Yunfei Xu
Vclip: Face-based Speaker Generation by Face-voice Association Learning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:This paper discusses the task of face-based speech synthesis, a kind of personalized speech synthesis where the synthesized voices are constrained to perceptually match with a reference face image. Due to the lack of TTS-quality audio-visual corpora, previous approaches suffer from either low synthesis quality or domain mismatch induced by a knowledge transfer scheme. This paper proposes a new approach called Vclip that utilizes the facial-semantic knowledge of the CLIP encoder on noisy audio-visual data to learn the association between face and voice efficiently, achieving 89.63% cross-modal verification AUC score on Voxceleb testset. The proposed method then uses a retrieval-based strategy, combined with GMM-based speaker generation module for a downstream TTS system, to produce probable target speakers given reference images. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed Vclip system in conjunction with the retrieval step can bridge the gap between face and voice features for face-based speech synthesis. And using the feedback information distilled from downstream TTS helps to synthesize voices that match closely with reference faces. Demos available at sos1sos2sixteen.github.io/vclip.
SongGLM: Lyric-to-Melody Generation with 2D Alignment Encoding and Multi-Task Pre-Training
Dec 24, 2024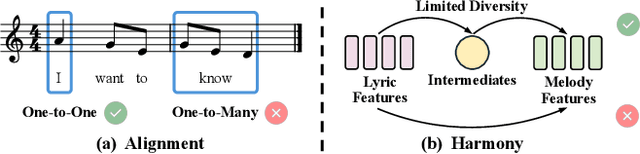
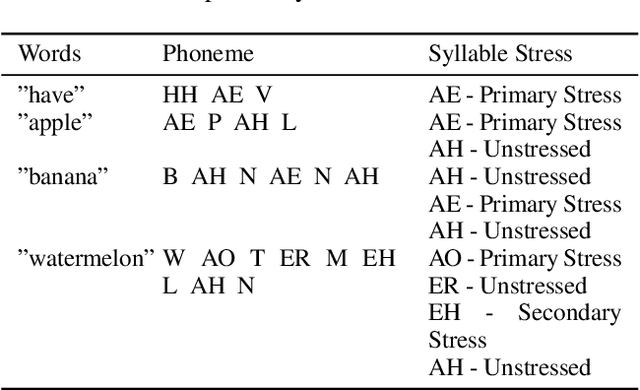
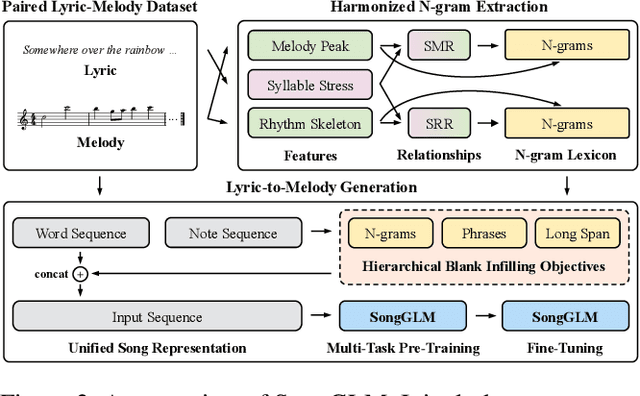

Abstract:Lyric-to-melody generation aims to automatically create melodies based on given lyrics, requiring the capture of complex and subtle correlations between them. However, previous works usually suffer from two main challenges: 1) lyric-melody alignment modeling, which is often simplified to one-syllable/word-to-one-note alignment, while others have the problem of low alignment accuracy; 2) lyric-melody harmony modeling, which usually relies heavily on intermediates or strict rules, limiting model's capabilities and generative diversity. In this paper, we propose SongGLM, a lyric-to-melody generation system that leverages 2D alignment encoding and multi-task pre-training based on the General Language Model (GLM) to guarantee the alignment and harmony between lyrics and melodies. Specifically, 1) we introduce a unified symbolic song representation for lyrics and melodies with word-level and phrase-level (2D) alignment encoding to capture the lyric-melody alignment; 2) we design a multi-task pre-training framework with hierarchical blank infilling objectives (n-gram, phrase, and long span), and incorporate lyric-melody relationships into the extraction of harmonized n-grams to ensure the lyric-melody harmony. We also construct a large-scale lyric-melody paired dataset comprising over 200,000 English song pieces for pre-training and fine-tuning. The objective and subjective results indicate that SongGLM can generate melodies from lyrics with significant improvements in both alignment and harmony, outperforming all the previous baseline methods.
Adversarial Attacks and Robust Defenses in Speaker Embedding based Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech System
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:Speaker embedding based zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems enable high-quality speech synthesis for unseen speakers using minimal data. However, these systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where an attacker introduces imperceptible perturbations to the original speaker's audio waveform, leading to synthesized speech sounds like another person. This vulnerability poses significant security risks, including speaker identity spoofing and unauthorized voice manipulation. This paper investigates two primary defense strategies to address these threats: adversarial training and adversarial purification. Adversarial training enhances the model's robustness by integrating adversarial examples during the training process, thereby improving resistance to such attacks. Adversarial purification, on the other hand, employs diffusion probabilistic models to revert adversarially perturbed audio to its clean form. Experimental results demonstrate that these defense mechanisms can significantly reduce the impact of adversarial perturbations, enhancing the security and reliability of speaker embedding based zero-shot TTS systems in adversarial environments.
LLM-DER:A Named Entity Recognition Method Based on Large Language Models for Chinese Coal Chemical Domain
Sep 16, 2024Abstract:Domain-specific Named Entity Recognition (NER), whose goal is to recognize domain-specific entities and their categories, provides an important support for constructing domain knowledge graphs. Currently, deep learning-based methods are widely used and effective in NER tasks, but due to the reliance on large-scale labeled data. As a result, the scarcity of labeled data in a specific domain will limit its application.Therefore, many researches started to introduce few-shot methods and achieved some results. However, the entity structures in specific domains are often complex, and the current few-shot methods are difficult to adapt to NER tasks with complex features.Taking the Chinese coal chemical industry domain as an example,there exists a complex structure of multiple entities sharing a single entity, as well as multiple relationships for the same pair of entities, which affects the NER task under the sample less condition.In this paper, we propose a Large Language Models (LLMs)-based entity recognition framework LLM-DER for the domain-specific entity recognition problem in Chinese, which enriches the entity information by generating a list of relationships containing entity types through LLMs, and designing a plausibility and consistency evaluation method to remove misrecognized entities, which can effectively solve the complex structural entity recognition problem in a specific domain.The experimental results of this paper on the Resume dataset and the self-constructed coal chemical dataset Coal show that LLM-DER performs outstandingly in domain-specific entity recognition, not only outperforming the existing GPT-3.5-turbo baseline, but also exceeding the fully-supervised baseline, verifying its effectiveness in entity recognition.
MetaBGM: Dynamic Soundtrack Transformation For Continuous Multi-Scene Experiences With Ambient Awareness And Personalization
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces MetaBGM, a groundbreaking framework for generating background music that adapts to dynamic scenes and real-time user interactions. We define multi-scene as variations in environmental contexts, such as transitions in game settings or movie scenes. To tackle the challenge of converting backend data into music description texts for audio generation models, MetaBGM employs a novel two-stage generation approach that transforms continuous scene and user state data into these texts, which are then fed into an audio generation model for real-time soundtrack creation. Experimental results demonstrate that MetaBGM effectively generates contextually relevant and dynamic background music for interactive applications.
The DKU-OPPO System for the 2022 Spoofing-Aware Speaker Verification Challenge
Jul 15, 2022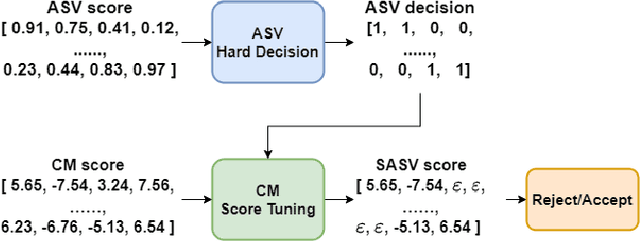
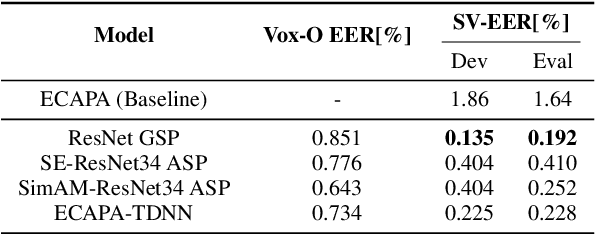
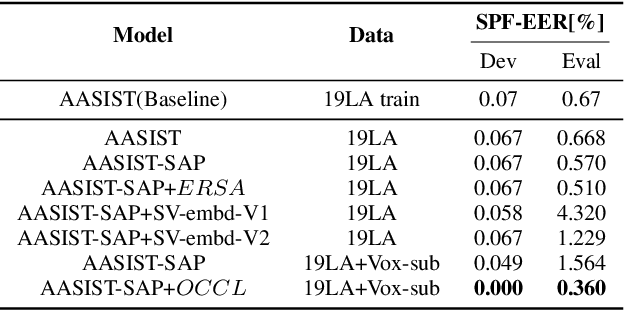
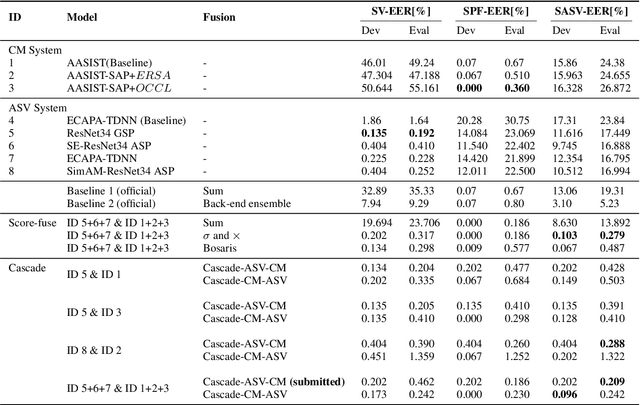
Abstract:This paper describes our DKU-OPPO system for the 2022 Spoofing-Aware Speaker Verification (SASV) Challenge. First, we split the joint task into speaker verification (SV) and spoofing countermeasure (CM), these two tasks which are optimized separately. For ASV systems, four state-of-the-art methods are employed. For CM systems, we propose two methods on top of the challenge baseline to further improve the performance, namely Embedding Random Sampling Augmentation (ERSA) and One-Class Confusion Loss(OCCL). Second, we also explore whether SV embedding could help improve CM system performance. We observe a dramatic performance degradation of existing CM systems on the domain-mismatched Voxceleb2 dataset. Third, we compare different fusion strategies, including parallel score fusion and sequential cascaded systems. Compared to the 1.71% SASV-EER baseline, our submitted cascaded system obtains a 0.21% SASV-EER on the challenge official evaluation set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge