Boxi Cao
Memorizing is Not Enough: Deep Knowledge Injection Through Reasoning
Apr 01, 2025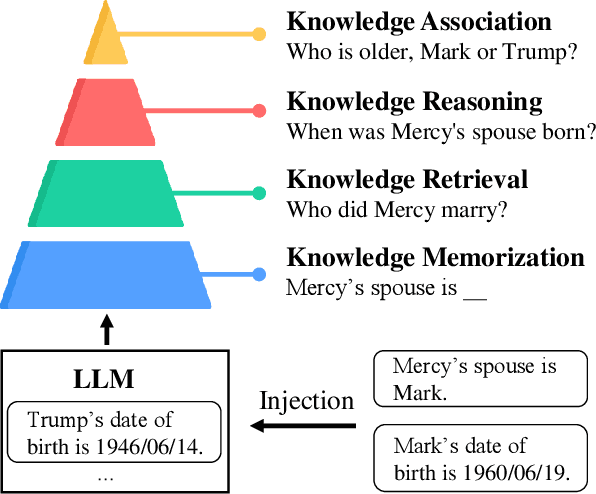
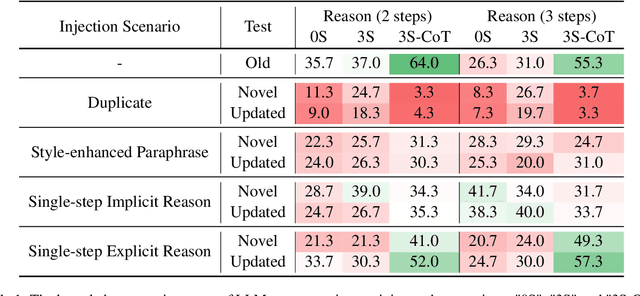
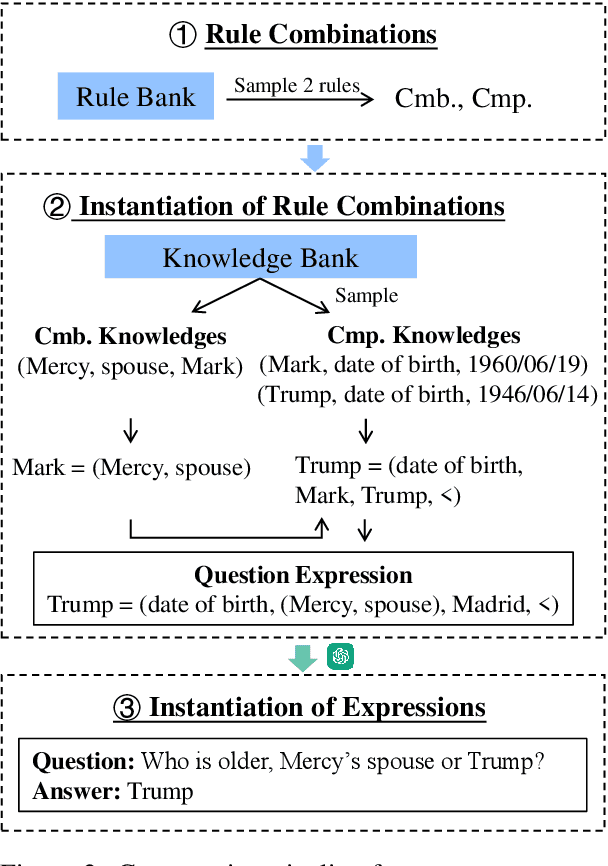
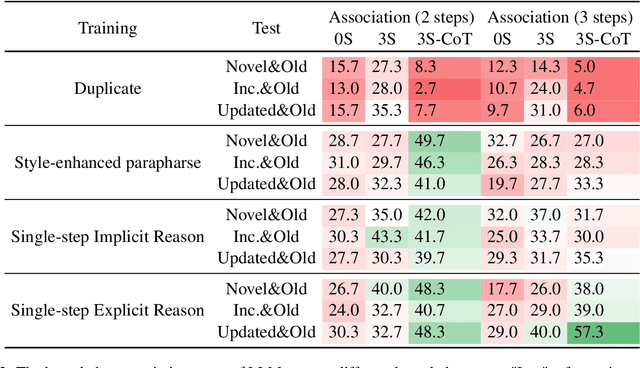
Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) excel in knowledge recall and reasoning, their static nature leads to outdated information as the real world evolves or when adapting to domain-specific knowledge, highlighting the need for effective knowledge injection. However, current research on knowledge injection remains superficial, mainly focusing on knowledge memorization and retrieval. This paper proposes a four-tier knowledge injection framework that systematically defines the levels of knowledge injection: memorization, retrieval, reasoning, and association. Based on this framework, we introduce DeepKnowledge, a synthetic experimental testbed designed for fine-grained evaluation of the depth of knowledge injection across three knowledge types (novel, incremental, and updated). We then explore various knowledge injection scenarios and evaluate the depth of knowledge injection for each scenario on the benchmark. Experimental results reveal key factors to reach each level of knowledge injection for LLMs and establish a mapping between the levels of knowledge injection and the corresponding suitable injection methods, aiming to provide a comprehensive approach for efficient knowledge injection across various levels.
Search, Verify and Feedback: Towards Next Generation Post-training Paradigm of Foundation Models via Verifier Engineering
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:The evolution of machine learning has increasingly prioritized the development of powerful models and more scalable supervision signals. However, the emergence of foundation models presents significant challenges in providing effective supervision signals necessary for further enhancing their capabilities. Consequently, there is an urgent need to explore novel supervision signals and technical approaches. In this paper, we propose verifier engineering, a novel post-training paradigm specifically designed for the era of foundation models. The core of verifier engineering involves leveraging a suite of automated verifiers to perform verification tasks and deliver meaningful feedback to foundation models. We systematically categorize the verifier engineering process into three essential stages: search, verify, and feedback, and provide a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art research developments within each stage. We believe that verifier engineering constitutes a fundamental pathway toward achieving Artificial General Intelligence.
Multi-Facet Counterfactual Learning for Content Quality Evaluation
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:Evaluating the quality of documents is essential for filtering valuable content from the current massive amount of information. Conventional approaches typically rely on a single score as a supervision signal for training content quality evaluators, which is inadequate to differentiate documents with quality variations across multiple facets. In this paper, we propose Multi-facet cOunterfactual LEarning (MOLE), a framework for efficiently constructing evaluators that perceive multiple facets of content quality evaluation. Given a specific scenario, we prompt large language models to generate counterfactual content that exhibits variations in critical quality facets compared to the original document. Furthermore, we leverage a joint training strategy based on contrastive learning and supervised learning to enable the evaluator to distinguish between different quality facets, resulting in more accurate predictions of content quality scores. Experimental results on 2 datasets across different scenarios demonstrate that our proposed MOLE framework effectively improves the correlation of document content quality evaluations with human judgments, which serve as a valuable toolkit for effective information acquisition.
Critic-CoT: Boosting the reasoning abilities of large language model via Chain-of-thoughts Critic
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Self-critic has become an important mechanism for enhancing the reasoning performance of LLMs. However, current approaches mainly involve basic prompts without further training, which tend to be over-simplified, leading to limited accuracy.Moreover, there is a lack of in-depth investigation of the relationship between LLM's ability to criticism and its task-solving performance.To address these issues, we propose Critic-CoT, a novel framework that pushes LLMs toward System-2-like critic capability, via step-wise CoT reasoning format and distant-supervision data construction, without the need for human annotation. Experiments on GSM8K and MATH show that via filtering out invalid solutions or iterative refinement, our enhanced model boosts task-solving performance, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our method. Further, we find that training on critique and refinement alone improves the generation. We hope our work could shed light on future research on improving the reasoning and critic ability of LLMs.
StructEval: Deepen and Broaden Large Language Model Assessment via Structured Evaluation
Aug 07, 2024Abstract:Evaluation is the baton for the development of large language models. Current evaluations typically employ a single-item assessment paradigm for each atomic test objective, which struggles to discern whether a model genuinely possesses the required capabilities or merely memorizes/guesses the answers to specific questions. To this end, we propose a novel evaluation framework referred to as StructEval. Starting from an atomic test objective, StructEval deepens and broadens the evaluation by conducting a structured assessment across multiple cognitive levels and critical concepts, and therefore offers a comprehensive, robust and consistent evaluation for LLMs. Experiments on three widely-used benchmarks demonstrate that StructEval serves as a reliable tool for resisting the risk of data contamination and reducing the interference of potential biases, thereby providing more reliable and consistent conclusions regarding model capabilities. Our framework also sheds light on the design of future principled and trustworthy LLM evaluation protocols.
Beyond Correctness: Benchmarking Multi-dimensional Code Generation for Large Language Models
Jul 16, 2024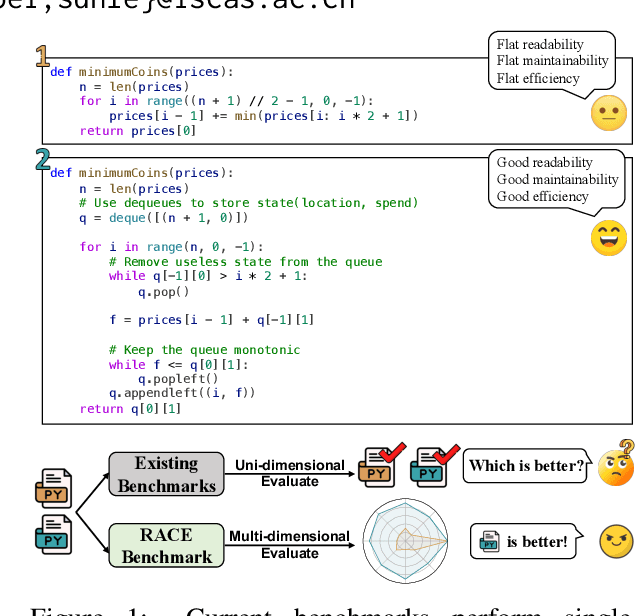
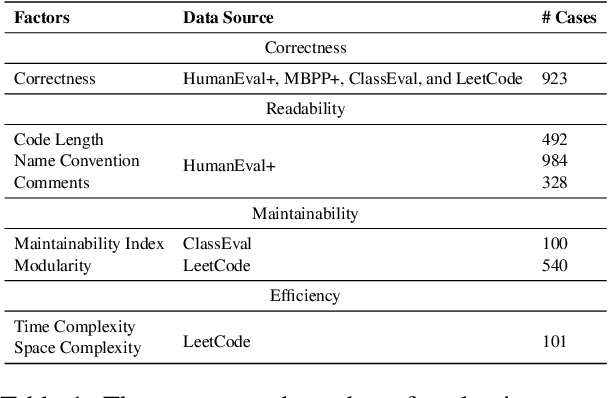
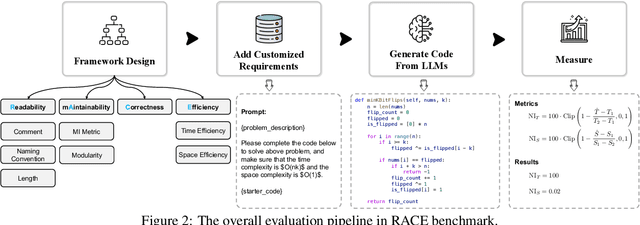
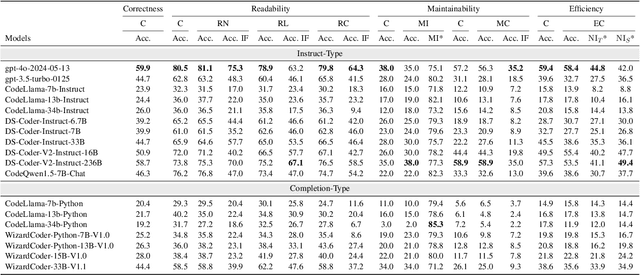
Abstract:In recent years, researchers have proposed numerous benchmarks to evaluate the impressive coding capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on assessing the correctness of code generated by LLMs, while neglecting other critical dimensions that also significantly impact code quality. Therefore, this paper proposes the RACE benchmark, which comprehensively evaluates the quality of code generated by LLMs across 4 dimensions: Readability, mAintainability, Correctness, and Efficiency. Specifically, considering the demand-dependent nature of dimensions beyond correctness, we design various types of user requirements for each dimension to assess the model's ability to generate correct code that also meets user demands. We evaluate 18 representative LLMs on RACE and find that: 1) the current LLMs' ability to generate high-quality code on demand does not yet meet the requirements of software development; 2) readability serves as a critical indicator of the overall quality of generated code; 3) most LLMs exhibit an inherent preference for specific coding style. These findings can help researchers gain a deeper understanding of the coding capabilities of current LLMs and shed light on future directions for model improvement.
Towards Scalable Automated Alignment of LLMs: A Survey
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Alignment is the most critical step in building large language models (LLMs) that meet human needs. With the rapid development of LLMs gradually surpassing human capabilities, traditional alignment methods based on human-annotation are increasingly unable to meet the scalability demands. Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore new sources of automated alignment signals and technical approaches. In this paper, we systematically review the recently emerging methods of automated alignment, attempting to explore how to achieve effective, scalable, automated alignment once the capabilities of LLMs exceed those of humans. Specifically, we categorize existing automated alignment methods into 4 major categories based on the sources of alignment signals and discuss the current status and potential development of each category. Additionally, we explore the underlying mechanisms that enable automated alignment and discuss the essential factors that make automated alignment technologies feasible and effective from the fundamental role of alignment.
Towards Universal Dense Blocking for Entity Resolution
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Blocking is a critical step in entity resolution, and the emergence of neural network-based representation models has led to the development of dense blocking as a promising approach for exploring deep semantics in blocking. However, previous advanced self-supervised dense blocking approaches require domain-specific training on the target domain, which limits the benefits and rapid adaptation of these methods. To address this issue, we propose UniBlocker, a dense blocker that is pre-trained on a domain-independent, easily-obtainable tabular corpus using self-supervised contrastive learning. By conducting domain-independent pre-training, UniBlocker can be adapted to various downstream blocking scenarios without requiring domain-specific fine-tuning. To evaluate the universality of our entity blocker, we also construct a new benchmark covering a wide range of blocking tasks from multiple domains and scenarios. Our experiments show that the proposed UniBlocker, without any domain-specific learning, significantly outperforms previous self- and unsupervised dense blocking methods and is comparable and complementary to the state-of-the-art sparse blocking methods.
URL: Universal Referential Knowledge Linking via Task-instructed Representation Compression
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:Linking a claim to grounded references is a critical ability to fulfill human demands for authentic and reliable information. Current studies are limited to specific tasks like information retrieval or semantic matching, where the claim-reference relationships are unique and fixed, while the referential knowledge linking (RKL) in real-world can be much more diverse and complex. In this paper, we propose universal referential knowledge linking (URL), which aims to resolve diversified referential knowledge linking tasks by one unified model. To this end, we propose a LLM-driven task-instructed representation compression, as well as a multi-view learning approach, in order to effectively adapt the instruction following and semantic understanding abilities of LLMs to referential knowledge linking. Furthermore, we also construct a new benchmark to evaluate ability of models on referential knowledge linking tasks across different scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that universal RKL is challenging for existing approaches, while the proposed framework can effectively resolve the task across various scenarios, and therefore outperforms previous approaches by a large margin.
Spiral of Silences: How is Large Language Model Killing Information Retrieval? -- A Case Study on Open Domain Question Answering
Apr 18, 2024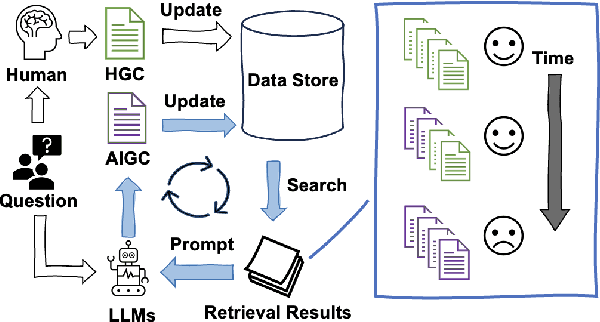



Abstract:The practice of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with retrieval systems, has become increasingly prevalent. However, the repercussions of LLM-derived content infiltrating the web and influencing the retrieval-generation feedback loop are largely uncharted territories. In this study, we construct and iteratively run a simulation pipeline to deeply investigate the short-term and long-term effects of LLM text on RAG systems. Taking the trending Open Domain Question Answering (ODQA) task as a point of entry, our findings reveal a potential digital "Spiral of Silence" effect, with LLM-generated text consistently outperforming human-authored content in search rankings, thereby diminishing the presence and impact of human contributions online. This trend risks creating an imbalanced information ecosystem, where the unchecked proliferation of erroneous LLM-generated content may result in the marginalization of accurate information. We urge the academic community to take heed of this potential issue, ensuring a diverse and authentic digital information landscape.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge