Haiqing Wang
Reverse Attitude Statistics Based Star Map Identification Method
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:The star tracker is generally affected by the atmospheric background light and the aerodynamic environment when working in near space, which results in missing stars or false stars. Moreover, high-speed maneuvering may cause star trailing, which reduces the accuracy of the star position. To address the challenges for starmap identification, a reverse attitude statistics based method is proposed to handle position noise, false stars, and missing stars. Conversely to existing methods which match before solving for attitude, this method introduces attitude solving into the matching process, and obtains the final match and the correct attitude simultaneously by frequency statistics. Firstly, based on stable angular distance features, the initial matching is obtained by utilizing spatial hash indexing. Then, the dual-vector attitude determination is introduced to calculate potential attitude. Finally, the star pairs are accurately matched by applying a frequency statistics filtering method. In addition, Bayesian optimization is employed to find optimal parameters under the impact of noises, which is able to enhance the algorithm performance further. In this work, the proposed method is validated in simulation, field test and on-orbit experiment. Compared with the state-of-the-art, the identification rate is improved by more than 14.3%, and the solving time is reduced by over 28.5%.
Explainable Behavior Cloning: Teaching Large Language Model Agents through Learning by Demonstration
Oct 30, 2024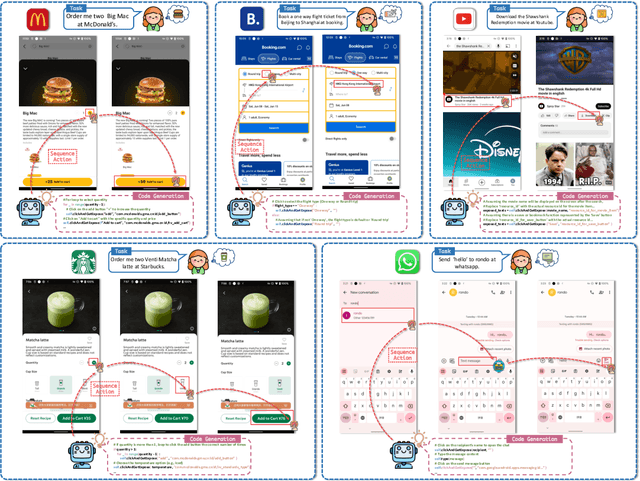
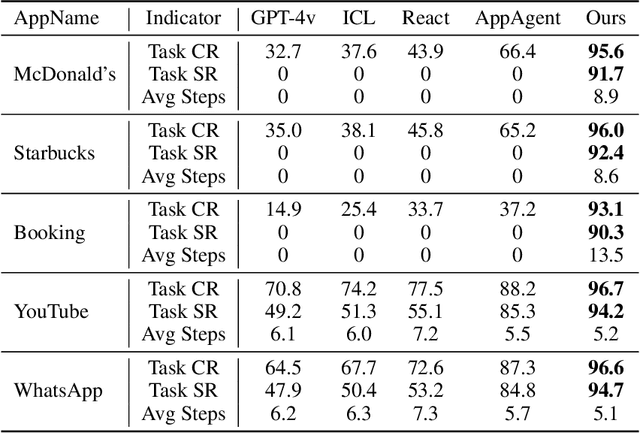
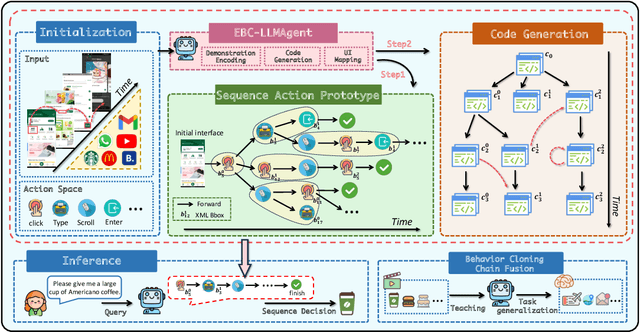
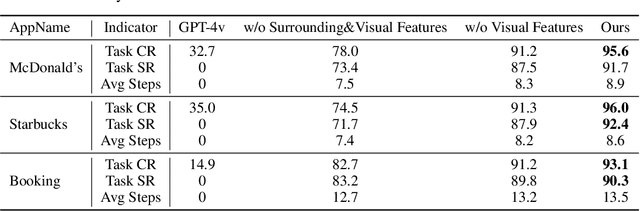
Abstract:Autonomous mobile app interaction has become increasingly important with growing complexity of mobile applications. Developing intelligent agents that can effectively navigate and interact with mobile apps remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose an Explainable Behavior Cloning LLM Agent (EBC-LLMAgent), a novel approach that combines large language models (LLMs) with behavior cloning by learning demonstrations to create intelligent and explainable agents for autonomous mobile app interaction. EBC-LLMAgent consists of three core modules: Demonstration Encoding, Code Generation, and UI Mapping, which work synergistically to capture user demonstrations, generate executable codes, and establish accurate correspondence between code and UI elements. We introduce the Behavior Cloning Chain Fusion technique to enhance the generalization capabilities of the agent. Extensive experiments on five popular mobile applications from diverse domains demonstrate the superior performance of EBC-LLMAgent, achieving high success rates in task completion, efficient generalization to unseen scenarios, and the generation of meaningful explanations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge