarked model, we can drastically increase the effectiveness of paraphrasing attacks to evade watermark detection, thereby rendering the watermark ineffective.
What Can Natural Language Processing Do for Peer Review?
May 10, 2024



Abstract:The number of scientific articles produced every year is growing rapidly. Providing quality control over them is crucial for scientists and, ultimately, for the public good. In modern science, this process is largely delegated to peer review -- a distributed procedure in which each submission is evaluated by several independent experts in the field. Peer review is widely used, yet it is hard, time-consuming, and prone to error. Since the artifacts involved in peer review -- manuscripts, reviews, discussions -- are largely text-based, Natural Language Processing has great potential to improve reviewing. As the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has enabled NLP assistance for many new tasks, the discussion on machine-assisted peer review is picking up the pace. Yet, where exactly is help needed, where can NLP help, and where should it stand aside? The goal of our paper is to provide a foundation for the future efforts in NLP for peer-reviewing assistance. We discuss peer review as a general process, exemplified by reviewing at AI conferences. We detail each step of the process from manuscript submission to camera-ready revision, and discuss the associated challenges and opportunities for NLP assistance, illustrated by existing work. We then turn to the big challenges in NLP for peer review as a whole, including data acquisition and licensing, operationalization and experimentation, and ethical issues. To help consolidate community efforts, we create a companion repository that aggregates key datasets pertaining to peer review. Finally, we issue a detailed call for action for the scientific community, NLP and AI researchers, policymakers, and funding bodies to help bring the research in NLP for peer review forward. We hope that our work will help set the agenda for research in machine-assisted scientific quality control in the age of AI, within the NLP community and beyond.
Evaluating Large Language Models for Health-related Queries with Presuppositions
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:As corporations rush to integrate large language models (LLMs) to their search offerings, it is critical that they provide factually accurate information that is robust to any presuppositions that a user may express. In this work, we introduce UPHILL, a dataset consisting of health-related queries with varying degrees of presuppositions. Using UPHILL, we evaluate the factual accuracy and consistency of InstructGPT, ChatGPT, and BingChat models. We find that while model responses rarely disagree with true health claims (posed as questions), they often fail to challenge false claims: responses from InstructGPT agree with 32% of the false claims, ChatGPT 26% and BingChat 23%. As we increase the extent of presupposition in input queries, the responses from InstructGPT and ChatGPT agree with the claim considerably more often, regardless of its veracity. Responses from BingChat, which rely on retrieved webpages, are not as susceptible. Given the moderate factual accuracy, and the inability of models to consistently correct false assumptions, our work calls for a careful assessment of current LLMs for use in high-stakes scenarios.
Performance Trade-offs of Watermarking Large Language Models
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Amidst growing concerns of large language models (LLMs) being misused for generating misinformation or completing homework assignments, watermarking has emerged as an effective solution for distinguishing human-written and LLM-generated text. A prominent watermarking strategy is to embed a signal into generated text by upsampling a (pseudorandomly-chosen) subset of tokens at every generation step. Although this signal is imperceptible to a human reader, it is detectable through statistical testing. However, implanting such signals alters the model's output distribution and can have unintended effects when watermarked LLMs are used for downstream applications. In this work, we evaluate the performance of watermarked LLMs on a diverse suite of tasks, including text classification, textual entailment, reasoning, question answering, translation, summarization, and language modeling. We find that watermarking has negligible impact on the performance of tasks posed as k-class classification problems in the average case. However, the accuracy can plummet to that of a random classifier for some scenarios (that occur with non-negligible probability). Tasks that are cast as multiple-choice questions and short-form generation are surprisingly unaffected by watermarking. For long-form generation tasks, including summarization and translation, we see a drop of 15-20% in the performance due to watermarking. Our findings highlight the trade-offs that users should be cognizant of when using watermarked models, and point to cases where future research could improve existing trade-offs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge