Hong Qi
Dynamic Spatial-temporal Hypergraph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-based Action Recognition
Feb 17, 2023



Abstract:Skeleton-based action recognition relies on the extraction of spatial-temporal topological information. Hypergraphs can establish prior unnatural dependencies for the skeleton. However, the existing methods only focus on the construction of spatial topology and ignore the time-point dependence. This paper proposes a dynamic spatial-temporal hypergraph convolutional network (DST-HCN) to capture spatial-temporal information for skeleton-based action recognition. DST-HCN introduces a time-point hypergraph (TPH) to learn relationships at time points. With multiple spatial static hypergraphs and dynamic TPH, our network can learn more complete spatial-temporal features. In addition, we use the high-order information fusion module (HIF) to fuse spatial-temporal information synchronously. Extensive experiments on NTU RGB+D, NTU RGB+D 120, and NW-UCLA datasets show that our model achieves state-of-the-art, especially compared with hypergraph methods.
End-to-End Entity Detection with Proposer and Regressor
Oct 19, 2022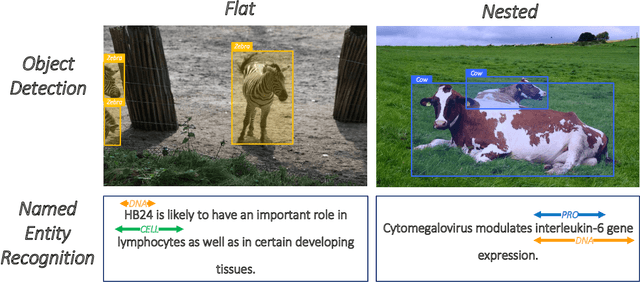
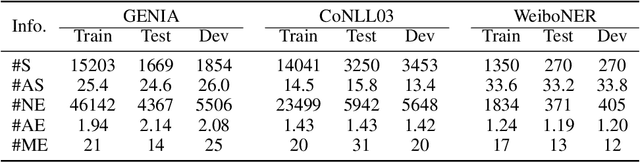
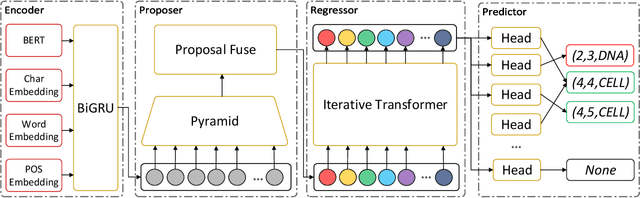
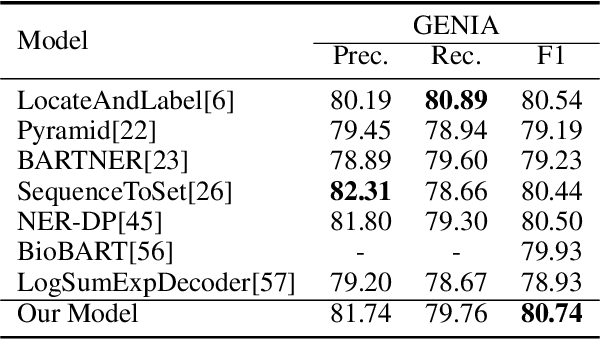
Abstract:Named entity recognition is a traditional task in natural language processing. In particular, nested entity recognition receives extensive attention for the widespread existence of the nesting scenario. The latest research migrates the well-established paradigm of set prediction in object detection to cope with entity nesting. However, the manual creation of query vectors, which fail to adapt to the rich semantic information in the context, limits these approaches. An end-to-end entity detection approach with proposer and regressor is presented in this paper to tackle the issues. First, the proposer utilizes the feature pyramid network to generate high-quality entity proposals. Then, the regressor refines the proposals for generating the final prediction. The model adopts encoder-only architecture and thus obtains the advantages of the richness of query semantics, high precision of entity localization, and easiness for model training. Moreover, we introduce the novel spatially modulated attention and progressive refinement for further improvement. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model achieves advanced performance in flat and nested NER, achieving a new state-of-the-art F1 score of 80.74 on the GENIA dataset and 72.38 on the WeiboNER dataset.
Type-supervised sequence labeling based on the heterogeneous star graph for named entity recognition
Oct 19, 2022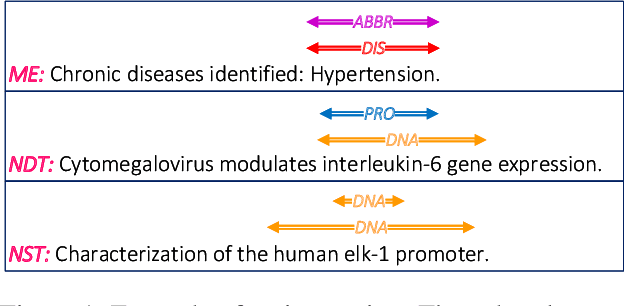
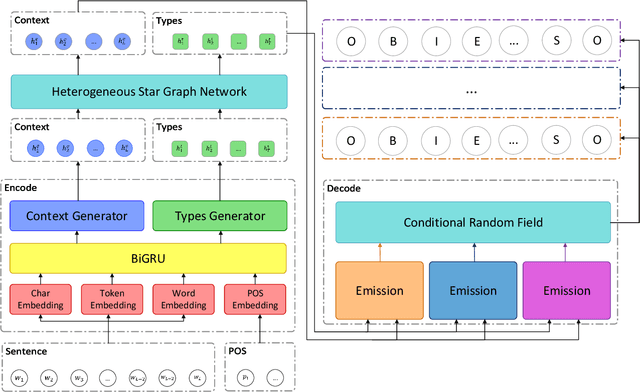
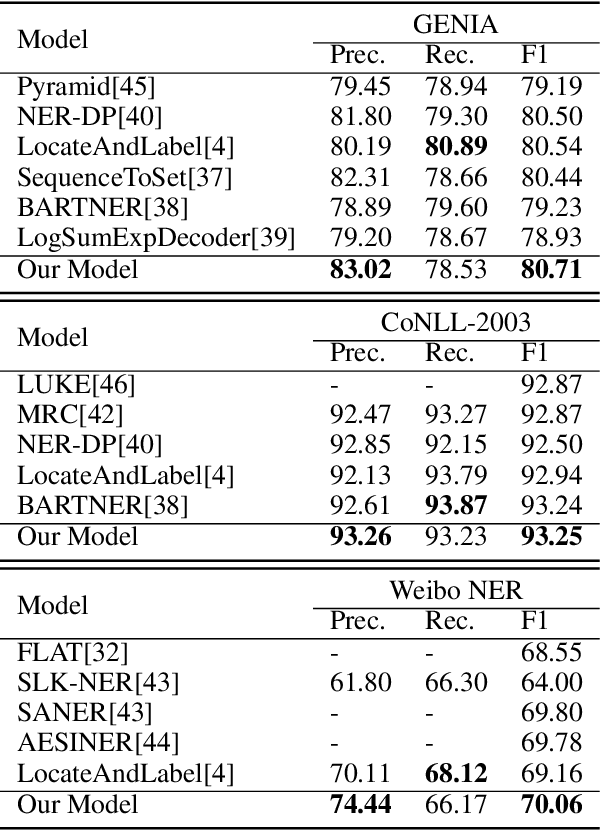
Abstract:Named entity recognition is a fundamental task in natural language processing, identifying the span and category of entities in unstructured texts. The traditional sequence labeling methodology ignores the nested entities, i.e. entities included in other entity mentions. Many approaches attempt to address this scenario, most of which rely on complex structures or have high computation complexity. The representation learning of the heterogeneous star graph containing text nodes and type nodes is investigated in this paper. In addition, we revise the graph attention mechanism into a hybrid form to address its unreasonableness in specific topologies. The model performs the type-supervised sequence labeling after updating nodes in the graph. The annotation scheme is an extension of the single-layer sequence labeling and is able to cope with the vast majority of nested entities. Extensive experiments on public NER datasets reveal the effectiveness of our model in extracting both flat and nested entities. The method achieved state-of-the-art performance on both flat and nested datasets. The significant improvement in accuracy reflects the superiority of the multi-layer labeling strategy.
Spirit Distillation: A Model Compression Method with Multi-domain Knowledge Transfer
Apr 29, 2021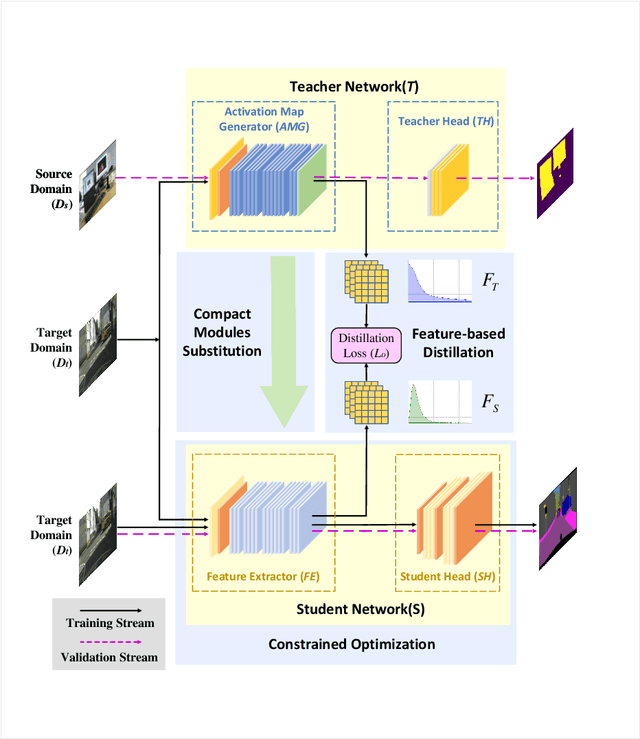
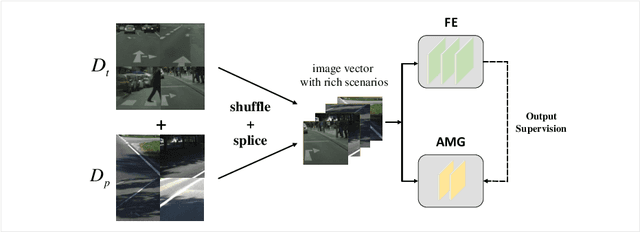
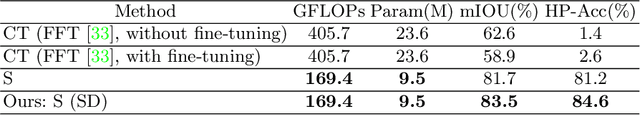
Abstract:Recent applications pose requirements of both cross-domain knowledge transfer and model compression to machine learning models due to insufficient training data and limited computational resources. In this paper, we propose a new knowledge distillation model, named Spirit Distillation (SD), which is a model compression method with multi-domain knowledge transfer. The compact student network mimics out a representation equivalent to the front part of the teacher network, through which the general knowledge can be transferred from the source domain (teacher) to the target domain (student). To further improve the robustness of the student, we extend SD to Enhanced Spirit Distillation (ESD) in exploiting a more comprehensive knowledge by introducing the proximity domain which is similar to the target domain for feature extraction. Results demonstrate that our method can boost mIOU and high-precision accuracy by 1.4% and 8.2% respectively with 78.2% segmentation variance, and can gain a precise compact network with only 41.8% FLOPs.
Spirit Distillation: Precise Real-time Semantic Segmentation of Road Scenes with Insufficient Data
Apr 17, 2021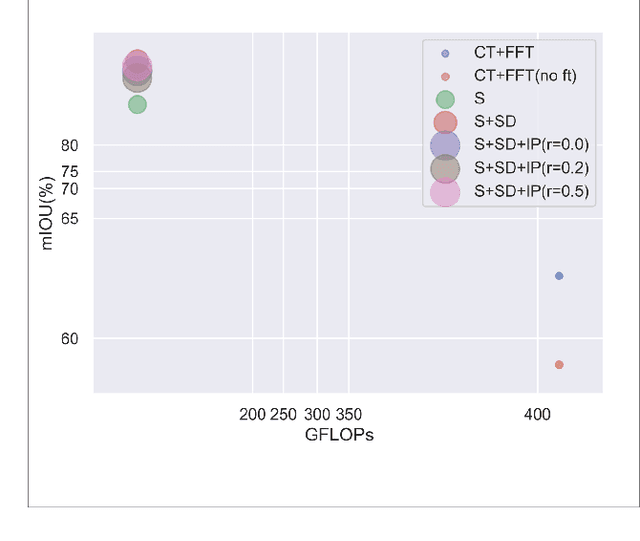
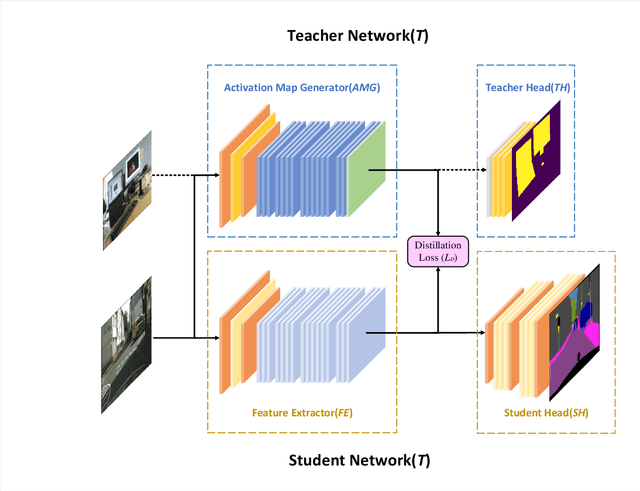
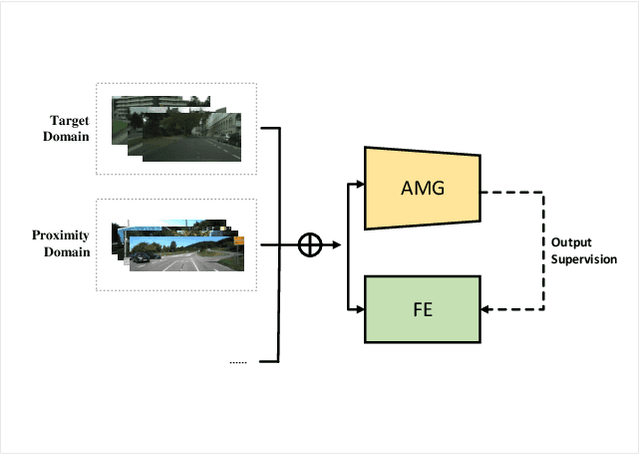
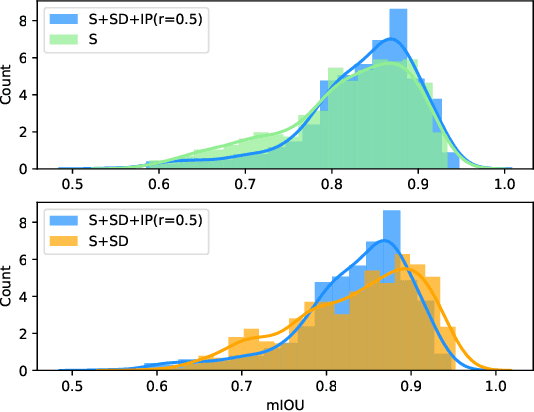
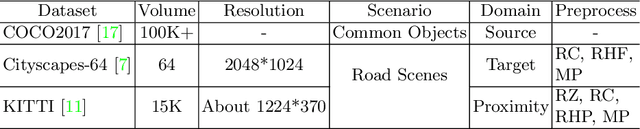
Abstract:Semantic segmentation of road scenes is one of the key technologies for realizing autonomous driving scene perception, and the effectiveness of deep Convolutional Neural Networks(CNNs) for this task has been demonstrated. State-of-art CNNs for semantic segmentation suffer from excessive computations as well as large-scale training data requirement. Inspired by the ideas of Fine-tuning-based Transfer Learning (FTT) and feature-based knowledge distillation, we propose a new knowledge distillation method for cross-domain knowledge transference and efficient data-insufficient network training, named Spirit Distillation(SD), which allow the student network to mimic the teacher network to extract general features, so that a compact and accurate student network can be trained for real-time semantic segmentation of road scenes. Then, in order to further alleviate the trouble of insufficient data and improve the robustness of the student, an Enhanced Spirit Distillation (ESD) method is proposed, which commits to exploit a more comprehensive general features extraction capability by considering images from both the target and the proximity domains as input. To our knowledge, this paper is a pioneering work on the application of knowledge distillation to few-shot learning. Persuasive experiments conducted on Cityscapes semantic segmentation with the prior knowledge transferred from COCO2017 and KITTI demonstrate that our methods can train a better student network (mIOU and high-precision accuracy boost by 1.4% and 8.2% respectively, with 78.2% segmentation variance) with only 41.8% FLOPs (see Fig. 1).
Activation Map Adaptation for Effective Knowledge Distillation
Oct 26, 2020
Abstract:Model compression becomes a recent trend due to the requirement of deploying neural networks on embedded and mobile devices. Hence, both accuracy and efficiency are of critical importance. To explore a balance between them, a knowledge distillation strategy is proposed for general visual representation learning. It utilizes our well-designed activation map adaptive module to replace some blocks of the teacher network, exploring the most appropriate supervisory features adaptively during the training process. Using the teacher's hidden layer output to prompt the student network to train so as to transfer effective semantic information.To verify the effectiveness of our strategy, this paper applied our method to cifar-10 dataset. Results demonstrate that the method can boost the accuracy of the student network by 0.6% with 6.5% loss reduction, and significantly improve its training speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge