Ziyang Meng
HomoFM: Deep Homography Estimation with Flow Matching
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Deep homography estimation has broad applications in computer vision and robotics. Remarkable progresses have been achieved while the existing methods typically treat it as a direct regression or iterative refinement problem and often struggling to capture complex geometric transformations or generalize across different domains. In this work, we propose HomoFM, a new framework that introduces the flow matching technique from generative modeling into the homography estimation task for the first time. Unlike the existing methods, we formulate homography estimation problem as a velocity field learning problem. By modeling a continuous and point-wise velocity field that transforms noisy distributions into registered coordinates, the proposed network recovers high-precision transformations through a conditional flow trajectory. Furthermore, to address the challenge of domain shifts issue, e.g., the cases of multimodal matching or varying illumination scenarios, we integrate a gradient reversal layer (GRL) into the feature extraction backbone. This domain adaptation strategy explicitly constrains the encoder to learn domain-invariant representations, significantly enhancing the network's robustness. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, showing that HomoFM outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both estimation accuracy and robustness on standard benchmarks. Code and data resource are available at https://github.com/hmf21/HomoFM.
An Efficient and Multi-Modal Navigation System with One-Step World Model
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Navigation is a fundamental capability for mobile robots. While the current trend is to use learning-based approaches to replace traditional geometry-based methods, existing end-to-end learning-based policies often struggle with 3D spatial reasoning and lack a comprehensive understanding of physical world dynamics. Integrating world models-which predict future observations conditioned on given actions-with iterative optimization planning offers a promising solution due to their capacity for imagination and flexibility. However, current navigation world models, typically built on pure transformer architectures, often rely on multi-step diffusion processes and autoregressive frame-by-frame generation. These mechanisms result in prohibitive computational latency, rendering real-time deployment impossible. To address this bottleneck, we propose a lightweight navigation world model that adopts a one-step generation paradigm and a 3D U-Net backbone equipped with efficient spatial-temporal attention. This design drastically reduces inference latency, enabling high-frequency control while achieving superior predictive performance. We also integrate this model into an optimization-based planning framework utilizing anchor-based initialization to handle multi-modal goal navigation tasks. Extensive closed-loop experiments in both simulation and real-world environments demonstrate our system's superior efficiency and robustness compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
Learning Diverse Skills for Behavior Models with Mixture of Experts
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Imitation learning has demonstrated strong performance in robotic manipulation by learning from large-scale human demonstrations. While existing models excel at single-task learning, it is observed in practical applications that their performance degrades in the multi-task setting, where interference across tasks leads to an averaging effect. To address this issue, we propose to learn diverse skills for behavior models with Mixture of Experts, referred to as Di-BM. Di-BM associates each expert with a distinct observation distribution, enabling experts to specialize in sub-regions of the observation space. Specifically, we employ energy-based models to represent expert-specific observation distributions and jointly train them alongside the corresponding action models. Our approach is plug-and-play and can be seamlessly integrated into standard imitation learning methods. Extensive experiments on multiple real-world robotic manipulation tasks demonstrate that Di-BM significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, fine-tuning the pretrained Di-BM on novel tasks exhibits superior data efficiency and the reusable of expert-learned knowledge. Code is available at https://github.com/robotnav-bot/Di-BM.
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025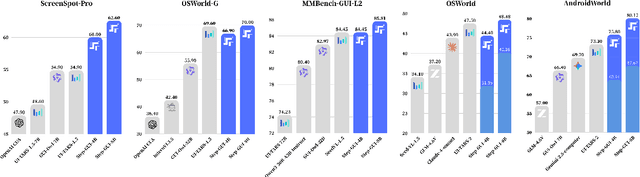
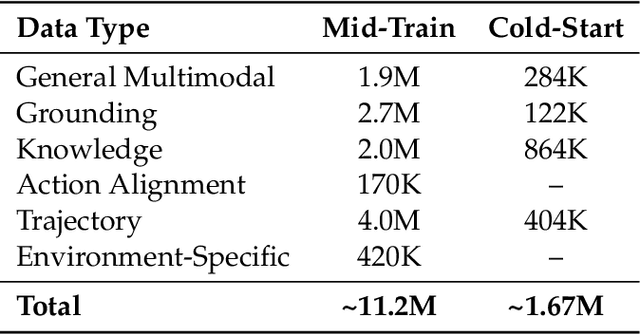
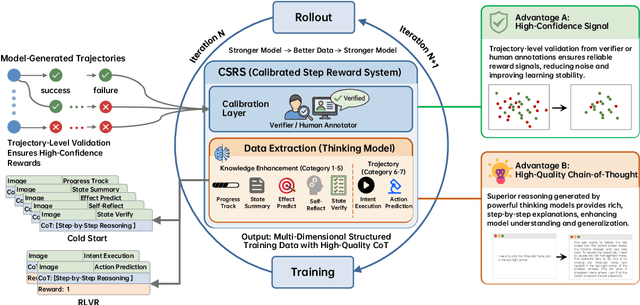

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
Prompt2Auto: From Motion Prompt to Automated Control via Geometry-Invariant One-Shot Gaussian Process Learning
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Learning from demonstration allows robots to acquire complex skills from human demonstrations, but conventional approaches often require large datasets and fail to generalize across coordinate transformations. In this paper, we propose Prompt2Auto, a geometry-invariant one-shot Gaussian process (GeoGP) learning framework that enables robots to perform human-guided automated control from a single motion prompt. A dataset-construction strategy based on coordinate transformations is introduced that enforces invariance to translation, rotation, and scaling, while supporting multi-step predictions. Moreover, GeoGP is robust to variations in the user's motion prompt and supports multi-skill autonomy. We validate the proposed approach through numerical simulations with the designed user graphical interface and two real-world robotic experiments, which demonstrate that the proposed method is effective, generalizes across tasks, and significantly reduces the demonstration burden. Project page is available at: https://prompt2auto.github.io
VGA: Vision GUI Assistant -- Minimizing Hallucinations through Image-Centric Fine-Tuning
Jun 20, 2024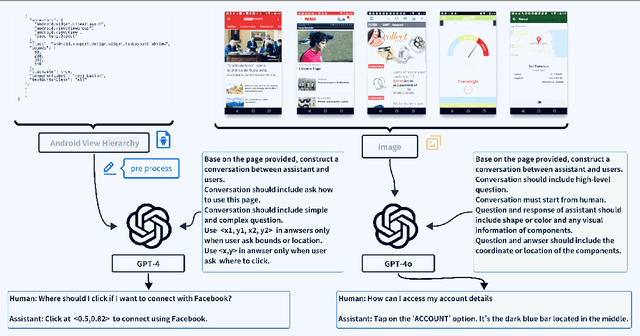
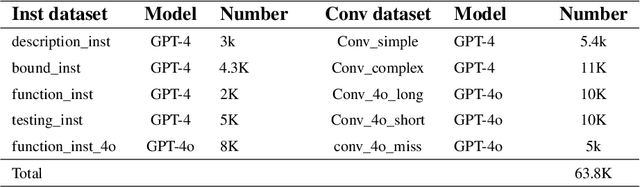
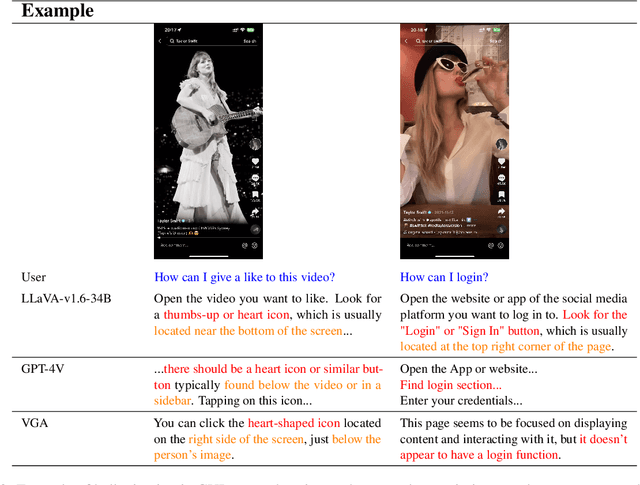
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly improve performance in image comprehension tasks, such as formatted charts and rich-content images. Yet, Graphical User Interface (GUI) pose a greater challenge due to their structured format and detailed textual information. Existing LVLMs often overly depend on internal knowledge and neglect image content, resulting in hallucinations and incorrect responses in GUI comprehension.To address these issues, we introduce VGA, a fine-tuned model designed for comprehensive GUI understanding. Our model aims to enhance the interpretation of visual data of GUI and reduce hallucinations. We first construct a Vision Question Answering (VQA) dataset of 63.8k high-quality examples with our propose Referent Method, which ensures the model's responses are highly depend on visual content within the image. We then design a two-stage fine-tuning method called Foundation and Advanced Comprehension (FAC) to enhance both the model's ability to extract information from image content and alignment with human intent. Experiments show that our approach enhances the model's ability to extract information from images and achieves state-of-the-art results in GUI understanding tasks. Our dataset and fine-tuning script will be released soon.
Robust Kalman filters with unknown covariance of multiplicative noise
Oct 17, 2021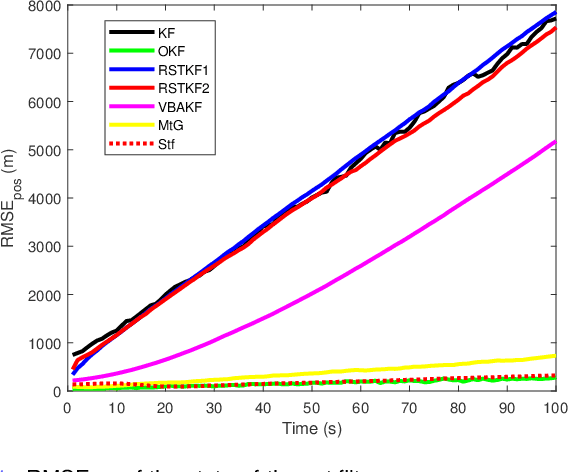
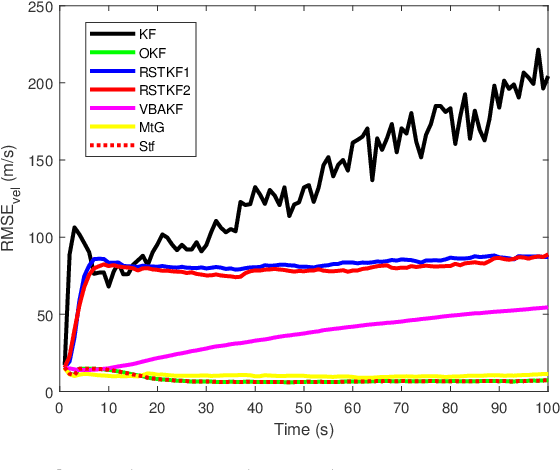
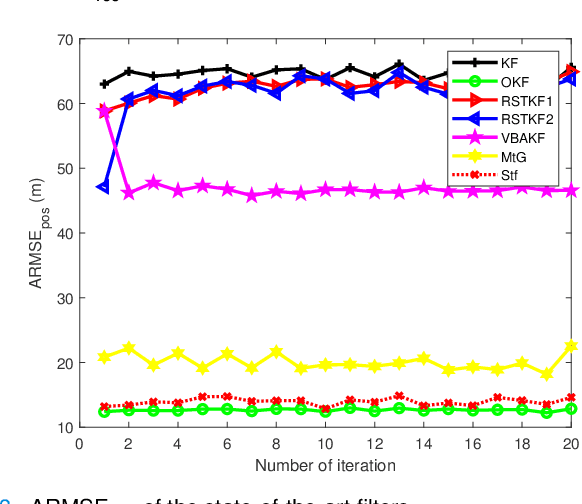
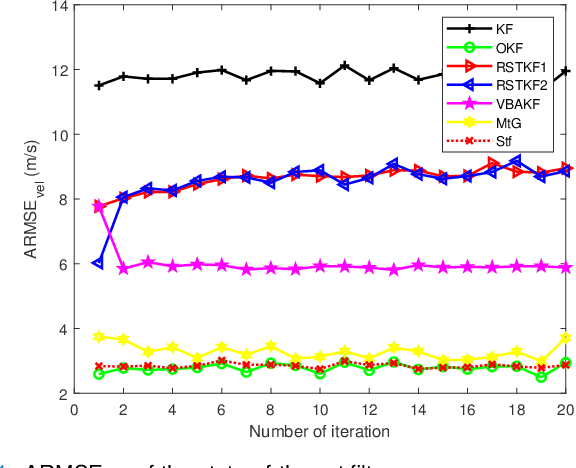
Abstract:In this paper, state and noise covariance estimation problems for linear system with unknown multiplicative noise are considered. The measurement likelihood is modelled as a mixture of two Gaussian distributions and a Student's $\emph{t}$ distribution, respectively. The unknown covariance of multiplicative noise is modelled as an inverse Gamma/Wishart distribution and the initial condition is formulated as the nominal covariance. By using robust design and choosing hierarchical priors, two variational Bayesian based robust Kalman filters are proposed. Stability and covergence of the proposed filters, the covariance parameters, the VB inference, and the estimation error dynamics are analyzed. The lower and upper bounds are also provided to guarantee the performance of the proposed filters. A target tracking simulation is provided to validate the effectiveness of the proposed filters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge