Albert Clapés
SoccerNet 2025 Challenges Results
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The SoccerNet 2025 Challenges mark the fifth annual edition of the SoccerNet open benchmarking effort, dedicated to advancing computer vision research in football video understanding. This year's challenges span four vision-based tasks: (1) Team Ball Action Spotting, focused on detecting ball-related actions in football broadcasts and assigning actions to teams; (2) Monocular Depth Estimation, targeting the recovery of scene geometry from single-camera broadcast clips through relative depth estimation for each pixel; (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, requiring the analysis of multiple synchronized camera views to classify fouls and their severity; and (4) Game State Reconstruction, aimed at localizing and identifying all players from a broadcast video to reconstruct the game state on a 2D top-view of the field. Across all tasks, participants were provided with large-scale annotated datasets, unified evaluation protocols, and strong baselines as starting points. This report presents the results of each challenge, highlights the top-performing solutions, and provides insights into the progress made by the community. The SoccerNet Challenges continue to serve as a driving force for reproducible, open research at the intersection of computer vision, artificial intelligence, and sports. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
Sparse-Dense Side-Tuner for efficient Video Temporal Grounding
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Video Temporal Grounding (VTG) involves Moment Retrieval (MR) and Highlight Detection (HD) based on textual queries. For this, most methods rely solely on final-layer features of frozen large pre-trained backbones, limiting their adaptability to new domains. While full fine-tuning is often impractical, parameter-efficient fine-tuning -- and particularly side-tuning (ST) -- has emerged as an effective alternative. However, prior ST approaches this problem from a frame-level refinement perspective, overlooking the inherent sparse nature of MR. To address this, we propose the Sparse-Dense Side-Tuner (SDST), the first anchor-free ST architecture for VTG. We also introduce the Reference-based Deformable Self-Attention, a novel mechanism that enhances the context modeling of the deformable attention -- a key limitation of existing anchor-free methods. Additionally, we present the first effective integration of InternVideo2 backbone into an ST framework, showing its profound implications in performance. Overall, our method significantly improves existing ST methods, achieving highly competitive or SOTA results on QVHighlights, TACoS, and Charades-STA, while reducing up to a 73% the parameter count w.r.t. the existing SOTA methods. The code is publicly accessible at https://github.com/davidpujol/SDST.
Action Anticipation from SoccerNet Football Video Broadcasts
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the way we analyze sports videos, whether to understand the actions of games in long untrimmed videos or to anticipate the player's motion in future frames. Despite these efforts, little attention has been given to anticipating game actions before they occur. In this work, we introduce the task of action anticipation for football broadcast videos, which consists in predicting future actions in unobserved future frames, within a five- or ten-second anticipation window. To benchmark this task, we release a new dataset, namely the SoccerNet Ball Action Anticipation dataset, based on SoccerNet Ball Action Spotting. Additionally, we propose a Football Action ANticipation TRAnsformer (FAANTRA), a baseline method that adapts FUTR, a state-of-the-art action anticipation model, to predict ball-related actions. To evaluate action anticipation, we introduce new metrics, including mAP@$\delta$, which evaluates the temporal precision of predicted future actions, as well as mAP@$\infty$, which evaluates their occurrence within the anticipation window. We also conduct extensive ablation studies to examine the impact of various task settings, input configurations, and model architectures. Experimental results highlight both the feasibility and challenges of action anticipation in football videos, providing valuable insights into the design of predictive models for sports analytics. By forecasting actions before they unfold, our work will enable applications in automated broadcasting, tactical analysis, and player decision-making. Our dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/MohamadDalal/FAANTRA.
Action Valuation in Sports: A Survey
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Action Valuation (AV) has emerged as a key topic in Sports Analytics, offering valuable insights by assigning scores to individual actions based on their contribution to desired outcomes. Despite a few surveys addressing related concepts such as Player Valuation, there is no comprehensive review dedicated to an in-depth analysis of AV across different sports. In this survey, we introduce a taxonomy with nine dimensions related to the AV task, encompassing data, methodological approaches, evaluation techniques, and practical applications. Through this analysis, we aim to identify the essential characteristics of effective AV methods, highlight existing gaps in research, and propose future directions for advancing the field.
SoccerNet 2024 Challenges Results
Sep 16, 2024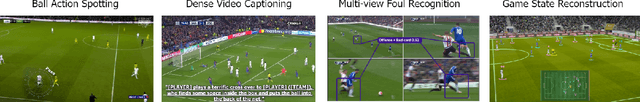
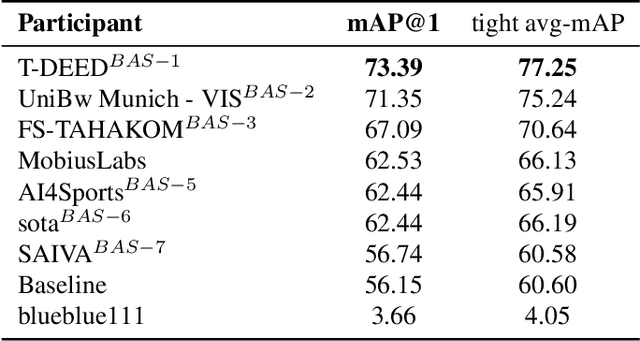
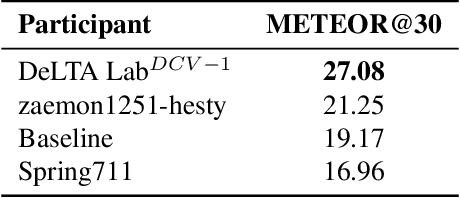
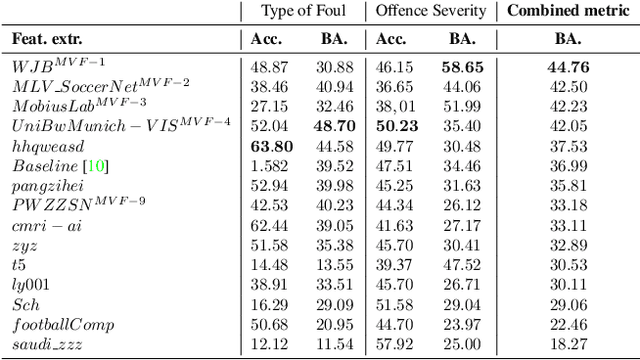
Abstract:The SoccerNet 2024 challenges represent the fourth annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. These challenges aim to advance research across multiple themes in football, including broadcast video understanding, field understanding, and player understanding. This year, the challenges encompass four vision-based tasks. (1) Ball Action Spotting, focusing on precisely localizing when and which soccer actions related to the ball occur, (2) Dense Video Captioning, focusing on describing the broadcast with natural language and anchored timestamps, (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, a novel task focusing on analyzing multiple viewpoints of a potential foul incident to classify whether a foul occurred and assess its severity, (4) Game State Reconstruction, another novel task focusing on reconstructing the game state from broadcast videos onto a 2D top-view map of the field. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
AI Competitions and Benchmarks: Dataset Development
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Machine learning is now used in many applications thanks to its ability to predict, generate, or discover patterns from large quantities of data. However, the process of collecting and transforming data for practical use is intricate. Even in today's digital era, where substantial data is generated daily, it is uncommon for it to be readily usable; most often, it necessitates meticulous manual data preparation. The haste in developing new models can frequently result in various shortcomings, potentially posing risks when deployed in real-world scenarios (eg social discrimination, critical failures), leading to the failure or substantial escalation of costs in AI-based projects. This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of established methodological tools, enriched by our practical experience, in the development of datasets for machine learning. Initially, we develop the tasks involved in dataset development and offer insights into their effective management (including requirements, design, implementation, evaluation, distribution, and maintenance). Then, we provide more details about the implementation process which includes data collection, transformation, and quality evaluation. Finally, we address practical considerations regarding dataset distribution and maintenance.
T-DEED: Temporal-Discriminability Enhancer Encoder-Decoder for Precise Event Spotting in Sports Videos
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce T-DEED, a Temporal-Discriminability Enhancer Encoder-Decoder for Precise Event Spotting in sports videos. T-DEED addresses multiple challenges in the task, including the need for discriminability among frame representations, high output temporal resolution to maintain prediction precision, and the necessity to capture information at different temporal scales to handle events with varying dynamics. It tackles these challenges through its specifically designed architecture, featuring an encoder-decoder for leveraging multiple temporal scales and achieving high output temporal resolution, along with temporal modules designed to increase token discriminability. Leveraging these characteristics, T-DEED achieves SOTA performance on the FigureSkating and FineDiving datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/arturxe2/T-DEED.
ASTRA: An Action Spotting TRAnsformer for Soccer Videos
Apr 02, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce ASTRA, a Transformer-based model designed for the task of Action Spotting in soccer matches. ASTRA addresses several challenges inherent in the task and dataset, including the requirement for precise action localization, the presence of a long-tail data distribution, non-visibility in certain actions, and inherent label noise. To do so, ASTRA incorporates (a) a Transformer encoder-decoder architecture to achieve the desired output temporal resolution and to produce precise predictions, (b) a balanced mixup strategy to handle the long-tail distribution of the data, (c) an uncertainty-aware displacement head to capture the label variability, and (d) input audio signal to enhance detection of non-visible actions. Results demonstrate the effectiveness of ASTRA, achieving a tight Average-mAP of 66.82 on the test set. Moreover, in the SoccerNet 2023 Action Spotting challenge, we secure the 3rd position with an Average-mAP of 70.21 on the challenge set.
SADA: Semantic adversarial unsupervised domain adaptation for Temporal Action Localization
Dec 20, 2023Abstract:Temporal Action Localization (TAL) is a complex task that poses relevant challenges, particularly when attempting to generalize on new -- unseen -- domains in real-world applications. These scenarios, despite realistic, are often neglected in the literature, exposing these solutions to important performance degradation. In this work, we tackle this issue by introducing, for the first time, an approach for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) in sparse TAL, which we refer to as Semantic Adversarial unsupervised Domain Adaptation (SADA). Our contribution is threefold: (1) we pioneer the development of a domain adaptation model that operates on realistic sparse action detection benchmarks; (2) we tackle the limitations of global-distribution alignment techniques by introducing a novel adversarial loss that is sensitive to local class distributions, ensuring finer-grained adaptation; and (3) we present a novel experimental setup, based on EpicKitchens100, that evaluates multiple types of domain shifts in a comprehensive manner. Our experimental results indicate that SADA improves the adaptation across domains when compared to fully supervised state-of-the-art and alternative UDA methods, attaining a relative performance boost of up to 14%.
SoccerNet 2023 Challenges Results
Sep 12, 2023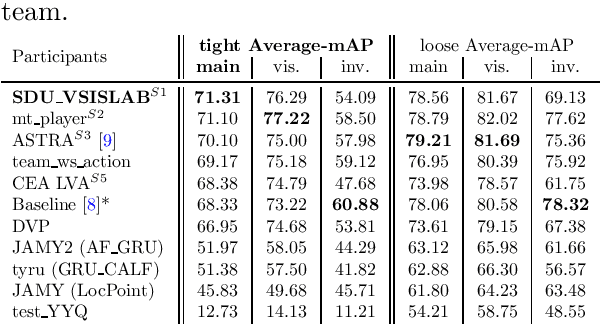
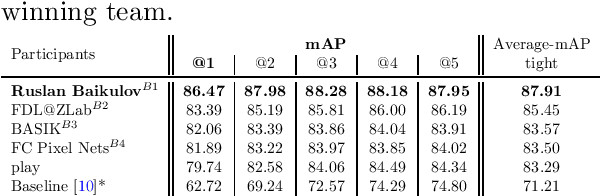
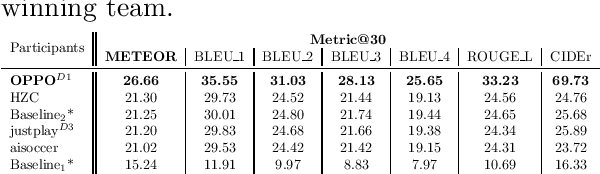
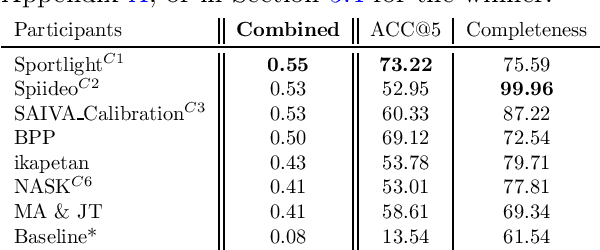
Abstract:The SoccerNet 2023 challenges were the third annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. For this third edition, the challenges were composed of seven vision-based tasks split into three main themes. The first theme, broadcast video understanding, is composed of three high-level tasks related to describing events occurring in the video broadcasts: (1) action spotting, focusing on retrieving all timestamps related to global actions in soccer, (2) ball action spotting, focusing on retrieving all timestamps related to the soccer ball change of state, and (3) dense video captioning, focusing on describing the broadcast with natural language and anchored timestamps. The second theme, field understanding, relates to the single task of (4) camera calibration, focusing on retrieving the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from images. The third and last theme, player understanding, is composed of three low-level tasks related to extracting information about the players: (5) re-identification, focusing on retrieving the same players across multiple views, (6) multiple object tracking, focusing on tracking players and the ball through unedited video streams, and (7) jersey number recognition, focusing on recognizing the jersey number of players from tracklets. Compared to the previous editions of the SoccerNet challenges, tasks (2-3-7) are novel, including new annotations and data, task (4) was enhanced with more data and annotations, and task (6) now focuses on end-to-end approaches. More information on the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards are available on https://www.soccer-net.org. Baselines and development kits can be found on https://github.com/SoccerNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge