Ching-An Cheng
Provably Learning from Language Feedback
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Interactively learning from observation and language feedback is an increasingly studied area driven by the emergence of large language model (LLM) agents. While impressive empirical demonstrations have been shown, so far a principled framing of these decision problems remains lacking. In this paper, we formalize the Learning from Language Feedback (LLF) problem, assert sufficient assumptions to enable learning despite latent rewards, and introduce $\textit{transfer eluder dimension}$ as a complexity measure to characterize the hardness of LLF problems. We show that transfer eluder dimension captures the intuition that information in the feedback changes the learning complexity of the LLF problem. We demonstrate cases where learning from rich language feedback can be exponentially faster than learning from reward. We develop a no-regret algorithm, called $\texttt{HELiX}$, that provably solves LLF problems through sequential interactions, with performance guarantees that scale with the transfer eluder dimension of the problem. Across several empirical domains, we show that $\texttt{HELiX}$ performs well even when repeatedly prompting LLMs does not work reliably. Our contributions mark a first step towards designing principled interactive learning algorithms from generic language feedback.
Streetwise Agents: Empowering Offline RL Policies to Outsmart Exogenous Stochastic Disturbances in RTC
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:The difficulty of exploring and training online on real production systems limits the scope of real-time online data/feedback-driven decision making. The most feasible approach is to adopt offline reinforcement learning from limited trajectory samples. However, after deployment, such policies fail due to exogenous factors that temporarily or permanently disturb/alter the transition distribution of the assumed decision process structure induced by offline samples. This results in critical policy failures and generalization errors in sensitive domains like Real-Time Communication (RTC). We solve this crucial problem of identifying robust actions in presence of domain shifts due to unseen exogenous stochastic factors in the wild. As it is impossible to learn generalized offline policies within the support of offline data that are robust to these unseen exogenous disturbances, we propose a novel post-deployment shaping of policies (Streetwise), conditioned on real-time characterization of out-of-distribution sub-spaces. This leads to robust actions in bandwidth estimation (BWE) of network bottlenecks in RTC and in standard benchmarks. Our extensive experimental results on BWE and other standard offline RL benchmark environments demonstrate a significant improvement ($\approx$ 18% on some scenarios) in final returns wrt. end-user metrics over state-of-the-art baselines.
How to Solve Contextual Goal-Oriented Problems with Offline Datasets?
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:We present a novel method, Contextual goal-Oriented Data Augmentation (CODA), which uses commonly available unlabeled trajectories and context-goal pairs to solve Contextual Goal-Oriented (CGO) problems. By carefully constructing an action-augmented MDP that is equivalent to the original MDP, CODA creates a fully labeled transition dataset under training contexts without additional approximation error. We conduct a novel theoretical analysis to demonstrate CODA's capability to solve CGO problems in the offline data setup. Empirical results also showcase the effectiveness of CODA, which outperforms other baseline methods across various context-goal relationships of CGO problem. This approach offers a promising direction to solving CGO problems using offline datasets.
Trace is the New AutoDiff -- Unlocking Efficient Optimization of Computational Workflows
Jun 23, 2024



Abstract:We study a class of optimization problems motivated by automating the design and update of AI systems like coding assistants, robots, and copilots. We propose an end-to-end optimization framework, Trace, which treats the computational workflow of an AI system as a graph akin to neural networks, based on a generalization of back-propagation. Optimization of computational workflows often involves rich feedback (e.g. console output or user's responses), heterogeneous parameters (e.g. prompts, hyper-parameters, codes), and intricate objectives (beyond maximizing a score). Moreover, its computation graph can change dynamically with the inputs and parameters. We frame a new mathematical setup of iterative optimization, Optimization with Trace Oracle (OPTO), to capture and abstract these properties so as to design optimizers that work across many domains. In OPTO, an optimizer receives an execution trace along with feedback on the computed output and updates parameters iteratively. Trace is the tool to implement OPTO in practice. Trace has a Python interface that efficiently converts a computational workflow into an OPTO instance using a PyTorch-like interface. Using Trace, we develop a general-purpose LLM-based optimizer called OptoPrime that can effectively solve OPTO problems. In empirical studies, we find that OptoPrime is capable of first-order numerical optimization, prompt optimization, hyper-parameter tuning, robot controller design, code debugging, etc., and is often competitive with specialized optimizers for each domain. We believe that Trace, OptoPrime and the OPTO framework will enable the next generation of interactive agents that automatically adapt using various kinds of feedback. Website: https://microsoft.github.io/Trace
The Importance of Directional Feedback for LLM-based Optimizers
May 26, 2024



Abstract:We study the potential of using large language models (LLMs) as an interactive optimizer for solving maximization problems in a text space using natural language and numerical feedback. Inspired by the classical optimization literature, we classify the natural language feedback into directional and non-directional, where the former is a generalization of the first-order feedback to the natural language space. We find that LLMs are especially capable of optimization when they are provided with {directional feedback}. Based on this insight, we design a new LLM-based optimizer that synthesizes directional feedback from the historical optimization trace to achieve reliable improvement over iterations. Empirically, we show our LLM-based optimizer is more stable and efficient in solving optimization problems, from maximizing mathematical functions to optimizing prompts for writing poems, compared with existing techniques.
Direct Nash Optimization: Teaching Language Models to Self-Improve with General Preferences
Apr 04, 2024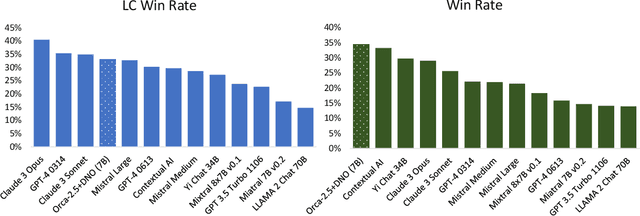
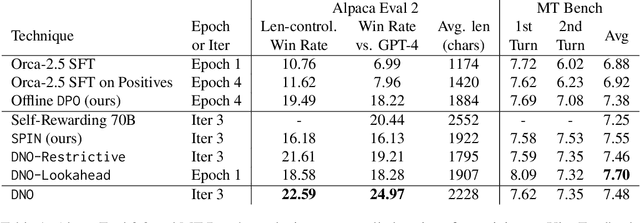
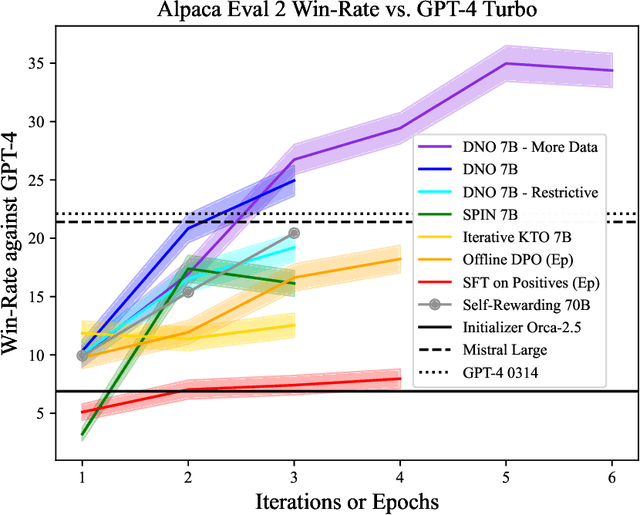
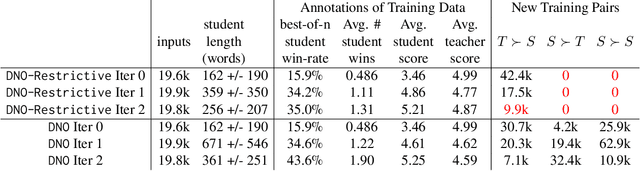
Abstract:This paper studies post-training large language models (LLMs) using preference feedback from a powerful oracle to help a model iteratively improve over itself. The typical approach for post-training LLMs involves Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), which traditionally separates reward learning and subsequent policy optimization. However, such a reward maximization approach is limited by the nature of "point-wise" rewards (such as Bradley-Terry model), which fails to express complex intransitive or cyclic preference relations. While advances on RLHF show reward learning and policy optimization can be merged into a single contrastive objective for stability, they yet still remain tethered to the reward maximization framework. Recently, a new wave of research sidesteps the reward maximization presumptions in favor of directly optimizing over "pair-wise" or general preferences. In this paper, we introduce Direct Nash Optimization (DNO), a provable and scalable algorithm that marries the simplicity and stability of contrastive learning with theoretical generality from optimizing general preferences. Because DNO is a batched on-policy algorithm using a regression-based objective, its implementation is straightforward and efficient. Moreover, DNO enjoys monotonic improvement across iterations that help it improve even over a strong teacher (such as GPT-4). In our experiments, a resulting 7B parameter Orca-2.5 model aligned by DNO achieves the state-of-the-art win-rate against GPT-4-Turbo of 33% on AlpacaEval 2.0 (even after controlling for response length), an absolute gain of 26% (7% to 33%) over the initializing model. It outperforms models with far more parameters, including Mistral Large, Self-Rewarding LM (70B parameters), and older versions of GPT-4.
PRISE: Learning Temporal Action Abstractions as a Sequence Compression Problem
Feb 16, 2024Abstract:Temporal action abstractions, along with belief state representations, are a powerful knowledge sharing mechanism for sequential decision making. In this work, we propose a novel view that treats inducing temporal action abstractions as a sequence compression problem. To do so, we bring a subtle but critical component of LLM training pipelines -- input tokenization via byte pair encoding (BPE) -- to the seemingly distant task of learning skills of variable time span in continuous control domains. We introduce an approach called Primitive Sequence Encoding (PRISE) that combines continuous action quantization with BPE to learn powerful action abstractions. We empirically show that high-level skills discovered by PRISE from a multitask set of robotic manipulation demonstrations significantly boost the performance of both multitask imitation learning as well as few-shot imitation learning on unseen tasks. Our code will be released at https://github.com/FrankZheng2022/PRISE.
LLF-Bench: Benchmark for Interactive Learning from Language Feedback
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:We introduce a new benchmark, LLF-Bench (Learning from Language Feedback Benchmark; pronounced as "elf-bench"), to evaluate the ability of AI agents to interactively learn from natural language feedback and instructions. Learning from language feedback (LLF) is essential for people, largely because the rich information this feedback provides can help a learner avoid much of trial and error and thereby speed up the learning process. Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently enabled AI agents to comprehend natural language -- and hence AI agents can potentially benefit from language feedback during learning like humans do. But existing interactive benchmarks do not assess this crucial capability: they either use numeric reward feedback or require no learning at all (only planning or information retrieval). LLF-Bench is designed to fill this omission. LLF-Bench is a diverse collection of sequential decision-making tasks that includes user recommendation, poem writing, navigation, and robot control. The objective of an agent is to interactively solve these tasks based on their natural-language instructions and the feedback received after taking actions. Crucially, to ensure that the agent actually "learns" from the feedback, LLF-Bench implements several randomization techniques (such as paraphrasing and environment randomization) to ensure that the task isn't familiar to the agent and that the agent is robust to various verbalizations. In addition, LLF-Bench provides a unified OpenAI Gym interface for all its tasks and allows the users to easily configure the information the feedback conveys (among suggestion, explanation, and instantaneous performance) to study how agents respond to different types of feedback. Together, these features make LLF-Bench a unique research platform for developing and testing LLF agents.
Interactive Robot Learning from Verbal Correction
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:The ability to learn and refine behavior after deployment has become ever more important for robots as we design them to operate in unstructured environments like households. In this work, we design a new learning system based on large language model (LLM), OLAF, that allows everyday users to teach a robot using verbal corrections when the robot makes mistakes, e.g., by saying "Stop what you're doing. You should move closer to the cup." A key feature of OLAF is its ability to update the robot's visuomotor neural policy based on the verbal feedback to avoid repeating mistakes in the future. This is in contrast to existing LLM-based robotic systems, which only follow verbal commands or corrections but not learn from them. We demonstrate the efficacy of our design in experiments where a user teaches a robot to perform long-horizon manipulation tasks both in simulation and on physical hardware, achieving on average 20.0% improvement in policy success rate. Videos and more results are at https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/olaf/
Goal Representations for Instruction Following: A Semi-Supervised Language Interface to Control
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Our goal is for robots to follow natural language instructions like "put the towel next to the microwave." But getting large amounts of labeled data, i.e. data that contains demonstrations of tasks labeled with the language instruction, is prohibitive. In contrast, obtaining policies that respond to image goals is much easier, because any autonomous trial or demonstration can be labeled in hindsight with its final state as the goal. In this work, we contribute a method that taps into joint image- and goal- conditioned policies with language using only a small amount of language data. Prior work has made progress on this using vision-language models or by jointly training language-goal-conditioned policies, but so far neither method has scaled effectively to real-world robot tasks without significant human annotation. Our method achieves robust performance in the real world by learning an embedding from the labeled data that aligns language not to the goal image, but rather to the desired change between the start and goal images that the instruction corresponds to. We then train a policy on this embedding: the policy benefits from all the unlabeled data, but the aligned embedding provides an interface for language to steer the policy. We show instruction following across a variety of manipulation tasks in different scenes, with generalization to language instructions outside of the labeled data. Videos and code for our approach can be found on our website: http://tiny.cc/grif .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge