Andrei A. Rusu
DiPaCo: Distributed Path Composition
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Progress in machine learning (ML) has been fueled by scaling neural network models. This scaling has been enabled by ever more heroic feats of engineering, necessary for accommodating ML approaches that require high bandwidth communication between devices working in parallel. In this work, we propose a co-designed modular architecture and training approach for ML models, dubbed DIstributed PAth COmposition (DiPaCo). During training, DiPaCo distributes computation by paths through a set of shared modules. Together with a Local-SGD inspired optimization (DiLoCo) that keeps modules in sync with drastically reduced communication, Our approach facilitates training across poorly connected and heterogeneous workers, with a design that ensures robustness to worker failures and preemptions. At inference time, only a single path needs to be executed for each input, without the need for any model compression. We consider this approach as a first prototype towards a new paradigm of large-scale learning, one that is less synchronous and more modular. Our experiments on the widely used C4 benchmark show that, for the same amount of training steps but less wall-clock time, DiPaCo exceeds the performance of a 1 billion-parameter dense transformer language model by choosing one of 256 possible paths, each with a size of 150 million parameters.
Asynchronous Local-SGD Training for Language Modeling
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:Local stochastic gradient descent (Local-SGD), also referred to as federated averaging, is an approach to distributed optimization where each device performs more than one SGD update per communication. This work presents an empirical study of {\it asynchronous} Local-SGD for training language models; that is, each worker updates the global parameters as soon as it has finished its SGD steps. We conduct a comprehensive investigation by examining how worker hardware heterogeneity, model size, number of workers, and optimizer could impact the learning performance. We find that with naive implementations, asynchronous Local-SGD takes more iterations to converge than its synchronous counterpart despite updating the (global) model parameters more frequently. We identify momentum acceleration on the global parameters when worker gradients are stale as a key challenge. We propose a novel method that utilizes a delayed Nesterov momentum update and adjusts the workers' local training steps based on their computation speed. This approach, evaluated with models up to 150M parameters on the C4 dataset, matches the performance of synchronous Local-SGD in terms of perplexity per update step, and significantly surpasses it in terms of wall clock time.
DiLoCo: Distributed Low-Communication Training of Language Models
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLM) have become a critical component in many applications of machine learning. However, standard approaches to training LLM require a large number of tightly interconnected accelerators, with devices exchanging gradients and other intermediate states at each optimization step. While it is difficult to build and maintain a single computing cluster hosting many accelerators, it might be easier to find several computing clusters each hosting a smaller number of devices. In this work, we propose a distributed optimization algorithm, Distributed Low-Communication (DiLoCo), that enables training of language models on islands of devices that are poorly connected. The approach is a variant of federated averaging, where the number of inner steps is large, the inner optimizer is AdamW, and the outer optimizer is Nesterov momentum. On the widely used C4 dataset, we show that DiLoCo on 8 workers performs as well as fully synchronous optimization while communicating 500 times less. DiLoCo exhibits great robustness to the data distribution of each worker. It is also robust to resources becoming unavailable over time, and vice versa, it can seamlessly leverage resources that become available during training.
NEVIS'22: A Stream of 100 Tasks Sampled from 30 Years of Computer Vision Research
Nov 15, 2022Abstract:We introduce the Never Ending VIsual-classification Stream (NEVIS'22), a benchmark consisting of a stream of over 100 visual classification tasks, sorted chronologically and extracted from papers sampled uniformly from computer vision proceedings spanning the last three decades. The resulting stream reflects what the research community thought was meaningful at any point in time. Despite being limited to classification, the resulting stream has a rich diversity of tasks from OCR, to texture analysis, crowd counting, scene recognition, and so forth. The diversity is also reflected in the wide range of dataset sizes, spanning over four orders of magnitude. Overall, NEVIS'22 poses an unprecedented challenge for current sequential learning approaches due to the scale and diversity of tasks, yet with a low entry barrier as it is limited to a single modality and each task is a classical supervised learning problem. Moreover, we provide a reference implementation including strong baselines and a simple evaluation protocol to compare methods in terms of their trade-off between accuracy and compute. We hope that NEVIS'22 can be useful to researchers working on continual learning, meta-learning, AutoML and more generally sequential learning, and help these communities join forces towards more robust and efficient models that efficiently adapt to a never ending stream of data. Implementations have been made available at https://github.com/deepmind/dm_nevis.
Continual Unsupervised Representation Learning
Oct 31, 2019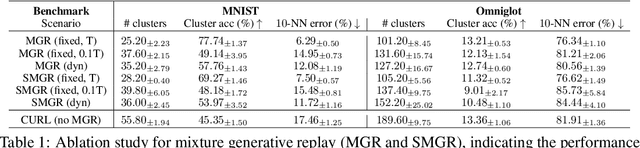
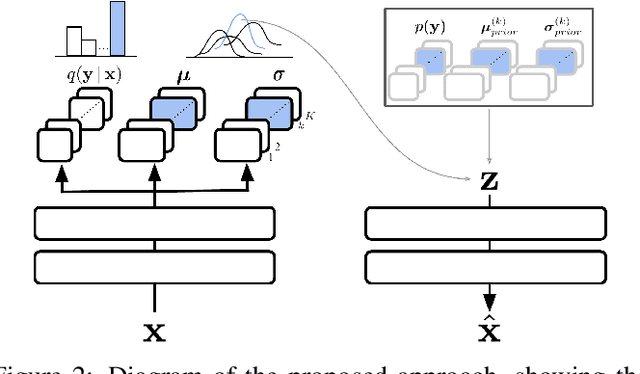
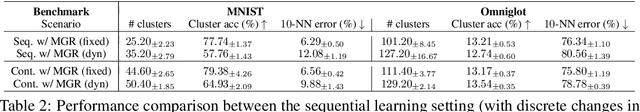
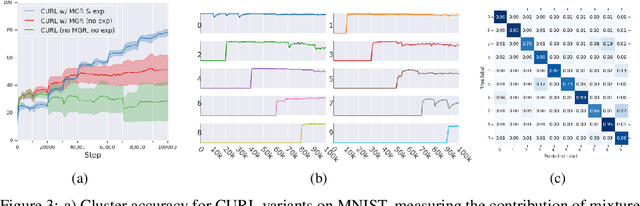
Abstract:Continual learning aims to improve the ability of modern learning systems to deal with non-stationary distributions, typically by attempting to learn a series of tasks sequentially. Prior art in the field has largely considered supervised or reinforcement learning tasks, and often assumes full knowledge of task labels and boundaries. In this work, we propose an approach (CURL) to tackle a more general problem that we will refer to as unsupervised continual learning. The focus is on learning representations without any knowledge about task identity, and we explore scenarios when there are abrupt changes between tasks, smooth transitions from one task to another, or even when the data is shuffled. The proposed approach performs task inference directly within the model, is able to dynamically expand to capture new concepts over its lifetime, and incorporates additional rehearsal-based techniques to deal with catastrophic forgetting. We demonstrate the efficacy of CURL in an unsupervised learning setting with MNIST and Omniglot, where the lack of labels ensures no information is leaked about the task. Further, we demonstrate strong performance compared to prior art in an i.i.d setting, or when adapting the technique to supervised tasks such as incremental class learning.
Meta-Learning with Warped Gradient Descent
Aug 30, 2019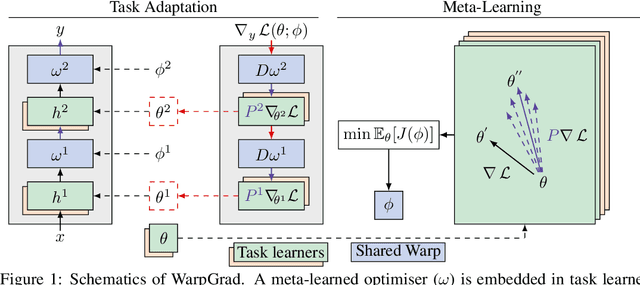
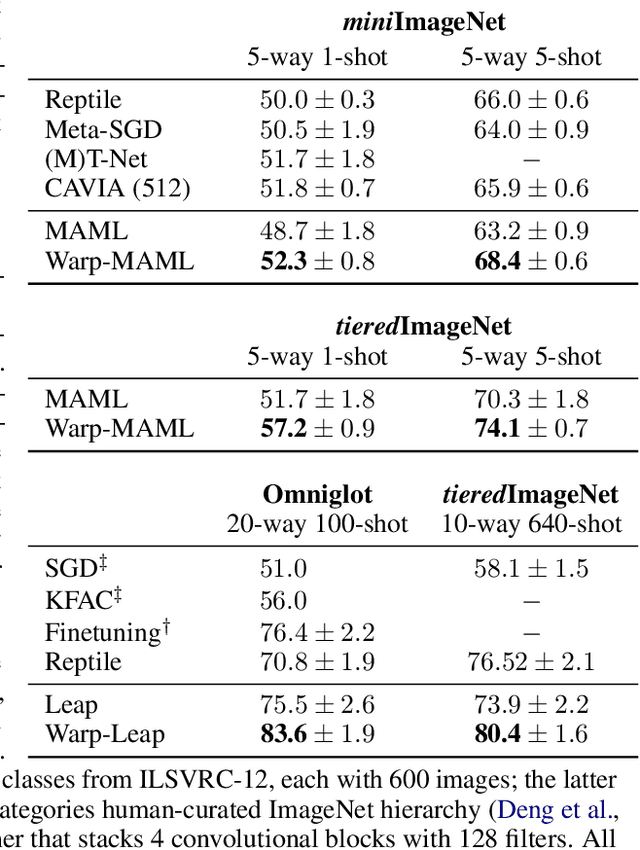
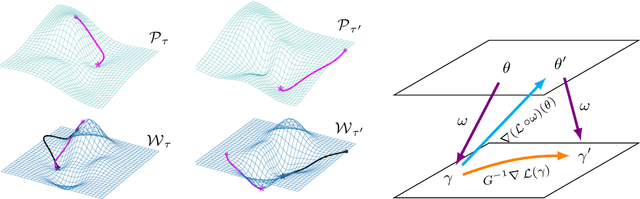
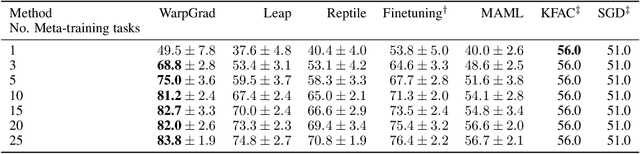
Abstract:A versatile and effective approach to meta-learning is to infer a gradient-based up-date rule directly from data that promotes rapid learning of new tasks from the same distribution. Current methods rely on backpropagating through the learning process, limiting their scope to few-shot learning. In this work, we introduce Warped Gradient Descent (WarpGrad), a family of modular optimisers that can scale to arbitrary adaptation processes. WarpGrad methods meta-learn to warp task loss surfaces across the joint task-parameter distribution to facilitate gradient descent, which is achieved by a reparametrisation of neural networks that interleaves warp layers in the architecture. These layers are shared across task learners and fixed during adaptation; they represent a projection of task parameters into a meta-learned space that is conducive to task adaptation and standard backpropagation induces a form of gradient preconditioning. WarpGrad methods are computationally efficient and easy to implement as they rely on parameter sharing and backpropagation. They are readily combined with other meta-learners and can scale both in terms of model size and length of adaptation trajectories as meta-learning warp parameters do not require differentiation through task adaptation processes. We show empirically that WarpGrad optimisers meta-learn a warped space where gradient descent is well behaved, with faster convergence and better performance in a variety of settings, including few-shot, standard supervised, continual, and reinforcement learning.
Task Agnostic Continual Learning via Meta Learning
Jun 12, 2019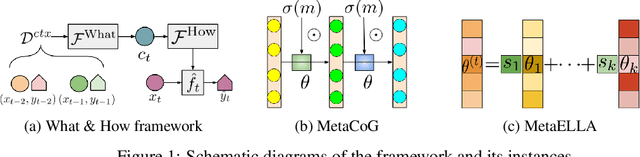

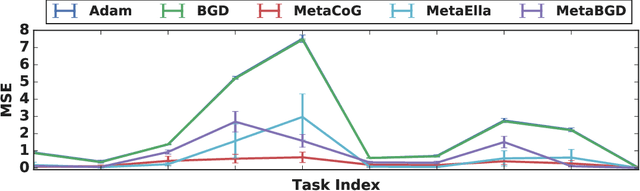
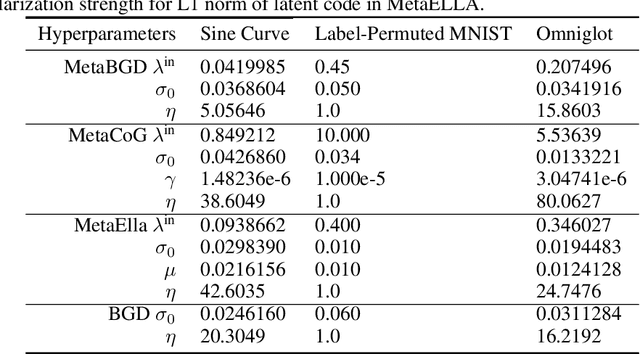
Abstract:While neural networks are powerful function approximators, they suffer from catastrophic forgetting when the data distribution is not stationary. One particular formalism that studies learning under non-stationary distribution is provided by continual learning, where the non-stationarity is imposed by a sequence of distinct tasks. Most methods in this space assume, however, the knowledge of task boundaries, and focus on alleviating catastrophic forgetting. In this work, we depart from this view and move the focus towards faster remembering -- i.e measuring how quickly the network recovers performance rather than measuring the network's performance without any adaptation. We argue that in many settings this can be more effective and that it opens the door to combining meta-learning and continual learning techniques, leveraging their complementary advantages. We propose a framework specific for the scenario where no information about task boundaries or task identity is given. It relies on a separation of concerns into what task is being solved and how the task should be solved. This framework is implemented by differentiating task specific parameters from task agnostic parameters, where the latter are optimized in a continual meta learning fashion, without access to multiple tasks at the same time. We showcase this framework in a supervised learning scenario and discuss the implication of the proposed formalism.
Meta-Learning with Latent Embedding Optimization
Sep 28, 2018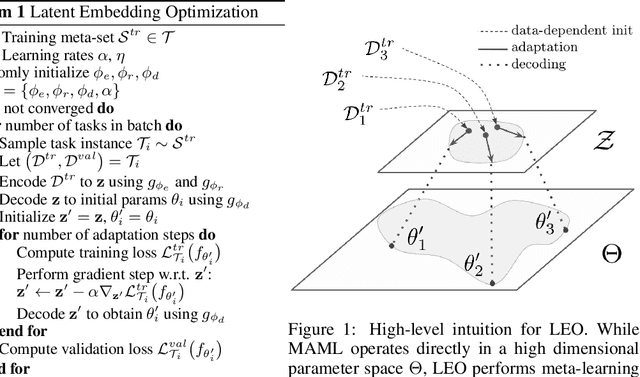
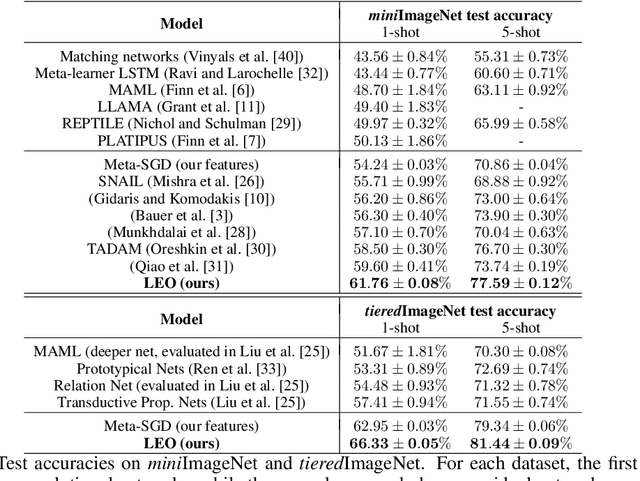
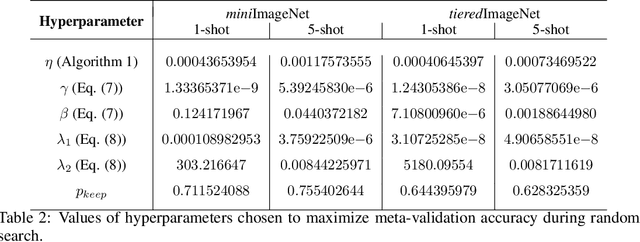
Abstract:Gradient-based meta-learning techniques are both widely applicable and proficient at solving challenging few-shot learning and fast adaptation problems. However, they have practical difficulties when operating on high-dimensional parameter spaces in extreme low-data regimes. We show that it is possible to bypass these limitations by learning a data-dependent latent generative representation of model parameters, and performing gradient-based meta-learning in this low-dimensional latent space. The resulting approach, latent embedding optimization (LEO), decouples the gradient-based adaptation procedure from the underlying high-dimensional space of model parameters. Our evaluation shows that LEO can achieve state-of-the-art performance on the competitive miniImageNet and tieredImageNet few-shot classification tasks. Further analysis indicates LEO is able to capture uncertainty in the data, and can perform adaptation more effectively by optimizing in latent space.
Meta-Learning by the Baldwin Effect
Jun 22, 2018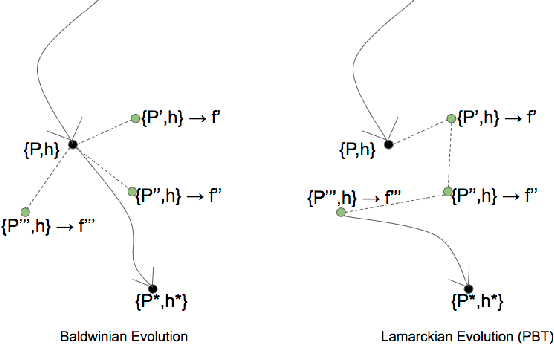
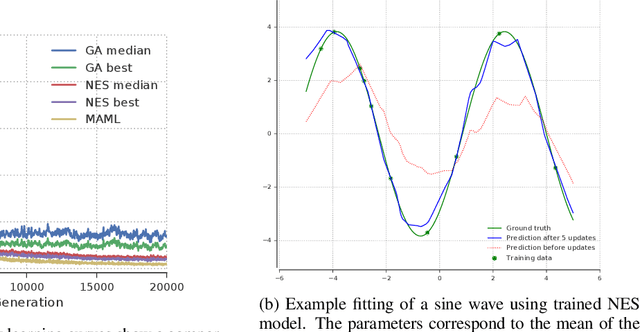
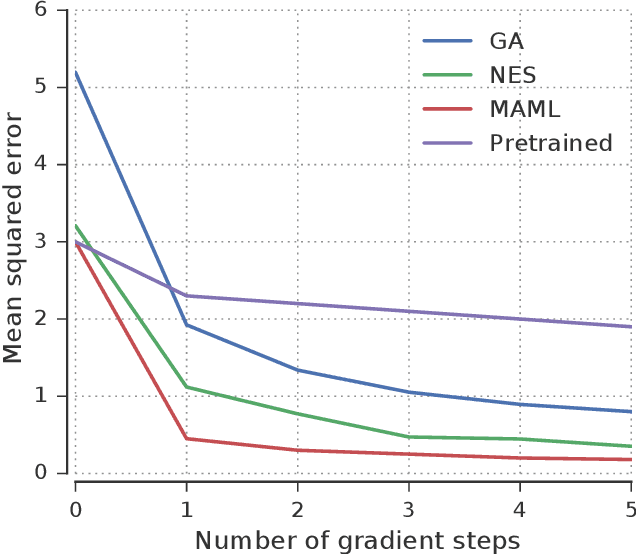
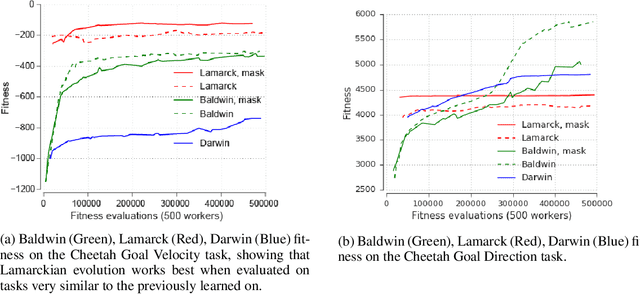
Abstract:The scope of the Baldwin effect was recently called into question by two papers that closely examined the seminal work of Hinton and Nowlan. To this date there has been no demonstration of its necessity in empirically challenging tasks. Here we show that the Baldwin effect is capable of evolving few-shot supervised and reinforcement learning mechanisms, by shaping the hyperparameters and the initial parameters of deep learning algorithms. Furthermore it can genetically accommodate strong learning biases on the same set of problems as a recent machine learning algorithm called MAML "Model Agnostic Meta-Learning" which uses second-order gradients instead of evolution to learn a set of reference parameters (initial weights) that can allow rapid adaptation to tasks sampled from a distribution. Whilst in simple cases MAML is more data efficient than the Baldwin effect, the Baldwin effect is more general in that it does not require gradients to be backpropagated to the reference parameters or hyperparameters, and permits effectively any number of gradient updates in the inner loop. The Baldwin effect learns strong learning dependent biases, rather than purely genetically accommodating fixed behaviours in a learning independent manner.
DARLA: Improving Zero-Shot Transfer in Reinforcement Learning
Jun 06, 2018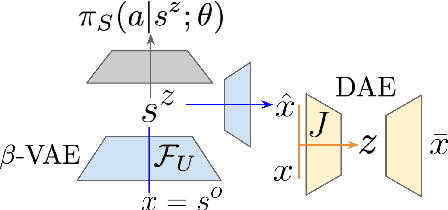
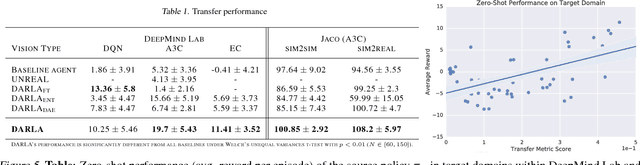
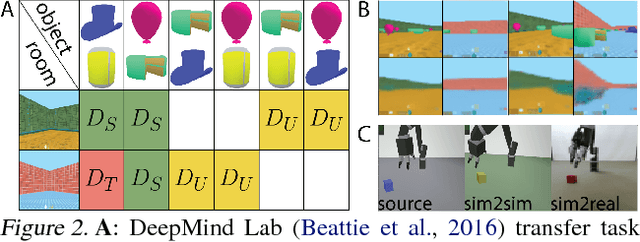
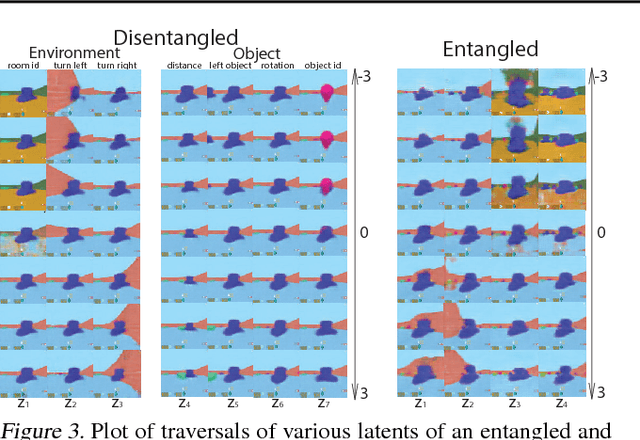
Abstract:Domain adaptation is an important open problem in deep reinforcement learning (RL). In many scenarios of interest data is hard to obtain, so agents may learn a source policy in a setting where data is readily available, with the hope that it generalises well to the target domain. We propose a new multi-stage RL agent, DARLA (DisentAngled Representation Learning Agent), which learns to see before learning to act. DARLA's vision is based on learning a disentangled representation of the observed environment. Once DARLA can see, it is able to acquire source policies that are robust to many domain shifts - even with no access to the target domain. DARLA significantly outperforms conventional baselines in zero-shot domain adaptation scenarios, an effect that holds across a variety of RL environments (Jaco arm, DeepMind Lab) and base RL algorithms (DQN, A3C and EC).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge