Shiju Zhao
You Need an Encoder for Native Position-Independent Caching
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The Key-Value (KV) cache of Large Language Models (LLMs) is prefix-based, making it highly inefficient for processing contexts retrieved in arbitrary order. Position-Independent Caching (PIC) has been proposed to enable KV reuse without positional constraints; however, existing approaches often incur substantial accuracy degradation, limiting their practical adoption. To address this issue, we propose native PIC by reintroducing the encoder to prevalent decoder-only LLMs and explicitly training it to support PIC. We further develop COMB, a PIC-aware caching system that integrates seamlessly with existing inference frameworks. Experimental results show that COMB reduces Time-to-First-Token (TTFT) by 51-94% and increases throughput by 3$\times$ with comparable accuracy. Furthermore, the quality improvement when using DeepSeek-V2-Lite-Chat demonstrates the applicability of COMB to other types of decoder-only LLMs. Our code is available at https://github.com/shijuzhao/Comb.
Lil: Less is Less When Applying Post-Training Sparse-Attention Algorithms in Long-Decode Stage
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities across a wide range of complex tasks and are increasingly deployed at scale, placing significant demands on inference efficiency. Prior work typically decomposes inference into prefill and decode stages, with the decode stage dominating total latency. To reduce time and memory complexity in the decode stage, a line of work introduces sparse-attention algorithms. In this paper, we show, both empirically and theoretically, that sparse attention can paradoxically increase end-to-end complexity: information loss often induces significantly longer sequences, a phenomenon we term ``Less is Less'' (Lil). To mitigate the Lil problem, we propose an early-stopping algorithm that detects the threshold where information loss exceeds information gain during sparse decoding. Our early-stopping algorithm reduces token consumption by up to 90% with a marginal accuracy degradation of less than 2% across reasoning-intensive benchmarks.
MPIC: Position-Independent Multimodal Context Caching System for Efficient MLLM Serving
Feb 04, 2025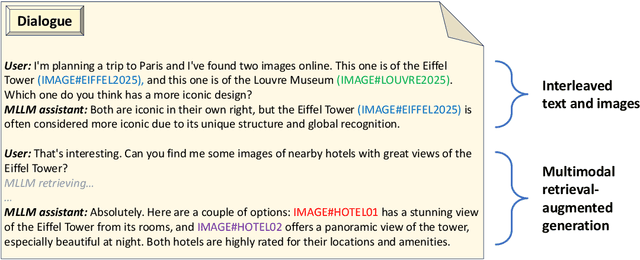
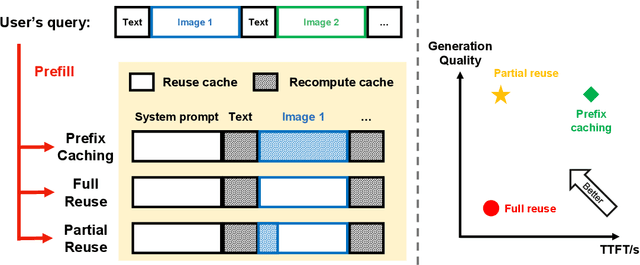
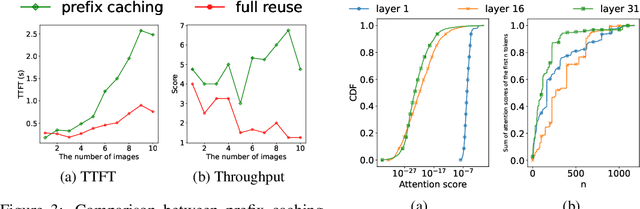
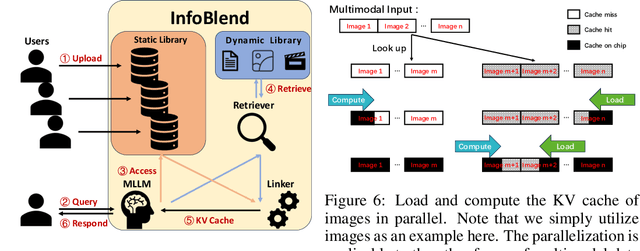
Abstract:The context caching technique is employed to accelerate the Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) inference by prevailing serving platforms currently. However, this approach merely reuses the Key-Value (KV) cache of the initial sequence of prompt, resulting in full KV cache recomputation even if the prefix differs slightly. This becomes particularly inefficient in the context of interleaved text and images, as well as multimodal retrieval-augmented generation. This paper proposes position-independent caching as a more effective approach for multimodal information management. We have designed and implemented a caching system, named MPIC, to address both system-level and algorithm-level challenges. MPIC stores the KV cache on local or remote disks when receiving multimodal data, and calculates and loads the KV cache in parallel during inference. To mitigate accuracy degradation, we have incorporated integrated reuse and recompute mechanisms within the system. The experimental results demonstrate that MPIC can achieve up to 54% reduction in response time compared to existing context caching systems, while maintaining negligible or no accuracy loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge