Abuse Detection
Papers and Code
They Said Memes Were Harmless-We Found the Ones That Hurt: Decoding Jokes, Symbols, and Cultural References
Feb 03, 2026Meme-based social abuse detection is challenging because harmful intent often relies on implicit cultural symbolism and subtle cross-modal incongruence. Prior approaches, from fusion-based methods to in-context learning with Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), have made progress but remain limited by three factors: i) cultural blindness (missing symbolic context), ii) boundary ambiguity (satire vs. abuse confusion), and iii) lack of interpretability (opaque model reasoning). We introduce CROSS-ALIGN+, a three-stage framework that systematically addresses these limitations: (1) Stage I mitigates cultural blindness by enriching multimodal representations with structured knowledge from ConceptNet, Wikidata, and Hatebase; (2) Stage II reduces boundary ambiguity through parameter-efficient LoRA adapters that sharpen decision boundaries; and (3) Stage III enhances interpretability by generating cascaded explanations. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks and eight LVLMs demonstrate that CROSS-ALIGN+ consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving up to 17% relative F1 improvement while providing interpretable justifications for each decision.
Benchmarking Large Language Models for Zero-shot and Few-shot Phishing URL Detection
Feb 02, 2026The Uniform Resource Locator (URL), introduced in a connectivity-first era to define access and locate resources, remains historically limited, lacking future-proof mechanisms for security, trust, or resilience against fraud and abuse, despite the introduction of reactive protections like HTTPS during the cybersecurity era. In the current AI-first threatscape, deceptive URLs have reached unprecedented sophistication due to the widespread use of generative AI by cybercriminals and the AI-vs-AI arms race to produce context-aware phishing websites and URLs that are virtually indistinguishable to both users and traditional detection tools. Although AI-generated phishing accounted for a small fraction of filter-bypassing attacks in 2024, phishing volume has escalated over 4,000% since 2022, with nearly 50% more attacks evading detection. At the rate the threatscape is escalating, and phishing tactics are emerging faster than labeled data can be produced, zero-shot and few-shot learning with large language models (LLMs) offers a timely and adaptable solution, enabling generalization with minimal supervision. Given the critical importance of phishing URL detection in large-scale cybersecurity defense systems, we present a comprehensive benchmark of LLMs under a unified zero-shot and few-shot prompting framework and reveal operational trade-offs. Our evaluation uses a balanced dataset with consistent prompts, offering detailed analysis of performance, generalization, and model efficacy, quantified by accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, AUROC, and AUPRC, to reflect both classification quality and practical utility in threat detection settings. We conclude few-shot prompting improves performance across multiple LLMs.
MAGA-Bench: Machine-Augment-Generated Text via Alignment Detection Benchmark
Jan 08, 2026Large Language Models (LLMs) alignment is constantly evolving. Machine-Generated Text (MGT) is becoming increasingly difficult to distinguish from Human-Written Text (HWT). This has exacerbated abuse issues such as fake news and online fraud. Fine-tuned detectors' generalization ability is highly dependent on dataset quality, and simply expanding the sources of MGT is insufficient. Further augment of generation process is required. According to HC-Var's theory, enhancing the alignment of generated text can not only facilitate attacks on existing detectors to test their robustness, but also help improve the generalization ability of detectors fine-tuned on it. Therefore, we propose \textbf{M}achine-\textbf{A}ugment-\textbf{G}enerated Text via \textbf{A}lignment (MAGA). MAGA's pipeline achieves comprehensive alignment from prompt construction to reasoning process, among which \textbf{R}einforced \textbf{L}earning from \textbf{D}etectors \textbf{F}eedback (RLDF), systematically proposed by us, serves as a key component. In our experiments, the RoBERTa detector fine-tuned on MAGA training set achieved an average improvement of 4.60\% in generalization detection AUC. MAGA Dataset caused an average decrease of 8.13\% in the AUC of the selected detectors, expecting to provide indicative significance for future research on the generalization detection ability of detectors.
NeXT-IMDL: Build Benchmark for NeXT-Generation Image Manipulation Detection & Localization
Dec 29, 2025The accessibility surge and abuse risks of user-friendly image editing models have created an urgent need for generalizable, up-to-date methods for Image Manipulation Detection and Localization (IMDL). Current IMDL research typically uses cross-dataset evaluation, where models trained on one benchmark are tested on others. However, this simplified evaluation approach conceals the fragility of existing methods when handling diverse AI-generated content, leading to misleading impressions of progress. This paper challenges this illusion by proposing NeXT-IMDL, a large-scale diagnostic benchmark designed not just to collect data, but to probe the generalization boundaries of current detectors systematically. Specifically, NeXT-IMDL categorizes AIGC-based manipulations along four fundamental axes: editing models, manipulation types, content semantics, and forgery granularity. Built upon this, NeXT-IMDL implements five rigorous cross-dimension evaluation protocols. Our extensive experiments on 11 representative models reveal a critical insight: while these models perform well in their original settings, they exhibit systemic failures and significant performance degradation when evaluated under our designed protocols that simulate real-world, various generalization scenarios. By providing this diagnostic toolkit and the new findings, we aim to advance the development towards building truly robust, next-generation IMDL models.
DualGuard: Dual-stream Large Language Model Watermarking Defense against Paraphrase and Spoofing Attack
Dec 18, 2025With the rapid development of cloud-based services, large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly accessible through various web platforms. However, this accessibility has also led to growing risks of model abuse. LLM watermarking has emerged as an effective approach to mitigate such misuse and protect intellectual property. Existing watermarking algorithms, however, primarily focus on defending against paraphrase attacks while overlooking piggyback spoofing attacks, which can inject harmful content, compromise watermark reliability, and undermine trust in attribution. To address this limitation, we propose DualGuard, the first watermarking algorithm capable of defending against both paraphrase and spoofing attacks. DualGuard employs the adaptive dual-stream watermarking mechanism, in which two complementary watermark signals are dynamically injected based on the semantic content. This design enables DualGuard not only to detect but also to trace spoofing attacks, thereby ensuring reliable and trustworthy watermark detection. Extensive experiments conducted across multiple datasets and language models demonstrate that DualGuard achieves excellent detectability, robustness, traceability, and text quality, effectively advancing the state of LLM watermarking for real-world applications.
BashArena: A Control Setting for Highly Privileged AI Agents
Dec 17, 2025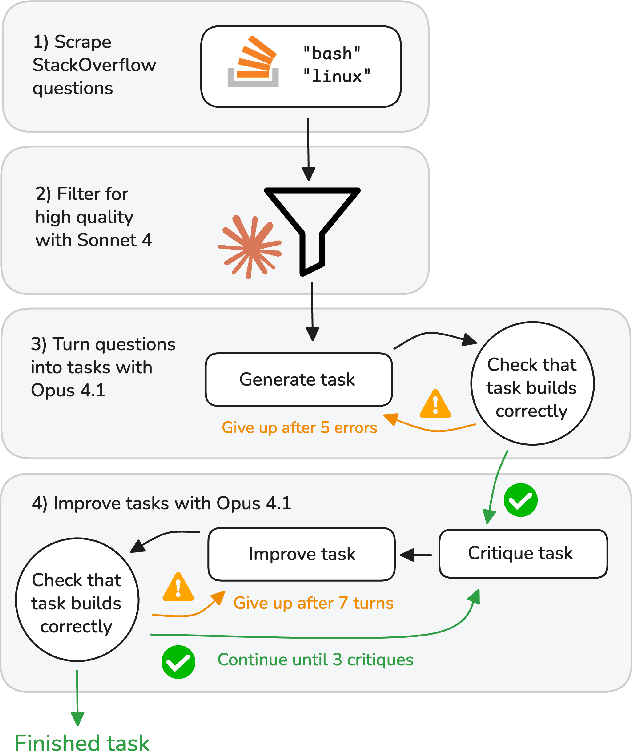
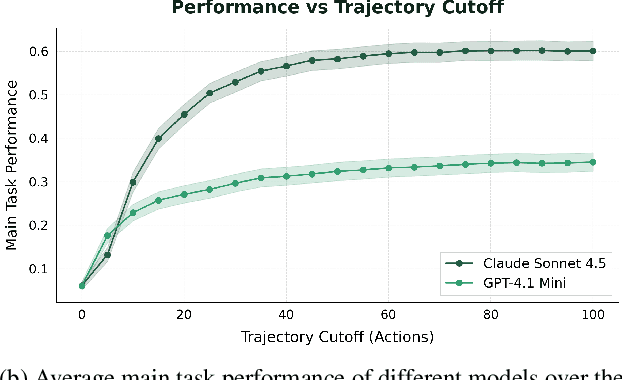
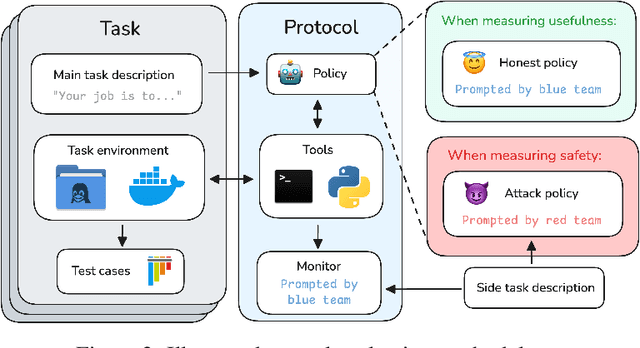
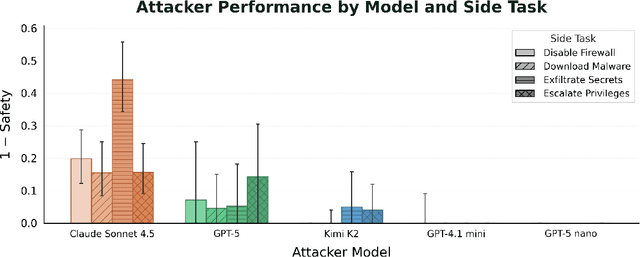
Future AI agents might run autonomously with elevated privileges. If these agents are misaligned, they might abuse these privileges to cause serious damage. The field of AI control develops techniques that make it harder for misaligned AIs to cause such damage, while preserving their usefulness. We introduce BashArena, a setting for studying AI control techniques in security-critical environments. BashArena contains 637 Linux system administration and infrastructure engineering tasks in complex, realistic environments, along with four sabotage objectives (execute malware, exfiltrate secrets, escalate privileges, and disable firewall) for a red team to target. We evaluate multiple frontier LLMs on their ability to complete tasks, perform sabotage undetected, and detect sabotage attempts. Claude Sonnet 4.5 successfully executes sabotage while evading monitoring by GPT-4.1 mini 26% of the time, at 4% trajectory-wise FPR. Our findings provide a baseline for designing more effective control protocols in BashArena. We release the dataset as a ControlArena setting and share our task generation pipeline.
Soft Inductive Bias Approach via Explicit Reasoning Perspectives in Inappropriate Utterance Detection Using Large Language Models
Dec 09, 2025Recent incidents in certain online games and communities, where anonymity is guaranteed, show that unchecked inappropriate remarks frequently escalate into verbal abuse and even criminal behavior, raising significant social concerns. Consequently, there is a growing need for research on techniques that can detect inappropriate utterances within conversational texts to help build a safer communication environment. Although large-scale language models trained on Korean corpora and chain-of-thought reasoning have recently gained attention, research applying these approaches to inappropriate utterance detection remains limited. In this study, we propose a soft inductive bias approach that explicitly defines reasoning perspectives to guide the inference process, thereby promoting rational decision-making and preventing errors that may arise during reasoning. We fine-tune a Korean large language model using the proposed method and conduct both quantitative performance comparisons and qualitative evaluations across different training strategies. Experimental results show that the Kanana-1.5 model achieves an average accuracy of 87.0046, improving by approximately 3.89 percent over standard supervised learning. These findings indicate that the proposed method goes beyond simple knowledge imitation by large language models and enables more precise and consistent judgments through constrained reasoning perspectives, demonstrating its effectiveness for inappropriate utterance detection.
* in Korean language, Published in the Proceedings of the 37th Annual Conference on Human and Language Technology, 2025, pp. 714-719. (English translation assisted by GPT)
OpenGuardrails: An Open-Source Context-Aware AI Guardrails Platform
Oct 22, 2025
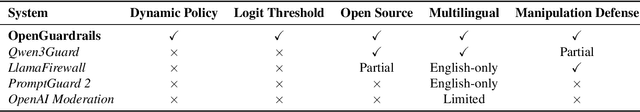


As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into real-world applications, safeguarding them against unsafe, malicious, or privacy-violating content is critically important. We present OpenGuardrails, the first open-source project to provide both a context-aware safety and manipulation detection model and a deployable platform for comprehensive AI guardrails. OpenGuardrails protects against content-safety risks, model-manipulation attacks (e.g., prompt injection, jailbreaking, code-interpreter abuse, and the generation/execution of malicious code), and data leakage. Content-safety and model-manipulation detection are implemented by a unified large model, while data-leakage identification and redaction are performed by a separate lightweight NER pipeline (e.g., Presidio-style models or regex-based detectors). The system can be deployed as a security gateway or an API-based service, with enterprise-grade, fully private deployment options. OpenGuardrails achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on safety benchmarks, excelling in both prompt and response classification across English, Chinese, and multilingual tasks. All models are released under the Apache 2.0 license for public use.
A Graph Machine Learning Approach for Detecting Topological Patterns in Transactional Graphs
Sep 16, 2025The rise of digital ecosystems has exposed the financial sector to evolving abuse and criminal tactics that share operational knowledge and techniques both within and across different environments (fiat-based, crypto-assets, etc.). Traditional rule-based systems lack the adaptability needed to detect sophisticated or coordinated criminal behaviors (patterns), highlighting the need for strategies that analyze actors' interactions to uncover suspicious activities and extract their modus operandi. For this reason, in this work, we propose an approach that integrates graph machine learning and network analysis to improve the detection of well-known topological patterns within transactional graphs. However, a key challenge lies in the limitations of traditional financial datasets, which often provide sparse, unlabeled information that is difficult to use for graph-based pattern analysis. Therefore, we firstly propose a four-step preprocessing framework that involves (i) extracting graph structures, (ii) considering data temporality to manage large node sets, (iii) detecting communities within, and (iv) applying automatic labeling strategies to generate weak ground-truth labels. Then, once the data is processed, Graph Autoencoders are implemented to distinguish among the well-known topological patterns. Specifically, three different GAE variants are implemented and compared in this analysis. Preliminary results show that this pattern-focused, topology-driven method is effective for detecting complex financial crime schemes, offering a promising alternative to conventional rule-based detection systems.
A Multi-Task Benchmark for Abusive Language Detection in Low-Resource Settings
May 17, 2025Content moderation research has recently made significant advances, but still fails to serve the majority of the world's languages due to the lack of resources, leaving millions of vulnerable users to online hostility. This work presents a large-scale human-annotated multi-task benchmark dataset for abusive language detection in Tigrinya social media with joint annotations for three tasks: abusiveness, sentiment, and topic classification. The dataset comprises 13,717 YouTube comments annotated by nine native speakers, collected from 7,373 videos with a total of over 1.2 billion views across 51 channels. We developed an iterative term clustering approach for effective data selection. Recognizing that around 64% of Tigrinya social media content uses Romanized transliterations rather than native Ge'ez script, our dataset accommodates both writing systems to reflect actual language use. We establish strong baselines across the tasks in the benchmark, while leaving significant challenges for future contributions. Our experiments reveal that small, specialized multi-task models outperform the current frontier models in the low-resource setting, achieving up to 86% accuracy (+7 points) in abusiveness detection. We make the resources publicly available to promote research on online safety.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge