Jiaxing Yu
Diff-V2M: A Hierarchical Conditional Diffusion Model with Explicit Rhythmic Modeling for Video-to-Music Generation
Nov 12, 2025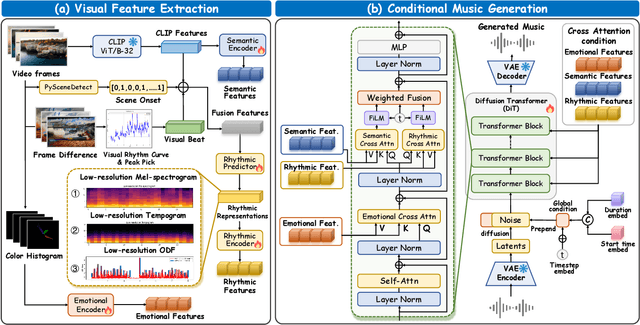
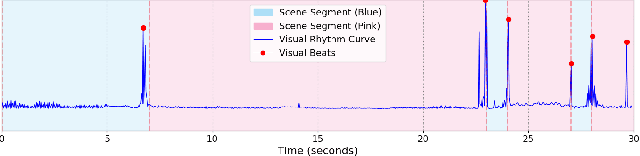
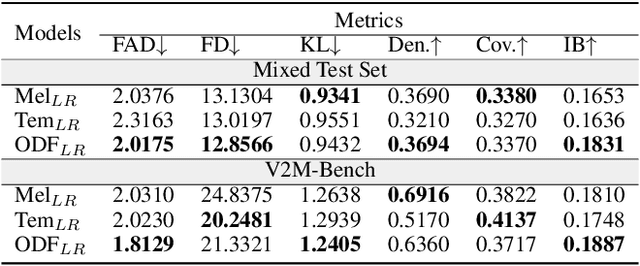
Abstract:Video-to-music (V2M) generation aims to create music that aligns with visual content. However, two main challenges persist in existing methods: (1) the lack of explicit rhythm modeling hinders audiovisual temporal alignments; (2) effectively integrating various visual features to condition music generation remains non-trivial. To address these issues, we propose Diff-V2M, a general V2M framework based on a hierarchical conditional diffusion model, comprising two core components: visual feature extraction and conditional music generation. For rhythm modeling, we begin by evaluating several rhythmic representations, including low-resolution mel-spectrograms, tempograms, and onset detection functions (ODF), and devise a rhythmic predictor to infer them directly from videos. To ensure contextual and affective coherence, we also extract semantic and emotional features. All features are incorporated into the generator via a hierarchical cross-attention mechanism, where emotional features shape the affective tone via the first layer, while semantic and rhythmic features are fused in the second cross-attention layer. To enhance feature integration, we introduce timestep-aware fusion strategies, including feature-wise linear modulation (FiLM) and weighted fusion, allowing the model to adaptively balance semantic and rhythmic cues throughout the diffusion process. Extensive experiments identify low-resolution ODF as a more effective signal for modeling musical rhythm and demonstrate that Diff-V2M outperforms existing models on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in terms of objective metrics and subjective comparisons. Demo and code are available at https://Tayjsl97.github.io/Diff-V2M-Demo/.
A Survey on Music Generation from Single-Modal, Cross-Modal, and Multi-Modal Perspectives: Data, Methods, and Challenges
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal music generation, using multiple modalities like images, video, and text alongside musical scores and audio as guidance, is an emerging research area with broad applications. This paper reviews this field, categorizing music generation systems from the perspective of modalities. It covers modality representation, multi-modal data alignment, and their utilization to guide music generation. We also discuss current datasets and evaluation methods. Key challenges in this area include effective multi-modal integration, large-scale comprehensive datasets, and systematic evaluation methods. Finally, we provide an outlook on future research directions focusing on multi-modal fusion, alignment, data, and evaluation.
SongGLM: Lyric-to-Melody Generation with 2D Alignment Encoding and Multi-Task Pre-Training
Dec 24, 2024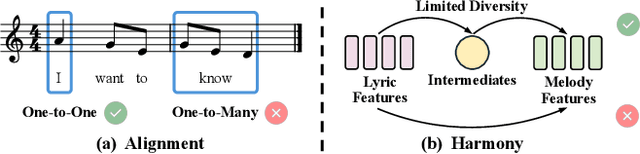
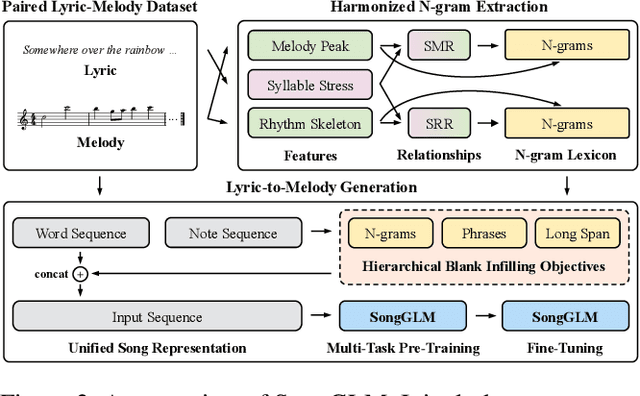

Abstract:Lyric-to-melody generation aims to automatically create melodies based on given lyrics, requiring the capture of complex and subtle correlations between them. However, previous works usually suffer from two main challenges: 1) lyric-melody alignment modeling, which is often simplified to one-syllable/word-to-one-note alignment, while others have the problem of low alignment accuracy; 2) lyric-melody harmony modeling, which usually relies heavily on intermediates or strict rules, limiting model's capabilities and generative diversity. In this paper, we propose SongGLM, a lyric-to-melody generation system that leverages 2D alignment encoding and multi-task pre-training based on the General Language Model (GLM) to guarantee the alignment and harmony between lyrics and melodies. Specifically, 1) we introduce a unified symbolic song representation for lyrics and melodies with word-level and phrase-level (2D) alignment encoding to capture the lyric-melody alignment; 2) we design a multi-task pre-training framework with hierarchical blank infilling objectives (n-gram, phrase, and long span), and incorporate lyric-melody relationships into the extraction of harmonized n-grams to ensure the lyric-melody harmony. We also construct a large-scale lyric-melody paired dataset comprising over 200,000 English song pieces for pre-training and fine-tuning. The objective and subjective results indicate that SongGLM can generate melodies from lyrics with significant improvements in both alignment and harmony, outperforming all the previous baseline methods.
MuDiT & MuSiT: Alignment with Colloquial Expression in Description-to-Song Generation
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Amid the rising intersection of generative AI and human artistic processes, this study probes the critical yet less-explored terrain of alignment in human-centric automatic song composition. We propose a novel task of Colloquial Description-to-Song Generation, which focuses on aligning the generated content with colloquial human expressions. This task is aimed at bridging the gap between colloquial language understanding and auditory expression within an AI model, with the ultimate goal of creating songs that accurately satisfy human auditory expectations and structurally align with musical norms. Current datasets are limited due to their narrow descriptive scope, semantic gaps and inaccuracies. To overcome data scarcity in this domain, we present the Caichong Music Dataset (CaiMD). CaiMD is manually annotated by both professional musicians and amateurs, offering diverse perspectives and a comprehensive understanding of colloquial descriptions. Unlike existing datasets pre-set with expert annotations or auto-generated ones with inherent biases, CaiMD caters more sufficiently to our purpose of aligning AI-generated music with widespread user-desired results. Moreover, we propose an innovative single-stage framework called MuDiT/MuSiT for enabling effective human-machine alignment in song creation. This framework not only achieves cross-modal comprehension between colloquial language and auditory music perceptions but also ensures generated songs align with user-desired results. MuDiT/MuSiT employs one DiT/SiT model for end-to-end generation of musical components like melody, harmony, rhythm, vocals, and instrumentation. The approach ensures harmonious sonic cohesiveness amongst all generated musical components, facilitating better resonance with human auditory expectations.
MelodyGLM: Multi-task Pre-training for Symbolic Melody Generation
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:Pre-trained language models have achieved impressive results in various music understanding and generation tasks. However, existing pre-training methods for symbolic melody generation struggle to capture multi-scale, multi-dimensional structural information in note sequences, due to the domain knowledge discrepancy between text and music. Moreover, the lack of available large-scale symbolic melody datasets limits the pre-training improvement. In this paper, we propose MelodyGLM, a multi-task pre-training framework for generating melodies with long-term structure. We design the melodic n-gram and long span sampling strategies to create local and global blank infilling tasks for modeling the local and global structures in melodies. Specifically, we incorporate pitch n-grams, rhythm n-grams, and their combined n-grams into the melodic n-gram blank infilling tasks for modeling the multi-dimensional structures in melodies. To this end, we have constructed a large-scale symbolic melody dataset, MelodyNet, containing more than 0.4 million melody pieces. MelodyNet is utilized for large-scale pre-training and domain-specific n-gram lexicon construction. Both subjective and objective evaluations demonstrate that MelodyGLM surpasses the standard and previous pre-training methods. In particular, subjective evaluations show that, on the melody continuation task, MelodyGLM gains average improvements of 0.82, 0.87, 0.78, and 0.94 in consistency, rhythmicity, structure, and overall quality, respectively. Notably, MelodyGLM nearly matches the quality of human-composed melodies on the melody inpainting task.
PDAugment: Data Augmentation by Pitch and Duration Adjustments for Automatic Lyrics Transcription
Sep 17, 2021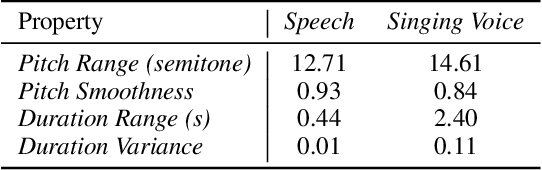
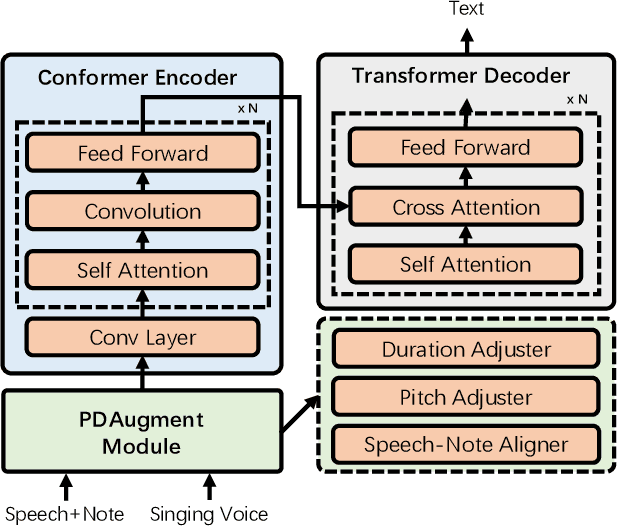
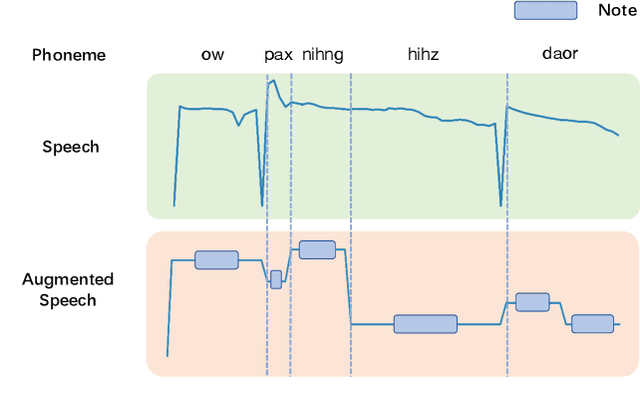

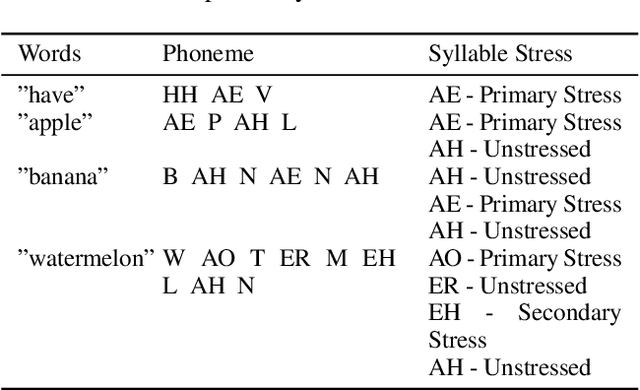
Abstract:Automatic lyrics transcription (ALT), which can be regarded as automatic speech recognition (ASR) on singing voice, is an interesting and practical topic in academia and industry. ALT has not been well developed mainly due to the dearth of paired singing voice and lyrics datasets for model training. Considering that there is a large amount of ASR training data, a straightforward method is to leverage ASR data to enhance ALT training. However, the improvement is marginal when training the ALT system directly with ASR data, because of the gap between the singing voice and standard speech data which is rooted in music-specific acoustic characteristics in singing voice. In this paper, we propose PDAugment, a data augmentation method that adjusts pitch and duration of speech at syllable level under the guidance of music scores to help ALT training. Specifically, we adjust the pitch and duration of each syllable in natural speech to those of the corresponding note extracted from music scores, so as to narrow the gap between natural speech and singing voice. Experiments on DSing30 and Dali corpus show that the ALT system equipped with our PDAugment outperforms previous state-of-the-art systems by 5.9% and 18.1% WERs respectively, demonstrating the effectiveness of PDAugment for ALT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge