Jiaqi Zheng
You Need an Encoder for Native Position-Independent Caching
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The Key-Value (KV) cache of Large Language Models (LLMs) is prefix-based, making it highly inefficient for processing contexts retrieved in arbitrary order. Position-Independent Caching (PIC) has been proposed to enable KV reuse without positional constraints; however, existing approaches often incur substantial accuracy degradation, limiting their practical adoption. To address this issue, we propose native PIC by reintroducing the encoder to prevalent decoder-only LLMs and explicitly training it to support PIC. We further develop COMB, a PIC-aware caching system that integrates seamlessly with existing inference frameworks. Experimental results show that COMB reduces Time-to-First-Token (TTFT) by 51-94% and increases throughput by 3$\times$ with comparable accuracy. Furthermore, the quality improvement when using DeepSeek-V2-Lite-Chat demonstrates the applicability of COMB to other types of decoder-only LLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/shijuzhao/Comb.
SpikySpace: A Spiking State Space Model for Energy-Efficient Time Series Forecasting
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Time-series forecasting often operates under tight power and latency budgets in fields like traffic management, industrial condition monitoring, and on-device sensing. These applications frequently require near real-time responses and low energy consumption on edge devices. Spiking neural networks (SNNs) offer event-driven computation and ultra-low power by exploiting temporal sparsity and multiplication-free computation. Yet existing SNN-based time-series forecasters often inherit complex transformer blocks, thereby losing much of the efficiency benefit. To solve the problem, we propose SpikySpace, a spiking state-space model (SSM) that reduces the quadratic cost in the attention block to linear time via selective scanning. Further, we replace dense SSM updates with sparse spike trains and execute selective scans only on spike events, thereby avoiding dense multiplications while preserving the SSM's structured memory. Because complex operations such as exponentials and divisions are costly on neuromorphic chips, we introduce simplified approximations of SiLU and Softplus to enable a neuromorphic-friendly model architecture. In matched settings, SpikySpace reduces estimated energy consumption by 98.73% and 96.24% compared to two state-of-the-art transformer based approaches, namely iTransformer and iSpikformer, respectively. In standard time series forecasting datasets, SpikySpace delivers competitive accuracy while substantially reducing energy cost and memory traffic. As the first full spiking state-space model, SpikySpace bridges neuromorphic efficiency with modern sequence modeling, marking a practical and scalable path toward efficient time series forecasting systems.
PrivacyCD: Hierarchical Unlearning for Protecting Student Privacy in Cognitive Diagnosis
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:The need to remove specific student data from cognitive diagnosis (CD) models has become a pressing requirement, driven by users' growing assertion of their "right to be forgotten". However, existing CD models are largely designed without privacy considerations and lack effective data unlearning mechanisms. Directly applying general purpose unlearning algorithms is suboptimal, as they struggle to balance unlearning completeness, model utility, and efficiency when confronted with the unique heterogeneous structure of CD models. To address this, our paper presents the first systematic study of the data unlearning problem for CD models, proposing a novel and efficient algorithm: hierarchical importanceguided forgetting (HIF). Our key insight is that parameter importance in CD models exhibits distinct layer wise characteristics. HIF leverages this via an innovative smoothing mechanism that combines individual and layer, level importance, enabling a more precise distinction of parameters associated with the data to be unlearned. Experiments on three real world datasets show that HIF significantly outperforms baselines on key metrics, offering the first effective solution for CD models to respond to user data removal requests and for deploying high-performance, privacy preserving AI systems
P-MIA: A Profiled-Based Membership Inference Attack on Cognitive Diagnosis Models
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:Cognitive diagnosis models (CDMs) are pivotal for creating fine-grained learner profiles in modern intelligent education platforms. However, these models are trained on sensitive student data, raising significant privacy concerns. While membership inference attacks (MIA) have been studied in various domains, their application to CDMs remains a critical research gap, leaving their privacy risks unquantified. This paper is the first to systematically investigate MIA against CDMs. We introduce a novel and realistic grey box threat model that exploits the explainability features of these platforms, where a model's internal knowledge state vectors are exposed to users through visualizations such as radar charts. We demonstrate that these vectors can be accurately reverse-engineered from such visualizations, creating a potent attack surface. Based on this threat model, we propose a profile-based MIA (P-MIA) framework that leverages both the model's final prediction probabilities and the exposed internal knowledge state vectors as features. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets against mainstream CDMs show that our grey-box attack significantly outperforms standard black-box baselines. Furthermore, we showcase the utility of P-MIA as an auditing tool by successfully evaluating the efficacy of machine unlearning techniques and revealing their limitations.
USD: A User-Intent-Driven Sampling and Dual-Debiasing Framework for Large-Scale Homepage Recommendations
Jul 09, 2025

Abstract:Large-scale homepage recommendations face critical challenges from pseudo-negative samples caused by exposure bias, where non-clicks may indicate inattention rather than disinterest. Existing work lacks thorough analysis of invalid exposures and typically addresses isolated aspects (e.g., sampling strategies), overlooking the critical impact of pseudo-positive samples - such as homepage clicks merely to visit marketing portals. We propose a unified framework for large-scale homepage recommendation sampling and debiasing. Our framework consists of two key components: (1) a user intent-aware negative sampling module to filter invalid exposure samples, and (2) an intent-driven dual-debiasing module that jointly corrects exposure bias and click bias. Extensive online experiments on Taobao demonstrate the efficacy of our framework, achieving significant improvements in user click-through rates (UCTR) by 35.4\% and 14.5\% in two variants of the marketing block on the Taobao homepage, Baiyibutie and Taobaomiaosha.
Physics-Assisted and Topology-Informed Deep Learning for Weather Prediction
May 08, 2025Abstract:Although deep learning models have demonstrated remarkable potential in weather prediction, most of them overlook either the \textbf{physics} of the underlying weather evolution or the \textbf{topology} of the Earth's surface. In light of these disadvantages, we develop PASSAT, a novel Physics-ASSisted And Topology-informed deep learning model for weather prediction. PASSAT attributes the weather evolution to two key factors: (i) the advection process that can be characterized by the advection equation and the Navier-Stokes equation; (ii) the Earth-atmosphere interaction that is difficult to both model and calculate. PASSAT also takes the topology of the Earth's surface into consideration, other than simply treating it as a plane. With these considerations, PASSAT numerically solves the advection equation and the Navier-Stokes equation on the spherical manifold, utilizes a spherical graph neural network to capture the Earth-atmosphere interaction, and generates the initial velocity fields that are critical to solving the advection equation from the same spherical graph neural network. In the $5.625^\circ$-resolution ERA5 data set, PASSAT outperforms both the state-of-the-art deep learning-based weather prediction models and the operational numerical weather prediction model IFS T42. Code and checkpoint are available at https://github.com/Yumenomae/PASSAT_5p625.
MPIC: Position-Independent Multimodal Context Caching System for Efficient MLLM Serving
Feb 04, 2025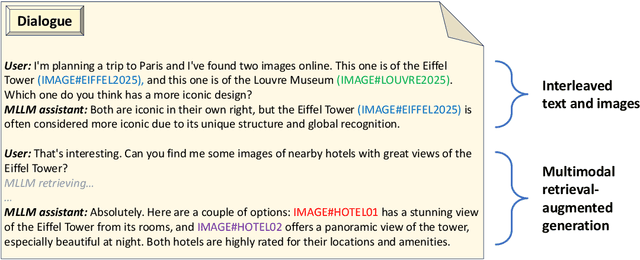
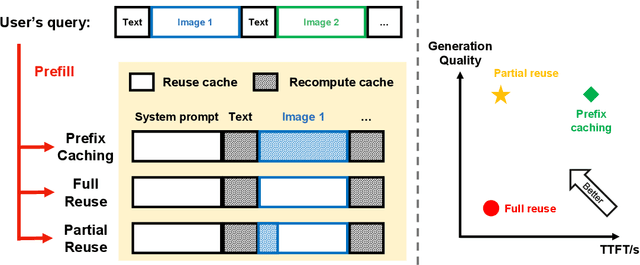
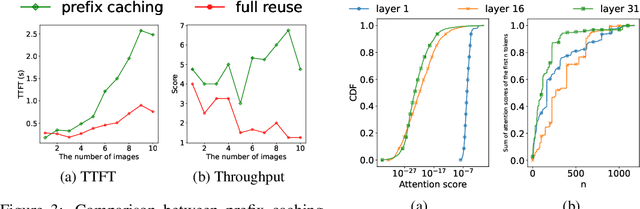
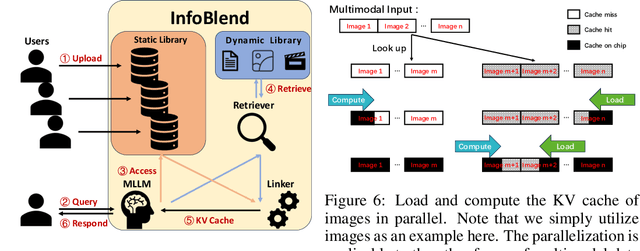
Abstract:The context caching technique is employed to accelerate the Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) inference by prevailing serving platforms currently. However, this approach merely reuses the Key-Value (KV) cache of the initial sequence of prompt, resulting in full KV cache recomputation even if the prefix differs slightly. This becomes particularly inefficient in the context of interleaved text and images, as well as multimodal retrieval-augmented generation. This paper proposes position-independent caching as a more effective approach for multimodal information management. We have designed and implemented a caching system, named MPIC, to address both system-level and algorithm-level challenges. MPIC stores the KV cache on local or remote disks when receiving multimodal data, and calculates and loads the KV cache in parallel during inference. To mitigate accuracy degradation, we have incorporated integrated reuse and recompute mechanisms within the system. The experimental results demonstrate that MPIC can achieve up to 54% reduction in response time compared to existing context caching systems, while maintaining negligible or no accuracy loss.
CSR:Achieving 1 Bit Key-Value Cache via Sparse Representation
Dec 16, 2024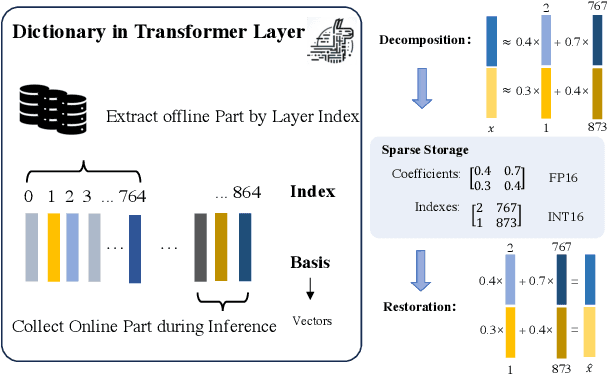
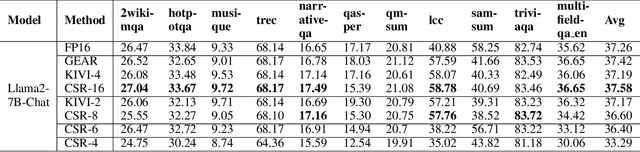
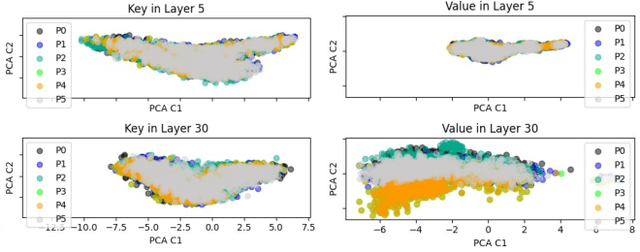
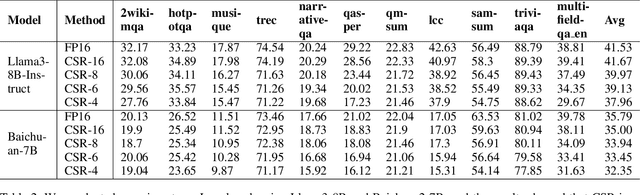
Abstract:The emergence of long-context text applications utilizing large language models (LLMs) has presented significant scalability challenges, particularly in memory footprint. The linear growth of the Key-Value (KV) cache responsible for storing attention keys and values to minimize redundant computations can lead to substantial increases in memory consumption, potentially causing models to fail to serve with limited memory resources. To address this issue, we propose a novel approach called Cache Sparse Representation (CSR), which converts the KV cache by transforming the dense Key-Value cache tensor into sparse indexes and weights, offering a more memory-efficient representation during LLM inference. Furthermore, we introduce NeuralDict, a novel neural network-based method for automatically generating the dictionary used in our sparse representation. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that CSR achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art KV cache quantization algorithms while maintaining robust functionality in memory-constrained environments.
Reinfier and Reintrainer: Verification and Interpretation-Driven Safe Deep Reinforcement Learning Frameworks
Oct 19, 2024Abstract:Ensuring verifiable and interpretable safety of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is crucial for its deployment in real-world applications. Existing approaches like verification-in-the-loop training, however, face challenges such as difficulty in deployment, inefficient training, lack of interpretability, and suboptimal performance in property satisfaction and reward performance. In this work, we propose a novel verification-driven interpretation-in-the-loop framework Reintrainer to develop trustworthy DRL models, which are guaranteed to meet the expected constraint properties. Specifically, in each iteration, this framework measures the gap between the on-training model and predefined properties using formal verification, interprets the contribution of each input feature to the model's output, and then generates the training strategy derived from the on-the-fly measure results, until all predefined properties are proven. Additionally, the low reusability of existing verifiers and interpreters motivates us to develop Reinfier, a general and fundamental tool within Reintrainer for DRL verification and interpretation. Reinfier features breakpoints searching and verification-driven interpretation, associated with a concise constraint-encoding language DRLP. Evaluations demonstrate that Reintrainer outperforms the state-of-the-art on six public benchmarks in both performance and property guarantees. Our framework can be accessed at https://github.com/Kurayuri/Reinfier.
STATE: A Robust ATE Estimator of Heavy-Tailed Metrics for Variance Reduction in Online Controlled Experiments
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Online controlled experiments play a crucial role in enabling data-driven decisions across a wide range of companies. Variance reduction is an effective technique to improve the sensitivity of experiments, achieving higher statistical power while using fewer samples and shorter experimental periods. However, typical variance reduction methods (e.g., regression-adjusted estimators) are built upon the intuitional assumption of Gaussian distributions and cannot properly characterize the real business metrics with heavy-tailed distributions. Furthermore, outliers diminish the correlation between pre-experiment covariates and outcome metrics, greatly limiting the effectiveness of variance reduction. In this paper, we develop a novel framework that integrates the Student's t-distribution with machine learning tools to fit heavy-tailed metrics and construct a robust average treatment effect estimator in online controlled experiments, which we call STATE. By adopting a variational EM method to optimize the loglikehood function, we can infer a robust solution that greatly eliminates the negative impact of outliers and achieves significant variance reduction. Moreover, we extend the STATE method from count metrics to ratio metrics by utilizing linear transformation that preserves unbiased estimation, whose variance reduction is more complex but less investigated in existing works. Finally, both simulations on synthetic data and long-term empirical results on Meituan experiment platform demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Compared with the state-of-the-art estimators (CUPAC/MLRATE), STATE achieves over 50% variance reduction, indicating it can reach the same statistical power with only half of the observations, or half the experimental duration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge