Xueru Wen
Coupled Variational Reinforcement Learning for Language Model General Reasoning
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:While reinforcement learning have achieved impressive progress in language model reasoning, they are constrained by the requirement for verifiable rewards. Recent verifier-free RL methods address this limitation by utilizing the intrinsic probabilities of LLMs generating reference answers as reward signals. However, these approaches typically sample reasoning traces conditioned only on the question. This design decouples reasoning-trace sampling from answer information, leading to inefficient exploration and incoherence between traces and final answers. In this paper, we propose \textit{\b{Co}upled \b{V}ariational \b{R}einforcement \b{L}earning} (CoVRL), which bridges variational inference and reinforcement learning by coupling prior and posterior distributions through a hybrid sampling strategy. By constructing and optimizing a composite distribution that integrates these two distributions, CoVRL enables efficient exploration while preserving strong thought-answer coherence. Extensive experiments on mathematical and general reasoning benchmarks show that CoVRL improves performance by 12.4\% over the base model and achieves an additional 2.3\% improvement over strong state-of-the-art verifier-free RL baselines, providing a principled framework for enhancing the general reasoning capabilities of language models.
The Devil Is in the Details: Tackling Unimodal Spurious Correlations for Generalizable Multimodal Reward Models
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Reward Models (MM-RMs) are crucial for aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences, particularly as LLMs increasingly interact with multimodal data. However, we find that MM-RMs trained on existing datasets often struggle to generalize to out-of-distribution data due to their reliance on unimodal spurious correlations, primarily text-only shortcuts within the training distribution, which prevents them from leveraging true multimodal reward functions. To address this, we introduce a Shortcut-aware MM-RM learning algorithm that mitigates this issue by dynamically reweighting training samples, shifting the distribution toward better multimodal understanding, and reducing dependence on unimodal spurious correlations. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements in generalization, downstream task performance, and scalability, establishing a more robust framework for multimodal reward modeling.
Cheems: A Practical Guidance for Building and Evaluating Chinese Reward Models from Scratch
Feb 24, 2025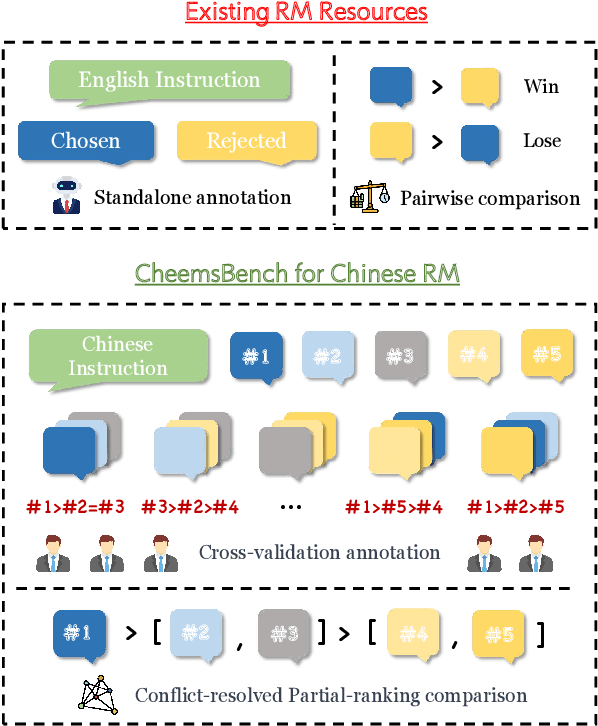
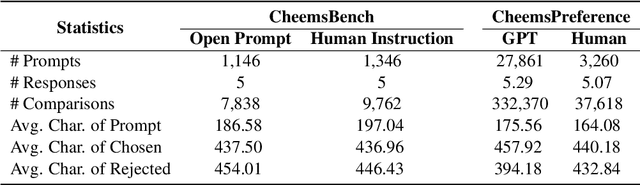
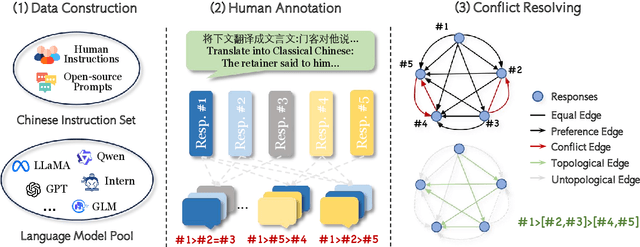
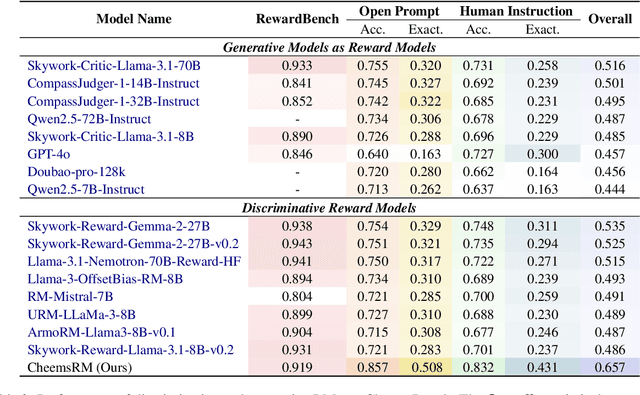
Abstract:Reward models (RMs) are crucial for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. However, most RM research is centered on English and relies heavily on synthetic resources, which leads to limited and less reliable datasets and benchmarks for Chinese. To address this gap, we introduce CheemsBench, a fully human-annotated RM evaluation benchmark within Chinese contexts, and CheemsPreference, a large-scale and diverse preference dataset annotated through human-machine collaboration to support Chinese RM training. We systematically evaluate open-source discriminative and generative RMs on CheemsBench and observe significant limitations in their ability to capture human preferences in Chinese scenarios. Additionally, based on CheemsPreference, we construct an RM that achieves state-of-the-art performance on CheemsBench, demonstrating the necessity of human supervision in RM training. Our findings reveal that scaled AI-generated data struggles to fully capture human preferences, emphasizing the importance of high-quality human supervision in RM development.
Scalable Oversight for Superhuman AI via Recursive Self-Critiquing
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:As AI capabilities increasingly surpass human proficiency in complex tasks, current alignment techniques including SFT and RLHF face fundamental challenges in ensuring reliable oversight. These methods rely on direct human assessment and become untenable when AI outputs exceed human cognitive thresholds. In response to this challenge, we explore two hypotheses: (1) critique of critique can be easier than critique itself, extending the widely-accepted observation that verification is easier than generation to the critique domain, as critique itself is a specialized form of generation; (2) this difficulty relationship is recursively held, suggesting that when direct evaluation is infeasible, performing high-order critiques (e.g., critique of critique of critique) offers a more tractable supervision pathway. To examine these hypotheses, we perform Human-Human, Human-AI, and AI-AI experiments across multiple tasks. Our results demonstrate encouraging evidence supporting these hypotheses and suggest that recursive self-critiquing is a promising direction for scalable oversight.
Transferable Post-training via Inverse Value Learning
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:As post-training processes utilize increasingly large datasets and base models continue to grow in size, the computational demands and implementation challenges of existing algorithms are escalating significantly. In this paper, we propose modeling the changes at the logits level during post-training using a separate neural network (i.e., the value network). After training this network on a small base model using demonstrations, this network can be seamlessly integrated with other pre-trained models during inference, enables them to achieve similar capability enhancements. We systematically investigate the best practices for this paradigm in terms of pre-training weights and connection schemes. We demonstrate that the resulting value network has broad transferability across pre-trained models of different parameter sizes within the same family, models undergoing continuous pre-training within the same family, and models with different vocabularies across families. In certain cases, it can achieve performance comparable to full-parameter fine-tuning. Furthermore, we explore methods to enhance the transferability of the value model and prevent overfitting to the base model used during training.
Rethinking Reward Model Evaluation: Are We Barking up the Wrong Tree?
Oct 08, 2024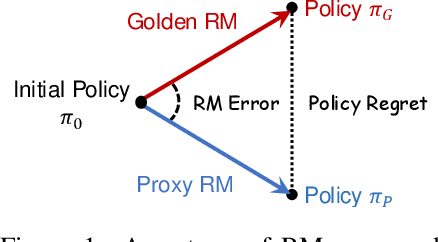
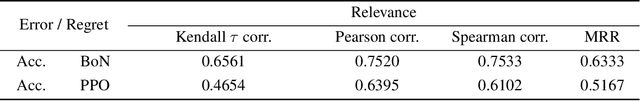
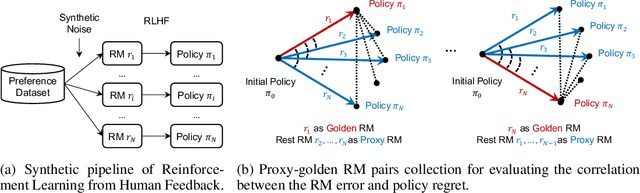
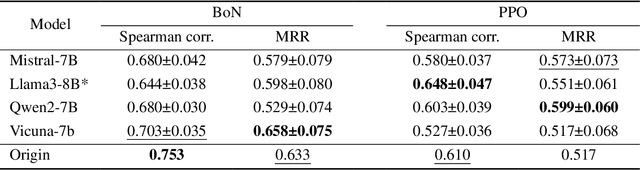
Abstract:Reward Models (RMs) are crucial for aligning language models with human preferences. Currently, the evaluation of RMs depends on measuring accuracy against a validation set of manually annotated preference data. Although this method is straightforward and widely adopted, the relationship between RM accuracy and downstream policy performance remains under-explored. In this work, we conduct experiments in a synthetic setting to investigate how differences in RM measured by accuracy translate into gaps in optimized policy performance. Our findings reveal that while there is a weak positive correlation between accuracy and downstream performance, policies optimized towards RMs with similar accuracy can exhibit quite different performance. Moreover, we discover that the way of measuring accuracy significantly impacts its ability to predict the final policy performance. Through the lens of Regressional Goodhart's effect, we identify the existence of exogenous variables impacting the relationship between RM quality measured by accuracy and policy model capability. This underscores the inadequacy of relying solely on accuracy to reflect their impact on policy optimization.
Critic-CoT: Boosting the reasoning abilities of large language model via Chain-of-thoughts Critic
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Self-critic has become an important mechanism for enhancing the reasoning performance of LLMs. However, current approaches mainly involve basic prompts without further training, which tend to be over-simplified, leading to limited accuracy.Moreover, there is a lack of in-depth investigation of the relationship between LLM's ability to criticism and its task-solving performance.To address these issues, we propose Critic-CoT, a novel framework that pushes LLMs toward System-2-like critic capability, via step-wise CoT reasoning format and distant-supervision data construction, without the need for human annotation. Experiments on GSM8K and MATH show that via filtering out invalid solutions or iterative refinement, our enhanced model boosts task-solving performance, which demonstrates the effectiveness of our method. Further, we find that training on critique and refinement alone improves the generation. We hope our work could shed light on future research on improving the reasoning and critic ability of LLMs.
On-Policy Fine-grained Knowledge Feedback for Hallucination Mitigation
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Hallucination occurs when large language models (LLMs) exhibit behavior that deviates from the boundaries of their knowledge during the response generation process. Previous learning-based methods focus on detecting knowledge boundaries and finetuning models with instance-level feedback, but they suffer from inaccurate signals due to off-policy data sampling and coarse-grained feedback. In this paper, we introduce \textit{\b{R}einforcement \b{L}earning \b{f}or \b{H}allucination} (RLFH), a fine-grained feedback-based online reinforcement learning method for hallucination mitigation. Unlike previous learning-based methods, RLFH enables LLMs to explore the boundaries of their internal knowledge and provide on-policy, fine-grained feedback on these explorations. To construct fine-grained feedback for learning reliable generation behavior, RLFH decomposes the outcomes of large models into atomic facts, provides statement-level evaluation signals, and traces back the signals to the tokens of the original responses. Finally, RLFH adopts the online reinforcement algorithm with these token-level rewards to adjust model behavior for hallucination mitigation. For effective on-policy optimization, RLFH also introduces an LLM-based fact assessment framework to verify the truthfulness and helpfulness of atomic facts without human intervention. Experiments on HotpotQA, SQuADv2, and Biography benchmarks demonstrate that RLFH can balance their usage of internal knowledge during the generation process to eliminate the hallucination behavior of LLMs.
Offline Pseudo Relevance Feedback for Efficient and Effective Single-pass Dense Retrieval
Aug 20, 2023


Abstract:Dense retrieval has made significant advancements in information retrieval (IR) by achieving high levels of effectiveness while maintaining online efficiency during a single-pass retrieval process. However, the application of pseudo relevance feedback (PRF) to further enhance retrieval effectiveness results in a doubling of online latency. To address this challenge, this paper presents a single-pass dense retrieval framework that shifts the PRF process offline through the utilization of pre-generated pseudo-queries. As a result, online retrieval is reduced to a single matching with the pseudo-queries, hence providing faster online retrieval. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is evaluated on the standard TREC DL and HARD datasets, and the results demonstrate its promise. Our code is openly available at https://github.com/Rosenberg37/OPRF.
Type-supervised sequence labeling based on the heterogeneous star graph for named entity recognition
Oct 19, 2022
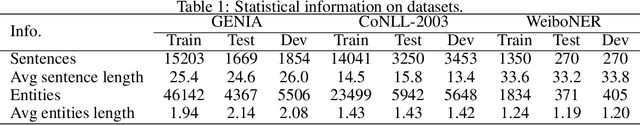
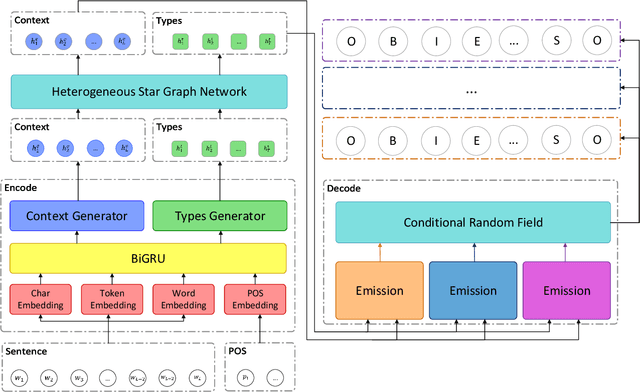
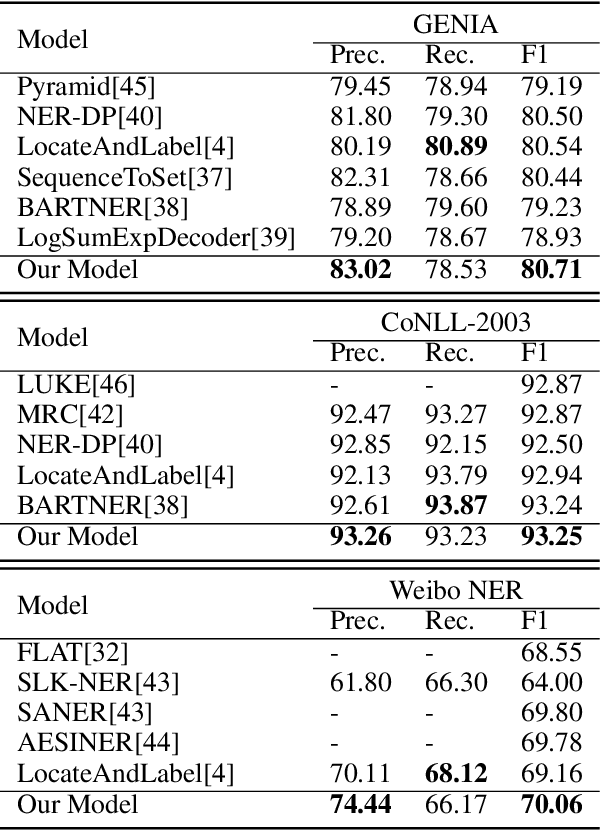
Abstract:Named entity recognition is a fundamental task in natural language processing, identifying the span and category of entities in unstructured texts. The traditional sequence labeling methodology ignores the nested entities, i.e. entities included in other entity mentions. Many approaches attempt to address this scenario, most of which rely on complex structures or have high computation complexity. The representation learning of the heterogeneous star graph containing text nodes and type nodes is investigated in this paper. In addition, we revise the graph attention mechanism into a hybrid form to address its unreasonableness in specific topologies. The model performs the type-supervised sequence labeling after updating nodes in the graph. The annotation scheme is an extension of the single-layer sequence labeling and is able to cope with the vast majority of nested entities. Extensive experiments on public NER datasets reveal the effectiveness of our model in extracting both flat and nested entities. The method achieved state-of-the-art performance on both flat and nested datasets. The significant improvement in accuracy reflects the superiority of the multi-layer labeling strategy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge