Chenyi Zhuang
V2P: Visual Attention Calibration for GUI Grounding via Background Suppression and Center Peaking
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Precise localization of GUI elements is crucial for the development of GUI agents. Traditional methods rely on bounding box or center-point regression, neglecting spatial interaction uncertainty and visual-semantic hierarchies. Recent methods incorporate attention mechanisms but still face two key issues: (1) ignoring processing background regions causes attention drift from the desired area, and (2) uniform modeling the target UI element fails to distinguish between its center and edges, leading to click imprecision. Inspired by how humans visually process and interact with GUI elements, we propose the Valley-to-Peak (V2P) method to address these issues. To mitigate background distractions, V2P introduces a suppression attention mechanism that minimizes the model's focus on irrelevant regions to highlight the intended region. For the issue of center-edge distinction, V2P applies a Fitts' Law-inspired approach by modeling GUI interactions as 2D Gaussian heatmaps where the weight gradually decreases from the center towards the edges. The weight distribution follows a Gaussian function, with the variance determined by the target's size. Consequently, V2P effectively isolates the target area and teaches the model to concentrate on the most essential point of the UI element. The model trained by V2P achieves the performance with 92.4\% and 52.5\% on two benchmarks ScreenSpot-v2 and ScreenSpot-Pro (see Fig.~\ref{fig:main_results_charts}). Ablations further confirm each component's contribution, underscoring V2P's generalizability in precise GUI grounding tasks and its potential for real-world deployment in future GUI agents.
From Failure to Mastery: Generating Hard Samples for Tool-use Agents
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:The advancement of LLM agents with tool-use capabilities requires diverse and complex training corpora. Existing data generation methods, which predominantly follow a paradigm of random sampling and shallow generation, often yield simple and homogeneous trajectories that fail to capture complex, implicit logical dependencies. To bridge this gap, we introduce HardGen, an automatic agentic pipeline designed to generate hard tool-use training samples with verifiable reasoning. Firstly, HardGen establishes a dynamic API Graph built upon agent failure cases, from which it samples to synthesize hard traces. Secondly, these traces serve as conditional priors to guide the instantiation of modular, abstract advanced tools, which are subsequently leveraged to formulate hard queries. Finally, the advanced tools and hard queries enable the generation of verifiable complex Chain-of-Thought (CoT), with a closed-loop evaluation feedback steering the continuous refinement of the process. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that a 4B parameter model trained with our curated dataset achieves superior performance compared to several leading open-source and closed-source competitors (e.g., GPT-5.2, Gemini-3-Pro and Claude-Opus-4.5). Our code, models, and dataset will be open-sourced to facilitate future research.
AWorld: Dynamic Multi-Agent System with Stable Maneuvering for Robust GAIA Problem Solving
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has empowered intelligent agents to leverage diverse external tools for solving complex real-world problems. However, as agents increasingly depend on multiple tools, they encounter new challenges: extended contexts from disparate sources and noisy or irrelevant tool outputs can undermine system reliability and accuracy. These challenges underscore the necessity for enhanced stability in agent-based systems. To address this, we introduce dynamic supervision and maneuvering mechanisms, constructing a robust and dynamic Multi-Agent System (MAS) architecture within the AWorld framework. In our approach, the Execution Agent invokes the Guard Agent at critical steps to verify and correct the reasoning process, effectively reducing errors arising from noise and bolstering problem-solving robustness. Extensive experiments on the GAIA test dataset reveal that our dynamic maneuvering mechanism significantly improves both the effectiveness and stability of solutions, outperforming single-agent system (SAS) and standard tool-augmented systems. As a result, our dynamic MAS system achieved first place among open-source projects on the prestigious GAIA leaderboard. These findings highlight the practical value of collaborative agent roles in developing more reliable and trustworthy intelligent systems.
Exploring Superior Function Calls via Reinforcement Learning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Function calling capabilities are crucial for deploying Large Language Models in real-world applications, yet current training approaches fail to develop robust reasoning strategies. Supervised fine-tuning produces models that rely on superficial pattern matching, while standard reinforcement learning methods struggle with the complex action space of structured function calls. We present a novel reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance group relative policy optimization through strategic entropy based exploration specifically tailored for function calling tasks. Our approach addresses three critical challenges in function calling: insufficient exploration during policy learning, lack of structured reasoning in chain-of-thought generation, and inadequate verification of parameter extraction. Our two-stage data preparation pipeline ensures high-quality training samples through iterative LLM evaluation and abstract syntax tree validation. Extensive experiments on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard demonstrate that this framework achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models with 86.02\% overall accuracy, outperforming standard GRPO by up to 6\% on complex multi-function scenarios. Notably, our method shows particularly strong improvements on code-pretrained models, suggesting that structured language generation capabilities provide an advantageous starting point for reinforcement learning in function calling tasks. We will release all the code, models and dataset to benefit the community.
FunReason: Enhancing Large Language Models' Function Calling via Self-Refinement Multiscale Loss and Automated Data Refinement
May 26, 2025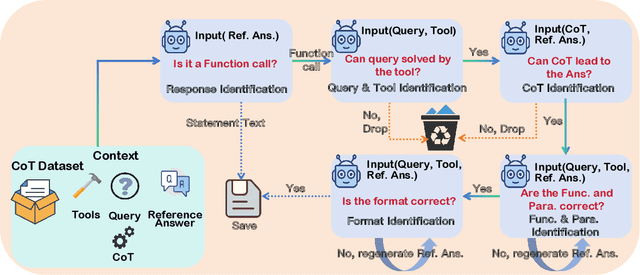
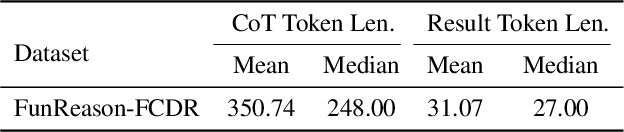
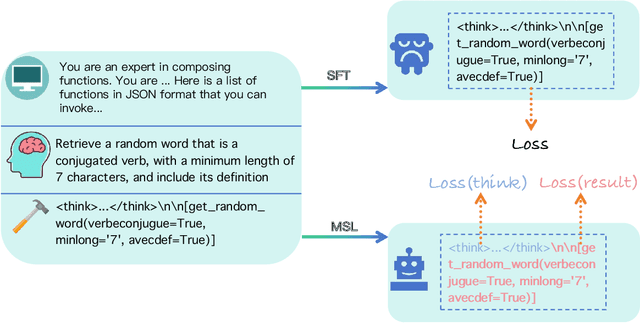

Abstract:The integration of large language models (LLMs) with function calling has emerged as a crucial capability for enhancing their practical utility in real-world applications. However, effectively combining reasoning processes with accurate function execution remains a significant challenge. Traditional training approaches often struggle to balance the detailed reasoning steps with the precision of function calls, leading to suboptimal performance. To address these limitations, we introduce FunReason, a novel framework that enhances LLMs' function calling capabilities through an automated data refinement strategy and a Self-Refinement Multiscale Loss (SRML) approach. FunReason leverages LLMs' natural reasoning abilities to generate high-quality training examples, focusing on query parseability, reasoning coherence, and function call precision. The SRML approach dynamically balances the contribution of reasoning processes and function call accuracy during training, addressing the inherent trade-off between these two critical aspects. FunReason achieves performance comparable to GPT-4o while effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning. FunReason provides a comprehensive solution for enhancing LLMs' function calling capabilities by introducing a balanced training methodology and a data refinement pipeline. For code and dataset, please refer to our repository at GitHub https://github.com/BingguangHao/FunReason
PiCo: Enhancing Text-Image Alignment with Improved Noise Selection and Precise Mask Control in Diffusion Models
May 06, 2025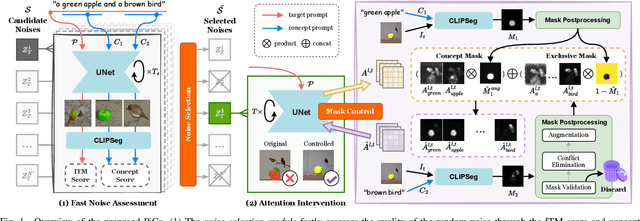
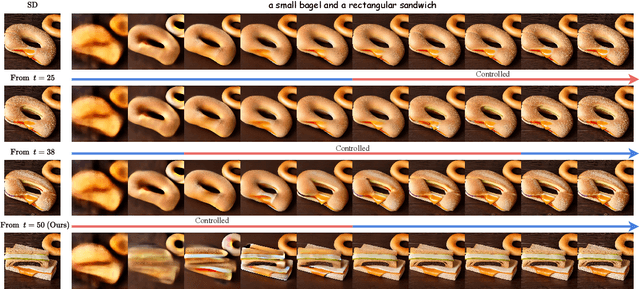


Abstract:Advanced diffusion models have made notable progress in text-to-image compositional generation. However, it is still a challenge for existing models to achieve text-image alignment when confronted with complex text prompts. In this work, we highlight two factors that affect this alignment: the quality of the randomly initialized noise and the reliability of the generated controlling mask. We then propose PiCo (Pick-and-Control), a novel training-free approach with two key components to tackle these two factors. First, we develop a noise selection module to assess the quality of the random noise and determine whether the noise is suitable for the target text. A fast sampling strategy is utilized to ensure efficiency in the noise selection stage. Second, we introduce a referring mask module to generate pixel-level masks and to precisely modulate the cross-attention maps. The referring mask is applied to the standard diffusion process to guide the reasonable interaction between text and image features. Extensive experiments have been conducted to verify the effectiveness of PiCo in liberating users from the tedious process of random generation and in enhancing the text-image alignment for diverse text descriptions.
Uni4D: A Unified Self-Supervised Learning Framework for Point Cloud Videos
Apr 07, 2025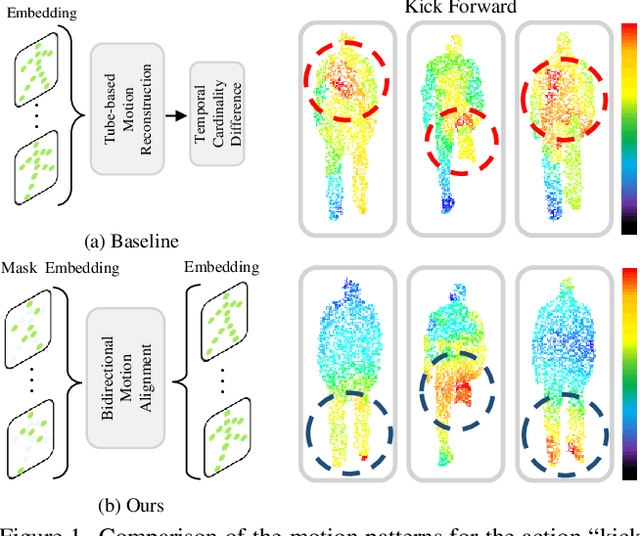
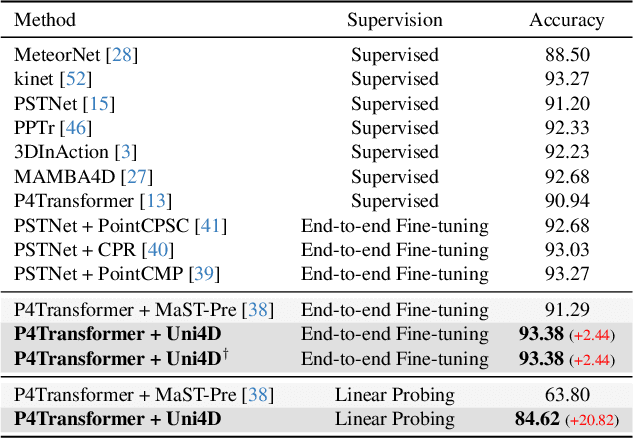
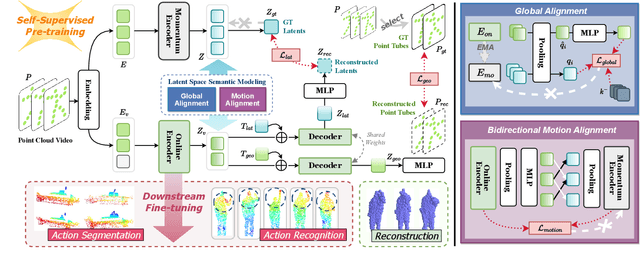

Abstract:Point cloud video representation learning is primarily built upon the masking strategy in a self-supervised manner. However, the progress is slow due to several significant challenges: (1) existing methods learn the motion particularly with hand-crafted designs, leading to unsatisfactory motion patterns during pre-training which are non-transferable on fine-tuning scenarios. (2) previous Masked AutoEncoder (MAE) frameworks are limited in resolving the huge representation gap inherent in 4D data. In this study, we introduce the first self-disentangled MAE for learning discriminative 4D representations in the pre-training stage. To address the first challenge, we propose to model the motion representation in a latent space. The second issue is resolved by introducing the latent tokens along with the typical geometry tokens to disentangle high-level and low-level features during decoding. Extensive experiments on MSR-Action3D, NTU-RGBD, HOI4D, NvGesture, and SHREC'17 verify this self-disentangled learning framework. We demonstrate that it can boost the fine-tuning performance on all 4D tasks, which we term Uni4D. Our pre-trained model presents discriminative and meaningful 4D representations, particularly benefits processing long videos, as Uni4D gets $+3.8\%$ segmentation accuracy on HOI4D, significantly outperforming either self-supervised or fully-supervised methods after end-to-end fine-tuning.
CSR:Achieving 1 Bit Key-Value Cache via Sparse Representation
Dec 16, 2024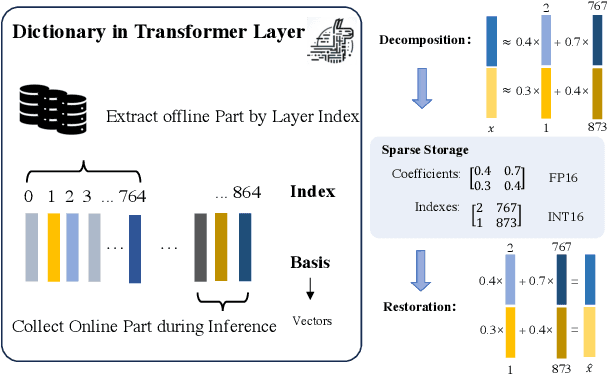
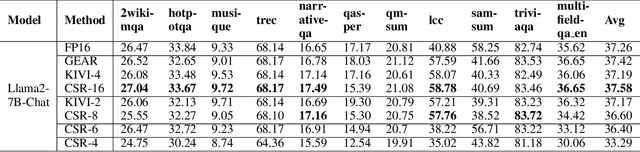
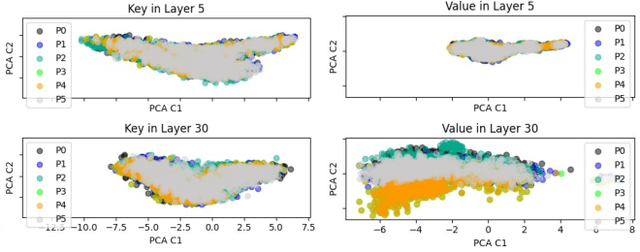
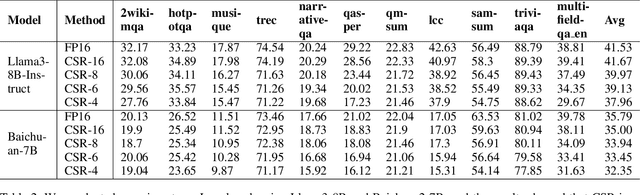
Abstract:The emergence of long-context text applications utilizing large language models (LLMs) has presented significant scalability challenges, particularly in memory footprint. The linear growth of the Key-Value (KV) cache responsible for storing attention keys and values to minimize redundant computations can lead to substantial increases in memory consumption, potentially causing models to fail to serve with limited memory resources. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach called Cache Sparse Representation (CSR), which converts the KV cache by transforming the dense Key-Value cache tensor into sparse indexes and weights, offering a more memory-efficient representation during LLM inference. Furthermore, we introduce NeuralDict, a novel neural network-based method for automatically generating the dictionary used in our sparse representation. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that CSR achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art KV cache quantization algorithms while maintaining robust functionality in memory-constrained environments.
Explainable Behavior Cloning: Teaching Large Language Model Agents through Learning by Demonstration
Oct 30, 2024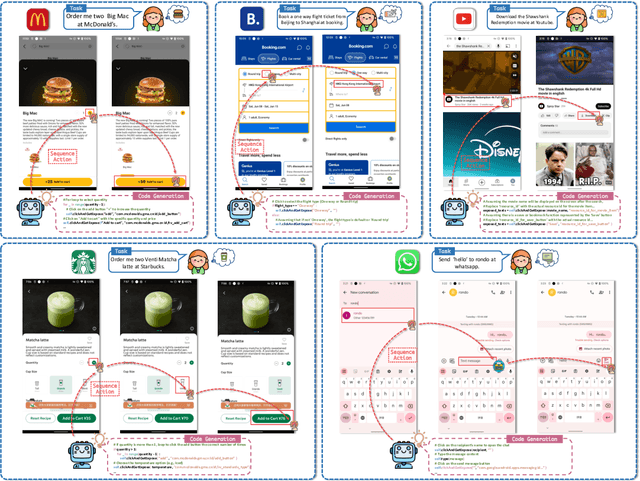
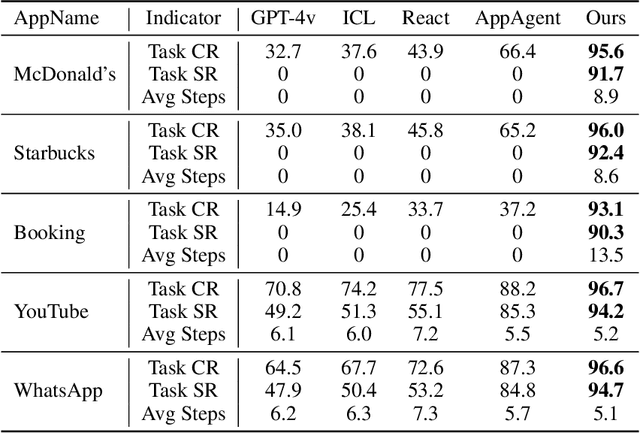
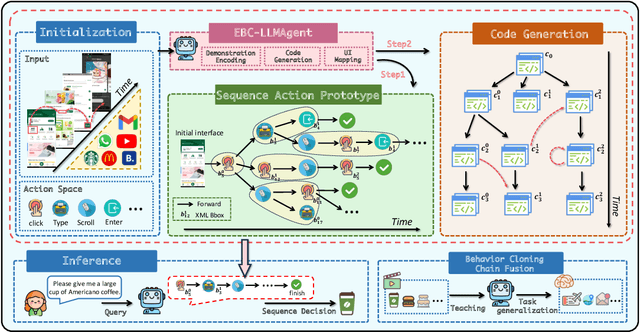
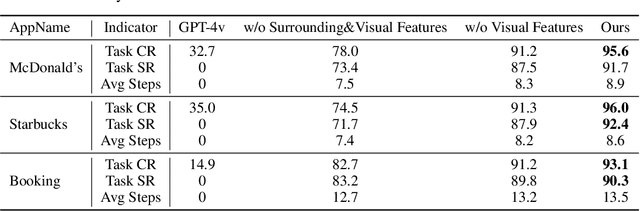
Abstract:Autonomous mobile app interaction has become increasingly important with growing complexity of mobile applications. Developing intelligent agents that can effectively navigate and interact with mobile apps remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose an Explainable Behavior Cloning LLM Agent (EBC-LLMAgent), a novel approach that combines large language models (LLMs) with behavior cloning by learning demonstrations to create intelligent and explainable agents for autonomous mobile app interaction. EBC-LLMAgent consists of three core modules: Demonstration Encoding, Code Generation, and UI Mapping, which work synergistically to capture user demonstrations, generate executable codes, and establish accurate correspondence between code and UI elements. We introduce the Behavior Cloning Chain Fusion technique to enhance the generalization capabilities of the agent. Extensive experiments on five popular mobile applications from diverse domains demonstrate the superior performance of EBC-LLMAgent, achieving high success rates in task completion, efficient generalization to unseen scenarios, and the generation of meaningful explanations.
DiffuseST: Unleashing the Capability of the Diffusion Model for Style Transfer
Oct 19, 2024
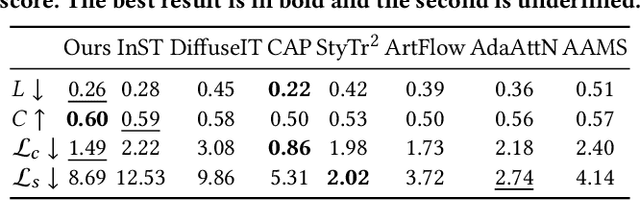
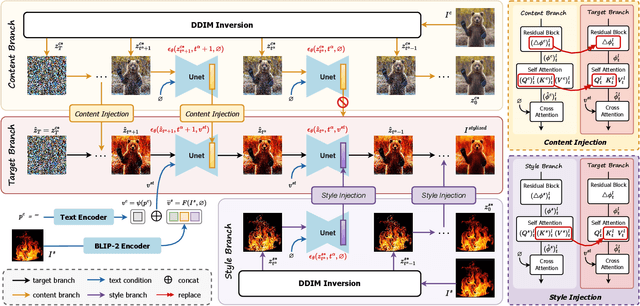
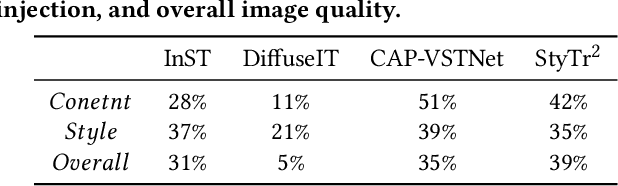
Abstract:Style transfer aims to fuse the artistic representation of a style image with the structural information of a content image. Existing methods train specific networks or utilize pre-trained models to learn content and style features. However, they rely solely on textual or spatial representations that are inadequate to achieve the balance between content and style. In this work, we propose a novel and training-free approach for style transfer, combining textual embedding with spatial features and separating the injection of content or style. Specifically, we adopt the BLIP-2 encoder to extract the textual representation of the style image. We utilize the DDIM inversion technique to extract intermediate embeddings in content and style branches as spatial features. Finally, we harness the step-by-step property of diffusion models by separating the injection of content and style in the target branch, which improves the balance between content preservation and style fusion. Various experiments have demonstrated the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed DiffeseST for achieving balanced and controllable style transfer results, as well as the potential to extend to other tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge