Junjie Yang
MedGEN-Bench: Contextually entangled benchmark for open-ended multimodal medical generation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:As Vision-Language Models (VLMs) increasingly gain traction in medical applications, clinicians are progressively expecting AI systems not only to generate textual diagnoses but also to produce corresponding medical images that integrate seamlessly into authentic clinical workflows. Despite the growing interest, existing medical visual benchmarks present notable limitations. They often rely on ambiguous queries that lack sufficient relevance to image content, oversimplify complex diagnostic reasoning into closed-ended shortcuts, and adopt a text-centric evaluation paradigm that overlooks the importance of image generation capabilities. To address these challenges, we introduce MedGEN-Bench, a comprehensive multimodal benchmark designed to advance medical AI research. MedGEN-Bench comprises 6,422 expert-validated image-text pairs spanning six imaging modalities, 16 clinical tasks, and 28 subtasks. It is structured into three distinct formats: Visual Question Answering, Image Editing, and Contextual Multimodal Generation. What sets MedGEN-Bench apart is its focus on contextually intertwined instructions that necessitate sophisticated cross-modal reasoning and open-ended generative outputs, moving beyond the constraints of multiple-choice formats. To evaluate the performance of existing systems, we employ a novel three-tier assessment framework that integrates pixel-level metrics, semantic text analysis, and expert-guided clinical relevance scoring. Using this framework, we systematically assess 10 compositional frameworks, 3 unified models, and 5 VLMs.
CLAPS: A CLIP-Unified Auto-Prompt Segmentation for Multi-Modal Retinal Imaging
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in foundation models, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), have significantly impacted medical image segmentation, especially in retinal imaging, where precise segmentation is vital for diagnosis. Despite this progress, current methods face critical challenges: 1) modality ambiguity in textual disease descriptions, 2) a continued reliance on manual prompting for SAM-based workflows, and 3) a lack of a unified framework, with most methods being modality- and task-specific. To overcome these hurdles, we propose CLIP-unified Auto-Prompt Segmentation (\CLAPS), a novel method for unified segmentation across diverse tasks and modalities in retinal imaging. Our approach begins by pre-training a CLIP-based image encoder on a large, multi-modal retinal dataset to handle data scarcity and distribution imbalance. We then leverage GroundingDINO to automatically generate spatial bounding box prompts by detecting local lesions. To unify tasks and resolve ambiguity, we use text prompts enhanced with a unique "modality signature" for each imaging modality. Ultimately, these automated textual and spatial prompts guide SAM to execute precise segmentation, creating a fully automated and unified pipeline. Extensive experiments on 12 diverse datasets across 11 critical segmentation categories show that CLAPS achieves performance on par with specialized expert models while surpassing existing benchmarks across most metrics, demonstrating its broad generalizability as a foundation model.
UOPSL: Unpaired OCT Predilection Sites Learning for Fundus Image Diagnosis Augmentation
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Significant advancements in AI-driven multimodal medical image diagnosis have led to substantial improvements in ophthalmic disease identification in recent years. However, acquiring paired multimodal ophthalmic images remains prohibitively expensive. While fundus photography is simple and cost-effective, the limited availability of OCT data and inherent modality imbalance hinder further progress. Conventional approaches that rely solely on fundus or textual features often fail to capture fine-grained spatial information, as each imaging modality provides distinct cues about lesion predilection sites. In this study, we propose a novel unpaired multimodal framework \UOPSL that utilizes extensive OCT-derived spatial priors to dynamically identify predilection sites, enhancing fundus image-based disease recognition. Our approach bridges unpaired fundus and OCTs via extended disease text descriptions. Initially, we employ contrastive learning on a large corpus of unpaired OCT and fundus images while simultaneously learning the predilection sites matrix in the OCT latent space. Through extensive optimization, this matrix captures lesion localization patterns within the OCT feature space. During the fine-tuning or inference phase of the downstream classification task based solely on fundus images, where paired OCT data is unavailable, we eliminate OCT input and utilize the predilection sites matrix to assist in fundus image classification learning. Extensive experiments conducted on 9 diverse datasets across 28 critical categories demonstrate that our framework outperforms existing benchmarks.
Towards Alignment-Centric Paradigm: A Survey of Instruction Tuning in Large Language Models
Aug 24, 2025



Abstract:Instruction tuning is a pivotal technique for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human intentions, safety constraints, and domain-specific requirements. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the full pipeline, encompassing (i) data collection methodologies, (ii) full-parameter and parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategies, and (iii) evaluation protocols. We categorized data construction into three major paradigms: expert annotation, distillation from larger models, and self-improvement mechanisms, each offering distinct trade-offs between quality, scalability, and resource cost. Fine-tuning techniques range from conventional supervised training to lightweight approaches, such as low-rank adaptation (LoRA) and prefix tuning, with a focus on computational efficiency and model reusability. We further examine the challenges of evaluating faithfulness, utility, and safety across multilingual and multimodal scenarios, highlighting the emergence of domain-specific benchmarks in healthcare, legal, and financial applications. Finally, we discuss promising directions for automated data generation, adaptive optimization, and robust evaluation frameworks, arguing that a closer integration of data, algorithms, and human feedback is essential for advancing instruction-tuned LLMs. This survey aims to serve as a practical reference for researchers and practitioners seeking to design LLMs that are both effective and reliably aligned with human intentions.
SphereDrag: Spherical Geometry-Aware Panoramic Image Editing
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Image editing has made great progress on planar images, but panoramic image editing remains underexplored. Due to their spherical geometry and projection distortions, panoramic images present three key challenges: boundary discontinuity, trajectory deformation, and uneven pixel density. To tackle these issues, we propose SphereDrag, a novel panoramic editing framework utilizing spherical geometry knowledge for accurate and controllable editing. Specifically, adaptive reprojection (AR) uses adaptive spherical rotation to deal with discontinuity; great-circle trajectory adjustment (GCTA) tracks the movement trajectory more accurate; spherical search region tracking (SSRT) adaptively scales the search range based on spherical location to address uneven pixel density. Also, we construct PanoBench, a panoramic editing benchmark, including complex editing tasks involving multiple objects and diverse styles, which provides a standardized evaluation framework. Experiments show that SphereDrag gains a considerable improvement compared with existing methods in geometric consistency and image quality, achieving up to 10.5% relative improvement.
Exploring Implicit Visual Misunderstandings in Multimodal Large Language Models through Attention Analysis
May 15, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements have enhanced the capability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to comprehend multi-image information. However, existing benchmarks primarily evaluate answer correctness, overlooking whether models genuinely comprehend the visual input. To address this, we define implicit visual misunderstanding (IVM), where MLLMs provide correct answers without fully comprehending the visual input. Through our analysis, we decouple the visual and textual modalities within the causal attention module, revealing that attention distribution increasingly converges on the image associated with the correct answer as the network layers deepen. This insight leads to the introduction of a scale-agnostic metric, \textit{attention accuracy}, and a novel benchmark for quantifying IVMs. Attention accuracy directly evaluates the model's visual understanding via internal mechanisms, remaining robust to positional biases for more reliable assessments. Furthermore, we extend our approach to finer granularities and demonstrate its effectiveness in unimodal scenarios, underscoring its versatility and generalizability.
A Physics-informed End-to-End Occupancy Framework for Motion Planning of Autonomous Vehicles
May 08, 2025Abstract:Accurate and interpretable motion planning is essential for autonomous vehicles (AVs) navigating complex and uncertain environments. While recent end-to-end occupancy prediction methods have improved environmental understanding, they typically lack explicit physical constraints, limiting safety and generalization. In this paper, we propose a unified end-to-end framework that integrates verifiable physical rules into the occupancy learning process. Specifically, we embed artificial potential fields (APF) as physics-informed guidance during network training to ensure that predicted occupancy maps are both data-efficient and physically plausible. Our architecture combines convolutional and recurrent neural networks to capture spatial and temporal dependencies while preserving model flexibility. Experimental results demonstrate that our method improves task completion rate, safety margins, and planning efficiency across diverse driving scenarios, confirming its potential for reliable deployment in real-world AV systems.
Feature Alignment and Representation Transfer in Knowledge Distillation for Large Language Models
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) is a technique for transferring knowledge from complex teacher models to simpler student models, significantly enhancing model efficiency and accuracy. It has demonstrated substantial advancements in various applications including image classification, object detection, language modeling, text classification, and sentiment analysis. Recent innovations in KD methods, such as attention-based approaches, block-wise logit distillation, and decoupling distillation, have notably improved student model performance. These techniques focus on stimulus complexity, attention mechanisms, and global information capture to optimize knowledge transfer. In addition, KD has proven effective in compressing large language models while preserving accuracy, reducing computational overhead, and improving inference speed. This survey synthesizes the latest literature, highlighting key findings, contributions, and future directions in knowledge distillation to provide insights for researchers and practitioners on its evolving role in artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Cross-cultural Deployment of Autonomous Vehicles Using Data-light Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:More than the adherence to specific traffic regulations, driving culture touches upon a more implicit part - an informal, conventional, collective behavioral pattern followed by drivers - that varies across countries, regions, and even cities. Such cultural divergence has become one of the biggest challenges in deploying autonomous vehicles (AVs) across diverse regions today. The current emergence of data-driven methods has shown a potential solution to enable culture-compatible driving through learning from data, but what if some underdeveloped regions cannot provide sufficient local data to inform driving culture? This issue is particularly significant for a broader global AV market. Here, we propose a cross-cultural deployment scheme for AVs, called data-light inverse reinforcement learning, designed to re-calibrate culture-specific AVs and assimilate them into other cultures. First, we report the divergence in driving cultures through a comprehensive comparative analysis of naturalistic driving datasets on highways from three countries: Germany, China, and the USA. Then, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our scheme by testing the expeditious cross-cultural deployment across these three countries, with cumulative testing mileage of over 56084 km. The performance is particularly advantageous when cross-cultural deployment is carried out without affluent local data. Results show that we can reduce the dependence on local data by a margin of 98.67% at best. This study is expected to bring a broader, fairer AV global market, particularly in those regions that lack enough local data to develop culture-compatible AVs.
Think When You Need: Self-Adaptive Chain-of-Thought Learning
Apr 04, 2025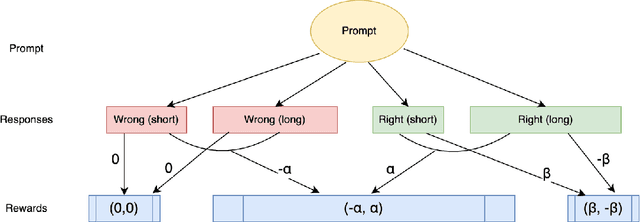
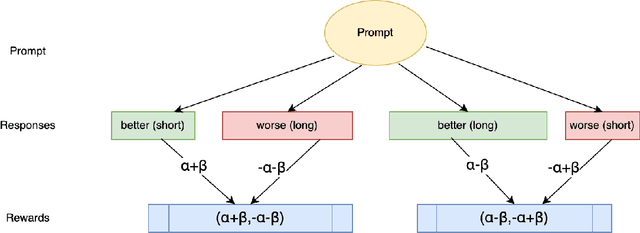
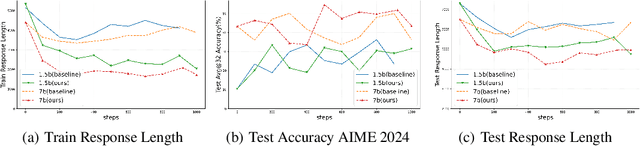
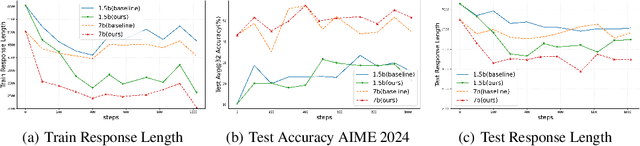
Abstract:Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning enhances language models' performance but often leads to inefficient "overthinking" on simple problems. We identify that existing approaches directly penalizing reasoning length fail to account for varying problem complexity. Our approach constructs rewards through length and quality comparisons, guided by theoretical assumptions that jointly enhance solution correctness with conciseness. Moreover, we further demonstrate our method to fuzzy tasks where ground truth is unavailable. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our method maintains accuracy while generating significantly more concise explanations, effectively teaching models to "think when needed."
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge