Zhijie Huang
Kanade: A Simple Disentangled Tokenizer for Spoken Language Modeling
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:A good language model starts with a good tokenizer. Tokenization is especially important for speech modeling, which must handle continuous signals that mix linguistic and non-linguistic information. A speech tokenizer should extract phonetics and prosody, suppress linguistically irrelevant information like speaker identity, and enable high-quality synthesis. We present Kanade, a single-layer disentangled speech tokenizer that realizes this ideal. Kanade separates out acoustic constants to create a single stream of tokens that captures rich phonetics and prosody. It does so without the need for auxiliary methods that existing disentangled codecs often rely on. Experiments show that Kanade achieves state-of-the-art speaker disentanglement and lexical availability, while maintaining excellent reconstruction quality.
CreoPep: A Universal Deep Learning Framework for Target-Specific Peptide Design and Optimization
May 05, 2025Abstract:Target-specific peptides, such as conotoxins, exhibit exceptional binding affinity and selectivity toward ion channels and receptors. However, their therapeutic potential remains underutilized due to the limited diversity of natural variants and the labor-intensive nature of traditional optimization strategies. Here, we present CreoPep, a deep learning-based conditional generative framework that integrates masked language modeling with a progressive masking scheme to design high-affinity peptide mutants while uncovering novel structural motifs. CreoPep employs an integrative augmentation pipeline, combining FoldX-based energy screening with temperature-controlled multinomial sampling, to generate structurally and functionally diverse peptides that retain key pharmacological properties. We validate this approach by designing conotoxin inhibitors targeting the $\alpha$7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, achieving submicromolar potency in electrophysiological assays. Structural analysis reveals that CreoPep-generated variants engage in both conserved and novel binding modes, including disulfide-deficient forms, thus expanding beyond conventional design paradigms. Overall, CreoPep offers a robust and generalizable platform that bridges computational peptide design with experimental validation, accelerating the discovery of next-generation peptide therapeutics.
KALE-LM: Unleash The Power Of AI For Science Via Knowledge And Logic Enhanced Large Model
Sep 27, 2024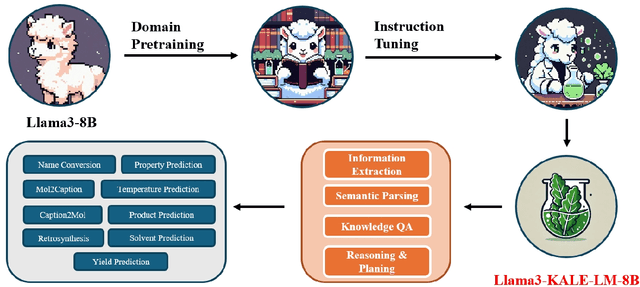
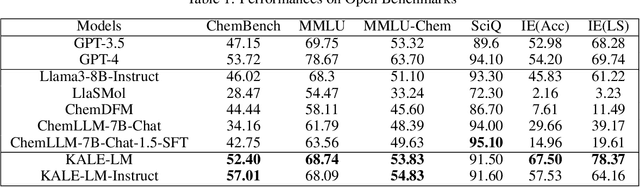
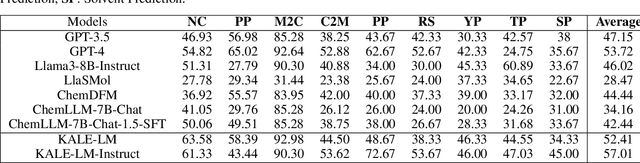
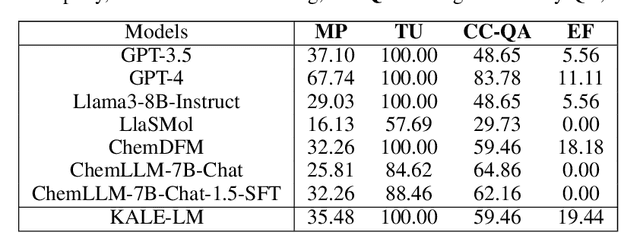
Abstract:Artificial intelligence is gradually demonstrating its immense potential, and increasing attention is being given to how AI can be harnessed to advance scientific research. In this vision paper, we present our perspectives on how AI can better assist scientific inquiry and explore corresponding technical approach. We have proposed and open-sourced a large model of our KALE-LM model series, Llama3-KALE-LM-Chem-8B, which has achieved outstanding performance in tasks related to the field of chemistry. We hope that our work serves as a strong starting point, helping to realize more intelligent AI and promoting the advancement of human science and technology, as well as societal development.
An Empirical Study of Data Ability Boundary in LLMs' Math Reasoning
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are displaying emergent abilities for math reasoning tasks,and there is a growing attention on enhancing the ability of open-source LLMs through supervised fine-tuning (SFT).In this paper, we aim to explore a general data strategy for supervised data to help optimize and expand math reasoning ability.Firstly, we determine the ability boundary of reasoning paths augmentation by identifying these paths' minimal optimal set.Secondly, we validate that different abilities of the model can be cumulatively enhanced by Mix of Minimal Optimal Sets of corresponding types of data, while our models MMOS achieve SOTA performance on series base models under much lower construction costs.Besides, we point out GSM-HARD is not really hard and today's LLMs no longer lack numerical robustness.Also, we provide an Auto Problem Generator for robustness testing and educational applications.Our code and data are publicly available at https://github.com/cyzhh/MMOS.
MelodyGLM: Multi-task Pre-training for Symbolic Melody Generation
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:Pre-trained language models have achieved impressive results in various music understanding and generation tasks. However, existing pre-training methods for symbolic melody generation struggle to capture multi-scale, multi-dimensional structural information in note sequences, due to the domain knowledge discrepancy between text and music. Moreover, the lack of available large-scale symbolic melody datasets limits the pre-training improvement. In this paper, we propose MelodyGLM, a multi-task pre-training framework for generating melodies with long-term structure. We design the melodic n-gram and long span sampling strategies to create local and global blank infilling tasks for modeling the local and global structures in melodies. Specifically, we incorporate pitch n-grams, rhythm n-grams, and their combined n-grams into the melodic n-gram blank infilling tasks for modeling the multi-dimensional structures in melodies. To this end, we have constructed a large-scale symbolic melody dataset, MelodyNet, containing more than 0.4 million melody pieces. MelodyNet is utilized for large-scale pre-training and domain-specific n-gram lexicon construction. Both subjective and objective evaluations demonstrate that MelodyGLM surpasses the standard and previous pre-training methods. In particular, subjective evaluations show that, on the melody continuation task, MelodyGLM gains average improvements of 0.82, 0.87, 0.78, and 0.94 in consistency, rhythmicity, structure, and overall quality, respectively. Notably, MelodyGLM nearly matches the quality of human-composed melodies on the melody inpainting task.
Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning
May 23, 2023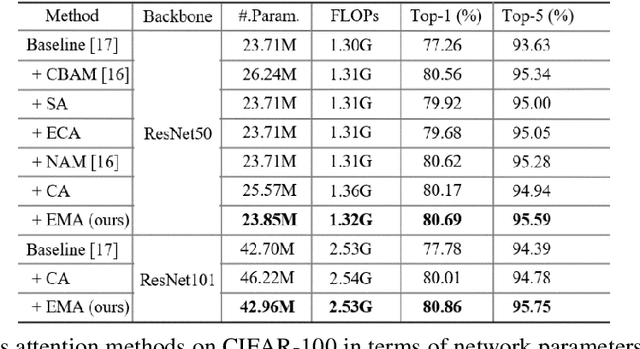
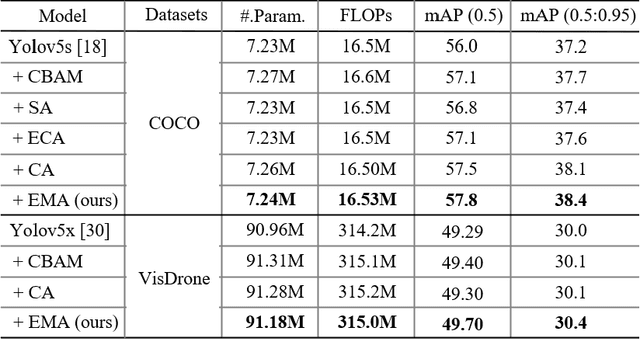

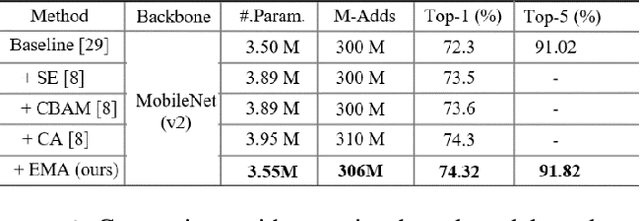
Abstract:Remarkable effectiveness of the channel or spatial attention mechanisms for producing more discernible feature representation are illustrated in various computer vision tasks. However, modeling the cross-channel relationships with channel dimensionality reduction may bring side effect in extracting deep visual representations. In this paper, a novel efficient multi-scale attention (EMA) module is proposed. Focusing on retaining the information on per channel and decreasing the computational overhead, we reshape the partly channels into the batch dimensions and group the channel dimensions into multiple sub-features which make the spatial semantic features well-distributed inside each feature group. Specifically, apart from encoding the global information to re-calibrate the channel-wise weight in each parallel branch, the output features of the two parallel branches are further aggregated by a cross-dimension interaction for capturing pixel-level pairwise relationship. We conduct extensive ablation studies and experiments on image classification and object detection tasks with popular benchmarks (e.g., CIFAR-100, ImageNet-1k, MS COCO and VisDrone2019) for evaluating its performance.
ACE: Zero-Shot Image to Image Translation via Pretrained Auto-Contrastive-Encoder
Feb 22, 2023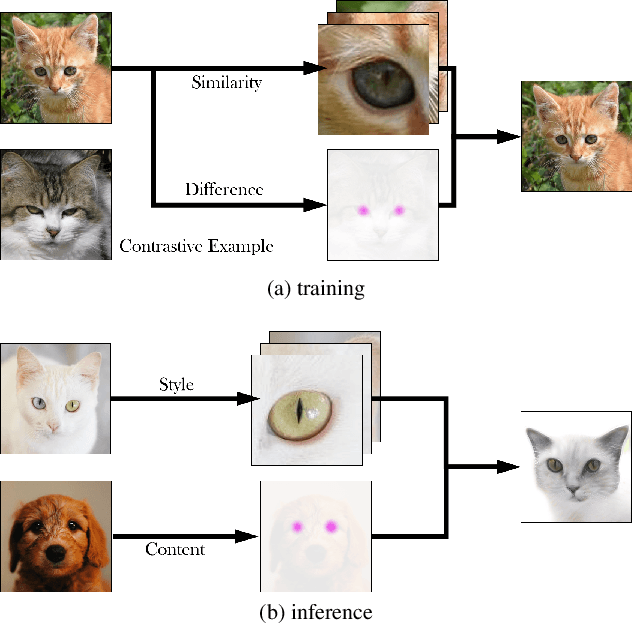



Abstract:Image-to-image translation is a fundamental task in computer vision. It transforms images from one domain to images in another domain so that they have particular domain-specific characteristics. Most prior works train a generative model to learn the mapping from a source domain to a target domain. However, learning such mapping between domains is challenging because data from different domains can be highly unbalanced in terms of both quality and quantity. To address this problem, we propose a new approach to extract image features by learning the similarities and differences of samples within the same data distribution via a novel contrastive learning framework, which we call Auto-Contrastive-Encoder (ACE). ACE learns the content code as the similarity between samples with the same content information and different style perturbations. The design of ACE enables us to achieve zero-shot image-to-image translation with no training on image translation tasks for the first time. Moreover, our learning method can learn the style features of images on different domains effectively. Consequently, our model achieves competitive results on multimodal image translation tasks with zero-shot learning as well. Additionally, we demonstrate the potential of our method in transfer learning. With fine-tuning, the quality of translated images improves in unseen domains. Even though we use contrastive learning, all of our training can be performed on a single GPU with the batch size of 8.
WuYun: Exploring hierarchical skeleton-guided melody generation using knowledge-enhanced deep learning
Jan 11, 2023Abstract:Although deep learning has revolutionized music generation, existing methods for structured melody generation follow an end-to-end left-to-right note-by-note generative paradigm and treat each note equally. Here, we present WuYun, a knowledge-enhanced deep learning architecture for improving the structure of generated melodies, which first generates the most structurally important notes to construct a melodic skeleton and subsequently infills it with dynamically decorative notes into a full-fledged melody. Specifically, we use music domain knowledge to extract melodic skeletons and employ sequence learning to reconstruct them, which serve as additional knowledge to provide auxiliary guidance for the melody generation process. We demonstrate that WuYun can generate melodies with better long-term structure and musicality and outperforms other state-of-the-art methods by 0.51 on average on all subjective evaluation metrics. Our study provides a multidisciplinary lens to design melodic hierarchical structures and bridge the gap between data-driven and knowledge-based approaches for numerous music generation tasks.
Enhancing Knowledge Tracing via Adversarial Training
Aug 10, 2021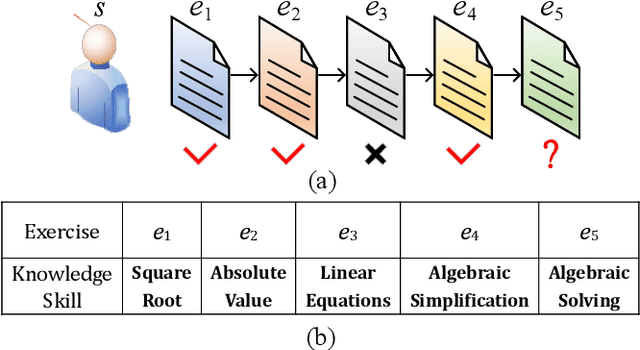
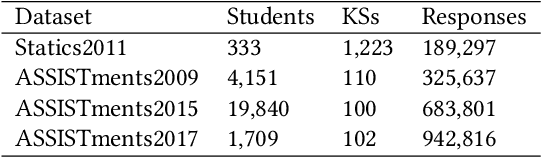
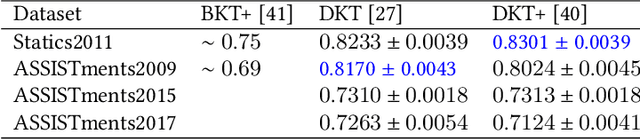
Abstract:We study the problem of knowledge tracing (KT) where the goal is to trace the students' knowledge mastery over time so as to make predictions on their future performance. Owing to the good representation capacity of deep neural networks (DNNs), recent advances on KT have increasingly concentrated on exploring DNNs to improve the performance of KT. However, we empirically reveal that the DNNs based KT models may run the risk of overfitting, especially on small datasets, leading to limited generalization. In this paper, by leveraging the current advances in adversarial training (AT), we propose an efficient AT based KT method (ATKT) to enhance KT model's generalization and thus push the limit of KT. Specifically, we first construct adversarial perturbations and add them on the original interaction embeddings as adversarial examples. The original and adversarial examples are further used to jointly train the KT model, forcing it is not only to be robust to the adversarial examples, but also to enhance the generalization over the original ones. To better implement AT, we then present an efficient attentive-LSTM model as KT backbone, where the key is a proposed knowledge hidden state attention module that adaptively aggregates information from previous knowledge hidden states while simultaneously highlighting the importance of current knowledge hidden state to make a more accurate prediction. Extensive experiments on four public benchmark datasets demonstrate that our ATKT achieves new state-of-the-art performance. Code is available at: \color{blue} {\url{https://github.com/xiaopengguo/ATKT}}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge